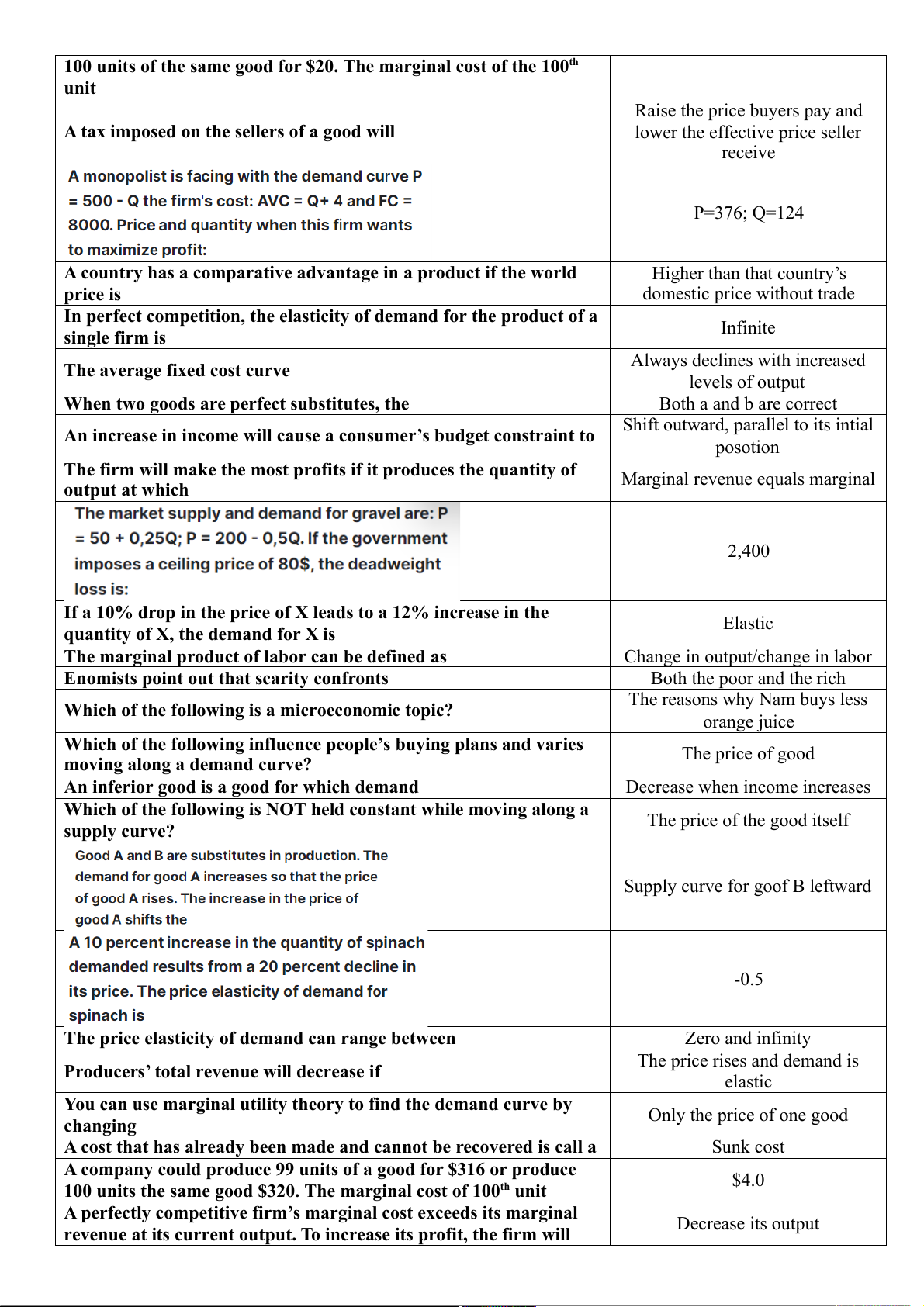
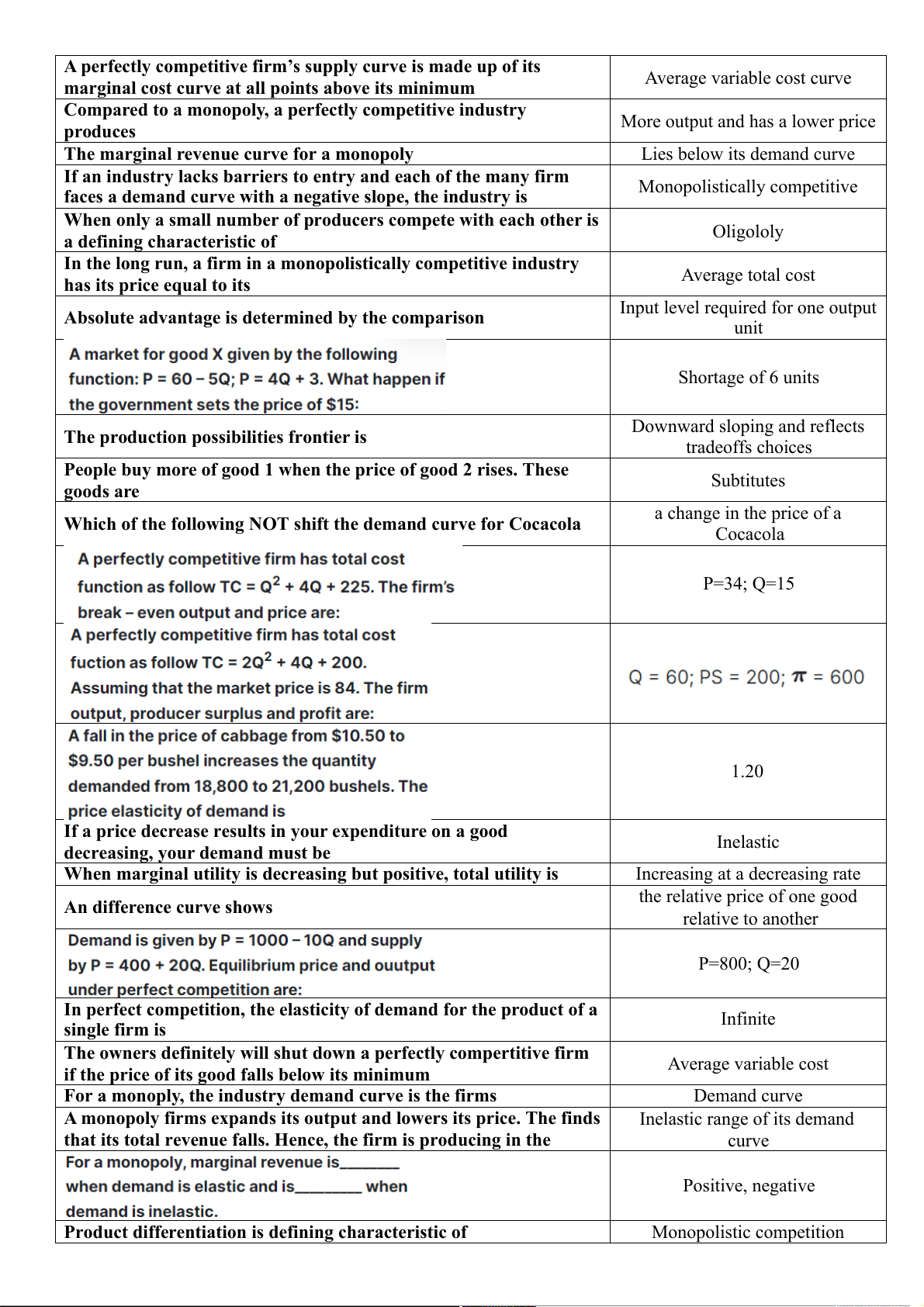

