






Preview text:
CHƯƠNG 4
Vi phân hàm nhiều biến
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
4.1 Hàm nhiều biến trong kinh tế
Bài 1. Tìm tập xác định (domain) các hàm sau: 4x z = x2 + y2 a) b) z = 4x − 3 c) − 3y z = y x + y2 4x3y d) z = − x e) f) √ z = z = √x x 2x − y − y g) q = √p √ h) 1 + 3p2 q = 5p1 p1 p − − 2
Bài 2. Tìm giá trị hàm tại các điểm đã chỉ ra. p1 + 4p2 5p a) 1 q − p2 b) 1 (p1, p2) = , tìm q q , tìm q p 1 (40, 35) . 1 (p1, p2) = 1 (50, 10) . 1 p p − 2 1 + 3p2 c) z (x, y) = xex+y tìm z (3, d) −3) .
f (x, y) = ye2x + y2 tìm f (0, 7) . ln (xy) e) f (x, y) = tìm f ( f) z (x, y) = x ln (y) x2 + y2 −3, −4) . − y ln (x) tìm z (1, 1) .
Bài 3. (Investment) The future value S of an investment earning 6% compounded continuously is a function
of the principal (vốn) P and the length of time t that the principal has been invested. It is given by S = f (P, t) = P e0.06t
Find f (2000, 20), and interpret (giải thích ý nghĩa) your answer.
Bài 4. (Utility – Hàm thỏa dụng) Suppose that the utility function for two goods X and Y is given by
U = xy2, and a consumer purchases (mua) 9 units of X and 6 units of Y .
a) If the consumer purchases 9 units of Y , how many units of X must be purchased to retain the same level of utility?
b) If the consumer purchases 81 units of X, how many units of Y must be purchased to retain the same level of utility?
c) Graph the indifference curve for the utility level found in parts (a) and (b). Use the graph to
confirm your answers to parts (a) and (b).
Bài 5. (Production - Hàm sản xuất) Suppose that a company’s production for Q units of its product is given 1 3
by the Cobb-Douglas production function Q = 30K 4 L 4 , where K is dollars of capital investment and L is labor hours. 47 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
a) Find Q if K = $10, 000 and L = 625 hours.
b) Show that if both K and L are doubled, then the output is doubled.
c) If capital investment is held at $10,000, graph Q as a function of L.
Bài 6. (Profit) The Kirk Kelly Kandy Company makes two kinds of candy, Kisses and Kreams. The profit,
in dollars, for the company is given by P (x, y) = 10x + 6.4y . − 0 001x − 20.025y2
where x is the number of pounds of Kisses sold per week and y is the number of pounds of Kreams.
What is the company’s profit if it sells
a) 20 pounds of Kisses and 10 pounds of Kreams?
b) 100 pounds of Kisses and 16 pounds of Kreams?
c) 10,000 pounds of Kisses and 256 pounds of Kreams?
Bài 7. Tìm đạo hàm riêng cấp 1 của các hàm sau: ∂z ∂z a) If z = x4 and − 5x2 + 6x + 3y3 . − 5y + 7 find ∂x ∂y
b) If z = x3 + 4x2y + 6y2 find z and x zy ∂f ∂f
c) If f (x, y) = (x3 + 2y2)3 find and . ∂x ∂y ∂f ∂f
d) If f (x, y) = p2x2 − 5y2 find and . ∂x ∂y ∂C ∂C e) If C (x, y) = 600 and − 4xy + 10x2y find . ∂x ∂y 2s ∂Q ∂Q f) If Q (s, t) = − 3t find and . s2 + t2 ∂s ∂t
g) If z = e2x + y ln x find z and x zy
h) Find the partial derivative of f (x, y) = 3x2 + 4x + 6xy with respect to y at x = 2, y = −1.
Bài 8. Tìm đạo hàm riêng cấp 2 của các hàm sau: z = x2 + 4x − 5y3 a) z = x2y − 4xy2 b) z = x2 + exy c) d) z = y2 − ln xy
e) If f (x, y) = x3y + 4xy4 find fxx (1, −1) . 2x f) If f (x, y) = find f x2 + y2
xx (−1, 4) , and fxy (−1, 4) . 48 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 9. (Cost) Suppose that the cost function (in dollars) of producing a product is C (x, y) = 25+2x2+3y2,
where x is the cost per pound for material (chi phí mỗi đơn vị nguyên liệu) and y is the cost per hour
for labor (chi phí của mỗi giờ công lao động).
a) If material costs are held constant, at what rate will the total cost increase for each $1-per-hour increase in labor?
b) If the labor costs are held constant, at what rate will the total cost increase for each increase of $1 in material cost?
