


Preview text:
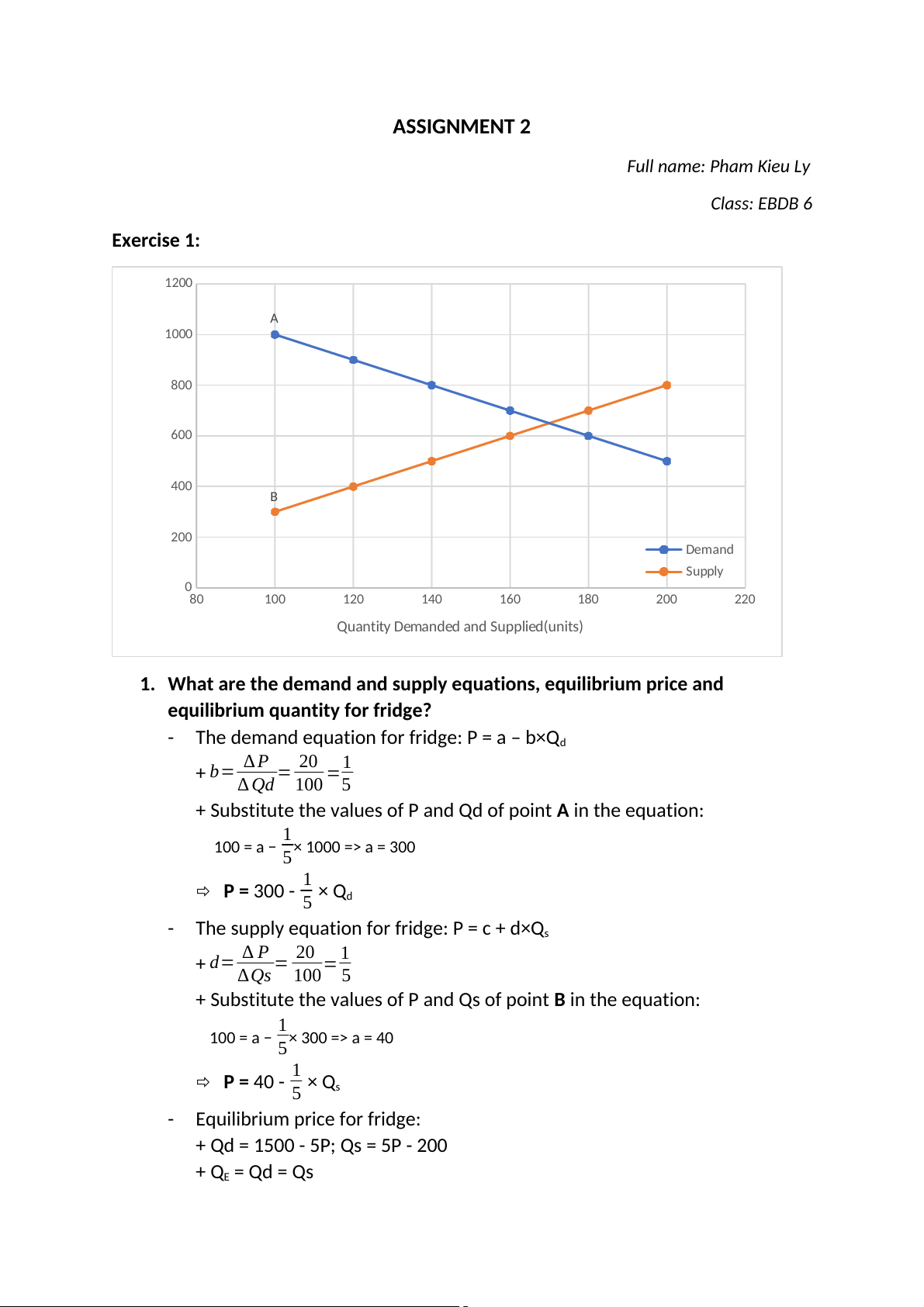
ASSIGNMENT 2 Full name: Pham Kieu Ly Class: EBDB 6 Exercise 1: 1200 A 1000 800 ) 600 e ($/unit ic Pr 400 B 200 Demand Supply 080 100 120 140 160 180 200 220
Quantity Demanded and Supplied(units)
1. What are the demand and supply equations, equilibrium price and
equilibrium quantity for fridge? -
The demand equation for fridge: P = a – b×Qd ∆ P 20 1 + b= = = ∆ Qd 100 5
+ Substitute the values of P and Qd of point A in the equation: 1
100 = a − × 1000 => a = 300 5 1 P = 300 - × Q 5 d -
The supply equation for fridge: P = c + d×Qs ∆ P 20 1 + d= = = ∆Qs 100 5
+ Substitute the values of P and Qs of point B in the equation: 1
100 = a − × 300 => a = 40 5 1 P = 40 - × Q 5 s - Equilibrium price for fridge:
+ Qd = 1500 - 5P; Qs = 5P - 200 + QE = Qd = Qs
1500 - 5P = 5P - 200 5 × Qs => P = 170 -
Equilibrium quantity for fridge:
+ QE = Qd => QE = 1500 - 5×170 => QE = 650
2. What are the surplus and shortage of fridge at the price of $200 and $110? -
The surplus of fridge at the price of $ 200 is:
∆Q = Qs – Qd = 800 – 500 = 300 (units) - At the price of $110:
+ Qd = 1500 - 5P = 1500 – 5×110 = 950
Qs = 5P – 200 = 5×110 – 200 = 350
The shortage of fridge at the price of $110 is:
∆Q = Qd – Qs = 950 - 350 = 600 (units)
3. Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, what happened for demand for
fridge if price of electricity increase? Given that quantity demanded for
fridge change 300 units at each price level, what are new equilibrium price
and new equilibrium quantity for fridge? -
If the supply of fridge is constant, the demand for fridge will decrease if price of electricity increase. -
