


Preview text:
HCMC University of Technology and Education
Faculty of Electrical & Electronic Engineering
No.1 Vo Van Ngan Street, Thu Duc Dist., HCMC, VN DIGITAL SYSTEM
NGUYEN THANH NGHIA , PhD 6/24/2024 1 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 1 Administration
1. Instructor: Thanh-Nghia Nguyen, PhD.
Email: nghiant@hcmute.edu.vn
https://sites.google.com/a/hcmute.edu.vn/thanh-nghia-nguyen/ 2. Textbook:
[1] Ronald J. Tocci, Neal S. Widmer, Gregory L. Moss Digital
Systems: Principles and Applications, 12th Ed. Peason, 2017.
[2] N T Duy, V D Dung, N T Hai, Giao Trinh: Ky Thuat So, NXB
ĐH Quốc Gia_Tp.HCM, 2019. * References
[3] John F. Wakerly, Digital Design: Principles and Practices,
4th Ed. Prentice Hall, 2007.
[4] Anil K. Maini, Digital Electronics, John Wily & Sons, 2007. NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 2 Administration 3. Grading:
Formative Exams: 50%
o Exam 1: 4 quizzes (10 questions), 15min/1 quiz (20%)
o Exam 2: an exam, each exam has 30
multichoice questions for 50 mins (25%) o Take attendance: 5% Summative Exam: 50% 4. Syllabus. NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 3 Administration 5. Softwares:
Proteus for modeling 6. Home work:
File name: Fullname_WeekX.rar Deadline: NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 4 Administration 7. Contents:
Chapter 1: Concepts - Numerical Systems - Codes
Chapter 2: Logic Gates and Boolean Algebra
Chapter 3: MSI Logic Circuits
Chapter 4: Sequential Logic Circuits
Chapter 5: TTL-CMOS Families
Chapter 6: Oscillators and Timers
Chapter 7: Memory Devices
Chapter 8: Digital Analog conversion NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 5
HCMC University of Technology and Education
Faculty of Electrical & Electronic Engineering
No.1 Vo Van Ngan Street, Thu Duc Dist., HCMC, VN CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