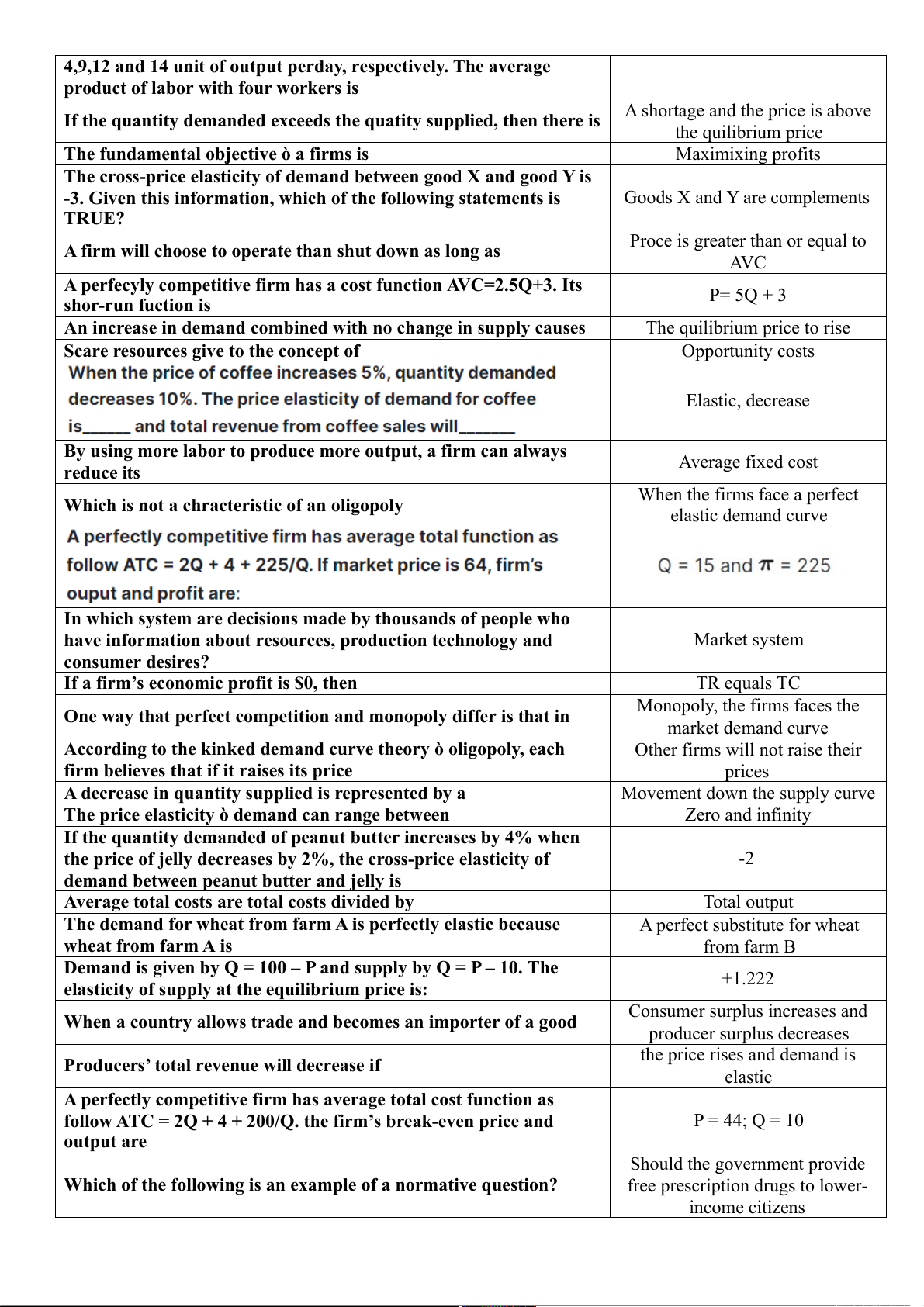