Bài 10. (Profit) Suppose that the profit (in dollars) from the sale of Kisses and Kreams is given by
P (x, y) = 10x + 6.4y − 0.001x2 − 0.025y2 ∂P
where x is the number of pounds of Kisses and y is the number of pounds of Kreams. Find , and ∂y
give the approximate rate of change of profit with respect to the number of pounds of Kreams that
are sold if 100 pounds of Kisses and 16 pounds of Kreams are currently being sold. What does this mean? ∂P XHD: Tìm (100; 16) và nêu ý nghĩa. ∂y Bài 11. ∂P
(Utility) If U = f (x, y) is the utility function for goods X and Y , the marginal utilityof X is ∂x ∂P
and the marginal utility of Y is
. If U = x2y2 , find the marginal utility of ∂y a) X. b) Y . 1 2
Bài 12. (Production) Suppose that the output Q (in units) of a certain company is Q = 75K 3 L3 , where K ∂Q
is the capital expenditures in thousands of dollars and L is the number of labor hours. Find and ∂K
∂Q when capital expenditures are $729,000 and the labor hours total 5832. Interpret each answer. ∂L
Bài 13. The cost (in dollars) of manufacturing one item is given by C (x, y) = 30 + 3x + 5y, where x is the
cost of 1 hour of labor and y is the cost of 1 pound of material.
a) If the hourly cost of labor is $20, and the material costs $3 per pound, what is the cost of manu- facturing one of these items?
b) Find and interpret the partial derivative of C with respect to x.
Bài 14. The total cost of producing 1 unit of a product is xy C (x, y) = 30 + 2x + 4y + dollars 50
where x is the cost per pound of raw materials and y is the cost per hour of labor. 49 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
a) If labor costs are held constant, at what rate will the total cost increase for each increase of $1 per pound in material cost?
b) If material costs are held constant, at what rate will the total cost increase for each $1 per hour increase in labor costs? Bài 15. x2y
The total cost of producing an item is C (x, y) = 40 + 4x + 6y + dollars, where x is the cost 100
per pound of raw materials and y is the cost per hour for labor. How will an increase of
a) $1 per pound of raw materials affect the total cost?
b) $1 per hour in labor costs affect the total cost?
Bài 16. The joint cost (in dollars) for two products is given by C (x, y) = 30 + x2 + 3y + 2xy, where x
represents the quantity of product X produced and y represents the quantity of product Y produced.
a) Find and interpret the marginal cost with respect to x if 8 units of product X and 10 units of product Y are produced.
b) Find and interpret the marginal cost with respect to y if 8 units of product X and 10 units of product Y are produced. q
Bài 17. Suppose that the production function for a product is z =
4xy, where x represents the num-
ber of workhours per month and y is the number of available machines. Determine the marginal productivity of a) x. b) y. 2 3
Bài 18. Suppose the production function for a product is z = 60x5 y 5 , where x is the capital expenditures
and y is the number of work-hours. Find the marginal productivity of a) x. b) y. 3 2
Bài 19. Suppose the Cobb-Douglas production function for a company is given by z = 400x5 y 5 , where x
is the company’s capital investment and y is the size of the labor force (in work-hours).
a) Find the marginal productivity of x.
b) If the current labor force is 1024 work-hours, substitute y = 1024 in your answer to part (a) and graph the result.
c) Find the marginal productivity of y. 50 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
d) If the current capital investment is $59,049, substitute x = 59, 049 in your answer to part (c) and graph the result.
Bài 20. (Profit) Suppose that the quarterly profit from the sale of Kisses and Kreams is given by P (x, y) = 10x + 6.4y .
− 0 001x2 − 0.025y2 dollars
where x is the number of pounds of Kisses and y is the number of pounds of Kreams. Selling how
many pounds of Kisses and Kreams will maximize profit? What is the maximum profit?
Bài 21. (Profit) The profit from the sales of two products is given by
P (x, y) = 20x + 70y − x2 − y2 dollars
where x is the number of units of product 1 sold and y is the number of units of product 2. Selling
how much of each product will maximize profit? What is the maximum profit?