NGUYEN THANH NGHIA , PhD 6/24/2024 6 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 6 Outline
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems- Code and applications. 2. Code Conversion. 3. Binary Add_Subtract. 4. Binary Multiply_Divide. 5. Signed Numbers.
6. Signed Addition_Subtraction with complement. 7. BCD Addition NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 7
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Analog-Digital Systems:
Why is digital technology important?
-The real world is mainly analog: Most physical quantities
are analog in nature such as velocity, temperature, liquid level, flow rate etc.
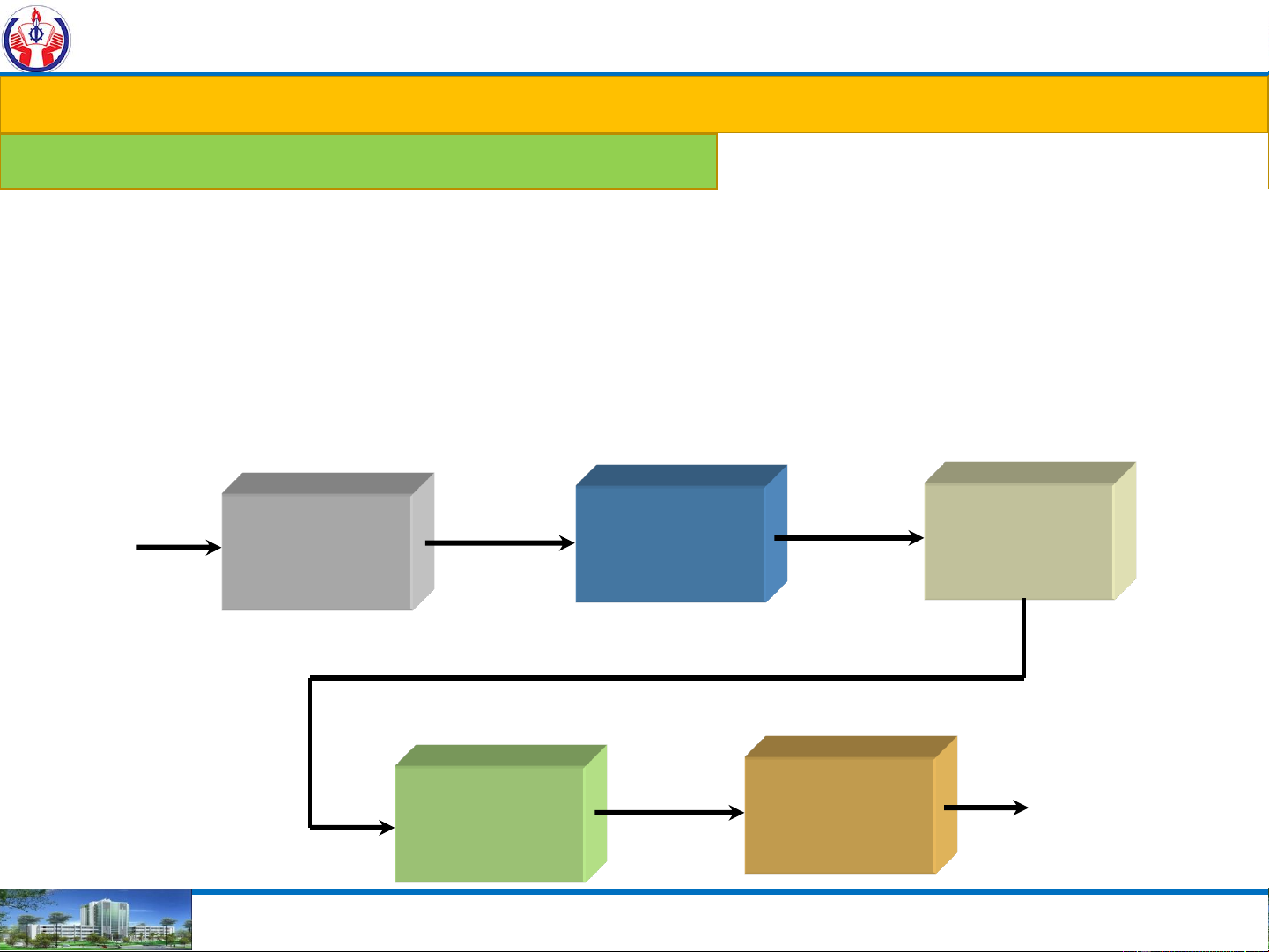
- Input-output conversion (Analog) Analog-to- (Digital) Measuring Digital digital Temperature device processing converter (Analog) (Digital) Digital-to- (Analog) Adjust analog Controller temperature converter NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 8