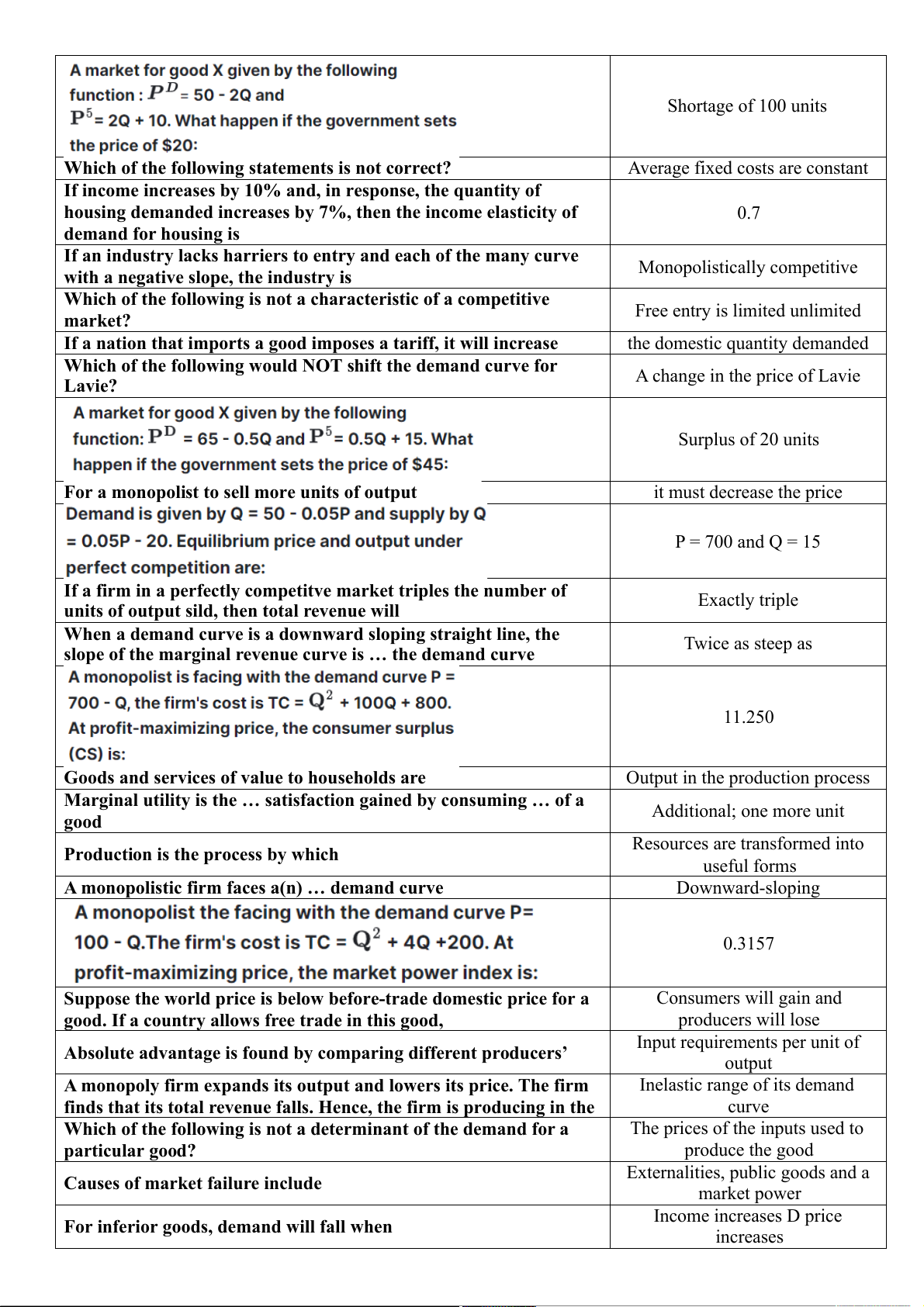
Preview text:
How we calculate marginal utility?
