













Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
TỔNG LIÊN ĐOÀN LAO ĐỘNG VIỆT NAM
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC TÔN ĐỨC THẮNG
KHOA TÀI CHÍNH NGÂN HÀNG
BÀI NGHIÊM CỨU NHÓM
MÔN: THỰC HÀNH MÔ HÌNH TOÁN KINH TẾ ĐỀ TÀI:
PHÂN TÍCH CÁC NHÂN TỐ ẢNH HƯỞNG ĐẾN
HIỆU QUẢ TÀI CHÍNH: NGHIÊN CỨU ĐIỂN
HÌNH TẠI CÁC CÔNG TY CỔ PHẦN NGÀNH
CÔNG NGHỆ THÔNG TIN ĐƯỢC NIÊM YẾT
TRÊN SÀN CHỨNG KHOÁN VIỆT NAM
Giảng viên hướng dẫn: PHÙNG QUANG HƯNG
Lớp: MÔ HÌNH TOÁN KINH TẾ (Ca 3, Thứ ba) – Nhóm: 03
Danh sách Sinh viên thực hiện :
VÕ HOÀNG NHÂN (B19H0263)
PHAN THANH HIẾU (B19H0195)
HỒ THỊ TUYẾT ĐOAN (B19H0177)
TỪ LÊ MINH NGÂN (B19H0247) lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
COMPANY LISTED INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ON VIETNAM STOCK EXCHANGE ABSTRACT:
The objective of the study is to examine the factors that affect the financial performance of
the companies from which to make some suggestions for managers to improve financial
performance. The study used data from 22 companies that share the information
technology sector listed on stock exchanges in Vietnam period 2007-2018 in the field of
information technology. The research results have shown that the effectiveness main (ROA)
of companies significantly affected by the ratio of the state capital (STATE), the
management capacity (MC), firm size (SIZE), and the company's business cycle (BS). On
the other hand, the study also pointed out the positive impact (+) of ROA on the
profitability ratio on equity (ROE).
Keywords: Production cycle business, financial performance, the company shares listed
information technology industry. VITECO Telecommunications
technology (VIE) ... However, there are 1. INTRODUCTION:
companies with profits after higher taxes
Today, technology is proliferating,
or even flourished during that period. For
especially in information technology have example, Van Lang Technology
an important role in bringing a new era of
Development and Investment Joint Stock modern advanced technologies
Company (VLA), Vietnam Electronics worldwide, including Vietnam.
and Informatics Corporation (VEC), ...
Therefore, need to understand the factors
This leads to the question: What factors
affecting financial performance and this
affect the financial performance of the
will be the baggage to participate in the
market in this area, most notably as ROA,
company shares listed on the stock
ROE, MC, SIZE, STATE, BS, CR, QR,
exchange in Vietnam? If so, how many
factors? In addition, the level of impact
and DFL. Vietnam's stock market in the
period 2011-2013 continuously fluctuated like?
strongly, seriously affecting companies.
The research focused on studying the
Two factors may explain this, which is
factors that affect the financial
endogenous and exogenous in which one
performance of the listed joint-stock
of the endogenous factors is very
important that the financial performance
of companies. When analyzing the
research and data companies in the
information technology industry, we
discovered that there are companies with
negative profits after tax during 2011,
2012, and 2013. For example, the
company technical Services Joint-stock Telecommunications (TST), JSC Telecommunications (UNI), JSC 2 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 4 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
Table 0. The previous related research Author
Research method and sample Research results
Investigate the factors affecting the Factors such as the profitability and growth of size of a company
employment in the manufacturing and economic ratios Agiomirgiannakis, G.,
sector of Greece in the period from that affect the growth Voulgaris, F. and
1995 to 1999, analyzing the question of of the company in
Papadogonas, T. (2006) whether factors such as company size, particular and the
age, leverage debt, management national economy in efficiency, and export-oriented general companies If company size is too large, it can harm financial Yuqi, L. (2008) performance due to
Determinant of bank profitability poorly controlled or even corruption
Based on the disclosure of timely Factors affecting the financial Liargovas and
annual reports to confirm and modify performance of the Skandalis (2008)
their expectations about the current
economic outlook and the future of the company company Factors affecting the financial
Based on the disclosure of timely performance of
Almajali, Y.A, Alamro, annual reports to confirm and modify insurance companies
S.H. and Al-Soub, Y.Z. their expectations about the current in Jordan listed in (2012)
economic outlook and the future of the Amman Stock company Exchange
companies listed on Vietnam's stock
exchanges, more precisely Corporation
Information Technology. The team used
the method of correlation analysis and
multiple regression analysis. Strictly
capacity management, business cycle
research also indicates factors the state
strong impact on financial performance.
capital ratios, company size, ratio of lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
Moreover, the group is strictly between
meaning of each financial indicators used the ROA and ROE depth.
in this study is what? And why they need to analyze the company shares
The layout of the study will include: information technology financial I. Introduction
performance on the stock market. i. Return on Asset (ROA) II. Basic theory
ROA (Return on Assets) - it is the return
a. The previous related research
on assets, an indicator showing the
correlation between the profitability of a b. The concept and meaning of
company compared to its main assets.
eachfinancial indicators used in the
ROA gives to know the effectiveness of
study III. Data and research methods
the company is using assets to generate earnings. IV. Research model, research hypotheses V.