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Analog-Digital Systems: What is analog What is digital Representation? Analog
Representation? Discrete signal signal Analog Continuous Digital Discrete NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 9
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
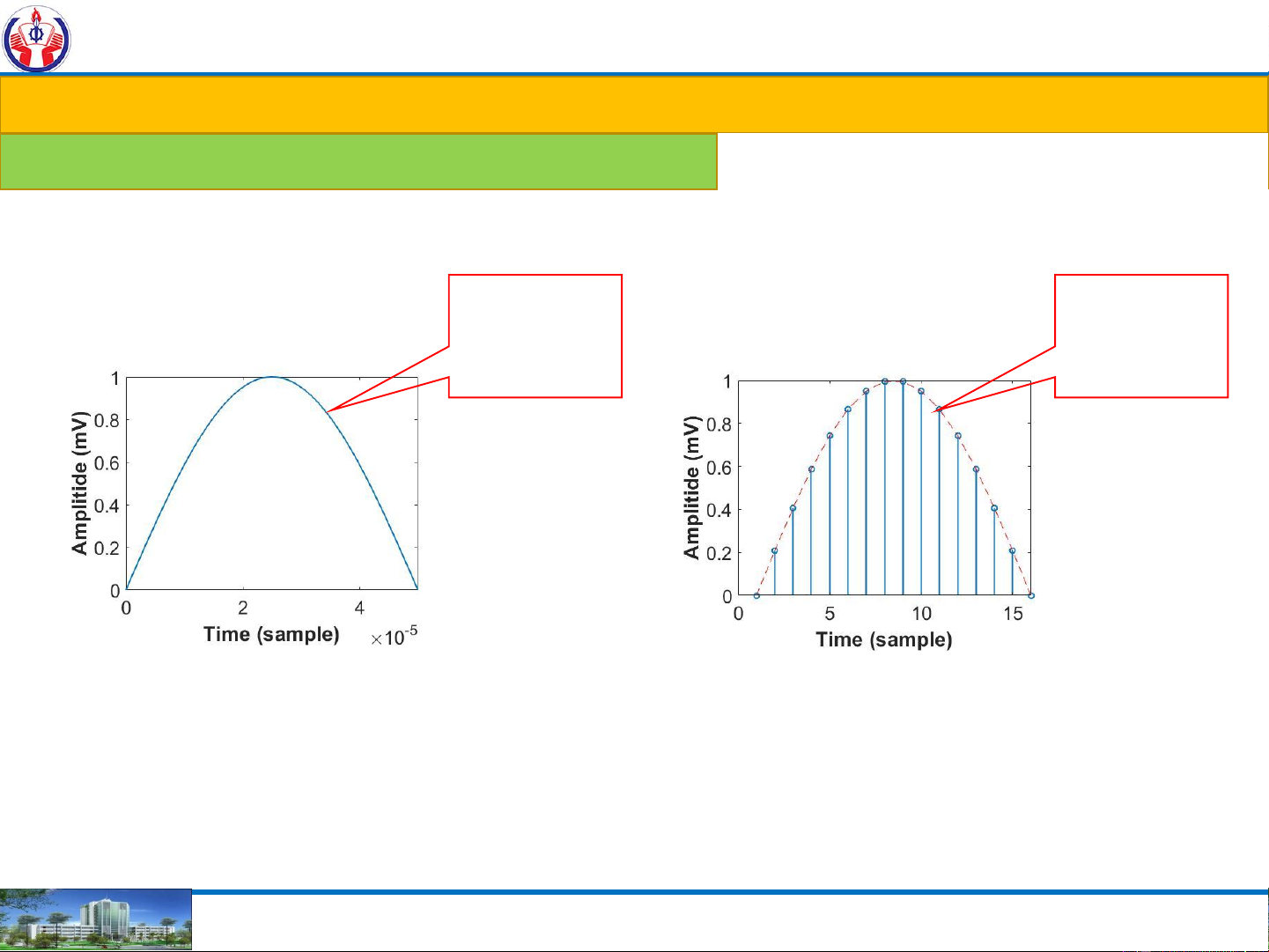
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Analog-Digital Systems: What is digital What is digital
Representation? Discrete Representation? Coding signal Analog Continuous Digital Discrete NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 10
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
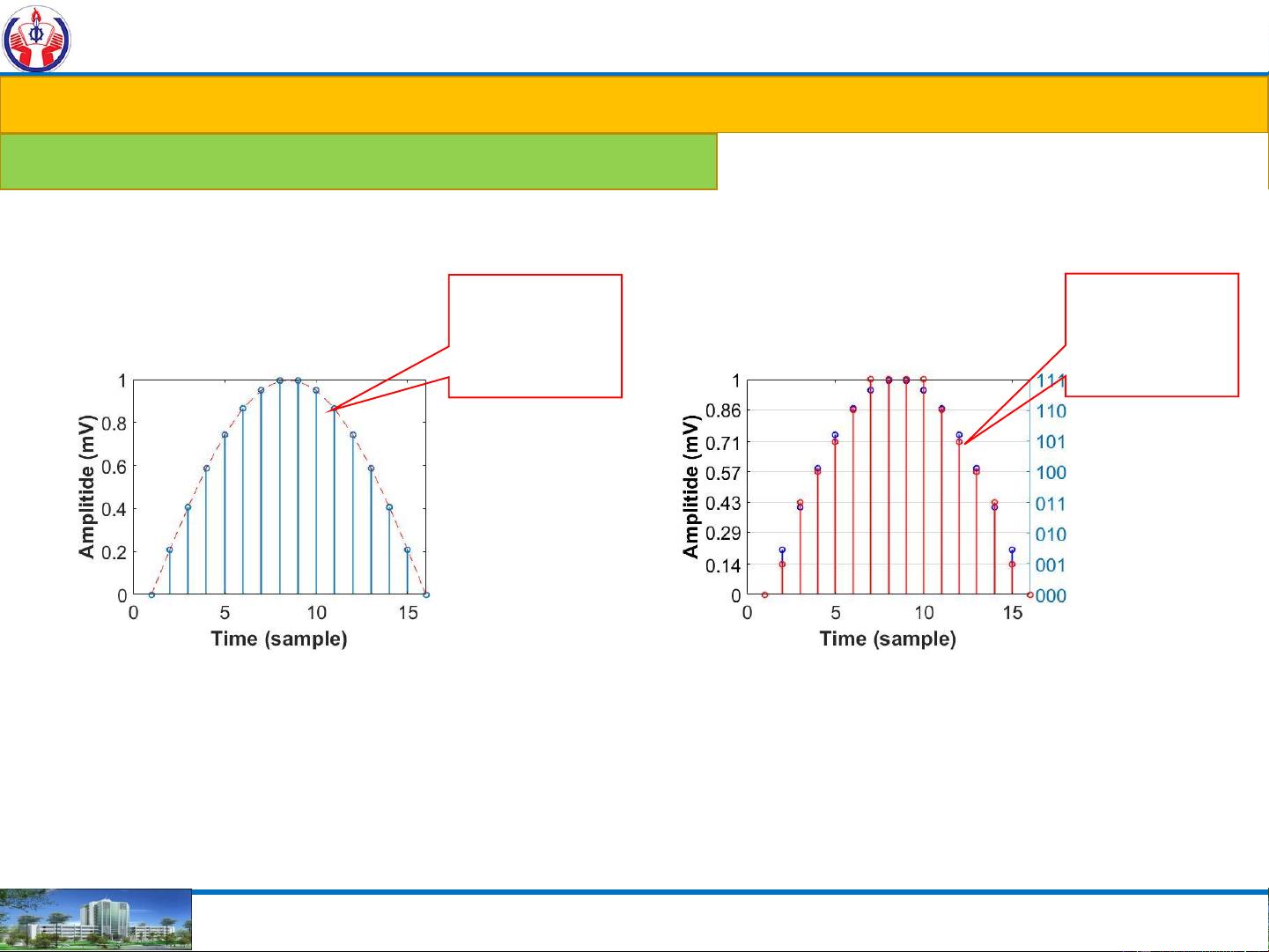
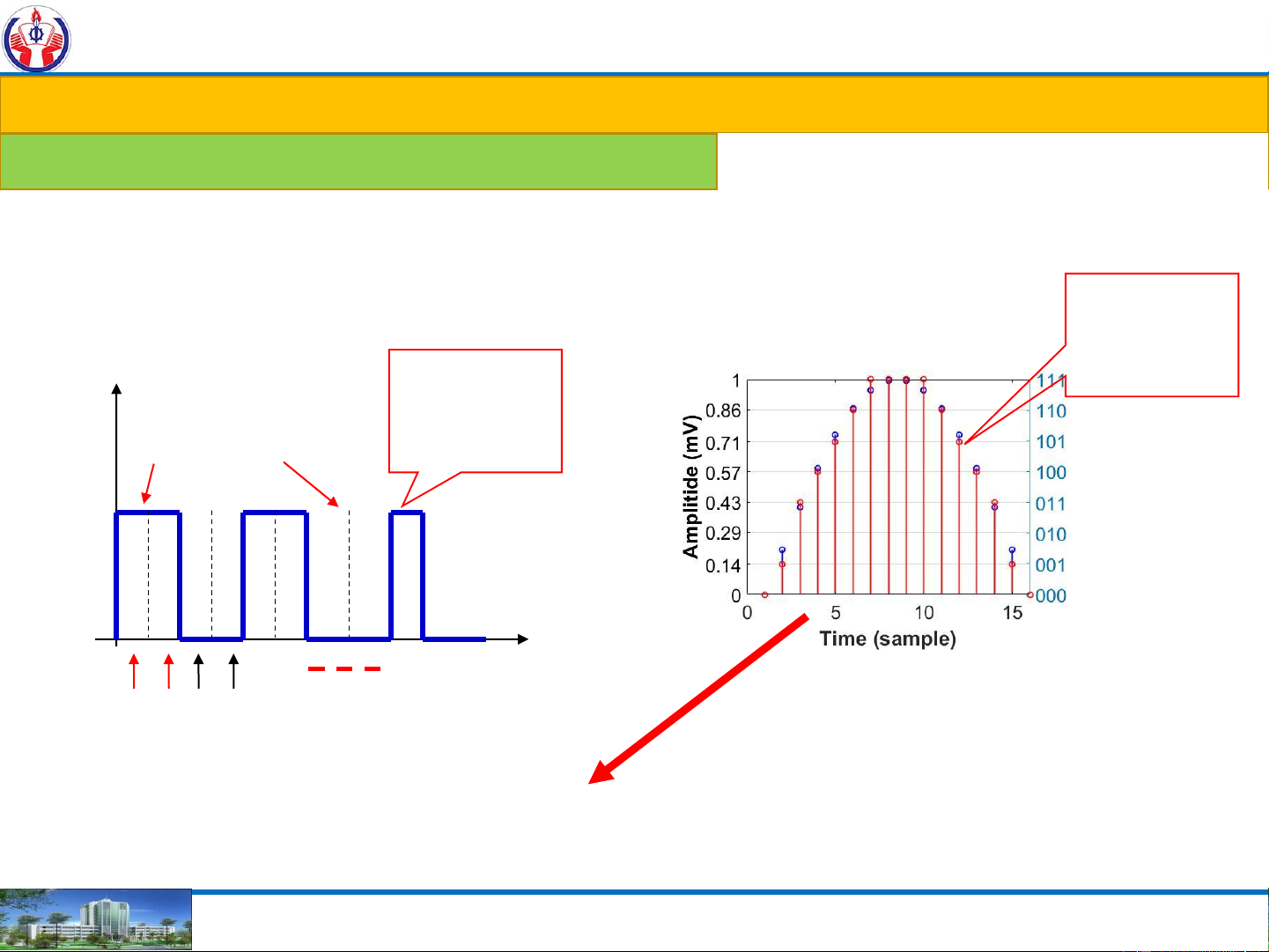
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Analog-Digital Systems: What is digital What is digital Representation? Representation? Coding Volt Digital signal High Low 1 0 time 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