An increase in demand caused no change in the equilibrium price. Perfectly elastic Thus, supply must be 20 plasma TVs that must be
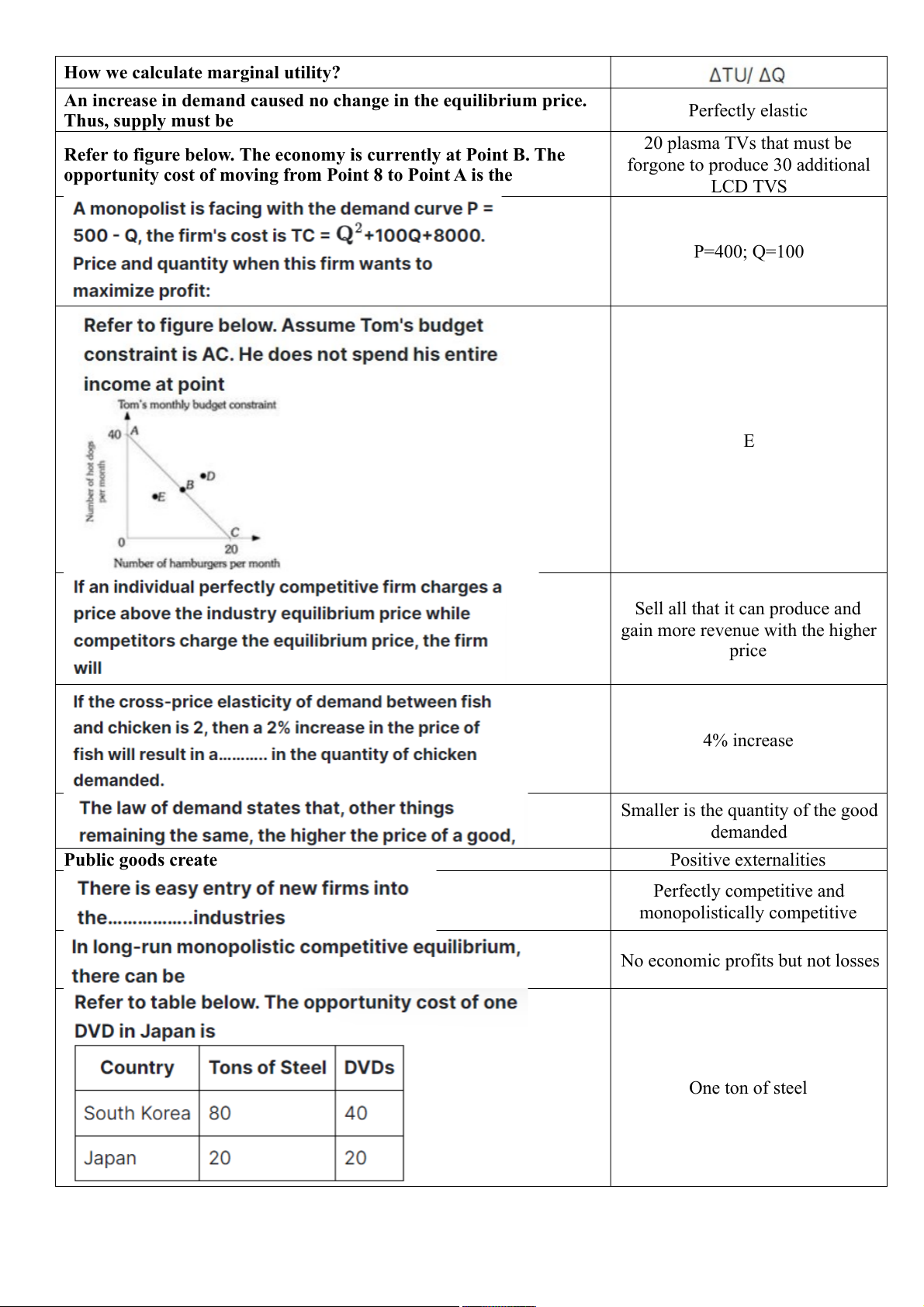
Refer to figure below. The economy is currently at Point B. The
forgone to produce 30 additional
opportunity cost of moving from Point 8 to Point A is the LCD TVS P=400; Q=100 E
Sell all that it can produce and
gain more revenue with the higher price 4% increase
Smaller is the quantity of the good demanded Public goods create Positive externalities Perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive
No economic profits but not losses One ton of steel Negative Free market system Make everyone better off P=10; Q=21 0.329 3 H 2000 Entry is relatively easy
Explicit costs plus the implicit costs Rival excludable P=40; Q=50 Zero All of the above
10 units of good X and 16 units of good Y Each Many firms each able to differentiate their product Q=11 and pi=0
When supply decreases and demand does not change, the Decreases and the price rises equilibrium quantity
Marginal proceeds are equivalent to price for which one of Perfect competition
following kinds of market structure Shortage of 6 units
Which of the following are NOT barriers to entry? Consent decrees
Increases the supply of fast-food
An increase in the number of fast-food restaurants meals +2.0
Will decrease if the shift is small,
In the kinded demand curve model of oligolopy, if the marginal cost
but stay the same if the shift is
curve shifts upward, then large P=2Q+2
Short-run costs that do NOT depend on the level of output are Fixed costs only
For a good that is a luxury, demand Tends to be elastic
If a price decrease results in your expenditure on a good Inelastic
decreasing, your demand must be
Economuc profit is the difference between total revenue and
Opportunity costs of production
When marginal utility is decreasing but positive, total utility is
Increasing at a decreasing rate
Which of the following would NOT shift the demand curve for
A change in the price of a turkey turkey?
Economic profit is the difference between total revenue and
Opportunity costs of production $10 and 100 units
Which of the following influences people’s buyin plans and varies The price of the good
moving along a demand curve?
Firms in monopolistic competition always will Earn an economic profit
If an industry lacks barriers to entry and each of the many firm Monopolistically competitive
faces a demand curve with a negative slope, the industry is Q=20;PS=800
People buy more of good I when the price of good 2 rises. These Substitutes goods are P=34; Q=15
The amount of money that a firm of its output is called Total revenue 0$
Average revenue quuals marginal For a competitve firm, revenue
The monopolist’s profit-maximizing quantity of output is Marginal cost and marginal
determined by the intersection of which of the following two revenue curves?
