Preview text:
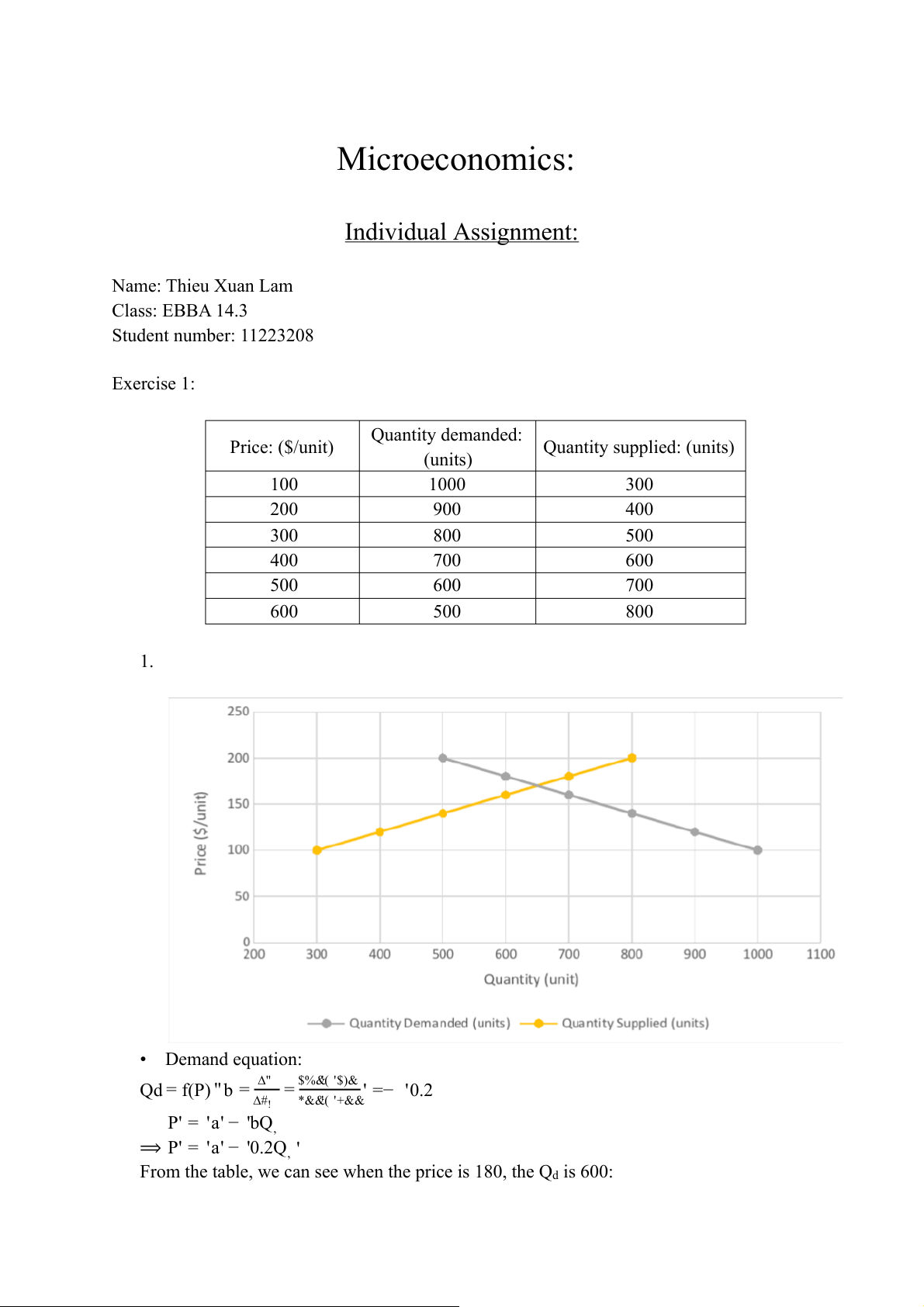
Microeconomics: Individual Assignment: Name: Thieu Xuan Lam Class: EBBA 14.3 Student number: 11223208 Exercise 1: Quantity demanded: Price: ($/unit) Quantity supplied: (units) (units) 100 1000 300 200 900 400 300 800 500 400 700 600 500 600 700 600 500 800 1. • Demand equation:
Qd = f(P) ' b = ∆" = $%&'( '$)& ' =− '0.2 ∆#! *&&'( '+&& P' = 'a' − 'bQ, ⟹ P' = 'a' − '0.2Q, '
From the table, we can see when the price is 180, the Qd is 600:
180 ' = ' a' − '0.2' × '600 ⟹ a ' = '300
⟹ P' = '300' − '0.2' × 'Q, ' • Supply equation:
Q- = f(P)' d = ∆" = $%&'( '$)& ' =0.2 ∆#" .&&'( '%&& P' = 'c' + 'dQ- ⟹ P' = 'c' +0.2Q-
