Preview text:
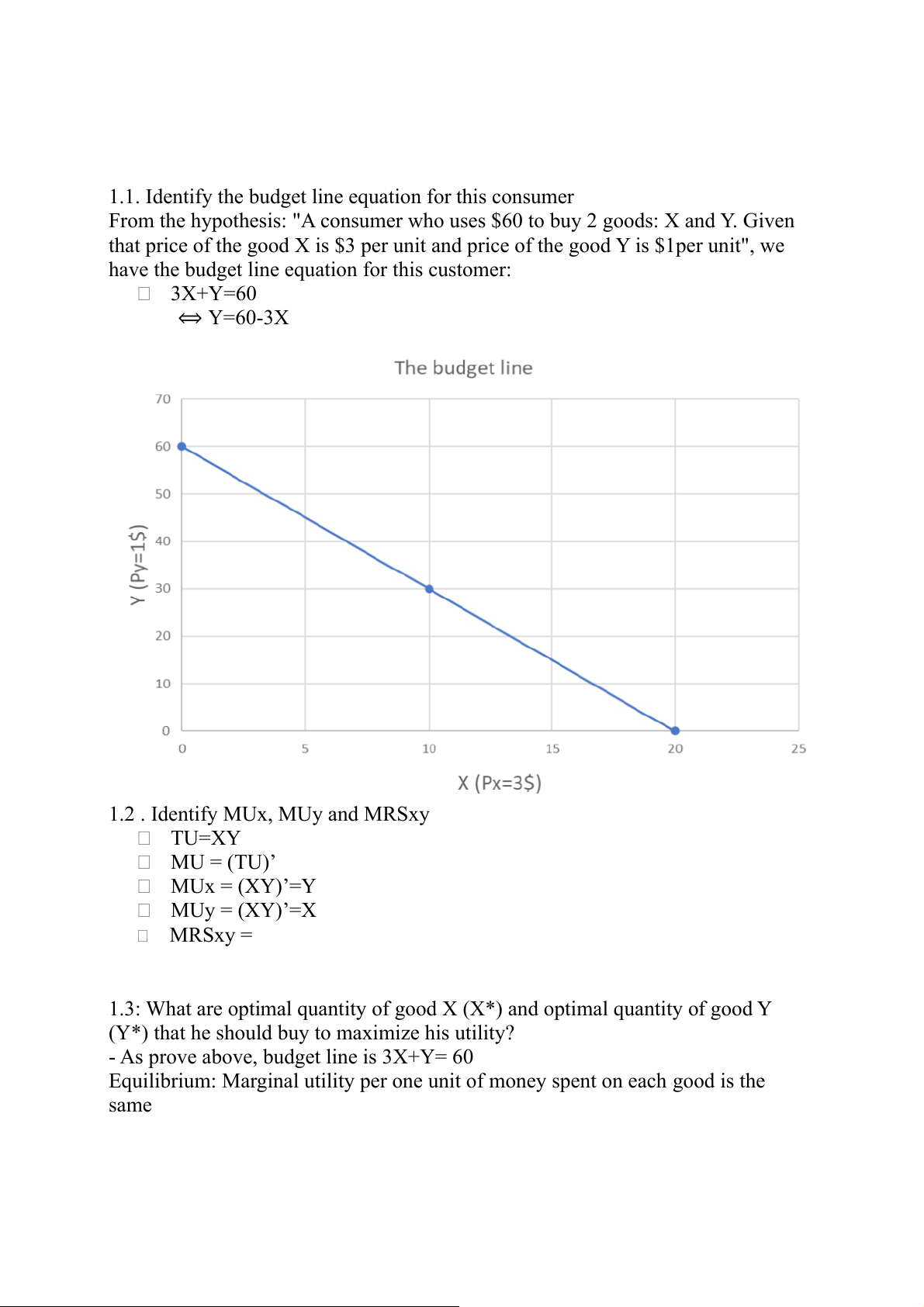
1.1. Identify the budget line equation for this consumer
From the hypothesis: "A consumer who uses $60 to buy 2 goods: X and Y. Given
that price of the good X is $3 per unit and price of the good Y is $1per unit", we
have the budget line equation for this customer: 3X+Y=60 ⟺ Y=60-3X
1.2 . Identify MUx, MUy and MRSxy TU=XY MU = (TU)’ MUx = (XY)’=Y MUy = (XY)’=X MRSxy =
1.3: What are optimal quantity of good X (X*) and optimal quantity of good Y
(Y*) that he should buy to maximize his utility?
