
Preview text:
Group members: Doan Hai Ninh Nguyen Le An Nguyen Thi Mai Anh Tran Huu Huy Chu Gia Tam Class: E-BBA13.2 Subject: Microeconomics Group assignment topic 2 Exercise 1:
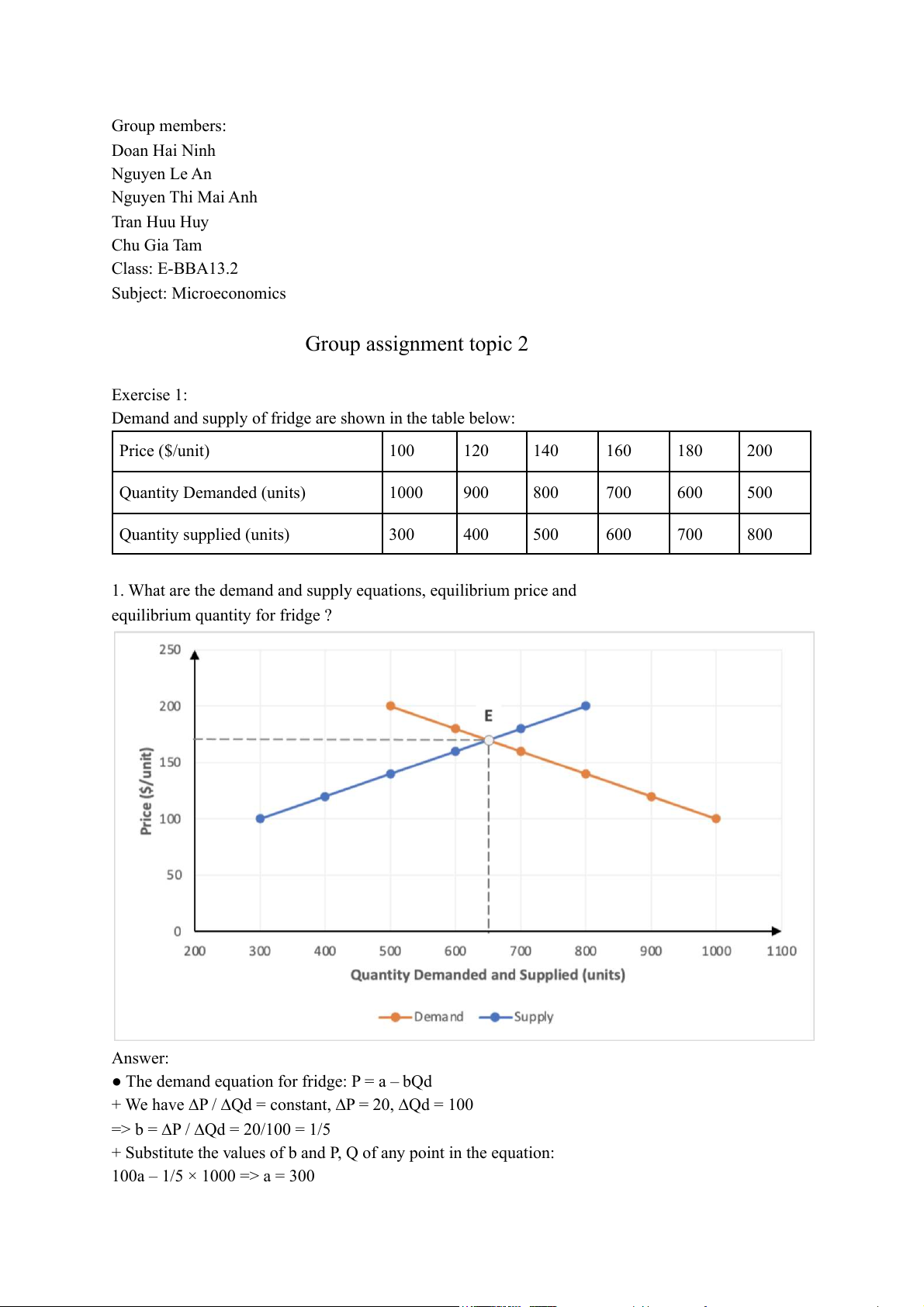
Demand and supply of fridge are shown in the table below: Price ($/unit) 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity Demanded (units) 1000 900 800 700 600 500 Quantity supplied (units) 300 400 500 600 700 800
1. What are the demand and supply equations, equilibrium price and
equilibrium quantity for fridge ? Answer:
● The demand equation for fridge: P = a – bQd
+ We have ∆P / ∆Qd = constant, ∆P = 20, ∆Qd = 100
=> b = ∆P / ∆Qd = 20/100 = 1/5
+ Substitute the values of b and P, Q of any point in the equation:
100a – 1/5 × 1000 => a = 300
So, the demand equation for fridge is: P = 300 – 1/5Qd
● The supply equation for fridge: P = c + dQs
+ We have ∆P / ∆Qs = constant, ∆P = 20, ∆Qs = 100
=> b = ∆P / ∆Qs = 20/100 = 1/5
+ Substitute the values of b and P, Q of any point in the equation:
100 = a + 1/5 × 300 => a = 40
So, the supply equation for fridge is: P = 40 + 1/5 × Qs