ROA shows that a business has invested Research results
how much profit on assets. The higher the
VI. Conclusions and recommendations
ROA, the use of corporate assets more VII. effectively. References ii. Return On Equity (ROE) 2. BASIC THEORY
ROE (Return On Equity) - it is the return
a. The previous related research
on equity, and return on equity also. If the
Financial performance important role for
analysis, there will be a lot of interesting
businesses in particular and the economy
information about the business results as
in general. There are many studies on
well as the financial picture of the
financial performance and the factors
business behind this indicator.
affecting it. Search gives different figures
on financial performance but the main index was ROA, ROE, MC, SIZE,
ROE shows one pile of equity which now
STATE, BS, CR, QR, and DFL, the
spent to serve activity, how much profit.
popularity index for measuring the
The higher the ROE, the use of corporate
competitiveness of the company's ROA funds as efficiently. and ROE. iii.
The size of business (SIZE) Large
Table 0. The previous related research
companies can exploit economies
b. The concept and meaning of each of scale and therefore more
financial indicators used in the study
efficient than small companies.
If the financial performance measures are The size of a business can be
a common and important concept and
evaluated based on criteria such as 6 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
the total number of employees,
BS = Turnaround time inventory +
total revenue, or total assets. Turnaround time accounts receivables
Company size is calculated by total assets is measured Shorter production cycles, which
indicates how efficient the use of
Moreover, small companies may have less
machinery and production areas.
energy than large companies can because
Production cycles affect working capital
they are difficult to compete with larger
needs and the effective use of working
companies, especially in a highly
capital in production. In competitive
competitive market. On the other hand,
markets, production cycles shorter change
when companies become larger, they may
the ability of the production system as
be ineffective, leading to reduced
possible to respond to the changes. financial performance.
Moreover, trade receivables faster iv.
Management competence in an
turnaround, the company recover the debt index (MC)
faster, increasing capital turnover, reduce
Management competence in an index
costs related to accounts receivable. The
(MC) is an indicator of leadership and
dual impact of the shortened business
supervision of the management level in
cycles increases profitability. the company. vi.
Degree Of Financial Leverage (DFL)
Degree Of Financial Leverage (DFL) is a
It may include the ability to plan and
combination between liabilities and
divide the work efficiently, respond
equity in the management of the financial
quickly to solve the problem, have policy of the enterprise.
indepth knowledge and skills necessary software. DFL= v. Business cycle (BS)
Degree Of Financial Leverage is the
Business cycle (BS) is the period from
degree of use of loans in the total capital
when the raw materials are put into
of a company in the hope of increasing
production until the finished product
return on equity (ROE), or earnings per
fabrication, inspection, and storage of ordinary share (EPS).
finished products. It includes the time to vii. Quick raito (QR)
complete the work in process technology;
Quick ratio (QR) is an indicator of the
time to deliver; technical testing time;
short-term liquidity position of the
work in progress stops at work, in the
company and measures the ability to meet intermediate repository, and non-
the short-term obligations of the company production shifts. with its liquid assets. lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
It shows the ability of the company to
business cycle (BS) Degree of Financial
immediately use assets almost his cash
Leverage (DFL) and the proportion of the
(assets that can be converted quickly into
state capital (state) and the percentage
cash) to pay the debts of your current, it is
measure the impact of factors such as
also known as the acid test ratio. solvency (QR, CR), capacity management committee (MC). viii. Current ratio (CR)
Current ratio (CR) is the ratio of liquidity
+ Advantages: it evaluates the efficiency
solvency measure short-term obligations
and performance of the company's
of the company or the obligations due
business operations, evaluates the within one year.
efficiency of the use of company
resources. The ratio of financial structure:
reflects the extent to which businesses use
It gives investors and analysts to know
to paying off debt reflects the degree of
how a company can maximize existing
financial autonomy of enterprises.
assets on the balance sheet accounting to
Moreover, it also guides the forecast and
meet its current liabilities and other
plans production and business activities, payables.
investment decisions and funding to deal 3. DATA AND RESEARCH
with the financial markets determine the risks and profits. METHODS
Research samples are 22 joint-stock
+ Disadvantages: we cannot recognize
companies in the information technology
inaccurate financial statements. The time
sector listed on stock exchanges period
element is not mentioned and is difficult
2007 - 2018. Group uses the information
to conclude the financial situation good or
gathered from the report prospectus,
bad. Moreover, the planning could not
financial reports, and information on the feasible for the business's
companies on the website of the company multidisciplinary activities.
and the site CafeF, Vietstock, cophieu68.
