









Preview text:
ĐỀ 1 MICROECONOMICS
I. RECOGNITION QUESTIONS (10 questions)
(Basic concepts, definitions, principles) 1. What is a “trade-off”?
A. The gain from consuming one more unit
B. The value of the next best alternative
C. Giving up one option to obtain another
D. The difference between revenue and cost.
2. Opportunity cost refers to:
A. Explicit monetary cost only
B. The best alternative forgone C. All sunk costs
D. The discount given by sellers
3. Rational people make decisions based on: A. Total benefits only
B. Marginal benefits and marginal costs C. Social benefits D. Costs only
4. Which of the following is an incentive? A. A natural disaster
B. A price increase that motivates buyers to reduce quantity demanded C. The existence of scarcity
D. A perfect competition market 5. Absolute advantage means: A. Lower opportunity cost
B. Higher productivity using the same resources C. Producing more varieties D. Lower selling price
6. Comparative advantage is based on: A. Lower accounting cost B. Lower opportunity cost C. Higher revenue D. Higher total output
7. A perfectly competitive market is characterized by: A. One seller
B. A few sellers dominating the market
C. Many buyers and sellers, identical products D. Government price control
8. The law of demand states that:
A. Price ↑ → Quantity demanded ↑
B. Price ↓ → Quantity demanded ↓
C. Price ↑ → Quantity demanded ↓ D. Quantity equals supply
9. A normal good is a good for which:
A. Demand rises when income falls
B. Demand falls when income rises
C. Demand stays unchanged regardless of income
D. Demand rises when income rises
10. Price elasticity of demand measures:
A. Sensitivity of price to supply
B. Responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price
C. Fluctuation in total revenue
D. Change in producer surplus
II. COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS (10 questions)
(Explain concepts, identify curve shifts, interpret diagrams)
11. When the demand curve shifts to the right, this implies:
A. Quantity demanded increases at every price B. Price must fall C. Supply decreases
D. Market becomes monopolistic
12. Which event would shift the supply curve to the left?
A. An improvement in technology
B. A decrease in input prices
C. An increase in taxes imposed on producers D. An increase in sellers 13. In equilibrium: A. Qd > Qs B. Qd < Qs C. Qd = Qs D. Price is always zero
14. A binding price ceiling causes: A. A surplus B. A shortage C. No effect
D. Increased producer surplus
15. Who bears more tax burden when demand is inelastic compared to supply? A. Buyers B. Sellers C. Government D. Both equally
16. Consumer surplus is defined as: A. Price – cost
B. Willingness to pay – price
C. Price – willingness to sell D. Revenue – cost
17. If a market creates negative externalities, then: A. Qmarket < Qoptimal B. Qmarket > Qoptimal C. Qmarket = Qoptimal
D. Government should subsidize the product 18. A bowed-out PPF implies: A. Constant opportunity cost
B. Increasing opportunity cost C. No opportunity cost
D. Inefficient production only
19. A tax creates deadweight loss because: A. It increases total surplus
B. It reduces government revenue
C. It reduces quantity traded below the efficient level D. It increases supply
20. A positive externality leads the free market to: A. Overproduce B. Underproduce C. Produce efficiently D. Produce at zero quantity
III. APPLICATION QUESTIONS (10 questions)
(Simple calculations, real-world examples, equilibrium shifts)
21. Demand function: Qd = 40 – 2P.
If P increases from 10 to 12, what is the percentage change in quantity demanded (using the midpoint formula)?
22. Supply function: Qs = –10 + 3P.
Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
23. If the government imposes a price floor above the equilibrium price, what will happen in the labor market? A. Labor shortage
B. Labor surplus (unemployment) C. Higher employment D. No change
24. Consider two goods: iPhone and AirPods.
If the price of iPhone decreases, what happens to the demand for AirPods?** A. Decrease B. Increase C. No change D. Becomes perfectly elastic
25. A consumer is willing to pay $80 for a pair of shoes. Market price is $50.
What is the consumer surplus?