Bài 22. (Production) Suppose that P = 3.78x2 + 1.5y2 − 0.09x3 − 0.01y3 tons is the production function
for a product with x units of one input and y units of a second input. Find the values of x and y that
will maximize production. What is the maximum production?
Bài 23. (Profit) Suppose that a manufacturer produces two brands of a product, brand 1 and brand 2. Sup-
pose the demand for brand 1 is x = 70
thousand units and the demand for brand 2 is −p1 y = 80−p2 thousand units, where p and
are prices in dollars. If the joint cost function is 1 p2 C = xy , in thou-
sands of dollars, how many of each brand should be produced to maximize profit? What is the maximum profit?
Bài 24. (Profit) A company manufactures two products, A and B. If x is the number of thousands of units of
A and y is the number of thousands of units of B, then the cost and revenue in thousands of dollars are C (x, y) = 2x2 , R (x, y) = 5x y.
− 2xy + y2 − 7x − 10y + 11 + 8
Find the number of each type of product that should be manufactured to maximize profit. What is the maximum profit?
Bài 25. Một công ty sản xuất độc quyền hai loại mặt hàng A và B với số lượng và giá bán tương ứng lần
lượt là x, y (sản phẩm) và 580 (ngàn đồng/sản phẩm), − 5x
740 − 8y (ngàn đồng/sản phẩm). Cho
biết hàm chi phí để sản xuất sản phẩm là C (x, y) = 2xy + 4 (ngàn đồng). Công ty nên sản xuất bao
nhiêu sản phẩm mỗi mặt hàng để lợi nhuận thu được là lớn nhất. 51 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 26. Giả sử công ty sản suất hai loại sản phẩm có sản lượng x, y với mức giá p1 = 60, p2 = 75 và hàm
chi phí là C (x, y) = x2 + xy + y2. Tìm mức sản lượng x, y để công ty đạt lợi nhuận lớn nhất. Tìm
lợi nhuận lớn nhất đó.
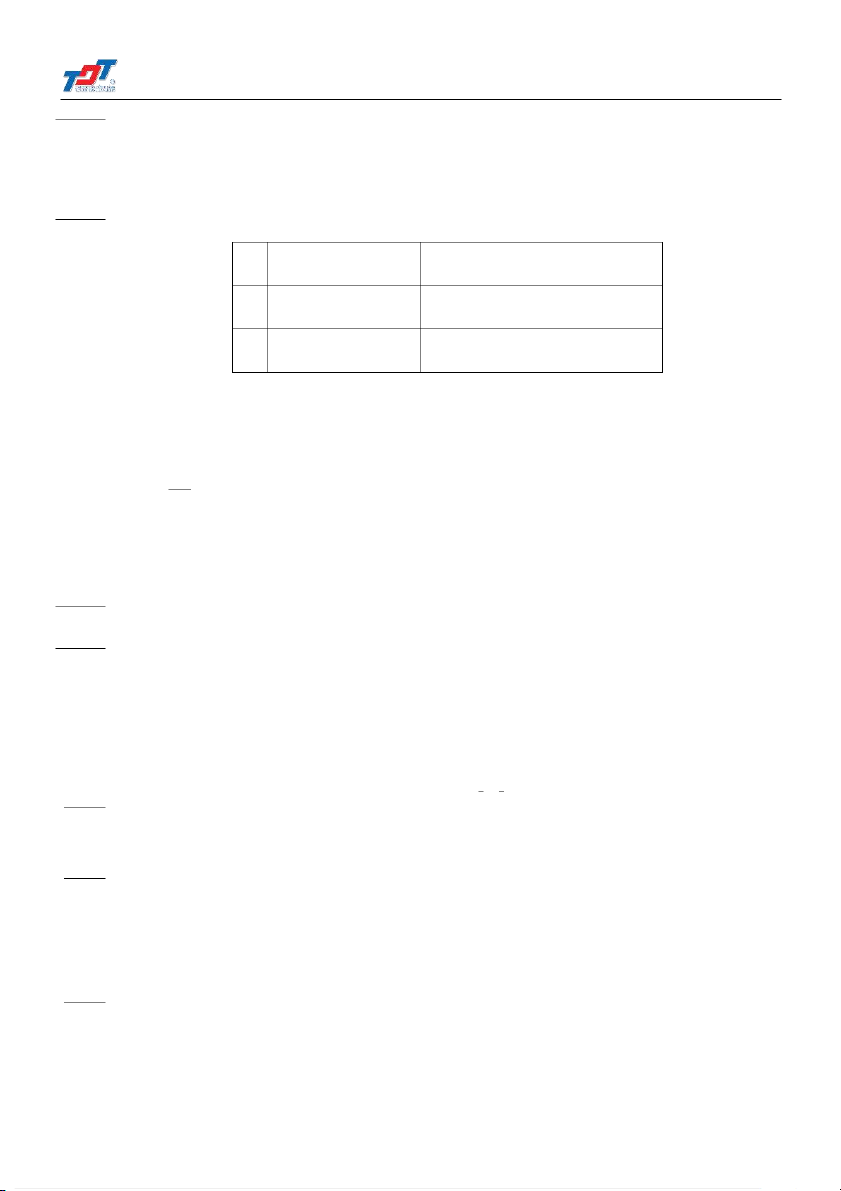
