






Preview text:
Chương 2: Lý thuyết cung-cầu -Khái niệm: -Luật cung/cầu -Mô tả cung/cầu:
- Phân biệt cung/cầu cá nhân và thị trường
- Các nhân tố tác động tới sự thay đổi của cung/cầu
1.Demand (Người tiêu dùng): (D):
- Definition: Cầu khác nhu cầu
The demand of any good is the amount of the good that buyers are willing and able to purchase, at each
price, in a given period of time, ceteris paribus.
Cầu là số lượng hàng hoá hoặc dịch vụ mà người tiêu dùng muốn mua và có khả năng mua ở các mức
giá khác nhau trong khoảng thời gian nhất định, ceteris paribus.
Muốn mua: nhu cầu phản ánh thị hiếu của người tiêu
Có khả năng mua: khả năng tài chính, đủ tiền để thỏa mãn nhu cầu
Cầu chỉ hình thành khi hai điều kiện trên được thỏa mãn.
Ví dụ: Macbook giới thiệu sản phẩm mới năm 2021 với mức giá dao động 40tr-120tr
Chiếc Macbook rất đẹp và cấu hình rất cao để phục vụ cho rất nhiều hoạt động học tập và giải trí. Trong
trường hợp này, người tiêu dùng đều thích và muốn mua sản phẩm nhưng mức giá của chiếc Mac được
đánh giá là quá đắt đối với phần lớn người tiêu dùng: Chúng ta muốn mua sản phẩm nhưng lại không đủ
khả năng tài chính để thỏa mãn nhu cầu của mình --> Cầu với Mac 2021 không hình thành.
Giả sử trường hợp khác là chúng ta đang cân đối một chiếc máy tính Asus model 2015 với mức giá 10tr.
Nhưng bề ngoài ko bắt mắt và cấu hình chỉ phục vụ cho các hoạt động cơ bản. Chúng ta đủ khả năng tài
chính chi trả cho sản phẩm nhưng chúng ta lại không muốn chi tiêu cho sản phẩm --> Cầu đối với Asus
model 2015 cũng không hình thành.
CƠ bản: Cầu phản ánh mối quan hệ giữa giá và lượng cầu
Phân biệt giữa khái niệm cầu và lượng cầu
Demand (cầu): Số lượng hàng hóa được mua ở các mức giá khác nhau o
Chỉ ra mối quan hệ giữa mức giá (P) và lượng cầu (Qd)
Quantity Demanded (lượng cầu): Số lượng hàng hóa được mua ở các một mức giá nhất định o P1 QD1 o P2 QD2 o … o Pn QDn
Relationship between the price and quantity demanded mentioned above is the demand
- Luật cầu: phản ánh cách người tiêu dùng phản ứng trước biến động giá cả
Mối quan hệ ngược chiều giữa giá cả và lượng cầu: P ↑→ Q ↓ D P ↓→ Q ↑ D
E.g., normally, price of pork is 15k/g, due to some reasons the price of pork increases to 20k/g. Whether
continue to buy but with a lower quantity or buy other meats like chicken, beef…
In words, Chúng ta mua hàng hóa ít đi khi mức giá tăng cao hơn và có xu thế mua nhiều hơn khi giá
giảm hành vi của người tiêu dùng trên thị trường
- Các cách mô tả cầu (based on the law of demand): Demand Schedule: Biểu cầu Demand curve: Đường cầu
Demand function: Hàm cầu: (D): Q = a-bP P= a’-b’Q o
a’: constant/intercept (The value of P when Q=0) o b’: slope of demand
- Phân biệt giữa cầu cá nhân và cầu thị trường:
Chú ý: Chúng ta chỉ quan tâm tới cầu thị trường vì sự thay đổi của cả thị trường mới dẫn tới sự biến động
giá cà sản lượng trên thị trường. Hành vi thay đổi của một cá nhân sẽ không có ảnh hưởng đáng kể tới giá thị trường.
Note: We only care about the market demand because the change in market demand leads to change in the
price and quantity in the market. Change in behavior of single demand (a typical buyer) do not
significantly affect the market price.