If an industry lasks barriers to entry and each of the many firm Monopolistically competitive
faces a demand curve with a negative slope, the industry is
The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly Lies below its demand curve
The adage, “There is no such things as a free lunch,” is used to People face tradeoffs
illustrate the principle that
In the markets for the factors of production in the circular-flow
Households are seller and firms diagram are buyers. Normative statements, they are When economists make
speaking not as scientists but as policy advisers. Accounting profit will exceed
If there are implicit costs of production, economic profit
For two individuals who engage in the same two productive
Have a comparative advantage in
activities, it is impossible for one of the two individuals to both activities
If good A and B are complements, then an 26. If goods increase in Less of good B being sold
the price of good A will result in
A cost that has already been made and cannot be recovered is Sunk cost called a
A perfetly competitive firm’s marginal cost exceeds its marginal Decrease its output
revenue at its current output. To increase its profit, the firm will
A company could produce 99 units of a good for $316 of produce Is $4.0
100 units of the same good for $20. The marginal cost of the 100th unit Raise the price buyers pay and
A tax imposed on the sellers of a good will
lower the effective price seller receive P=376; Q=124
A country has a comparative advantage in a product if the world Higher than that country’s price is domestic price without trade
In perfect competition, the elasticity of demand for the product of a Infinite single firm is Always declines with increased
The average fixed cost curve levels of output
When two goods are perfect substitutes, the Both a and b are correct
Shift outward, parallel to its intial
An increase in income will cause a consumer’s budget constraint to posotion
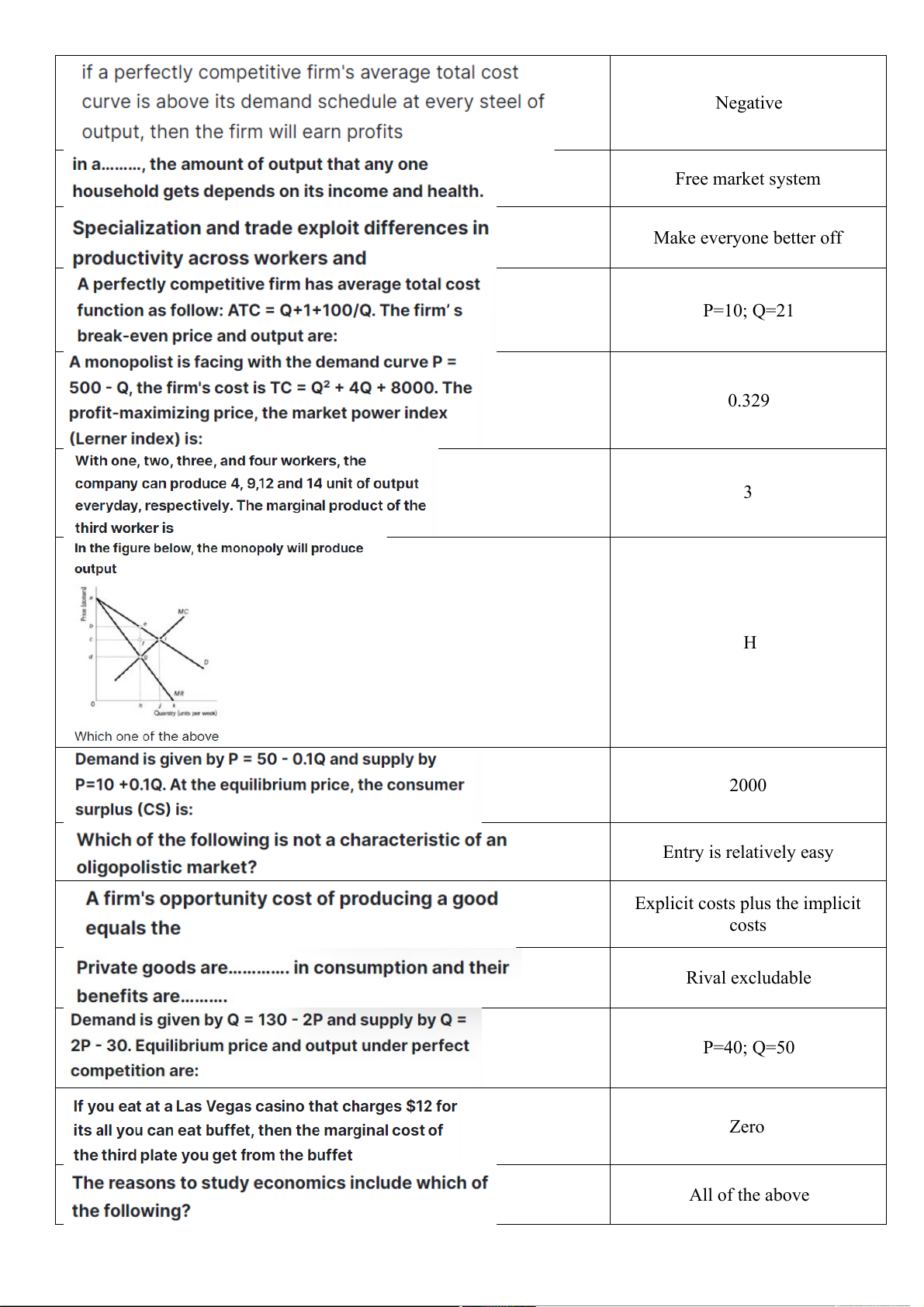
The firm will make the most profits if it produces the quantity of
Marginal revenue equals marginal output at which 2,400
If a 10% drop in the price of X leads to a 12% increase in the Elastic
quantity of X, the demand for X is
The marginal product of labor can be defined as
Change in output/change in labor
Enomists point out that scarity confronts Both the poor and the rich The reasons why Nam buys less
Which of the following is a microeconomic topic? orange juice
Which of the following influence people’s buying plans and varies The price of good
moving along a demand curve?