From the table, we can see when the price is 200, the Qs is 800: 200 ' =c ' + '0.2 ' × '800 ⟹ c' = 40 ⟹ P' = 40+ '0.2 ' × 'Q- '
• Equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity can be found at point E where:
P/ = 300 – 0.2' ×Q, = 40 + 0.2 ×Q-
Q, = Q- = Q/ ⟹ 0.4 × 'Q/ = 260 × 'Q/ = 650 (units) P/ = 170 ($/unit) 2.
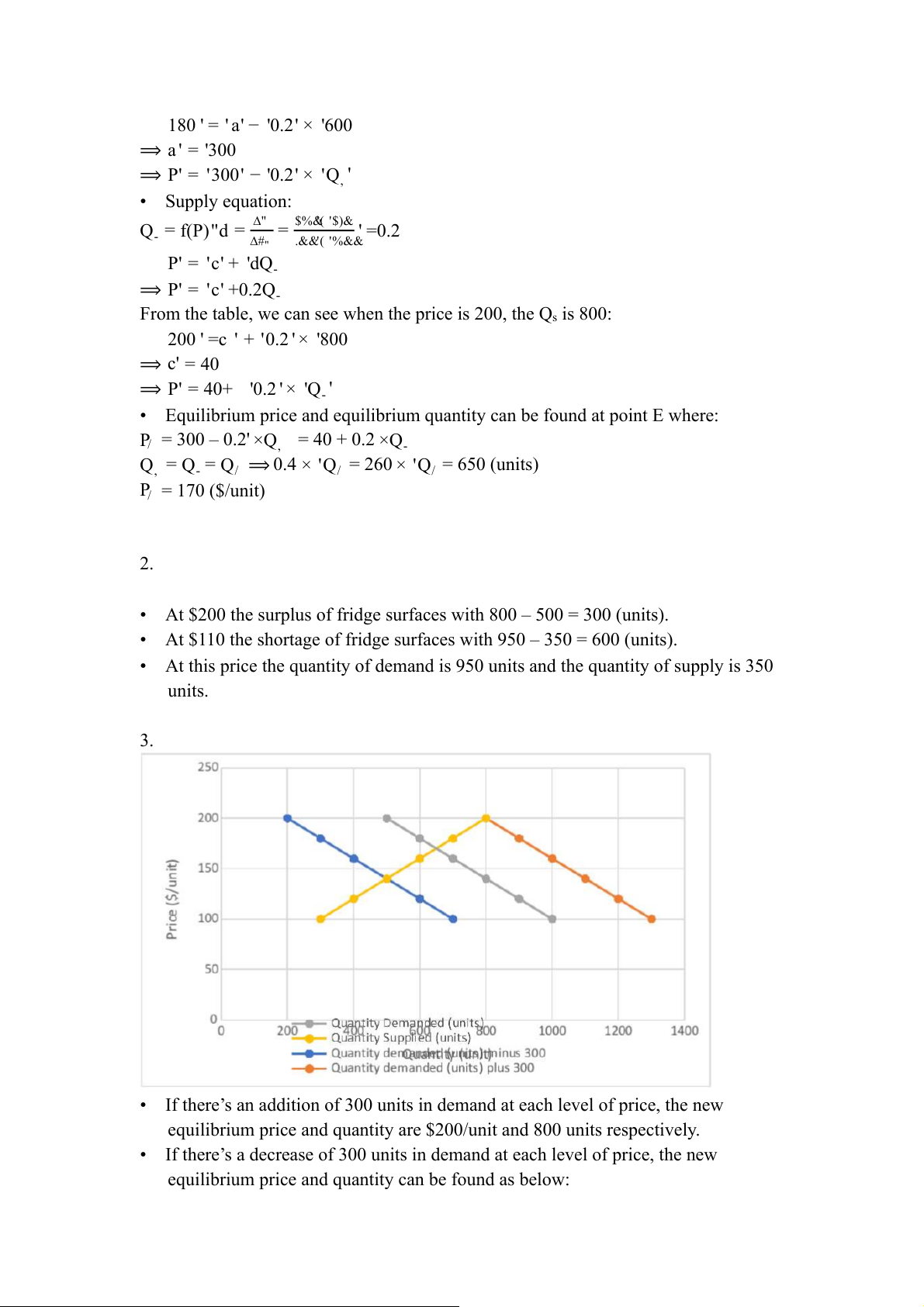
• At $200 the surplus of fridge surfaces with 800 – 500 = 300 (units).
• At $110 the shortage of fridge surfaces with 950 – 350 = 600 (units).
• At this price the quantity of demand is 950 units and the quantity of supply is 350 units. 3.