Trên thị trường có rất nhiều người mua và các cá nhân sẽ có các phản ứng (hành vi mua) khác nhau ở
cùng mức giá Cầu thị trường là tập hợp thông tin về giá và cầu của
tất cả các người mua này.
Cần xây dựng cầu thị trường từ tập hợp thông tin của cầu cá nhân.
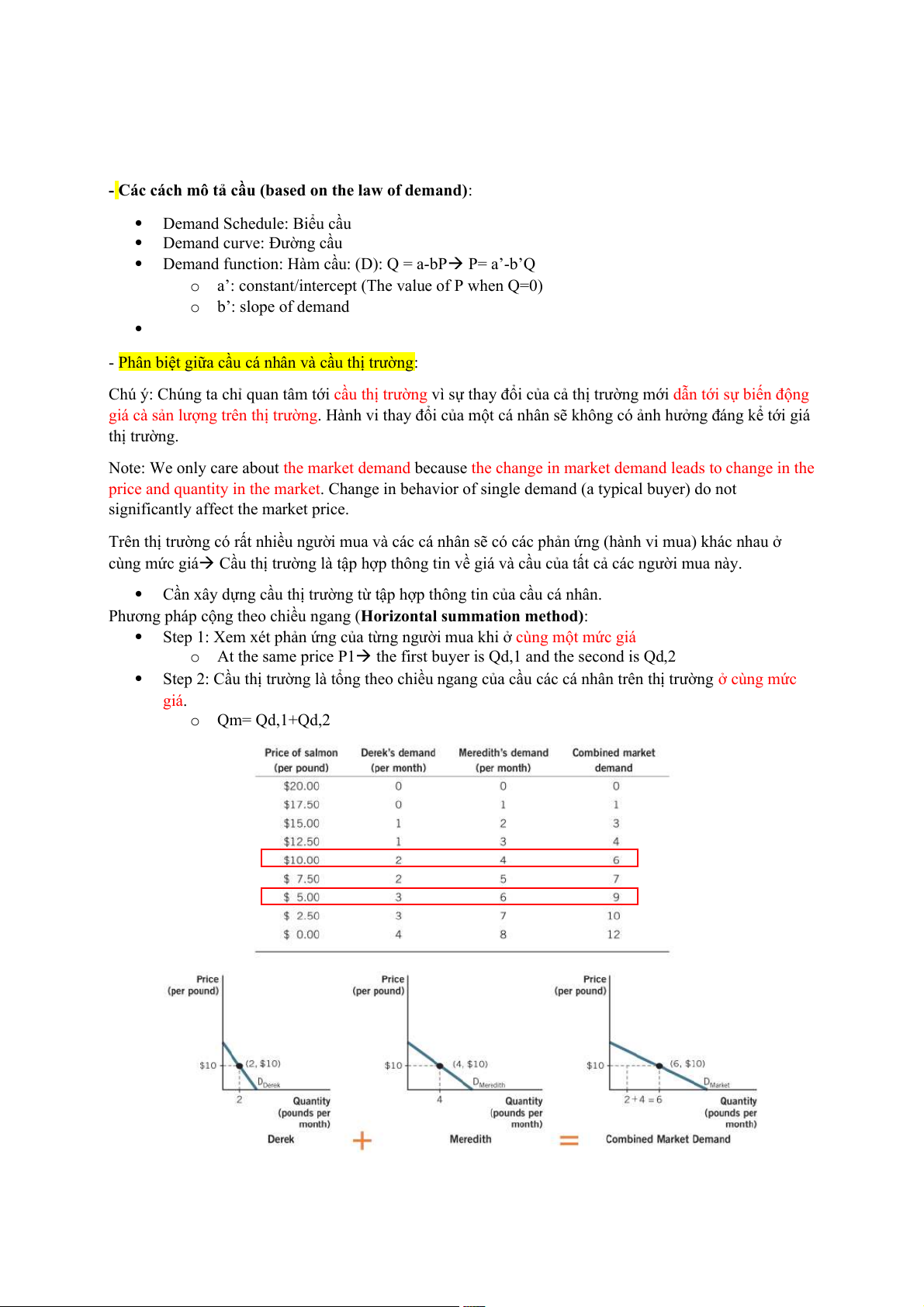
Phương pháp cộng theo chiều ngang (Horizontal summation method):
Step 1: Xem xét phản ứng của từng người mua khi ở cùng một mức giá o
At the same price P1 the first buyer is Qd,1 and the second is Qd ,2
Step 2: Cầu thị trường là tổng theo chiều ngang của cầu các cá nhân trên thị trường ở cùng mức giá. o Qm= Qd,1+Qd,2
At P=10, Qd of Derek is 2 units of salmon, , Qd of Meredith is 4 units of salmon, implying the market
quantinty demanded at the price P=10 is 2+4=6
Application: Adapting the horizontal summation method to construct the market demand function from the single demand function:
E.g., Assume that there are two buyers in the market of pork
(D1): Q =a−b P : the demand function of the first buyer d ,1 1
(D2): Q =c −d P : the demand function of the second buyer d ,2 2
What is the market demand function for pork?