x = 000 001 011 100 101 110 111 111 111 111 110 101 100 011 001 000 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 11
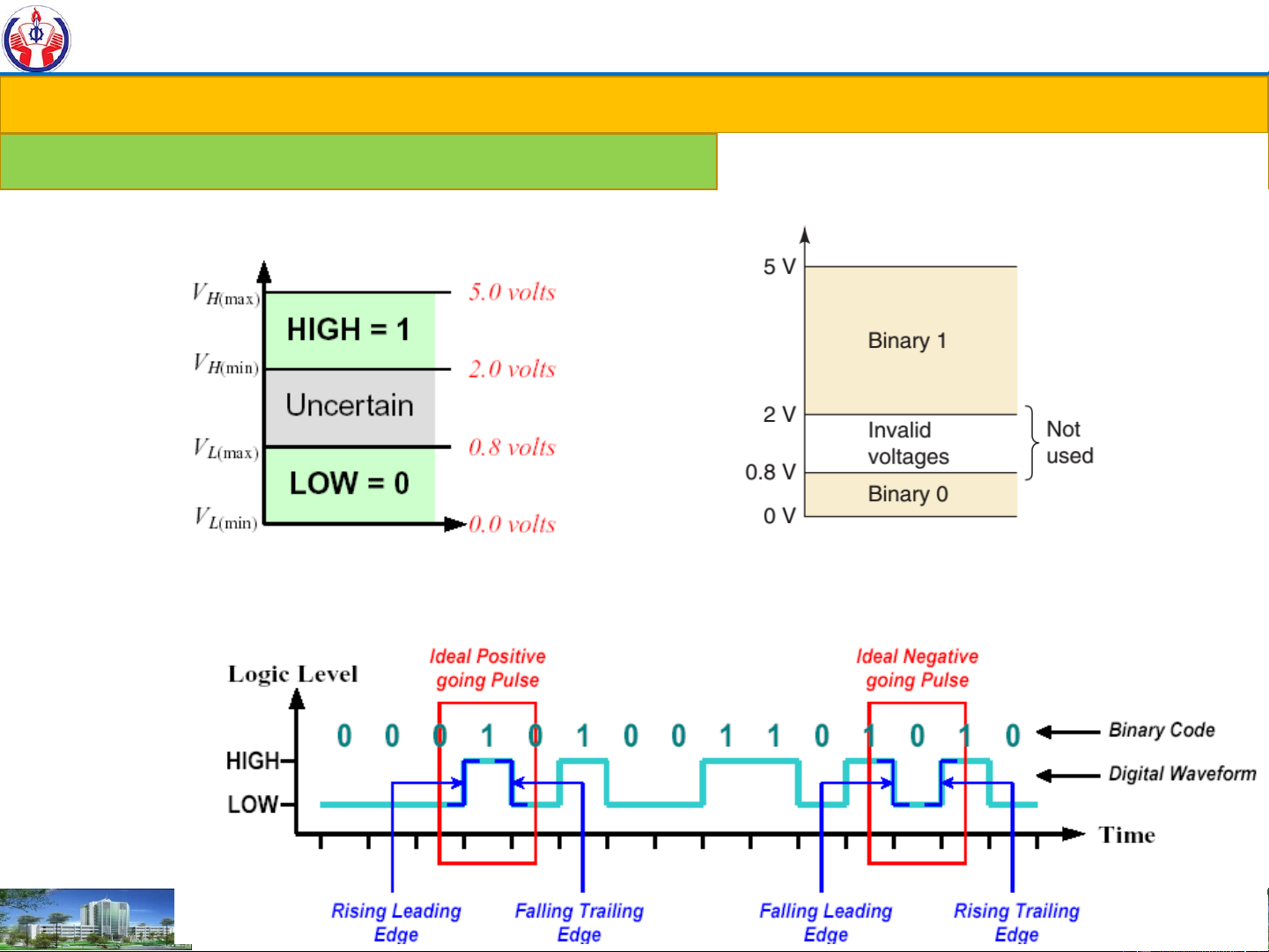
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Analog-Digital Systems: Logic levels: Waveform: NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 12
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Basic Concepts_digits:
Bit: a binary digit composed of 0 or 1 Byte: composed of 8 bits
Word: composed of 4 bytes and equal to 32 bits
Base 2 (binary digits): numbers composed of bits, EX: 10002, 1000B
Base 10 (decimal digit): numbers composed of the digits from 0-9, EX: 2907202410
Base 16 (hexa digit or hexadecimal): numbers composed of the digits
from 0-9 and letters A-F, EX: 168916, 4573AF16 , BAEH
Base 8 (octal digit): numbers composed of the digits from 0-7, EX: 20178
Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) code: 0000 to 1001 to represent the BCD BCD range 0 to 9. NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 13
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 14
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications Digital number systems:
Radix – r (or base): The radix or base of a number system
can be referred as the total number of different symbols
which can be used in a particular number system.
Weighted (or Positional): A positional number system is
also known as weighted number system.
Weighted = Radix Position Value:
Value= (coefficients x Weighted) EX: NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 15
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications
Digital number systems: Decimal system:
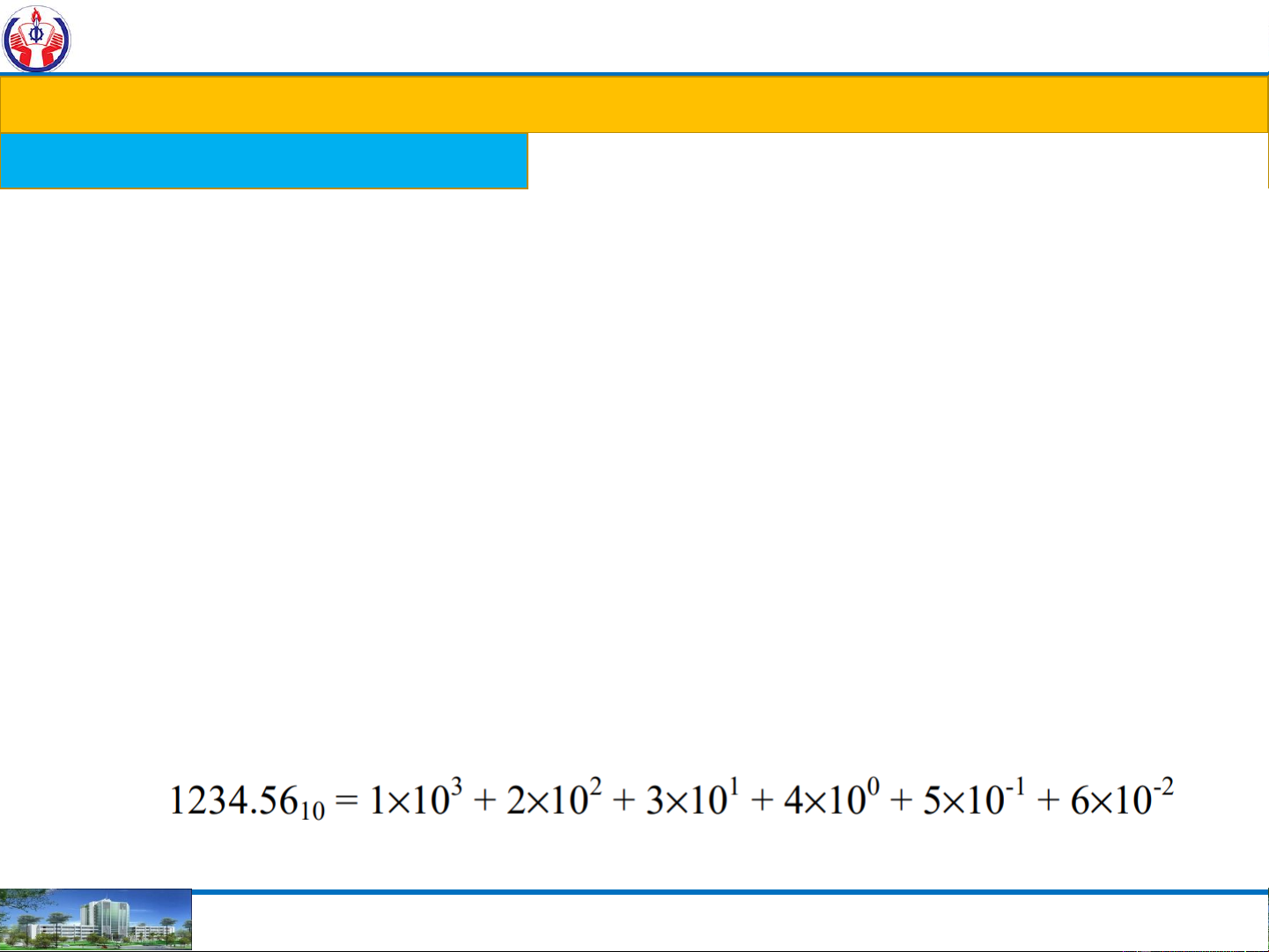
Radix – r (or base): =10. 4 0 7 . 6 2 5 102 101 100 . 10-1 10-2 10-3 4x102 0x101 7x100 . 6x10-1 2x10-2 5x10-3 400 0 7 . 0.6 0.02 0.005 MSD Decimal LSD point