26. A producer’s cost is $30. Market price is $45. What is the producer surplus?
27. Gasoline demand is inelastic.
If the government increases tax on gasoline, what will happen to total spending on gasoline? A. Decrease B. Increase C. Stay the same D. Fall to zero
28. Negative externality example:
A factory emits pollution, causing health costs for nearby residents. What is the social cost? A. Private cost only
B. Private cost + external cost
C. External cost – private cost D. Zero
29. If the supply curve shifts right more than demand shifts right, equilibrium price will: A. Increase B. Decrease C. Stay unchanged D. Become infinite
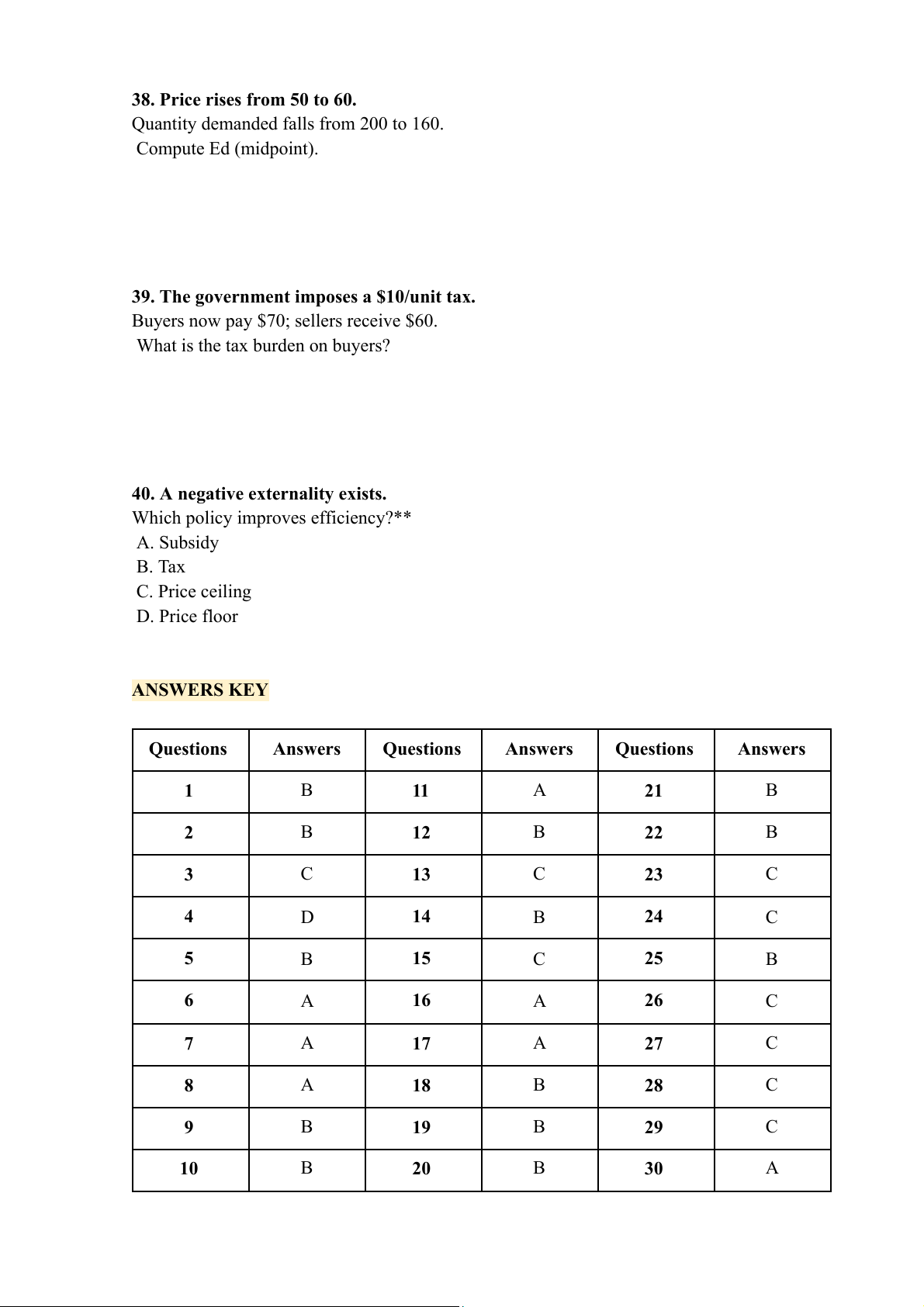
30. A country can produce more with the same resources due to improved technology. What happens to its PPF? A. Shifts inward B. Rotates inward C. Expands outward D. Remains unchanged ANSWERS KEY Questions Answers Questions Answers 1 C 11 A 2 B 12 C 3 B 13 C 4 B 14 B 5 B 15 A 6 B 16 B 7 C 17 B 8 C 18 B 9 D 19 C 10 B 20 B ĐỀ 2 MICROECONOMICS
I. Recognition Questions (15 items)
1. Which of the following is NOT one of the 10 Principles of Economics? A. People face trade-offs
B. Markets always allocate resources perfectly
C. People respond to incentives
D. Trade can make everyone better off
2. A “normal good” is one where:
A. Demand decreases when income increases
B. Demand increases when income increases C. It has close substitutes D. It has no substitutes
3. Inferior goods are defined as:
A. Goods consumers buy more of when income rises
B. Goods whose production cost is low
C. Goods consumers buy less of when income rises D. Goods always overpriced
4. Which market structure has identical products and price-taking firms? A. Monopoly B. Oligopoly C. Monopolistic competition D. Perfect competition
5. The supply curve represents:
A. Consumers’ willingness to buy
B. Producers’ willingness to sell C. Government regulation D. Total demand 6. The law of supply states: A. Price ↑ → Qs ↑ B. Price ↑ → Qs ↓
C. Price ↓ → Qs unchanged
D. Quantity depends only on demand 7. Market demand equals:
A. The sum of all individual demands
B. The maximum willingness to pay C. The average price D. None of the above
8. A binding price floor is set: A. Above equilibrium price B. Below equilibrium price C. At equilibrium price D. At zero price 9. Deadweight loss refers to: A. Government revenue
B. Total surplus lost due to a policy C. Producer surplus D. Consumer surplus
10. Cross-price elasticity is positive for: A. Complements B. Substitutes C. Inferior goods D. Necessities
11. A perfectly inelastic demand curve is: A. Vertical B. Horizontal C. Downward sloping D. Upward sloping
12. In the circular-flow diagram, households supply: A. Goods B. Factors of production C. Imports D. Tariffs
13. Opportunity cost includes: A. Explicit cost only B. Implicit cost only
C. Both explicit and implicit cost D. Fixed cost only
14. A positive externality causes: A. Overproduction B. Underproduction C. Market efficiency D. Zero production
15. A corrective tax is used to: A. Increase consumption B. Reduce deadweight loss
C. Internalize negative externalities D. Subsidize producers
II. Comprehension Questions (15 items)