An inferior good is a good for which demand Decrease when income increases
Which of the following is NOT held constant while moving along a The price of the good itself supply curve?
Supply curve for goof B leftward -0.5
The price elasticity of demand can range between Zero and infinity The price rises and demand is
Producers’ total revenue will decrease if elastic
You can use marginal utility theory to find the demand curve by Only the price of one good changing
A cost that has already been made and cannot be recovered is call a Sunk cost
A company could produce 99 units of a good for $316 or produce $4.0
100 units the same good $320. The marginal cost of 100th unit
A perfectly competitive firm’s marginal cost exceeds its marginal Decrease its output
revenue at its current output. To increase its profit, the firm will
A perfectly competitive firm’s supply curve is made up of its Average variable cost curve
marginal cost curve at all points above its minimum
Compared to a monopoly, a perfectly competitive industry
More output and has a lower price produces
The marginal revenue curve for a monopoly Lies below its demand curve
If an industry lacks barriers to entry and each of the many firm Monopolistically competitive
faces a demand curve with a negative slope, the industry is
When only a small number of producers compete with each other is Oligololy
a defining characteristic of
In the long run, a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry Average total cost
has its price equal to its
Input level required for one output
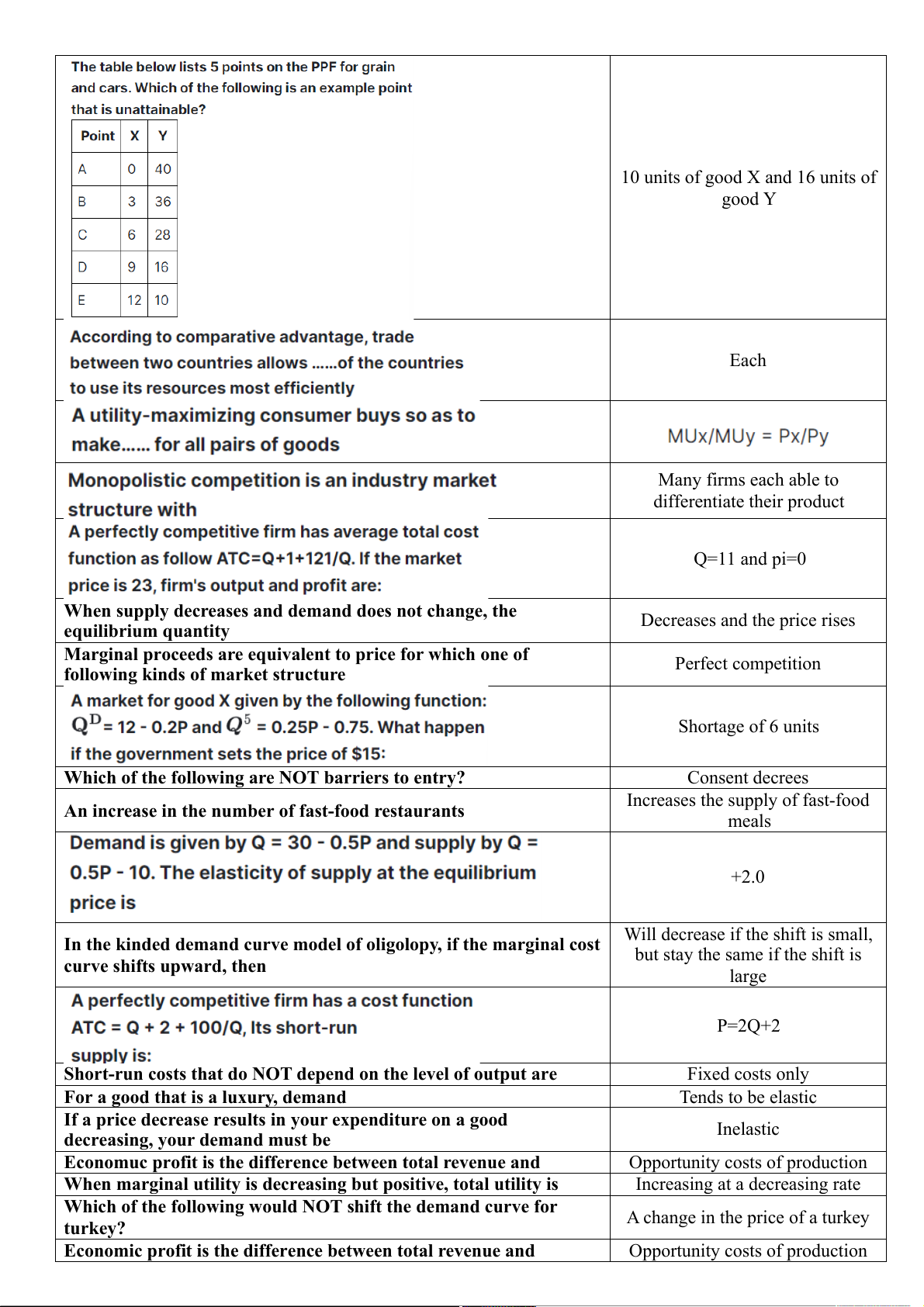
Absolute advantage is determined by the comparison unit Shortage of 6 units Downward sloping and reflects
The production possibilities frontier is tradeoffs choices
People buy more of good 1 when the price of good 2 rises. These Subtitutes goods are a change in the price of a
Which of the following NOT shift the demand curve for Cocacola Cocacola P=34; Q=15 1.20
If a price decrease results in your expenditure on a good Inelastic
decreasing, your demand must be
When marginal utility is decreasing but positive, total utility is
Increasing at a decreasing rate the relative price of one good
An difference curve shows relative to another P=800; Q=20
In perfect competition, the elasticity of demand for the product of a Infinite single firm is
The owners definitely will shut down a perfectly compertitive firm Average variable cost
if the price of its good falls below its minimum
For a monoply, the industry demand curve is the firms Demand curve
A monopoly firms expands its output and lowers its price. The finds Inelastic range of its demand
that its total revenue falls. Hence, the firm is producing in the curve Positive, negative
Product differentiation is defining characteristic of Monopolistic competition
According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly, each
Other firms will also lower theirs
firm believes that if it lowers its price,
A country has a comparative advantage in producing a product if
Higher domestic price when there the worlf price leved is no trade $70
Each of the following is a determinant of demand except Technology
Suppose that when income rises, the demand curve for computers Normal goods
shift to the right. In this case, we know computers are Downward sloping and reflects
The production possibilities frontier is tradeoffs in choices
Which of the following events would cause a movement upward The prices of tomatoes rises
and to the right along thes supply curve for tomatoes?