Solution: Hint: Need to transform the single function into the form Q=f(P) and determine the quantity
demanded of different buyers at the same price (P)
(D1): Q =a−b P d ,1
(D2): Q =c −d P d ,2
(Market Demand): Q =Q +Q =(a+ c) −(b+d ) P M d ,1 d , 2 Example:
(D1): P =10−Q : the demand function of the first buyer 1 d , 1
(D2): P =4−Q : the demand function of the second buyer 2 d , 2
What is the market demand function? (D1): Q =10−P d ,1 (D2): Q =4−P d ,2
The market demand function: Qm = Q +Q =14−2 P d ,1 d , 2 -- Determinants of Demand:
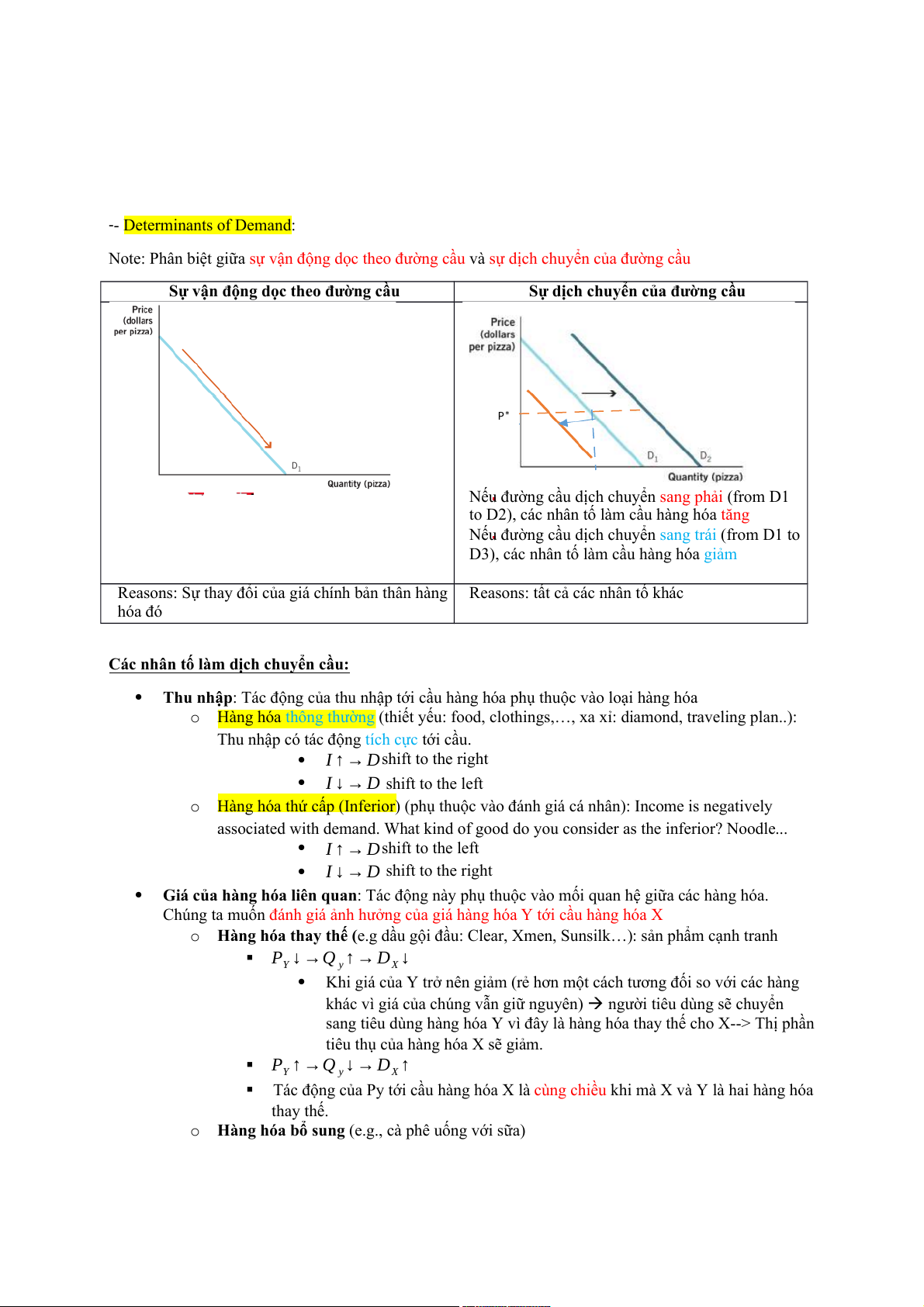
Note: Phân biệt giữa sự vận động dọc theo đường cầu và sự dịch chuyển của đường cầu
Sự vận động dọc theo đường cầu
Sự dịch chuyển của đường cầu P*
Nếu đường cầu dịch chuyển (from D1 sang phải
to D2), các nhân tố làm cầu hàng hóa tăng
Nếu đường cầu dịch chuyển sang trái (from D1 to
D3), các nhân tố làm cầu hàng hóa giảm
Reasons: Sự thay đổi của giá chính bản thân hàng Reasons: tất cả các nhân tố khác hóa đó
Các nhân tố làm dịch chuyển cầu:
Thu nhập: Tác động của thu nhập tới cầu hàng hóa phụ thuộc vào loại hàng hóa o
Hàng hóa thông thường (thiết yếu: food, clothings,…, xa xỉ: diamond, traveling plan..):
Thu nhập có tác động tích cực tới cầu.
I ↑ → D shift to the right
I ↓ → D shift to the left o