400 + 0 + 7 + 0.6 + 0.02 + 0.005 = 407.62510 MSD: Most Significant Digit LSD: Least significant digit NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 16
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications
Digital number systems: Binary system:
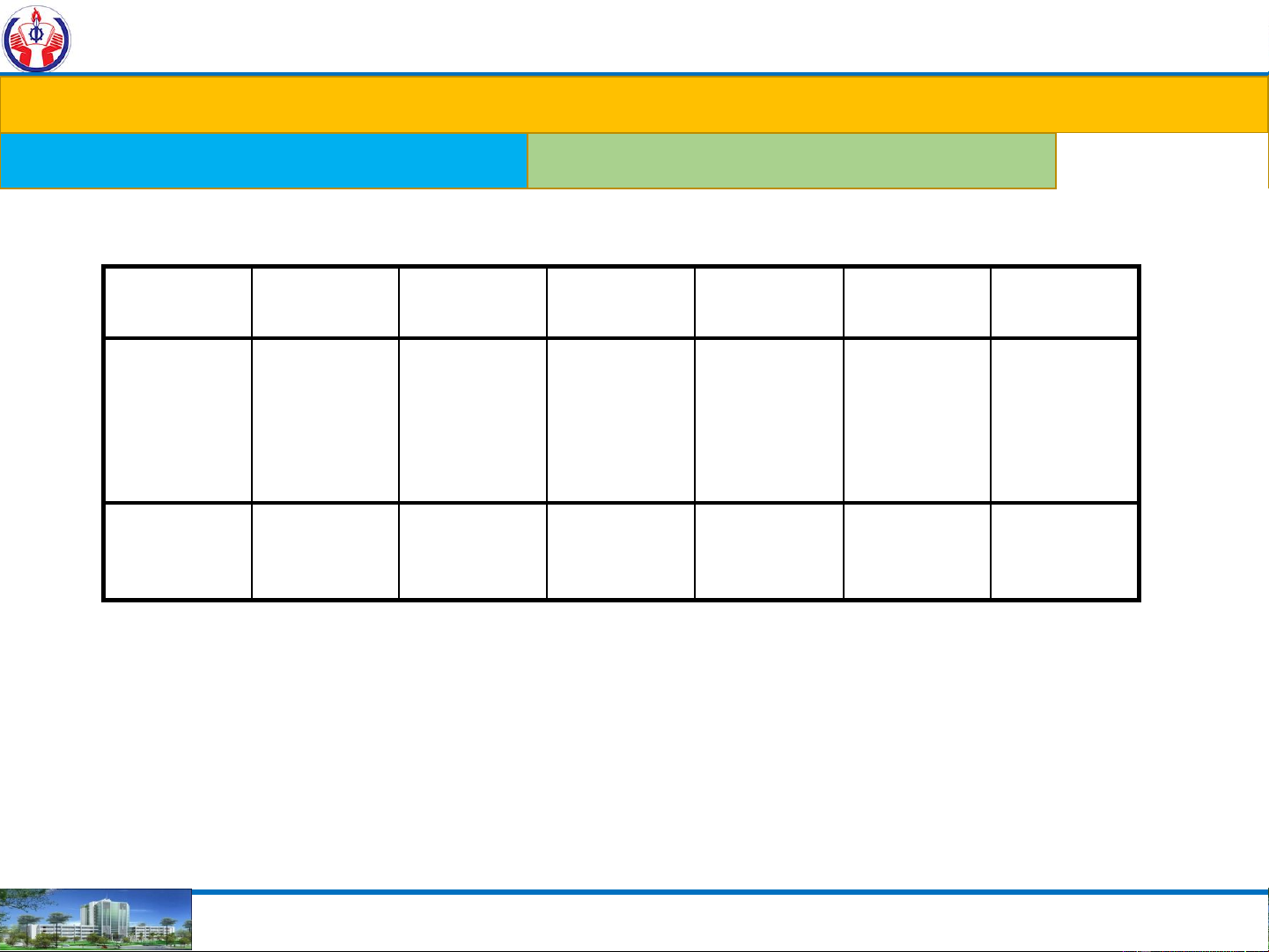
Radix – r (or base): =2. 1 0 1 . 0 1 1 22 21 20 . 2-1 2-2 2-3 1x22 0x21 1x20 . 0x2-1 1x2-2 1x2-3 4 0 1 . 0 0.25 0.125
4 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 0.25 + 0.125 = 5.37510
EX: 11010101 = (1x 27) + (1x 26) + (0x25) + (1x24) + (0x23) 2 + (1x22) + (0x 21 ) + (1x 20)
= 128 + 64 + 0x32 + 16 + 0x8 + 4 + 0x2 + 1 = 21310 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 17
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES
1. Introduction to Numerical Systems-Code and applications
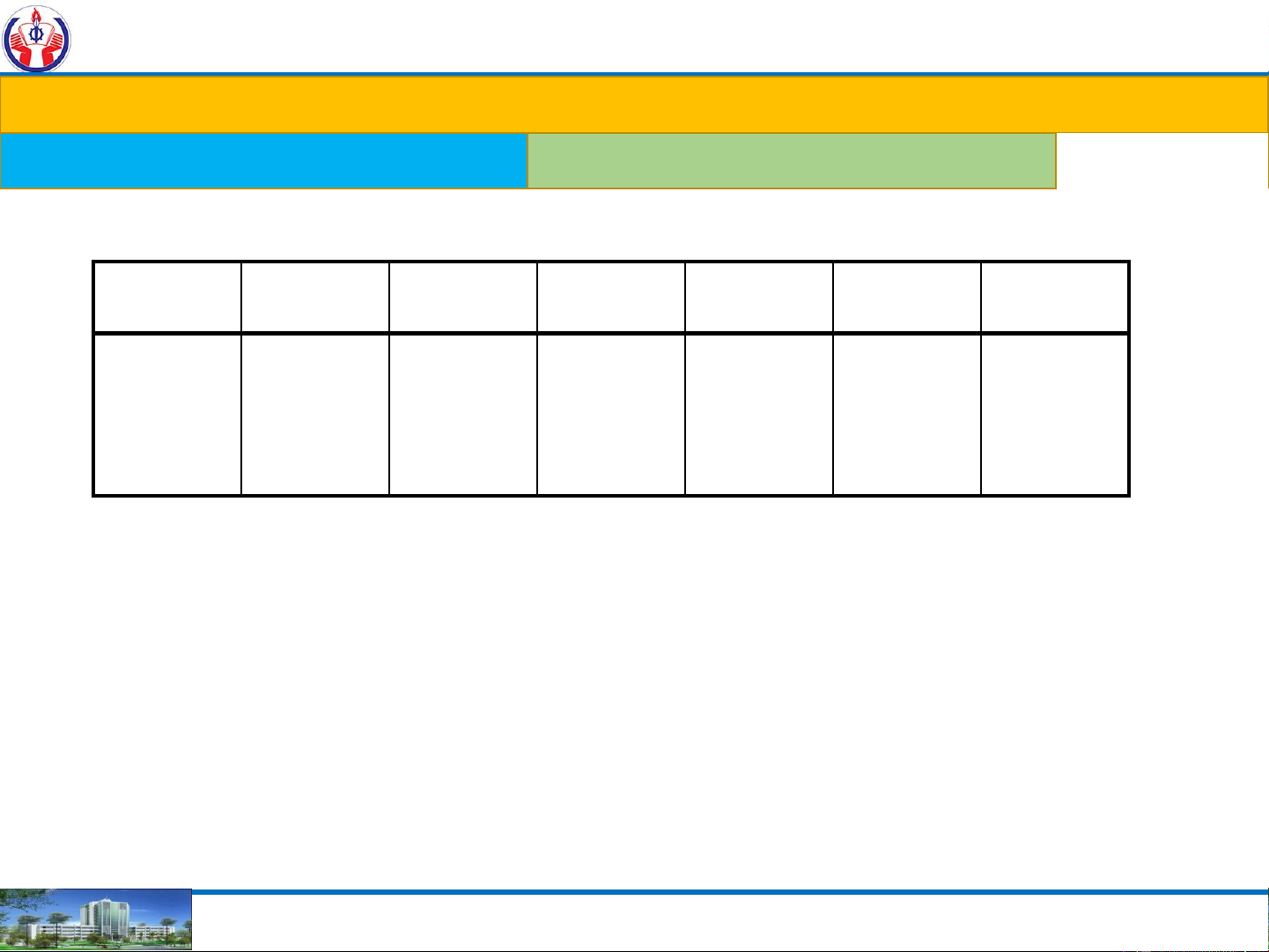