Bài 27. Công ty A sản xuất hai mặt hàng X và Y . Thông tin cho trong bảng sau Sản lượng Giá bán X x (nghìn sản phẩm)
p1 = 50 (nghìn đồng /sản phẩm) Y y (nghìn sản phẩm)
p2 = 80 (nghìn đồng /sản phẩm)
Hàm chi phí cho hai sản phẩm là C (x, y) = 5x2 + 3xy + 4y2.
a) Tìm hàm lợi nhuận P (x, y). ∂P b) Tìm (2; 3) ∂x
c) Công ty A phải chọn mức sản lượng (x, y) như thế nào đạt mức lợi nhuận lớn nhất. Tìm lợi nhuận lớn nhất đó.
Bài 28. Cho các hàm cầu Q1 = 40 − P1, Q2 = 30 − 0, 5P2. Hãy lập hàm doanh thu R (Q1, Q2) .
Bài 29. Cho hàm sản xuất Q = 10K0,3L0,2. Giá thuê một đơn vị K là £3, giá thuê một đơn vị L là £2 và
giá sản phẩm là p = £3. Lập hàm lợi nhuận π (K, L) .
4.2 Ý nghĩa đạo hàm riêng trong kinh tế 1 3
Bài 1. Cho hàm sản xuất của một doanh nghiệp là Q = 20K4 L4 . Tính QK (16, 81) ,
QL (16, 81) và giải thích ý nghĩa.
Bài 2. Cho hàm lợi ích U = 3xy 0 − 2x2 − y2, x, y > .
a) Tại (x0, y0) = (50, 60) nếu x tăng 1 đơn vị và y không đổi, hỏi lợi ích thay đổi thế nào?
b) Tính MUY (50, 60) giải thích ý nghĩa kết quả tìm được.
Bài 3. A firm sells two competing products whose demand schedules are q1 = 120 − 0.8p1 + 0.5p2, q2 = 160 + 0.4p1 p − 12 2
How will the price of good 2 affect the marginal revenue of good 1? 52 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 4. A firm operates with the production function Q = 820K0.3L0.2 and can buy inputs K and L at £ £ 65 and
40 respectively per unit. If it can sell its output at a fixed price of £12 per unit, what is
the relationship between increases in L and total profit? Will a change in K affect the extra profit
derived from marginal increases in L?
Bài 5. Cho hàm cầu D = 0.4Y 0.2p0.3 với Y là thu nhập, p là giá. Tính hệ số co dãn của cầu theo giá và của cầu theo thu nhập.