Besides, the group also uses statistical
The data analysis method used in the
analysis methods. Statistics is a system of
study is the ratio method. Analyzing
methods (collecting, synthesizing, and
financial ratios is the use of various
presenting data, and calculate the
techniques to analyze the financial
characteristics of the object of study) to
statements of the enterprise to grasp the
cater for the analysis, prediction, and
situation of the financial realities of the
decision making. Purpose cranes Group
business, which made plans for
was to examine the relationship between
production and business most effective the dependent variable and the
for calculating the ratios measuring the
independent variables, the paper uses the
financial performance (ROA, ROE),
statistical method described, correlation 8 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 matrix, check the phenomenon
used the three most popular in autocorrelation (Durbin-Watson), assessing the financial multiple regression method and
performance of the business. In multicollinearity test.
this study, the group will mainly use ROA and ROE to assess the 4. RESEARCH MODEL AND financial performance of the RESEARCH HYPOTHESES companies that share industry
a. Research model Based on research
information technology listed on
and the reality of Vietnam, offering
Vietnam's stock by these indicators theoretical models are: may reflect how to look past, shows the operation of the
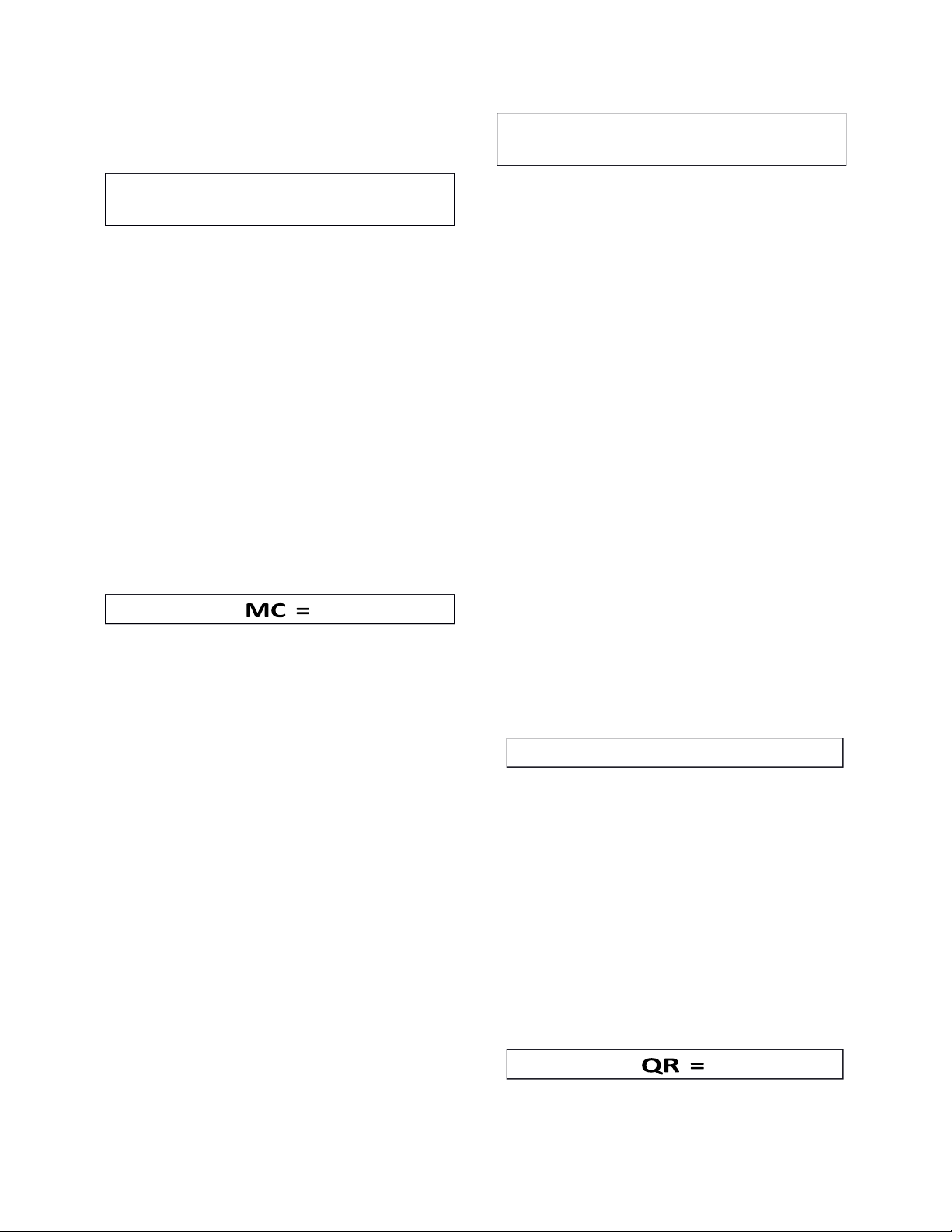
ROA = β0 + β1*STATE+ β2*CR+
enterprise business-like. Besides, β3*DFL+ β4*MC+ β5*SIZE+
these indicators also help us have a β6*BS+ β8*QR+ ε (1) look at easy ways to compare ROE = β0 + β1*ROA+ ε (2)
businesses together. Moreover, the final objective of financial ROA: Return on total assets management is to maximize the ROE: Return on equity
benefit of the owner so that after STATE: State capital ratio
examining the factors affecting the
DFL: Degree of Financial Leverage ROA, the authors examine the
MC: Management competence index impact of ROA over ROE.