Hàng hóa thứ cấp (Inferior) (phụ thuộc vào đánh giá cá nhân): Income is negatively
associated with demand. What kind of good do you consider as the inferior? Noodle...
I ↑ → D shift to the left
I ↓ → D shift to the right
Giá của hàng hóa liên quan: Tác động này phụ thuộc vào mối quan hệ giữa các hàng hóa.
Chúng ta muốn đánh giá ảnh hưởng của giá hàng hóa Y tới cầu hàng hóa X o
Hàng hóa thay thế (e.g dầu gội đầu: Clear, Xmen, Sunsilk…): sản phẩm cạnh tranh
P ↓ →Q ↑ → D ↓ Y y X
Khi giá của Y trở nên giảm (rẻ hơn một cách tương đối so với các hàng
khác vì giá của chúng vẫn giữ nguyên) người tiêu dùng sẽ chuyển
sang tiêu dùng hàng hóa Y vì đây là hàng hóa thay thế cho X--> Thị phần
tiêu thụ của hàng hóa X sẽ giảm.
P ↑ →Q ↓ → D ↑ Y y X
Tác động của Py tới cầu hàng hóa X là
khi mà X và Y là hai hàng hóa cùng chiều thay thế. o
Hàng hóa bổ sung (e.g., cà phê uống với sữa)
P ↓ →Q ↑ → D ↑ Y y X
Khi giá của Y (cà phê) rẻ hơn người tiêu dùng sẽ mua nhiều Y hơn và
vì X và Y (cà phê và sữa) được tiêu dùng cùng nhau nên cầu của sữa cũng sẽ tăng lên.
P ↑ →Q ↓ → D ↓ Y y X
Tác động của Py tới cầu hàng hóa X là ngược chiều khi mà X và Y là hai hàng hóa bổ sung.
Expectation: the change in price of goods in the future will affect the current demand? This factor is a
critical role in the financial market.