● Equilibrium price for fridge:
+ We have, Qd = 1500 - 5P; Qs = 5P – 200
QE = Qd = Qs => 1500 - 5P = 5P – 200 => P = 170
● Equilibrium quantity for fridge:
QE = Qd => QE = 1500 - 5×170 => QE = 650
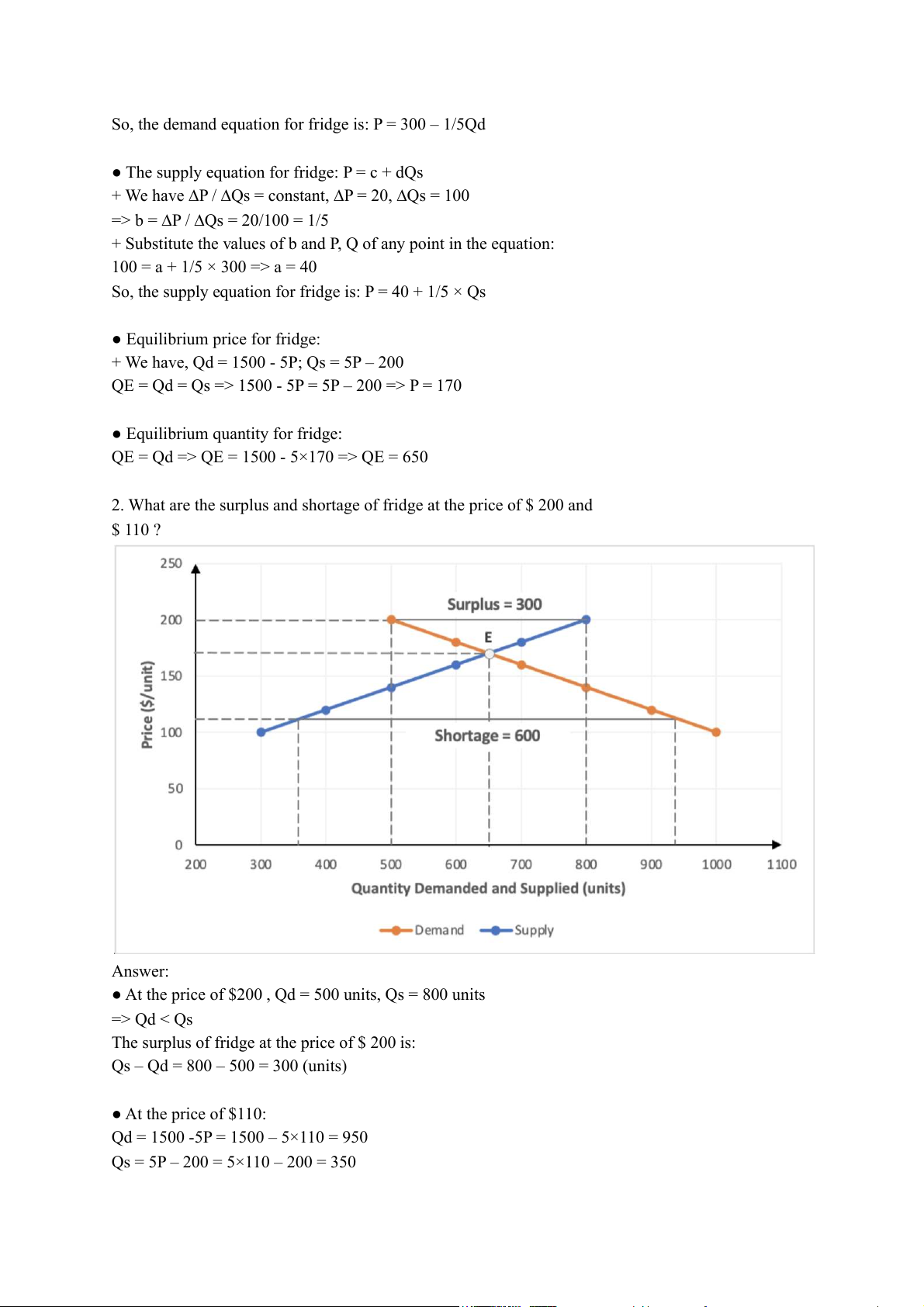
2. What are the surplus and shortage of fridge at the price of $ 200 and $ 110 ? Answer:
● At the price of $200 , Qd = 500 units, Qs = 800 units => Qd < Qs
The surplus of fridge at the price of $ 200 is:
Qs – Qd = 800 – 500 = 300 (units) ● At the price of $110:
Qd = 1500 -5P = 1500 – 5×110 = 950
Qs = 5P – 200 = 5×110 – 200 = 350 => Qd > Qs
The shortage of fridge at the price of $ 110 is:
Qd – Qs = 950 - 350 = 600 (units)
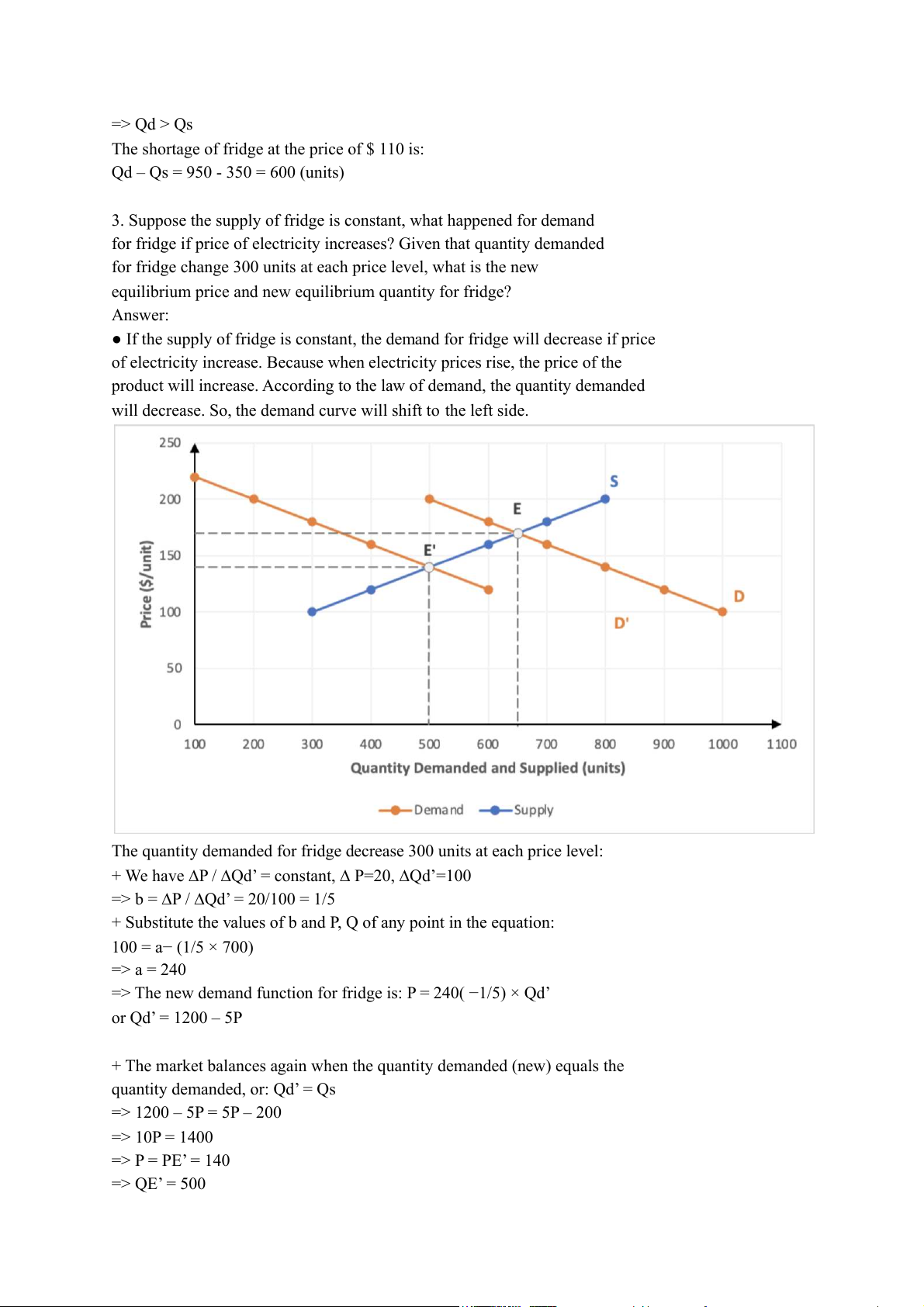
3. Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, what happened for demand
for fridge if price of electricity increases? Given that quantity demanded
for fridge change 300 units at each price level, what is the new
equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge? Answer:
● If the supply of fridge is constant, the demand for fridge will decrease if price