The quantity demanded for fridge change 300 units at each price level: 1200 Demand A Supply 1000 New Demand 800 ) 600 ($/unit e ic Pr 400 B 200 080 100 120 140 160 180 200 220
Quantity Demanded and Supplied(units) + New demand function: 1
100 = a − × 700 => a = 240 5 1 P = 240 - × Q 5 d’ -> Qd’ = 1200 – 5P
+ The market balances again when: Qd’ = Qs 1200 – 5P = 5P – 200
P = PE’ = 140 => QE’ = 500
So, the new equilibrium price and quantity is P = 140, Q = 500.
4. Suppose government imposes a tax of $10 per one units of fridge sold, what
are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge? -
If government imposes a tax of $10 per one units of fridge sold, the price
will increase $10 per one unit. 1
The new supply function: P = 50 + × Q 5 s’ QS’ = 5P – 250 - QS’ = Qd 5P - 250 = 1500 - 5P
P = PE’’ = 175 => QE’ = 625
5. Suppose government supports for the sellers the amount of $ 10 per one
units of fridge sold, what are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge? -
If government supports for the sellers the amount of $10 per one units of
fridge sold, the price will decrease $10 per one unit. 1
The new supply function: P = 30 + × Q 5 s’’ QS’’ = 5P – 150 - QS’’ = Qd 5P - 150 = 1500 - 5P
P = PE’’ = 165 => QE’ = 675 Exercise 2:
1. An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates -
If the Vietnamese personal income tax rates increase, the demand will
decrease because income of consumers is one of non-price factors. The
demand curve will shift to the left.
2. An increase in the price of steel -
If the price of steel increases, the supply will decrease because input prices
is one of non-price factors. The supply curve will shift to the left.