Let discuss about these cases: changes in demand: movement or shift? Shift to left or right?
1. On rainy days, customers are willing to pay more to buy umbrella.
Ans: Cause: the bad weather Demand increases Demand shift to RHS
2. Viettel decreases the calling fee at the weekend that cause amount of calling to increase.
Ans: Cause: a dreases in the calling fee quantity demanded increas es Movement
3. On Woman day, the prices of flowers are often higher than normal but people still buy lots of flowers.
Ans: Cause: On Woman day Demand increase Dmenad will shift to RHS
4. To reduce the amount of private transportation, the government increase the tax on gasoline.
2.Supply (Sellers): S: study the behavior of sellers in the market 2. Supply - Definition: - Law of Supply: - Reprentation of Supply:
- Distinguishing between single and market Supply:
E.g., Assume that there two branches of tooth brush in the market: PS and Close-up with the supply
function P=Q+2 , P=0,5Q+5 , respectively. What is Market Supply?
Hint: We need to transform the supply (demand) function into this form: Q=f(P)
(PS):P =Q +2 →Q =P−2 Ps PS Ps
(Close-up): P =0.5Q +5 →Q =2 P−10 C c c
(Market): Q =Q +Q =3 P−12 M Ps c
A complete example to observe how to adapt the horizontal summation method to construct the market demand/supply function. - Determinants of supply: - Input price Tax or Subsidy Effects: Hai điểm lưu ý:
Thuế có thể được đánh lên cả người mua và người bán Có hai loại thuế: o
Thuế sản lượng (Quantity tax): mức thuế được đánh lên các đơn vị sản xuất: t/đơn vị-->
tổng mức thuế doanh nghiệp phải trả sẽ phụ thuộc vào số lượng hàng hóa. o
Thuế cố định (Lump-sum tax): một
mà doanh nghiệp phải trả khi tham mức thuế cố định
gia vào thị trường bất kể họ sản xuất bao nhiêu sản phẩm.
Trong phần phân tích chúng ta chỉ tập trung vào phân tích tác động của thuế sản lượng tới người bán-->
cung giảm--> cung dịch chuyển sang trái
Tax (subsidy) policy directly impacts the cost of production, then cause supply curve shift to the left (right)
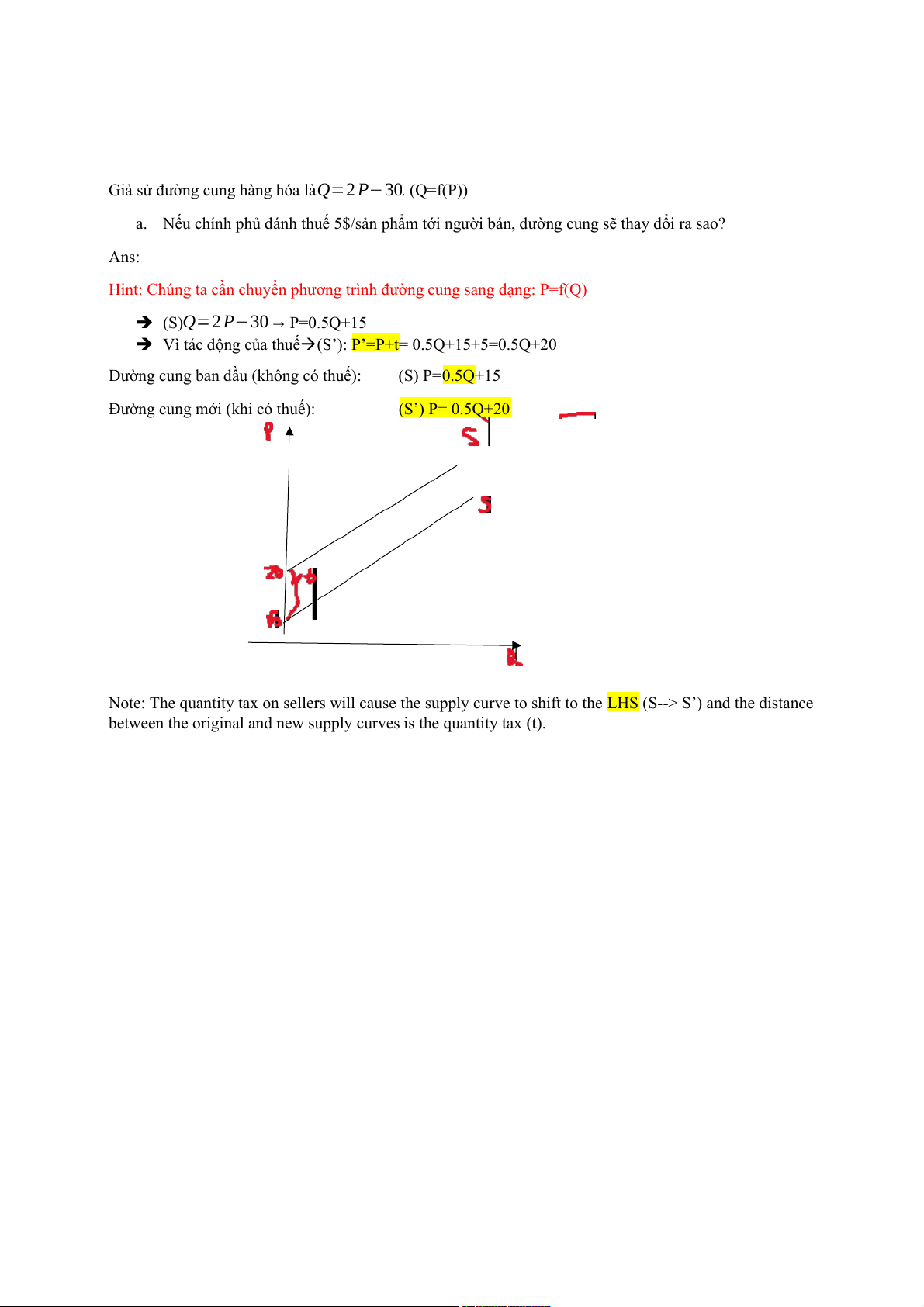
Giả sử đường cung hàng hóa làQ=2 P−30. (Q=f(P))
a. Nếu chính phủ đánh thuế 5$/sản phẩm tới người bán, đường cung sẽ thay đổi ra sao? Ans:
Hint: Chúng ta cần chuyển phương trình đường cung sang dạng: P=f(Q)
(S)Q=2 P−30→ P=0.5Q+15
Vì tác động của thuế(S’): P’=P+t= 0.5Q+15+5=0.5Q+20
Đường cung ban đầu (không có thuế): (S) P=0.5Q+15
Đường cung mới (khi có thuế): (S’) P= 0.5Q+20
Note: The quantity tax on sellers will cause the supply curve to shift to the LHS (S--> S’) and the distance
between the original and new supply curves is the quantity tax (t). 3. Market Equlibrium
Price of a cup of coffee is 20,oooVND Decide how many cups you want buy.
Price of pork: 15,000/gram. You observed the price of pork increases to 22,000 but you don’t what happen.