of electricity increase. Because when electricity prices rise, the price of the
product will increase. According to the law of demand, the quantity demanded
will decrease. So, the demand curve will shift to the left side.
The quantity demanded for fridge decrease 300 units at each price level:
+ We have ∆P / ∆Qd’ = constant, ∆ P=20, ∆Qd’=100
=> b = ∆P / ∆Qd’ = 20/100 = 1/5
+ Substitute the values of b and P, Q of any point in the equation: 100 = a− (1/5 × 700) => a = 240
=> The new demand function for fridge is: P = 240( −1/5) × Qd’ or Qd’ = 1200 – 5P
+ The market balances again when the quantity demanded (new) equals the
quantity demanded, or: Qd’ = Qs => 1200 – 5P = 5P – 200 => 10P = 1400 => P = PE’ = 140 => QE’ = 500
=> The new equilibrium price for fridge is 140$ and new equilibrium quantity for fridge is 500$
4. Suppose government imposes a tax of $ 10 per one unit of fridge sold,
what are new equilibrium prices and new equilibrium quantity for fridge? Answer:
+ Government imposes a tax of $10 per one units of fridge sold
=> The price will increase $10 per one units
+ The new supply function is P = 50 + 1/5 QS’ or QS’ = 5P – 250
+ The market balances again when the quantity supply (new) equals the quantity demanded, or: QS’ = Qd => 5P – 250 = 1500 -5P => 10P = 1750 => P = PE’ = 175
=> PE’ = 175 => QE’ = 625
The equilibrium price is $175 and equilibrium quantity is 625 units
5. Suppose government supports for the sellers the amount of $ 10 per
one unit of fridge sold, what are new equilibrium price and new
equilibrium quantity for fridge? Answer:
+ The government supports for the sellers the amount of $10 per one unit of
fridge sold, so the price will decrease $10 per one unit.
+ The new supply function: P = 30 + 1/5QS’ or QS’ = 5P - 150
+ When the new quantity supply equals the quantity demand, the market is in equilibrium again, or: QS’ = Qd => 5P - 150 = 1500 - 5P => P = PE’ = 165
=> QE’ = 5x165 - 150 = 675
So the new equilibrium price is $165 and the new equilibrium quantity is 675 units Exercise 2:
With the aid of diagrams, show how each of the following events affects
the supply and/or demand curve for motorcycles. In each case, show
and state the effect on the equilibrium price and quantity.