4.3 Cực trị hàm 2 biến
Bài 1. Tìm cực trị tự do của các hàm sau đây z = 4(x b) − y) − x2 − y2 a) z = x2 + xy + y2 + x − y + 1 z = x + y − xey c) z = (x − 1)2 + 2y2 d) z = 2x4 + y4 f) − x2 − 2y2 e) z = 2xy − 3x2 − 2y2 + 10 g) z = x3 + 3xy2 h) + 20 − 15x + 12y z = xy + 50 x y i) u = x2 + y2 + z2 j) − xy − x − 2z
u = x3 − y2 − 3x + 4y + z2 + z − 8 u = 2x3 + xy2 + 5x2 + y2 k)
l) u = x2 + xy + y2 − 3x − 6y m) u = x3 + y2 n) − 3xy f (x, y) = 4xy2 y2 + 2y 3 − 4x2 − y4 − − o) f (x, y) = 2x2 + 5y2 p) − 6xy + y − 1
f (x, y) = x2 + y2 + xy − 2x − 3y + 2
q) f (x, y) = y4 − 2xy2 + x2 + y2 + 4y + 3
Bài 2. Cho biết hàm lợi nhuận của một doanh nghiệp sản xuất hai loại sản phẩm là P (q + 120q 1, q2) = 160q1 − 3q2 1 − 2q1q2 − 2q2 2 2 − 18 Tìm q
để doanh nghiệp đạt lợi nhuận tối đa. 1, q2
Bài 3. Cho biết hàm lợi nhuận của một doanh nghiệp sản xuất hai loại sản phẩm là
P (q1, q2) = 15q1 + 12q2 − 3q1q22 − q31
Xác định sản lượng cần sản xuất q
để doanh nghiệp đạt lợi nhuận tối đa. 1, q2 53 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 4. Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất hai loại sản phẩm. Cho biết hàm cầu đối với hai loại sản phẩm đó là q1 = 1300 − p1, q2 = 675 p − 0.5 2
và hàm tổng chi phí T C = q 2
2. Hãy cho biết mức sản lượng và giá bán tương 1 + 3q1q2 + q2 q1, q2
ứng để doanh nghiệp đó thu được lợi nhuận tối đa.
Bài 5. Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất hai loại sản phẩm. Cho biết hàm cầu đối với hai loại sản phẩm đó là q1 = 25 − 0.5p1, q2 = 30 p − 2
và hàm tổng chi phí T C = q 2 2 và giá bán 1
+ 3q1q2 + q2 + 20. Hãy cho biết mức sản lượng q1, q2
tương ứng để doanh nghiệp đó thu được lợi nhuận tối đa.
Bài 6. Một hãng độc quyền sản xuất hai loại sản phẩm. Cho biết hàm cầu đối với hai loại sản phẩm đó là q1 = 50 − 0.5p1, q2 = 76 p − 2
và hàm tổng chi phí T C = 3q 2 2 và giá bán 1
+ 2q1q2 + 2q2 + 55. Hãy cho biết mức sản lượng q1, q2
tương ứng để doanh nghiệp đó thu được lợi nhuận tối đa.
Bài 7. A firm produces two products which are sold in two separate markets with the demand schedules p1 = 600 − 0.3q1, p2 = 500 . − 0 2q2
Production costs are related and the firm faces the total cost function
T C = 16 + 1.2q1 + 1.5q2 + 0.2q1q2
If the firm wishes to maximize total profits, how much of each product should it sell? What will the maximum profit level be?
Bài 8. A firm sells two products which are partial substitutes for each other. If the price of one product
increases then the demand for the other substitute product rises. The prices of the two products (in £) are p and
and their respective demand functions are 1 p2
q1 = 517 − 3.5p1 + 0.8p2, q2 = 770 p p − 4.4 2 + 1.4 1
What price should the firm charge for each product to maximize its total sales revenue?
Bài 9. A multiplant monopoly operates two plants whose total cost schedules are T C1 = 8.5 + 0.03q2, T C 1 2 = 5.2 + 0.04q2 2
If it faces the demand schedule p = 60
, how much should it produce in − 0.04q where q = q1 + q2
each plant in order to maximize profits? 54 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 10. Cho hàm sản xuất của hãng Q = 10K0.3L0.4, biết giá thuê một đơn vị tư bản K là 0.03, giá thuê
một đơn vị lao động L là 2 và giá sản phẩm là 4. Hãy xác định mức sử dụng K, L để hãng thu được lợi nhuận tối đa.
Bài 11. Doanh nghiệp cạnh tranh có hàm sản xuất
Q = −2K2 + 3KL − 3L2 + 30K + 20L, K, L > 0.
a) Hãy xác định mức sử dụng K, L để doanh nghiệp thu được sản lượng cực đại.
b) Cho biết giá thị trường của sản phẩm là p = 2 giá thuê vốn pK = 4, giá thuê lao động pL = 22.
Hãy xác định mức sử dụng K, L để hãng thu được lợi nhuận tối đa.
Bài 12. A firm sells its output in a perfectly competitive market at a fixed price of £200 per unit. It buys the
two inputs K and L at prices of £42 per unit and £5 per unit respectively, and faces the production function q = 3.1K0.3L0.25
What combination of K and L should it use to maximize profit?