• If there’s an addition of 300 units in demand at each level of price, the new
equilibrium price and quantity are $200/unit and 800 units respectively.
• If there’s a decrease of 300 units in demand at each level of price, the new
equilibrium price and quantity can be found as below:
• At Qd = 0, P = a = 240 ($/unit) • P = 240 – 0.2Qd
• P = 40 + 0.2Qs (Supply is constant)
• Pe = 240 – 0.2Qd = 40 + 0.2Qs, Qd = Qs = Qe
• ⟹ 0.4Qe = 200 ⟺ Qe = 500 (units), Pe = 140 ($/unit)
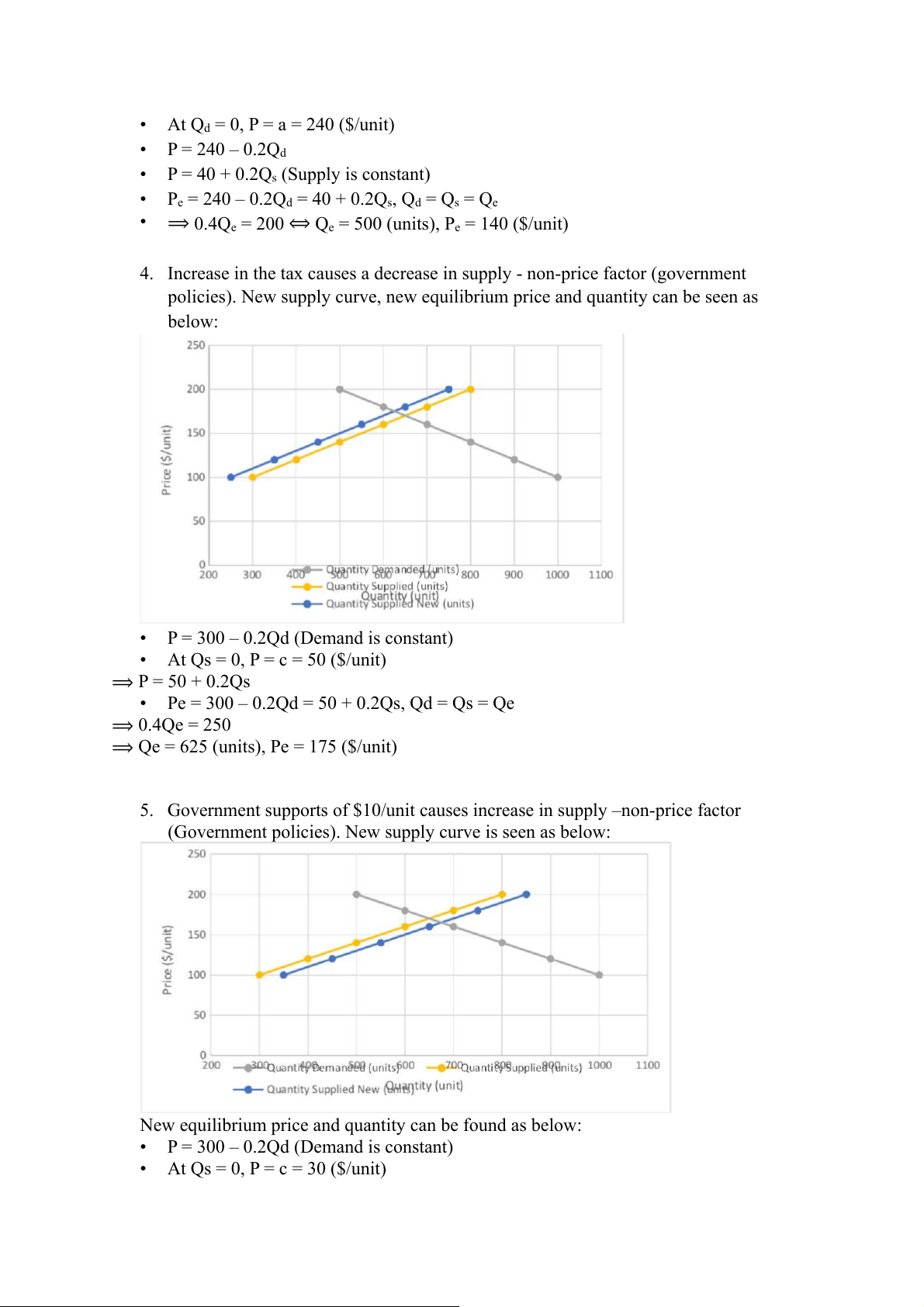
4. Increase in the tax causes a decrease in supply - non-price factor (government
policies). New supply curve, new equilibrium price and quantity can be seen as below:
• P = 300 – 0.2Qd (Demand is constant)
• At Qs = 0, P = c = 50 ($/unit) ⟹ P = 50 + 0.2Qs
• Pe = 300 – 0.2Qd = 50 + 0.2Qs, Qd = Qs = Qe ⟹ 0.4Qe = 250
⟹ Qe = 625 (units), Pe = 175 ($/unit)
5. Government supports of $10/unit causes increase in supply –non-price factor
(Government policies). New supply curve is seen as below:
New equilibrium price and quantity can be found as below:
• P = 300 – 0.2Qd (Demand is constant)
• At Qs = 0, P = c = 30 ($/unit) ⟹ P = 30 + 0.2Qs
• Pe = 300 – 0.2Qd = 30 + 0.2Qs, Qd = Qs = Qe
⟹ 0.4Qe = 270-> Qe = 675 (units), Pe = 165 ($/unit) Exercise 2: 1.