SIZE: The size of the company ii. BS: Business cycle
Short-term solvency (QR & CR) To
measure the short-term solvency QR, CR: Short-term solvency
of researchers usually use the
b. Research hypotheses
current ratio (CR) and quick ratio i. Financial performance The (QR). Solvency impacts on business performance of the
financial performance in detail:
enterprise is a general economic
According to Almajali et al (2012),
indicator that reflects the level of Maleya and Muturi (2013), the use of the elements of the
solvency relationship the same production process. Business
way with financial performance.
performance is also reflected in the
But conversely, Khalifa and Zurina maneuver of the corporate
(2013) indicate solvency opposite governance between theory and
impact on financial performance.
practice to make the most of the
So the research hypothesis pair is weakness of the manufacturing given as:
process, such as machinery and
H01: Short-term solvency does not affect
equipment, raw materials, labor to financial performance
improve profitability. Overall ROS, ROA, ROE is a measure lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 H11: Short-term solvency affects
Liargovas and Skandalis (2008), Lee financial performance
(2009), Amalendu (2010), Almajali, et al
(2012) showed the impact of firm size and iii.
Degree of Financial Leverage
efficiency finance. These studies present (DFL)
conflicting views on the relationship
Degree of Financial Leverage refers to the
between size and financial performance.
use of debt in the capital structure of the
However, the opposite view that the scale
company. The Degree of Financial
has a relationship inversely to the
Leverage is one of the important decisions
financial performance due to some
of financial managers because it is a
problems with corruption and several
double-edged sword and affects the
other reasons: operating inefficiencies
benefits and risks of the owner as well as
due to poor control. The hypothesis is
the market value of the company. Besides, given as:
many researchers consider the impact of
the degree of financial leverage on
H03: Company size does not affect
financial performance in detail: Ghosh, financial performance
Nag and Sirmans (2000), Berger and di
H13: Company size has an impact on
Patti (2006) in his study had indicated the financial performance
degree of financial leverage has a positive
impact on financial performance, but on v. Business cycle (BS)
the contrary, Gleason et al (2000),
A company's business is the period from
Simerly and Li (2000), Maleya and
when a company buys goods to when the
Muturi (2013) in his study again indicates
company sells goods and collects money.
the negative impact of the degree of
The company's business cycle shorter, financial leverage to financial
shorten the turnaround time and
performance. The hypothesis is given as:
inventory turnaround time, the accounts
H02: Degree of financial leverage has no receivable increasing
impact on financial performance
financial performance. The main reason
due to goods sold faster, less storage
H12: Degree of financial leverage has an
time, increasing sales, reducing costs of
impact on financial performance iv. The
inventory investment. Moreover, trade
size of the company (SIZE) Company size
receivables faster turnaround, the
has measured the size of total assets.
company recover the debt faster,
Enterprise-scale is one of the first criteria
increasing capital turnover, reduce costs
to the company affirmed its position in the
related to accounts receivable. The dual
sector and attract investments of
impact of the shortened business cycles
investors. Ammar et al (2003), Amato and
increases profitability. So the hypothesis Burson (2007), is given as: 10 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
H04: Business cycle has no impact on
team when it satisfies at least three of the financial performance
following five conditions: (1) The
average managerial experience is 20
H14: Business has an impact on financial
years, (2 The management group holds an performance
average of 34% of the company shares, vi.
State capital ratio (STATE)
(3) Most managers in the university
The state capital ratio is measured by the
graduate group (4) Average age of
percentage of state capital in total equity.
managers in the group from 50 to 60 years
The joint-stock company listed on the
old, ( 5) All managers in the group
stock market and have long years of
undertake innovation activities - an
operation of most of the large-scale
innovation that refers to the introduction
capital mainly been equitized. So the
of new products, new production hypothesis is given as:
technologies, new market developments
or reforms of organizational structure.
H05: The ratio of state capital has no
function in the company. The hypothesis
impact on financial performance is given:
H15: The ratio of state capital has an
H07: Management competence index has
impact on financial performance vii.
no impact on financial performance
Management competence index (MC)
H17: Management competence index has
According to Timmons (1994), successful
an impact on financial performance
companies have a significant contribution
to the skills and creativity of managers. 5. RESEARCH RESULTS
Bird (1995) also pointed out that the
a. Descriptive statisticsIn Table 1,
capacity to manage a strong impact on the
the Descriptive Statistics provide data
financial performance and operational
minimum, maximum and average, the
efficiency of the company. These
standard deviation of the independent successful companies are those
variables and the dependent variable of 22
companies that have managers capable of
companies share industry information
"core" - the ability to combine the
technology on the Stock Exchange in the
knowledge, experience, expertise, and
period 2007 to 2018, with observation is
skills to the executive management team
80. production and business cycle (BS),
to achieve the objectives of Co. (Coyne,
an average of about 309 days. The short-
Hall and Clifford, 1997). According to
term solvency of the company average
MaMerikas et al. (2006), “professionals”
(CR) is about 2.79 times. Degree of
are managers who meet the following two
financial leverage (DFL) average 0.42
criteria: (1) Have a university degree and
times. The ratio of management capacity
(2) Direct management or be part of the
(MC) averaged about 1,261 billion VND.
management team. (management team).