- As prove above, budget line is 3X+Y= 60
Equilibrium: Marginal utility per one unit of money spent on each good is the same ➔ Y=3X ( Due to )
Instead of the equation 60 = 3X+Y ➔ X=10 Y=30
So, the optimal quantity of good X (X*) and the optimal quantity of good Y (Y*)
are 10 units and 30 units respectively to maximize his utility. Exercise 2:
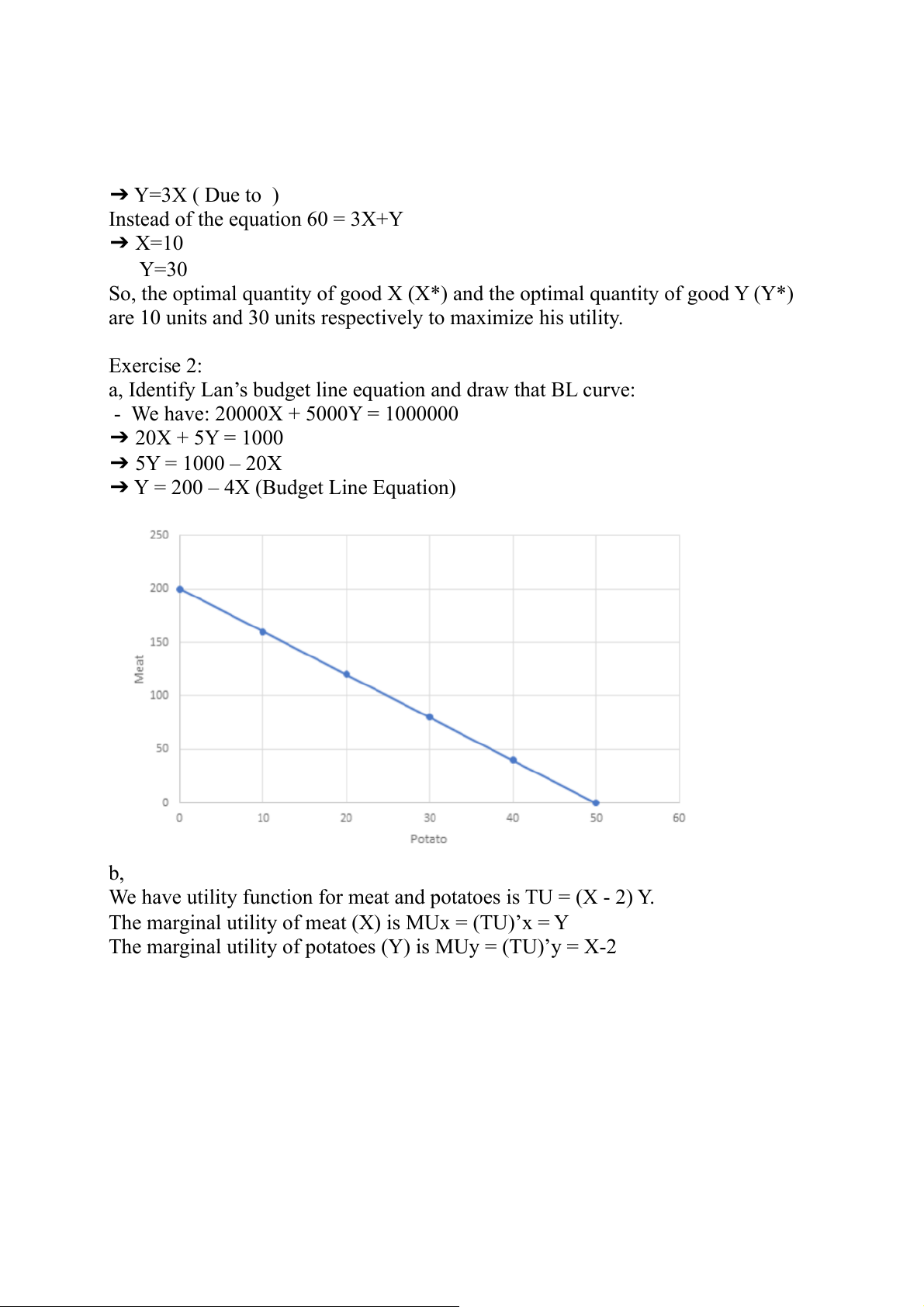
a, Identify Lan’s budget line equation and draw that BL curve:
- We have: 20000X + 5000Y = 1000000 ➔ 20X + 5Y = 1000 ➔ 5Y = 1000 – 20X
➔ Y = 200 – 4X (Budget Line Equation) b,
We have utility function for meat and potatoes is TU = (X - 2) Y.