Bài 13. A multiplant monopoly operates two plants whose total cost schedules are T C1 = 36 + 0.003q3, T C 1 2 = 45 + 0.005q3 2
If its total output is sold in a market where the demand schedule is p = 320−0.1q, where q = q1+q2,
how much should it produce in each plant to maximize total profits?
Bài 14. Một doanh nghiệp sản xuất hai loại hàng hóa trong thị trường cạnh tranh hoàn hảo có giá bán mỗi
mặt hàng tương ứng là P1 = 4 và P2 = 6
Hàm tổng chi phí T C = T C (Q 2 2 1, Q2) = 2Q1 + Q để
1Q2 + 2Q2 . Tìm mức sản lượng Q1, Q2
tối đa hóa lợi nhuận doanh nghiệp.
4.4 Cực trị có điều kiện
Bài 1. Tính cực trị có diều kiện của các hàm sau: a) f (x, y) = x + 2y, x2 + y2 = 5
b) f(x, y) = −x2 − 2y2, 3x − 2y = −22
c) f (x, y) = 3x − y, 3x2 + 4y2 = 208 d) f (x, y) = xy, x + y = 5 55 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN e) f (x, y) = x2 + y2, x + y = 1 2 3
f) f (x, y) = x − 2y − 2z, x2 + y2 + z2 = 9
Bài 2. A firm faces the production function Q = 12K0.4L0.4 and can buy the inputs K and L at prices per
unit of £40 and £5 respectively. If it has a budget of £800 what combination of K and L should it
use in order to produce the maximum possible output?
Bài 3. A firm faces the production function Q = 20K0.4L0.6. It can buy inputs K and L for £400 a unit
and £200 a unit respectively. What combination of L and K should be used to maximize output if
its input budget is constrained to £6, 000?
Bài 4. A firm faces the production function Q = 120L + 200K − L2 − 2K2
for positive values of Q. It can buy L at £5 a unit and K at £8 a unit and has a budget of £70.
What is the maximum output it can produce?
Bài 5. The utility a consumer derives from consuming the two goods A and B can be assumed to be
determined by the utility function U = 40A0.25B0.5. If A costs £4 a unit and B costs £10 a unit
and the consumer’s income is £600, what combination of A and B will maximize utility?
Bài 6. A firm operates with the production function Q = 4K0.6L0.4 and buys inputs K and L at prices per
unit of £40 and £15 respectively. What is the cheapest way of producing 600 units of output?
Bài 7. Cho biết hàm lợi ích tiêu dùng X U = x0.4y0.6.
Giả sử giá các mặt hàng tương ứng là 2 USD và 3 USD, thu nhập dành cho tiêu dùng là 130 USD.
Hãy xác định lượng cầu đối với mỗi mặt hàng để người tiêu dùng được lợi ích tối đa.
Bài 8. Cho biết hàm lợi ích tiêu dùng U = x1x2 + x1 + x2
Giả sử giá các mặt hàng tương ứng là 2 USD và 5 USD, thu nhập dành cho tiêu dùng là 51 USD.
Hãy xác định lượng cầu đối với mỗi mặt hàng để người tiêu dùng được lợi ích tối đa.
Bài 9. Cho biết hàm lợi ích tiêu dùng U = x 0.6 0.25 1 x2
Giả sử giá các mặt hàng tương ứng là 8 USD và 5 USD, thu nhập dành cho tiêu dùng là 680 USD.
Hãy xác định lượng cầu đối với mỗi mặt hàng để người tiêu dùng được lợi ích tối đa. Nếu thu nhập
dành cho tiêu dùng tăng lên 1 USD thì lợi ích tối đa thay đổi thế nào? 56 / 57
CHƯƠNG 4. VI PHÂN HÀM NHIỀU BIẾN
Bài 10. Tối thiểu hóa hàm chi tiêu C (x, y) = 3x + 4y, x, y > 0 trong điều kiện giữ mức lợi ích
U = 2 x.y = 337.5. Nêu mức lợi ích tăng thêm 1 đơn vị hỏi chi tiêu tối thiểu thay đổi thế nào?
Bài 11. Tối thiểu hóa hàm chi phí C (x, y) = x2 + 4y2 − 3xy + 10, x, y > 0 trong điều kiện giữ mức doanh thu R (x, y) = 5x + 4y = 508. 57 / 57