Quick ratio averaging time is 2:04. Rate
According to Liargovas and Skandalis
of Return on total assets (ROA) 3.8%
(2008), a company has a management
average in 12 years and the profitability lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
ratio on average equity 7.2%. The average
company size (SIZE) is about 552,354
billion VND. The proportion of state
ownership (STATE) average about 12.5%.
b. Check correlationIn Table 2, the
variables include the production and
business cycles (BS), ratio management
capacity (MC) have a significant impact
on the financial performance ROA. MC
impact the same way with financial
efficiency, while BS opposite impact financial performance. 12 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics variables Mean
Minimum Maximum Std. Deviation Observation BS 308.275 47.647 1243.352 212.482 80 CR 2.790 1.148 25.688 3.303 80 DFL 0.424 0.007 0.861 0.221 80 MC 1.261 -5.838 9.037 2.233 80 QR 2.038 0.512 17.425 2.526 80 ROA 0.038 -0.121 0.193 0.056 80 ROE 0.072 -0.309 0.324 0.099 80 SIZE 552.354 70.336 2983.032 688.897 80 STATE 0.125 0 0.590 0.155 80
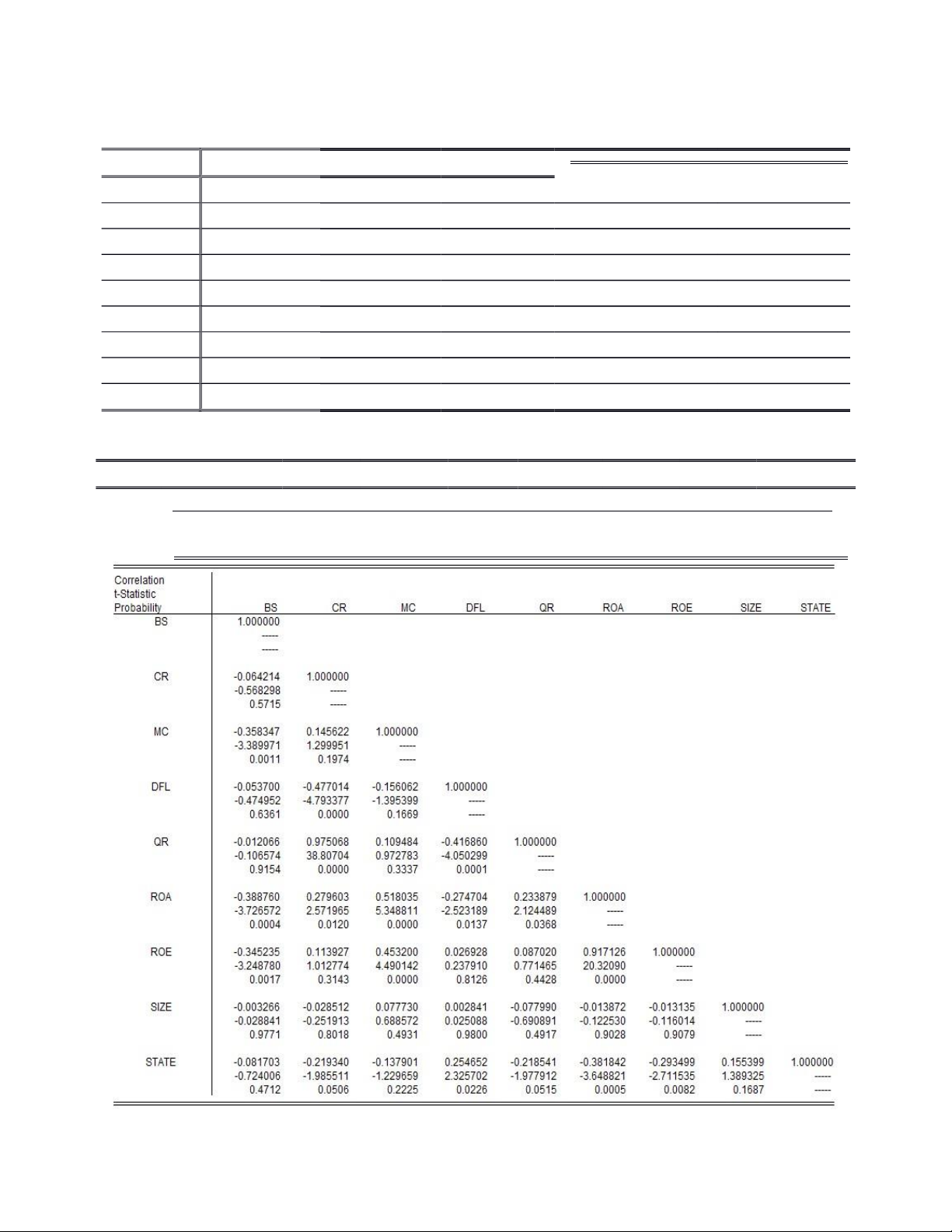
Table 2. Matrix correlation between ROA and the independent variables BS CR QR DFL MC SIZE STATE Correlation -0.388 0.279 0.234 -0.274 0.518 -0.013 -0.293 ROA Probability 0.000 0.012 0.036 0.013 0.000 0.907 0.008 lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
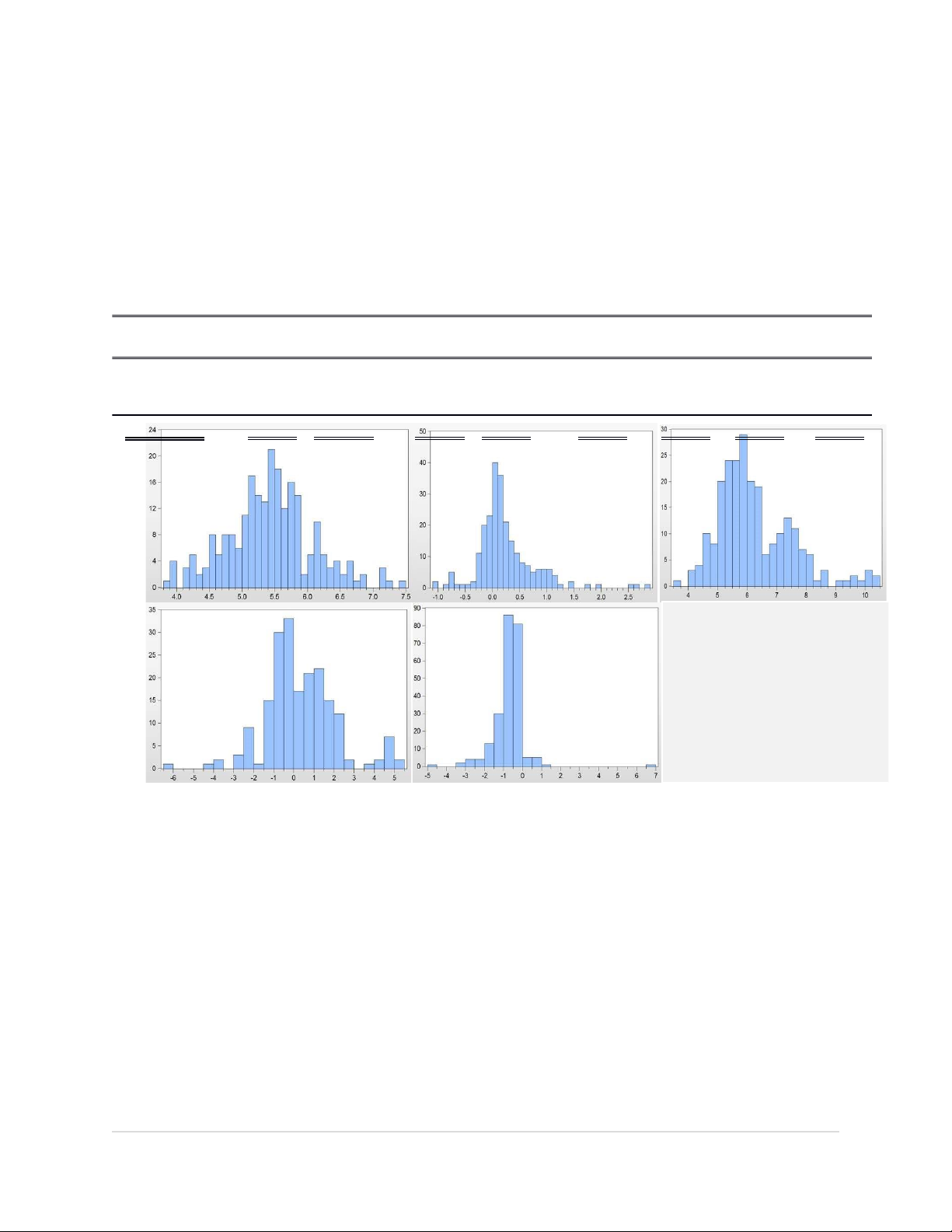