Digital number systems: Hexadecimal system:
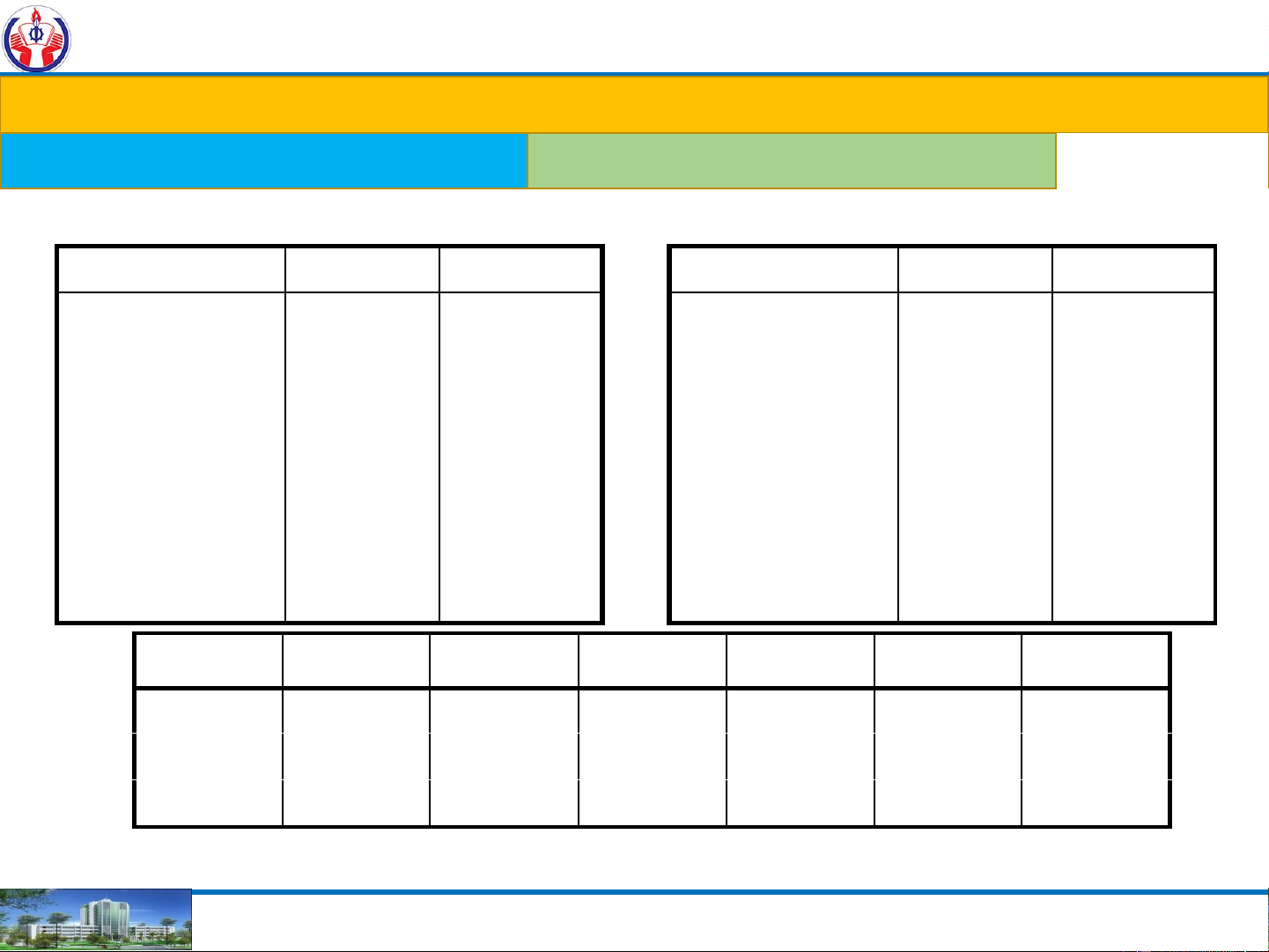
Radix – r (or base): =16. Hexadecimal Decimal Binary Hexadecimal Decimal Binary 0 0 0000 8 8 1000 1 1 0001 9 9 1001 2 2 0010 A 10 1010 3 3 0011 B 11 1011 4 4 0100 C 12 1100 5 5 0101 D 13 1101 6 6 0110 E 14 1110 7 7 0111 F 15 1111 5 A 0 . 4 D 1 162 161 160 . 16-1 16-2 16-3 5x162 10x161 0x160 . 4x16-1 13x16-2 1x16-3 1280 160 0 . 0.25 0.0508 0.0002
1280 + 160 + 0 + 0.25 + 0.0508 + 0.0002 = 1440.30110 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 18
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 19
C1: CONCEPTS - NUMERICAL SYSTEMS - CODES 2. Code Conversion Decimal to Binary Conversion:
Convert number 25 : 10 25 LSB = 12 + remainder of 1 2 12 = 6 + remainder of 0 2 6 = 3 + remainder of 0 2 3 = 1 + remainder of 1 2 MSB: Most significant bit 1 = 0 + remainder of 1 2 LSB: Least significant bit MSB 25 = 1 1 0 0 1 10 2 NGUYEN THANH NGHIA 20