Suppose buyers of computers and printers regard those two goods A decrease in the demand for
as complements. Then an increase in the price of computers will printers and a decrease in the cause quantity supplied of printers The demand curve will shift
upward by $20, and the effective
price received by sellers will less than $20
A market structure in which there are many firms selling products Monopolistic competition
that are similar but not indentical is known as
Economists normally assume that the goal of firm is to Maximize its profit
For a firm in perfectly competitive market, the price of Equal to marginal revenue
When quantity moves proportionately the same amount as price
Unit elastic and the price elasticity demand is of demand is 1
If the price elasticity of demand for good is 4.0, then a 10% 40% decrease in the quantity
increase in price results in a demanded Emphasize the benefits of
Advocates of the minimum wage teenagers of increase in the minimum wage CS=242; PS=121 L=0.30; DWL=50
Economics deals primarily with the concepts of Scarcity
Assume, for France, that the dosmestic price of tea without Other countries have a
international trade is higher than the word price of tea. This comparative advantage over suggests that France in producing tea
Which of the following would be most likely to have monopoly A local cable TV provider power? $45,000
Oliopoly is the market that has a
Which of the following statements is accurate? few large firms 1012.5
With one, two, three and four workers, the company can produce 3.5
4,9,12 and 14 unit of output perday, respectively. The average
product of labor with four workers is
A shortage and the price is above
If the quantity demanded exceeds the quatity supplied, then there is the quilibrium price
The fundamental objective ò a firms is Maximixing profits
The cross-price elasticity of demand between good X and good Y is
-3. Given this information, which of the following statements is Goods X and Y are complements TRUE?
Proce is greater than or equal to
A firm will choose to operate than shut down as long as AVC
A perfecyly competitive firm has a cost function AVC=2.5Q+3. Its P= 5Q + 3 shor-run fuction is
An increase in demand combined with no change in supply causes The quilibrium price to rise
Scare resources give to the concept of Opportunity costs Elastic, decrease
By using more labor to produce more output, a firm can always Average fixed cost reduce its When the firms face a perfect
Which is not a chracteristic of an oligopoly elastic demand curve
In which system are decisions made by thousands of people who
have information about resources, production technology and Market system consumer desires?
If a firm’s economic profit is $0, then TR equals TC Monopoly, the firms faces the
One way that perfect competition and monopoly differ is that in market demand curve
According to the kinked demand curve theory ò oligopoly, each
Other firms will not raise their
firm believes that if it raises its price prices
A decrease in quantity supplied is represented by a Movement down the supply curve
The price elasticity ò demand can range between Zero and infinity
If the quantity demanded of peanut butter increases by 4% when
the price of jelly decreases by 2%, the cross-price elasticity of -2
demand between peanut butter and jelly is
Average total costs are total costs divided by Total output
The demand for wheat from farm A is perfectly elastic because A perfect substitute for wheat wheat from farm A is from farm B
Demand is given by Q = 100 – P and supply by Q = P – 10. The +1.222
elasticity of supply at the equilibrium price is: Consumer surplus increases and
When a country allows trade and becomes an importer of a good producer surplus decreases the price rises and demand is
Producers’ total revenue will decrease if elastic
A perfectly competitive firm has average total cost function as
follow ATC = 2Q + 4 + 200/Q. the firm’s break-even price and P = 44; Q = 10 output are Should the government provide
Which of the following is an example of a normative question?
free prescription drugs to lower- income citizens Shortage of 100 units
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Average fixed costs are constant
If income increases by 10% and, in response, the quantity of
housing demanded increases by 7%, then the income elasticity of 0.7 demand for housing is
If an industry lacks harriers to entry and each of the many curve Monopolistically competitive
with a negative slope, the industry is
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a competitive
Free entry is limited unlimited market?