c. Test of the standard distribution To
variation from 1,165 VIF to 4114 to
estimate the linear regression to consider
model the phenomenon of no multi-
the variables have normal distribution or
collinearity between the independent
not. Initially, when examining several variables.
variables such as DFL, SIZE, MC, BS,
QR are not normally distributed variables
e. Check autocorrelation To examine
so the group moved into the natural
the serious autocorrelation often used at
Table 3. Check the normal distribution STATE CR
LNDFL ROA LNSIZE LNMC LNBS LNQR Skewnes 1.030 s 5.218 -1.998 1.302 0.779 -0.433 -0.428 1.771 Kurtosis 3.261 32.637 8.853 3.656 3.233 2.801 2.497 7.282 LNBS LNQR LNSIZE LNMC LNDFL VARIABLES HAVE CONVERTED TO NATURAL LOGA FUNCTION
logarithm function. After using this
the Durbin-Watson test, if the coefficient
method, it is almost all the variables was
of Durbin-Waston in the region from 1 to
transformed into a normal distribution
3 there will be no selfcorrelation
with the data in Table 3 is located.
phenomenon. Through Durbin-Watson test data on Eview8
multi-collinear when the VIF ratio greater
than 10. In Table 4, the coefficient of
d. Multi-collinearity test
Collinearity Statistics. The independent
Regression analysis to correlate the first
variables will have the phenomenon of
group will examine the phenomenon of
software with D = 1.582 (Table 5), the multi-collinear with model has no autocorrelation expertise phenomenon.