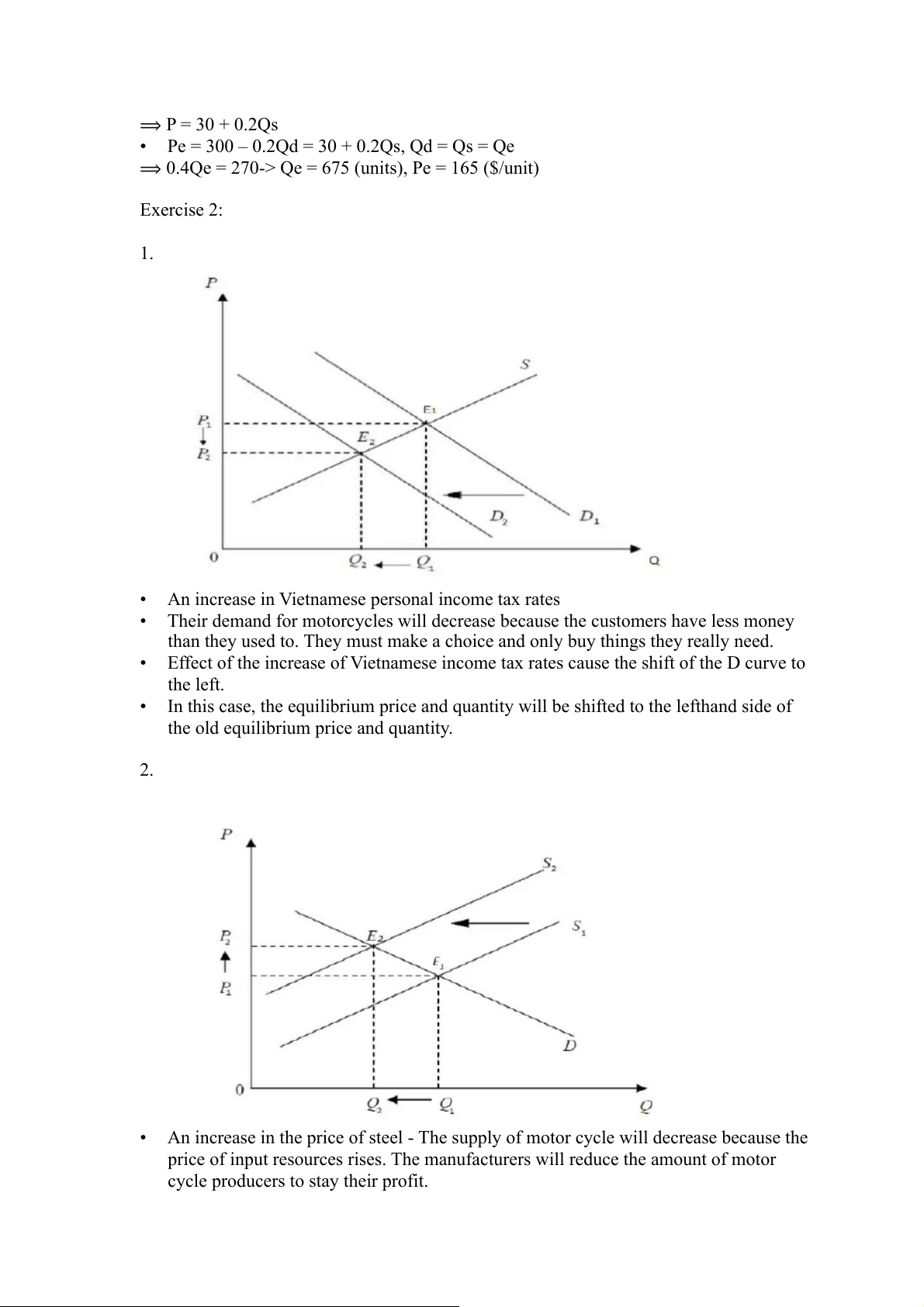
• An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates
• Their demand for motorcycles will decrease because the customers have less money
than they used to. They must make a choice and only buy things they really need.
• Effect of the increase of Vietnamese income tax rates cause the shift of the D curve to the left.
• In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the lefthand side of
the old equilibrium price and quantity. 2.
• An increase in the price of steel - The supply of motor cycle will decrease because the
price of input resources rises. The manufacturers will reduce the amount of motor
cycle producers to stay their profit.
• Effect of the increase of price of steel cause the shift of the S curve to the left.
• In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the lefthand side of
the old equilibrium price and quantity. 3.