If a nation that imports a good imposes a tariff, it will increase the domestic quantity demanded
Which of the following would NOT shift the demand curve for A change in the price of Lavie Lavie? Surplus of 20 units
For a monopolist to sell more units of output it must decrease the price P = 700 and Q = 15
If a firm in a perfectly competitve market triples the number of Exactly triple
units of output sild, then total revenue will
When a demand curve is a downward sloping straight line, the Twice as steep as
slope of the marginal revenue curve is … the demand curve 11.250
Goods and services of value to households are
Output in the production process
Marginal utility is the … satisfaction gained by consuming … of a Additional; one more unit good Resources are transformed into
Production is the process by which useful forms
A monopolistic firm faces a(n) … demand curve Downward-sloping 0.3157
Suppose the world price is below before-trade domestic price for a Consumers will gain and
good. If a country allows free trade in this good, producers will lose Input requirements per unit of
Absolute advantage is found by comparing different producers’ output
A monopoly firm expands its output and lowers its price. The firm Inelastic range of its demand
finds that its total revenue falls. Hence, the firm is producing in the curve
Which of the following is not a determinant of the demand for a
The prices of the inputs used to particular good? produce the good
Externalities, public goods and a
Causes of market failure include market power Income increases D price
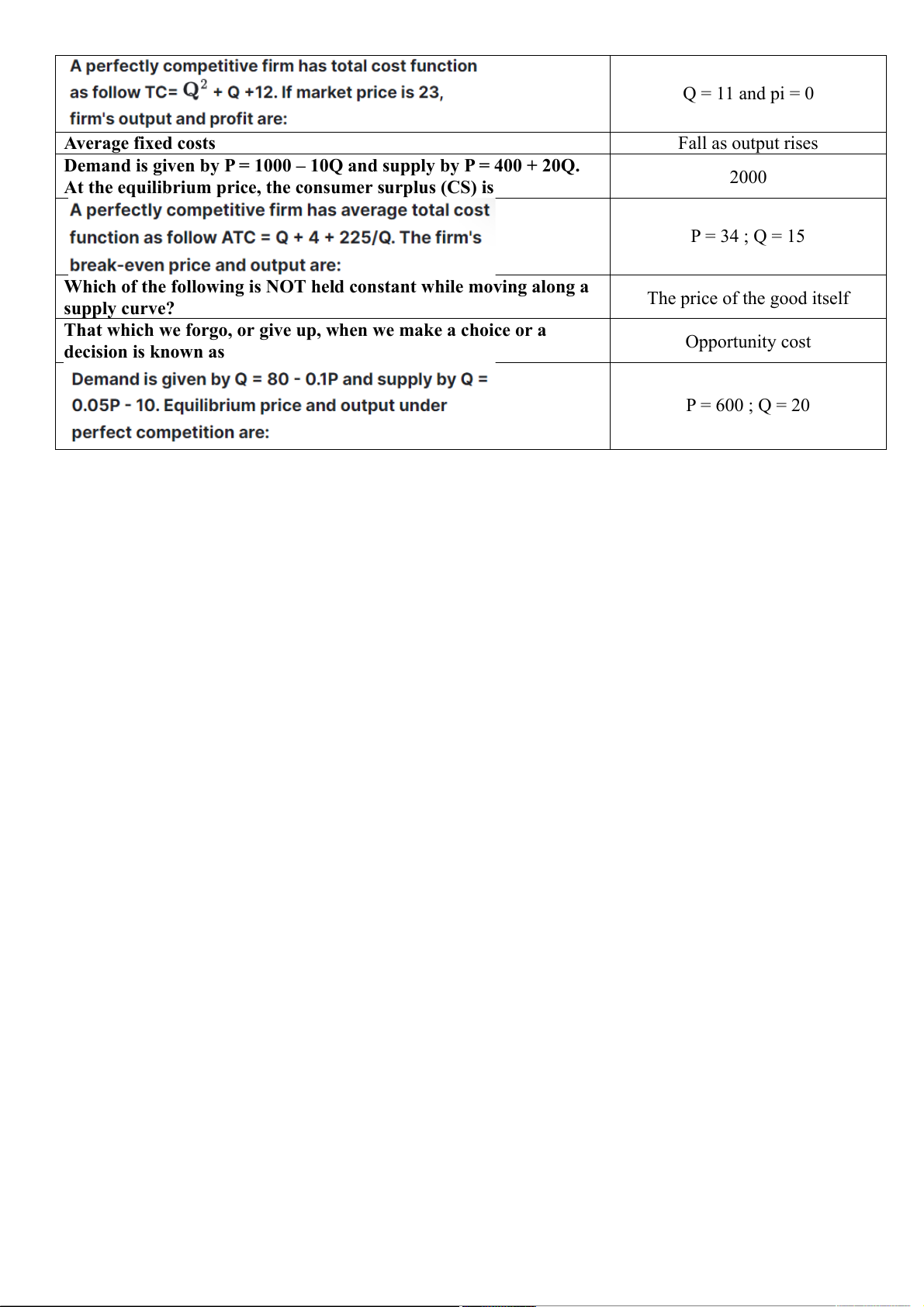
For inferior goods, demand will fall when increases Q = 11 and pi = 0 Average fixed costs Fall as output rises
Demand is given by P = 1000 – 10Q and supply by P = 400 + 20Q. 2000
At the equilibrium price, the consumer surplus (CS) is P = 34 ; Q = 15
Which of the following is NOT held constant while moving along a The price of the good itself supply curve?
That which we forgo, or give up, when we make a choice or a Opportunity cost decision is known as P = 600 ; Q = 20