Table 4. Verification of multi-collinearity phenomenon 2 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 STATE CR LNDFL LNSIZE LNMC LNBS LNQR 15 | P a g e VIF 1.165 3.552 2.729 1.866 2.893 2.037 4.114
Table 5. Test of Anova and Durbin-Watson R-squared 0.763673 Adjusted R-squared 0.736554
collinearity test team used multiple S.E of regression 0.024897
regression analysis to examine the Sum squared resid
relationship between the dependent 0.037812 Log likelihood
variable and independent variables. 161.1615 (Table 6) F-statistic 28.15958 Prob(F-statistic) 0.000000
f. Multiple Regression i.
Inspection of the suitability of the model ROA
We have R-Square = 0.763 (Table 5) is the
mean of independent variables was 76.3%
which explains the change of financial performance. Besides, through accreditation A-nova on the
appropriateness of the model and may
find this model perfectly suited to
consider the impact of the independent
variables to effectively finance at (Pvalue = 4.72% <5%). ii.
A multiple regression model of
ROA and explain its meaning
After checking the normal distribution,
the autocorrelation test and multi- Mean dependent var 0.047279 S.D. dependent var 0.048507 Akaike info criterion - 4.439463 Schwarz criterion - 4.180436 Hanna-Quinn criter - 4.336699 Durbin-Waston stat 1.582219 lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
- State capital ratio (STATE): P- Therefore, the state invested
value = 1.94% <5% can reject
the greater the profit achieved the hypothesis H0 or the rate at low levels.
of state capital has an impact on financial performance and - Management Competency
has a negative impact (-) at a Ratio 5% significance level.
(LnMC): P-value is very small and less Companies with large-scale
than 5% which means is enough to reject state capital will have solid
the hypothesis H0 or the ratio of the
financial resources, scale, and
capacity of the management of the
the protection of the state of
company has an impact on performance. the outputs. In addition, for
finance. On the other hand, the ratio of the companies in the sector
capacity of the Management Board with
Table 6. The multiple regression model of ROA Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C 0.267 0.033 7.957 0.0000 STATE -0.054 0.022 -2.401 0.0194 CR -0.003 0.002 -1.592 0.1166 LNDFL -0.008 0.006 -1.407 0.1644 LNMC 0.028 0.004 7.227 0.0000 LNSIZE -0.026 0.005 -5.576 0.0000 LNBS -0.011 0.005 -2.100 0.0399 LNQR 0.006 0.009 -1.592 0.5658
ROA = 0.267 – 0.054*STATE – 0.003*CR – 0.008*LNDFL + 0.028*LNMC –
0.026*LNSIZE – 0.011*LNBS + 0.006*LNQR
telematics with the proportion
effect positive (+) to the financial
of equity capital high state will
performance, is consistent with severe have products and services to
early work of Timmons (1994), Bird the public post for mutual
(1995), Liargovas and Skandalis (2008), interest leads to profits is
Almajali et al (2012), ... with companies maximized. Moreover,
in the field of information technology companies with state capital
leaders needed a deep understanding of
have been high, the profits also
technology and creativity they needed for
belong to the state, businesses
work, only some very needed in this field. and just enjoy a fixed rate. 4 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 - Company size (LnSIZE): the
Thus, this is fully consistent size of thecompany p-value
with the theory. For companies <5%, company size has a in the fields of information significant impact on the technology to manage two financial performance of the types of mobile assets company and the impact (inventories and trade counterclockwise (-) for
receivables) faster turnaround effectiveness main. This is will help companies shorten consistent with the serious the production cycle of research on the relationship business because of business between the size of Ammar et in this area, there are many al (2003), Amato and Burson electronic devices very fast
(2007), Lee (2009), ... indicate depreciation should shorten the financial performance the production cycle of decreases as firm size business. Since then, the
increases. When the size of the company will save the company is enhanced, the investment costs and the cost control process becomes of inventories, trade
Table 7. Simple regression between ROE and ROA Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. C 0.011 0.004 2.273 0.0239 27.858 R-squared 0.766819
ROE = 0.011 + 2.085 * RO A ROA 2.085 0.075 0.0000 17 | P a g e complex, difficult to manage, receivables management, and this leads to corruption and increase profits. some other reasons. For the field of information iii.
Regression model ROE and ROA technology, while increasing
In Table 7, a significant impact the size of the company, the
ROA ROE (return rate of equity personnel should raise the
and earnings per share) with p- level to adapt to the new
value <5%. Besides, Rsquared is equipment and software. meant 0767 was 76.7% ROA explains the change in ROE. - Business production cycle
Moreover, we can see the positive (LnBS): Thisindex has a
impact of ROA (+) with ROE. As negative impact (-) on a result, an increase in ROA financial performance and is increases ROE.
statistically significant at 5%. lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474 6. CONCLUSIONS AND 7. REFERENCES RECOMMENDATIONS
managing inventory and customer
Research by the group has shown that
receivables more efficiently, it will reduce
STATE, MC, SIZE, BS have a significant
the turnaround time of two types of assets.
impact on financial performance. In it,
Moreover, to improve the financial
STATE, SIZE, BS harms financial
performance of the company should focus performance or companies sector on increasing the capacity of
information technology wants to increase
management. Besides, serious also found
financial efficiency need to shorten the
no relationship in the same direction
production cycle of business by
between the ROA and ROE, to increase
the profitability ratio of equity companies
should adopt strategies to increase their
ability to generate profits of assets.