16. When supply decreases while demand increases, equilibrium price will: A. Increase B. Decrease C. Stay the same D. Become indeterminate 17. If Ed > 1, demand is: A. Elastic B. Inelastic C. Perfectly elastic D. Perfectly inelastic
18. Consumer surplus increases when: A. Price increases B. Price decreases C. Supply decreases D. Demand decreases
19. Which of the following will shift the PPF outward? A. A recession B. Improvement in technology C. Increase in unemployment D. Higher opportunity cost
20. A subsidy on producers will: A. Shift supply left B. Shift supply right C. Shift demand right D. Reduce quantity supplied
21. When the government imposes a tax on buyers, the demand curve: A. Shifts upward B. Shifts downward C. Does not shift D. Rotates
22. Which is an example of market power?
A. A perfectly competitive firm
B. A monopoly controlling price C. A farmer selling rice
D. A grocery store selling apples
23. If the government sets a binding price ceiling: A. Quantity supplied rises B. A surplus occurs C. A shortage occurs D. Total surplus increases
24. Which good is most likely to have inelastic demand? A. Blue jeans B. Soft drinks C. Insulin D. Restaurant meals
25. If supply is more elastic than demand, who bears more of a tax burden? A. Producers B. Consumers C. Government D. Neither
26. Deadweight loss increases when:
A. Elasticity of demand is low
B. Elasticity of supply is low
C. Elasticity of demand and supply are high
D. Both curves are perfectly inelastic 27. An external cost is: A. Cost paid by producers
B. Cost paid by the government
C. Cost imposed on bystanders D. Cost paid by consumers
28. A non-binding price ceiling will: A. Create shortage B. Create surplus C. Have no effect D. Reduce total surplus
29. Market equilibrium maximizes: A. Producer surplus B. Consumer surplus C. Total surplus D. Tax revenue
30. When demand increases more than supply increases: A. Price increases B. Price decreases C. Price stays constant D. Quantity decreases
III. Application Questions (10 items) (With simple calculations)
**31. Demand: Qd = 100 – 5P. Find Qd when P = 12.
**32. Supply: Qs = –20 + 10P. Find Qs when P = 5.
33. Find equilibrium price and quantity: Qd = 80 – 2P Qs = –10 + 4P
34. If income increases and demand for instant noodles decreases, instant noodles are: A. Normal goods B. Inferior goods C. Complement goods D. Substitutes
35. The price of coffee increases. What happens to the demand for tea (a substitute)? A. Decreases B. Increases C. Stays unchanged D. Becomes vertical
36. A consumer is willing to pay $120 for a jacket and buys it for $75. Find consumer surplus.
37. A producer’s cost is $50 and market price is $85. Find producer surplus.
38. Price rises from 50 to 60.
Quantity demanded falls from 200 to 160. Compute Ed (midpoint).
39. The government imposes a $10/unit tax.
Buyers now pay $70; sellers receive $60.
What is the tax burden on buyers?
40. A negative externality exists.
Which policy improves efficiency?** A. Subsidy B. Tax C. Price ceiling D. Price floor ANSWERS KEY Questions Answers Questions Answers Questions Answers 1 B 11 A 21 B 2 B 12 B 22 B 3 C 13 C 23 C 4 D 14 B 24 C 5 B 15 C 25 B 6 A 16 A 26 C 7 A 17 A 27 C 8 A 18 B 28 C 9 B 19 B 29 C 10 B 20 B 30 A