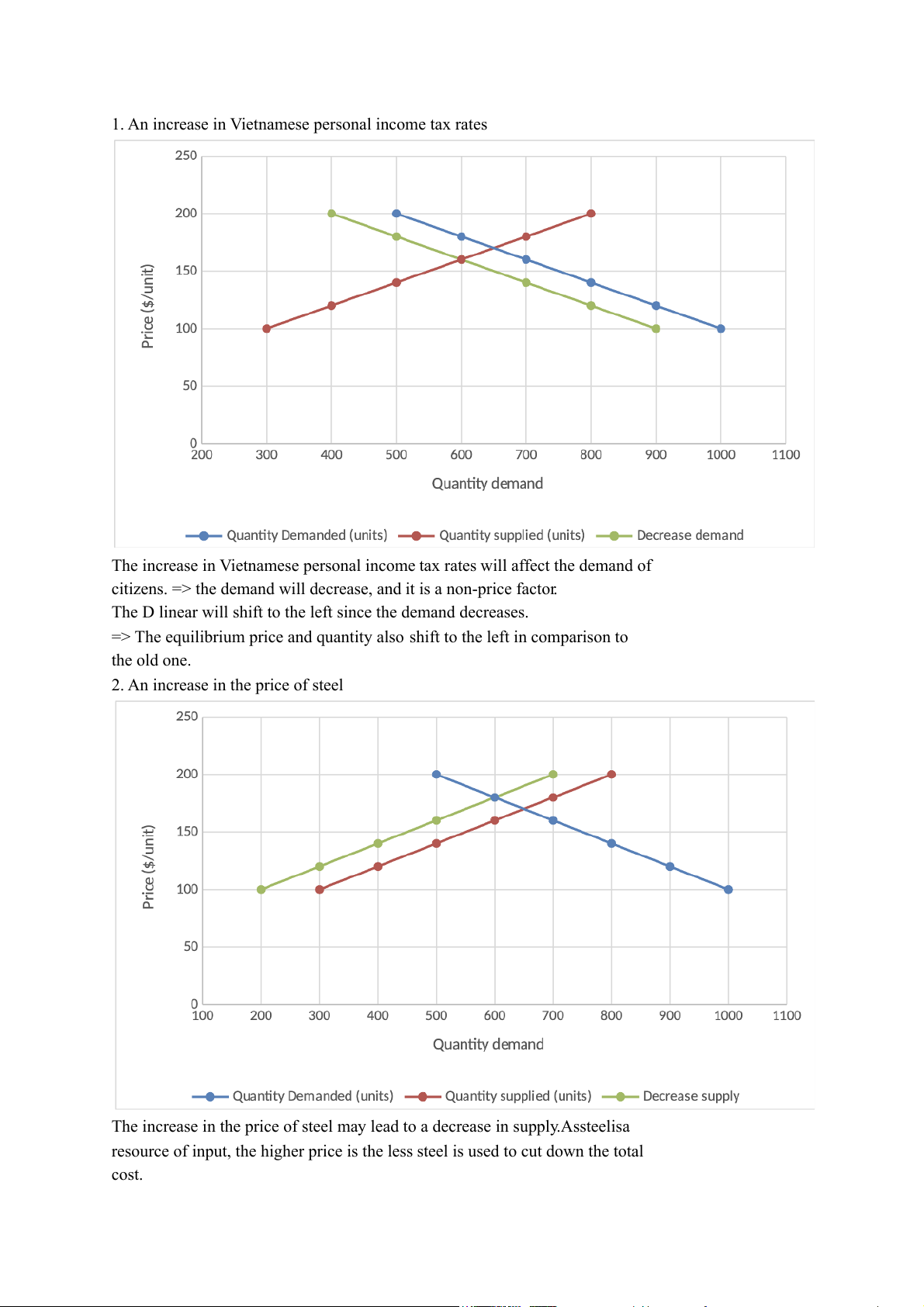
1. An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates
The increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates will affect the demand of
citizens. => the demand will decrease, and it is a non-price factor.
The D linear will shift to the left since the demand decreases.
=> The equilibrium price and quantity also shift to the left in comparison to the old one.
2. An increase in the price of steel
The increase in the price of steel may lead to a decrease in supply.Assteelisa
resource of input, the higher price is the less steel is used to cut down the total cost.
=> The S linear will shift to the left. Additionally, the new equilibrium price and
quantity also shift to the left in comparison to the old one.