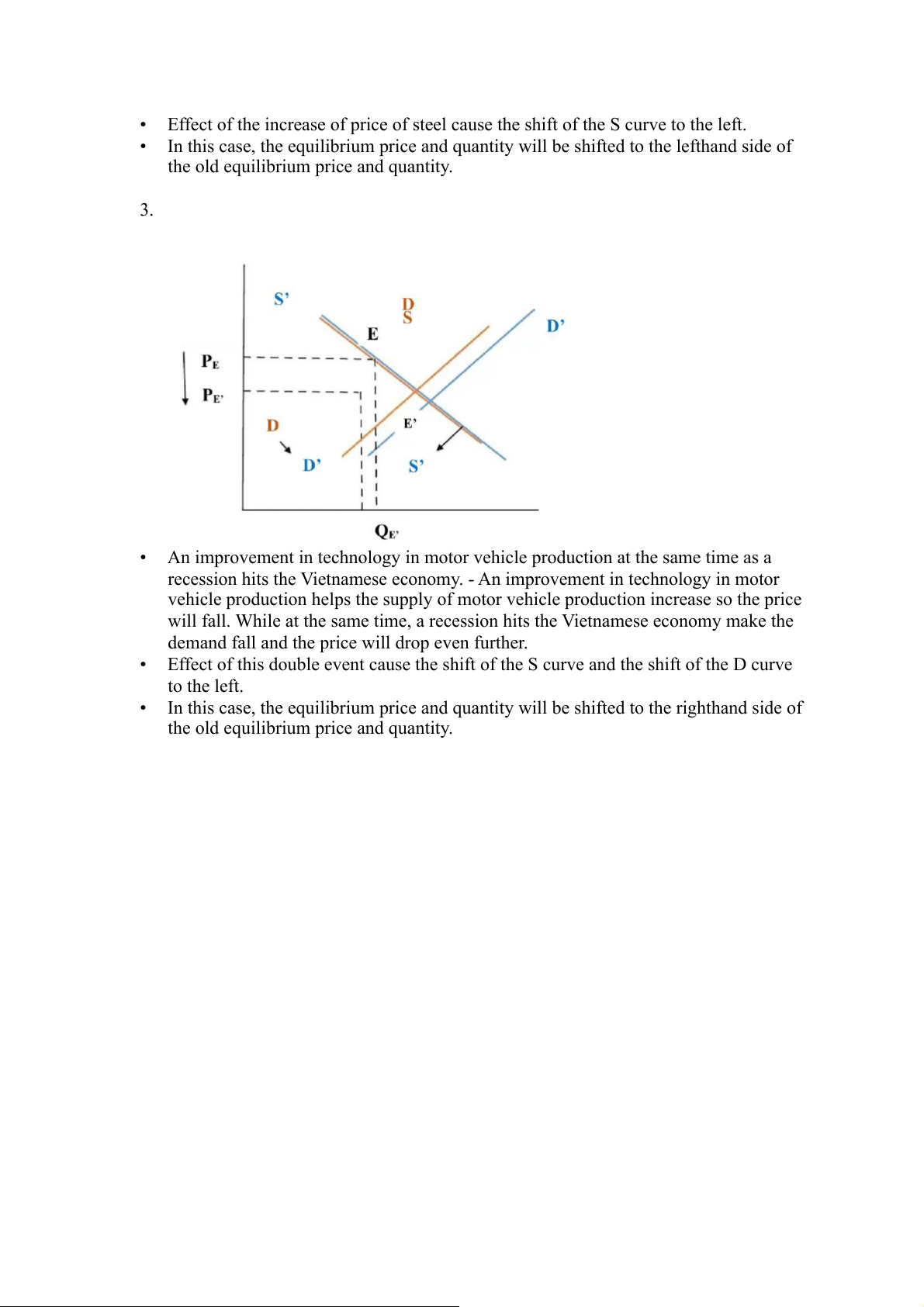
• An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same time as a
recession hits the Vietnamese economy. - An improvement in technology in motor
vehicle production helps the supply of motor vehicle production increase so the price
will fall. While at the same time, a recession hits the Vietnamese economy make the
demand fall and the price will drop even further.
• Effect of this double event cause the shift of the S curve and the shift of the D curve to the left.
• In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the righthand side of
the old equilibrium price and quantity.