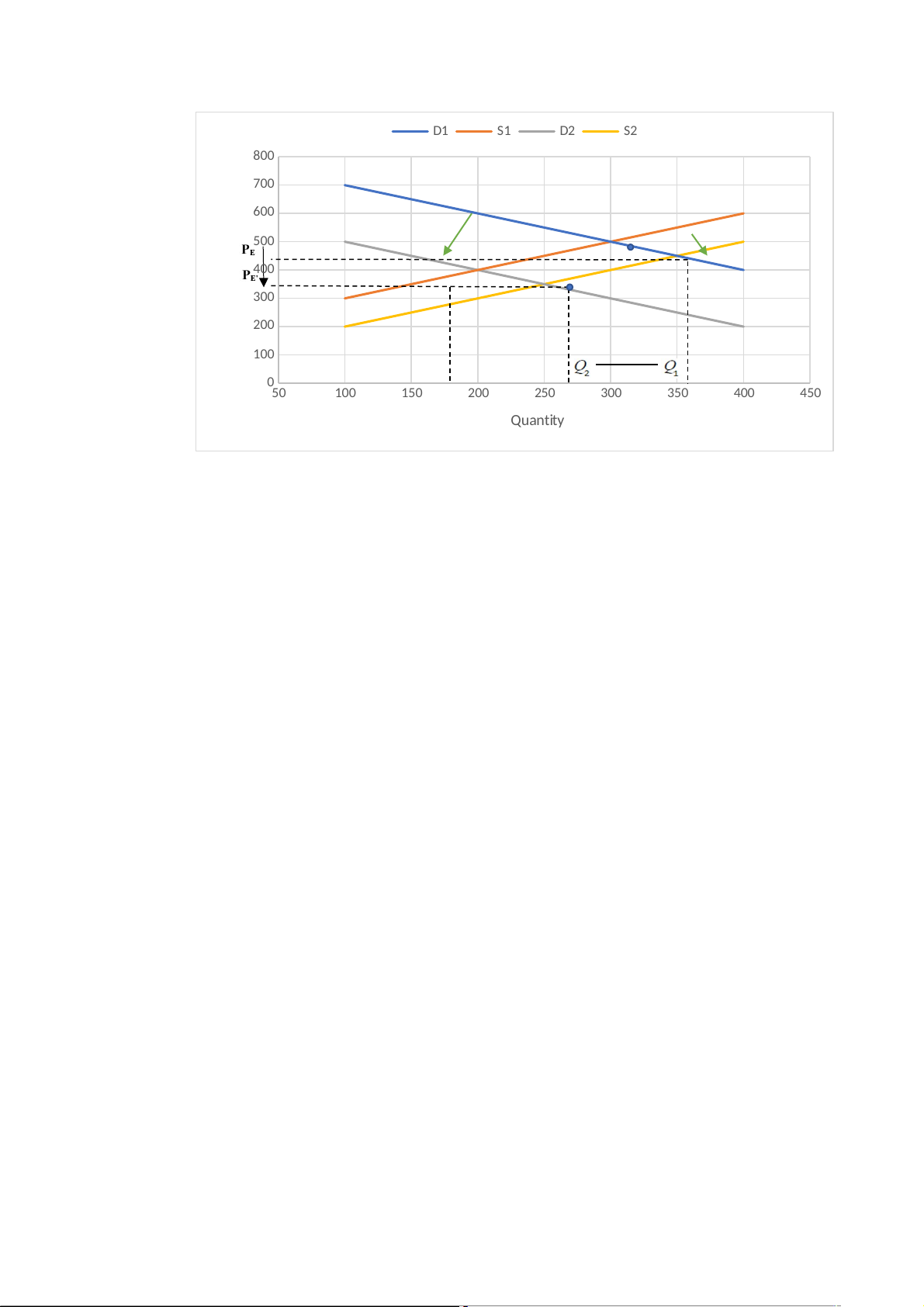
3. An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same time
as a recession hits the Vietnamese economy -
An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production will make the
supply grow. However, an economic recession in Viet Nam will make the
consumer demand drop. Therefore, the supply curve will be shifted to the
right and the demand curve will be shifted to the left. D1 S1 D2 S2 800 700 600 500 e 400 ic Pr 300 200 100 050 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 Quantity