The marginal utility of meat (X) is MUx = (TU)’x = Y
The marginal utility of potatoes (Y) is MUy = (TU)’y = X-2
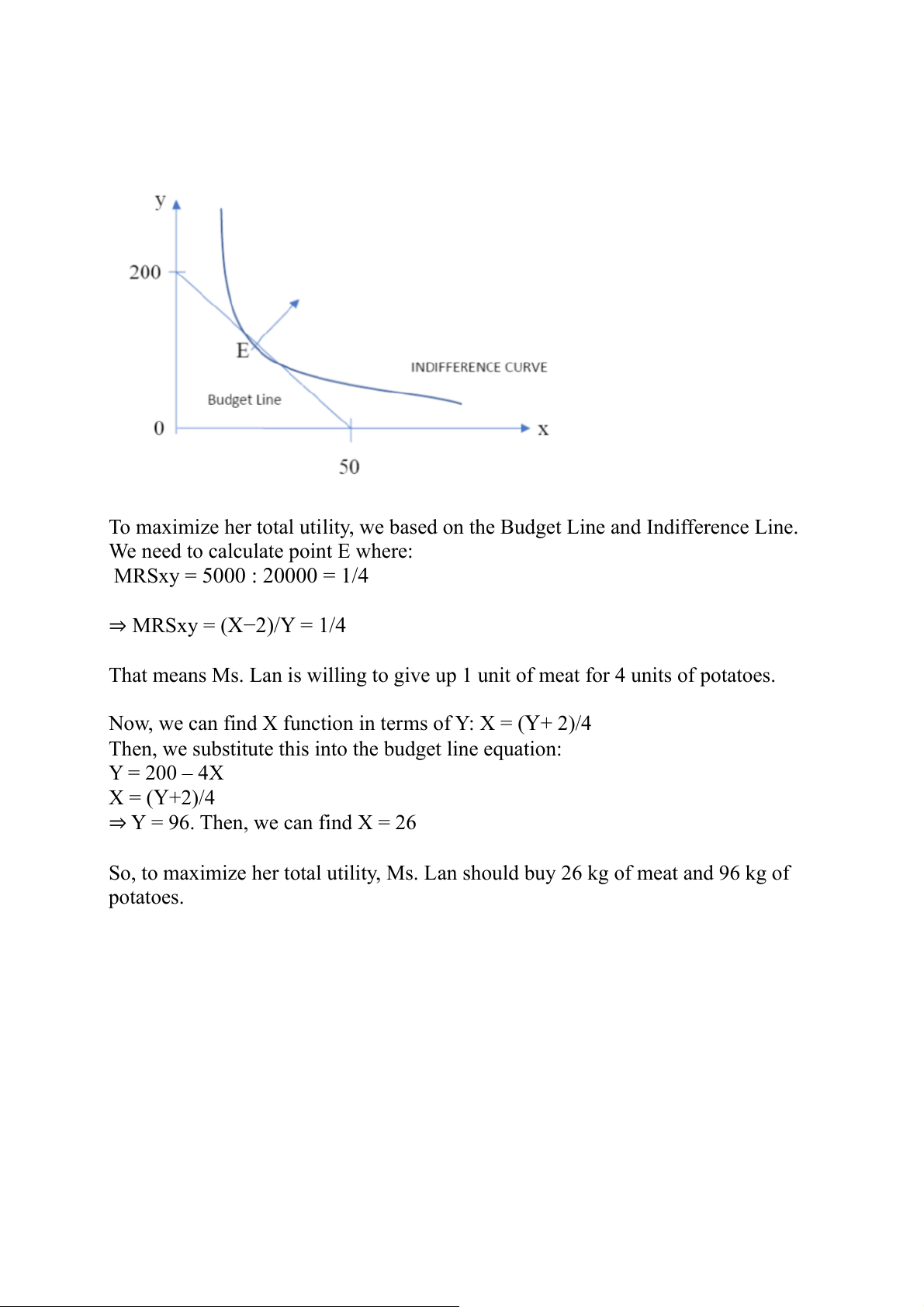
To maximize her total utility, we based on the Budget Line and Indifference Line.
We need to calculate point E where: MRSxy = 5000 : 20000 = 1/4 ⇒ MRSxy = (X−2)/Y = 1/4
That means Ms. Lan is willing to give up 1 unit of meat for 4 units of potatoes.
Now, we can find X function in terms of Y: X = (Y+ 2)/4
Then, we substitute this into the budget line equation: Y = 200 – 4X X = (Y+2)/4
⇒ Y = 96. Then, we can find X = 26
So, to maximize her total utility, Ms. Lan should buy 26 kg of meat and 96 kg of potatoes.