Agiomirgiannakis, G., Voulgaris, F. And Papadogonas, T. (2006), ‘Financial factors
affecting profitability and employment growth: the case of Greek manufacturing’,
Int. J. Financial Services Management, Issue 1, volume 2/3, pages 232 - 242.
Amalendu, Bhunia (2010), ‘Financial Performance of Indian Pharmaceutical Industry:
A Case Study’, Asian Journal of Management Research, Issue 1, volume 2, page 427-451.
Ammar, A., Hanna, A.S., Nordheim, E.V. andRussell, J.S. (2003), ‘Indicator Variables
Model of Firm's Size-Prof- itability Relationship of Electrical Contractors Using
Financial and Economic Data’, Journal of Construction Engineering and
Management, No. 129, page 192-197.
Amato, L.H. and Burson, T.E. (2007), ‘The effects of firm size on profit rates in the
financial services’, Journal of Economics and Economic Education Research, Issue 8, volume 1, page 67-81.
Almajali, Y.A, Alamro, S.H. and Al-Soub, Y.Z. (2012), 'Factors Affecting the Financial
Performance of Listed Companies at Amman Jordanian Insurance Stock Exchange',
Journal of Management Research, Issue 4, Volume 2, page 226- 289.
Berger, A. N and di Patti, E.B (2006), ‘Capital Structure and Financial performance: A
New Approach to Testing Agency Theory and an Application to the Banking
Industry’, Journal of Banking and Finance, No. 30, page 1065-1102
Bird, B. (1995), ‘Toward a theory of entrepreneurial competency.’ In J.A.Katz (ed)
Advances in Entrepreneurship, Firm Emerence, and Growth, Greenwich, CT: JAI Press 2, page 52–72. 6 | P a g e lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
Coyne, K.P., Hall, J.D. and Clifford, P.G. (1997), ‘Is your Core Competence a Mirage?’,
The McKinsey Quarterly, Issue 1, Page 40-45.
Ghosh, C., Nag, R., and Sirmans, C. (2000), ‘The pricing of seasoned equity offerings:
Evidence from REITs’, Real Estate Economics, Issue 28, page 363-384.
Gleason, K., Mathur, L. and Mathur, I. (2000), ‘The interrelationship between culture,
capital structure, and perfor- mance: Evidence from European retailers’, Journal of
Business Research, Issue 50, page 185-191.
Hart, S. L. and Ahuja, G. (1996), ‘Does it pay to be green? An empirical examination of
the relationship between emission reduction and firm performance’, Business
Strategy and the Environment, Issue 5, page 30-37.
Khalifa, M.K. and Zurina, S. (2013), ‘Financial Performance and Identify Affecting
Factors in this Performance of Nonoil Manufacturing Companies Listed on Libyan
Stock Market (LSM)’, European Journal of Business and Management, Issue 5, Volume 12, page 82-89.
Konar, S. and Cohen, M. A. (2001), ‘Does the Market Value Environmental
Performance?’, Review of Economics and Statistics, Issue 83, Volume 2, page 281- 309.
Russo, M.V. and Fouts, P.A. (1997), ‘A resource-based perspective on corporate
environmental performance and profitability’, Academy of Management Journal,
Issue 40, Volume 3, page 534–559.
Liargovas, P. and Skandalis, K. (2008), ‘Factor affecting firms’ financial performance:
The Case of Greece’, American Economic Review, Issue 48 page 261-297.
Lee, J. (2009), ‘Does Size Matter in Firm Performance? Evidence from US Public
Firms’, Int. J. of the Economics of Business’, Issue 16, Volume 2, page 189-203.
McGuire, J. B., Sundgren, A. and Schneeweis, T. (1988), ‘Corporate social
responsibility and firm financial performance’, Academy of Management Journal,
Issue 31, Volume 4, page 854- 872.
Maleya, M.O. and Muturi, W. (2013), ‘Factors Affecting the Financial Performance of
Listed Companies at the Nairobi Securities Exchange in Kenya’, Research Journal
of Finance and Accounting, Issue 4, Volume 15, page 99-104.
Tarawneh, M. (2006), ‘A Comparison of Financial Performance in the Banking Sector:
Some Evidence from Omani Commercial Banks’, International Research Journal of
Finance and Economics, Issue 3, page 103-112. lOMoAR cPSD| 46988474
Simerly, R. andLi, M. (2000), ‘Environmental dynamism, financial leverage and
performance: A theoretical integration and an empirical test’, Strategic
Management Journal, Vol. 21, volume 1, page 31-49.
Stanwick, S. andStanwick, P. (2000), ‘The relationship between environmental
disclosures and financialperformance: An empirical study of the US corporation ',
Eco-Management and Auditing, No. 7, page 155-164.
Timmons, J.A. (1994), New Venture Creation: Entrepreneurship for the 21st Century,
4th edition. Irwin Press, Chica- go.
Yuqi, L. (2008), ‘Determinants of Banks’ Profitability and Its Implication on Risk
Management Practices: Panel Evidence from the UK ', PhD Thesis, The University of Nottingham, UK.
Yuqi, L. (2008), 'The determinants of bank returns' and its implications for risk
management practices: Council evidence from UK', University of Nottingham, UK 8 | P a g e