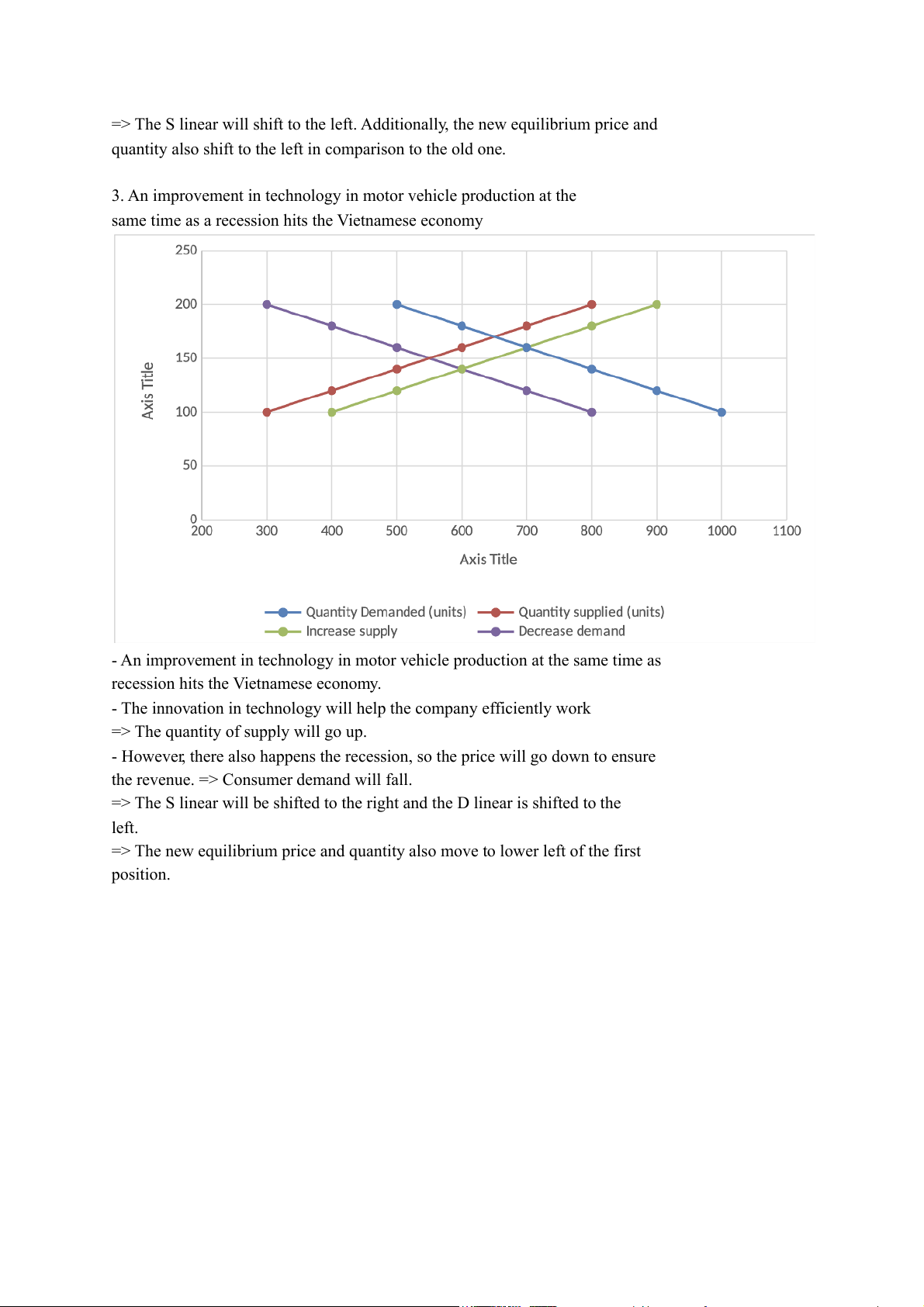
3. An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the
same time as a recession hits the Vietnamese economy
- An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same time as
recession hits the Vietnamese economy.
- The innovation in technology will help the company efficiently work
=> The quantity of supply will . go up
- However, there also happens the recession, so the price will go down to ensure
the revenue. => Consumer demand will fall.
=> The S linear will be shifted to the right and the D linear is shifted to the left.
=> The new equilibrium price and quantity also move to lower left of the first position.