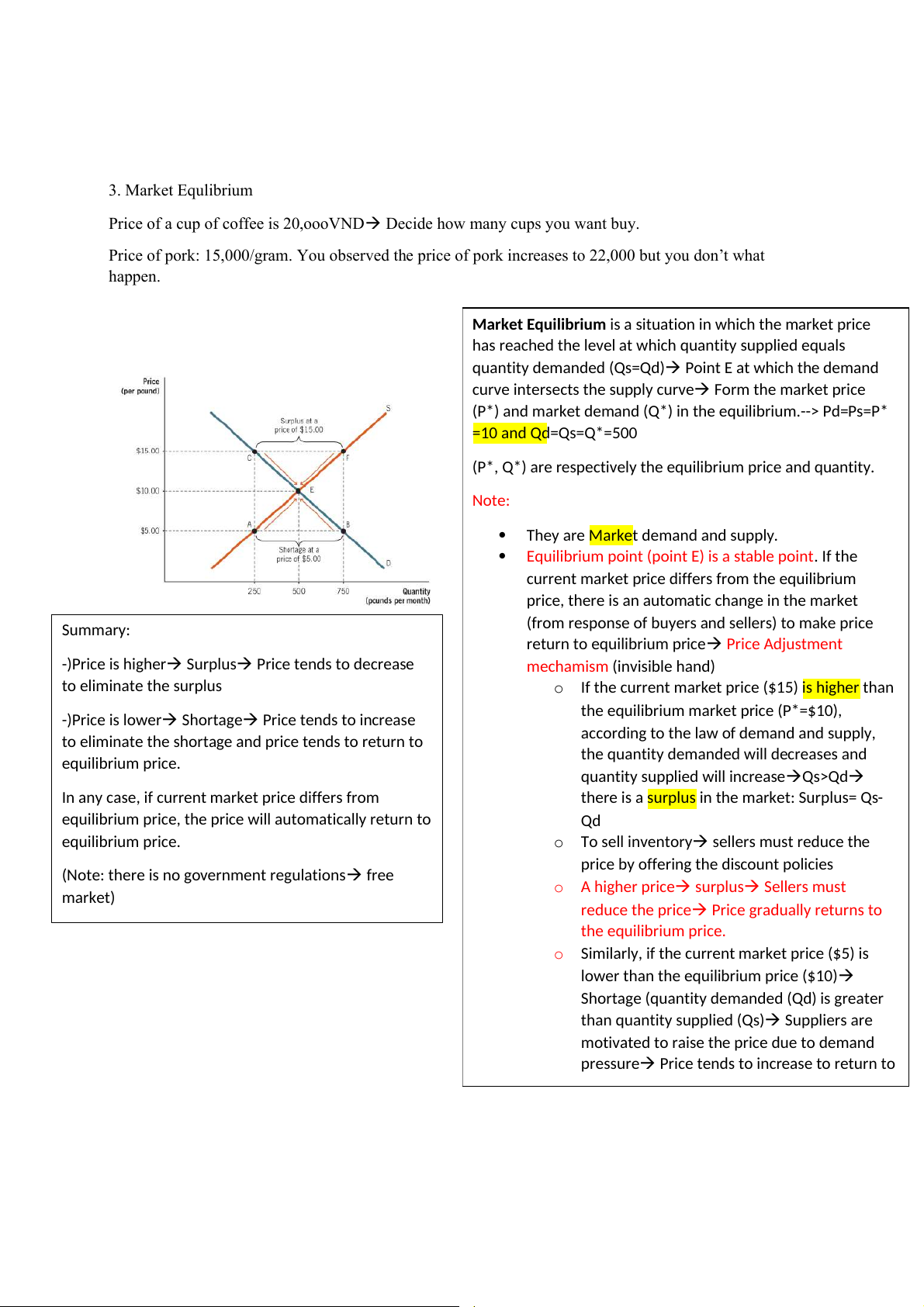
Market Equilibrium is a situation in which the market price
has reached the level at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded (Qs=Qd) Point E at which th e demand
curve intersects the supply curve Form the market price
(P*) and market demand (Q*) in the equilibrium.--> Pd=Ps=P* =10 and Qd=Qs=Q*=500
(P*, Q*) are respectively the equilibrium price and quantity. Note:
They are Market demand and supply.
Equilibrium point (point E) is a stable point. If the
current market price differs from the equilibrium
price, there is an automatic change in the market
(from response of buyers and sellers) to make price Summary:
return to equilibrium price Price Adjustment -)Price is higher Surplus Price tends to decrease mechamism (invisible hand) to eliminate the surplus o
If the current market price ($15) is higher than
the equilibrium market price (P*=$10), -)Price is lower Shortage Price tends to in crease
according to the law of demand and supply,
to eliminate the shortage and price tends to return to
the quantity demanded will decreases and equilibrium price.
quantity supplied will increaseQs>Qd
In any case, if current market price differs from
there is a surplus in the market: Surplus= Qs-
equilibrium price, the price will automatically return to Qd equilibrium price. o To sell inventory sellers must reduce th e
price by offering the discount policies
(Note: there is no government regulations free o A higher price surplus Sellers must market) reduce the price Price gradually returns to the equilibrium price. o
Similarly, if the current market price ($5) is
lower than the equilibrium price ($10)
Shortage (quantity demanded (Qd) is greater than quantity supplied (Qs) Suppliers are
motivated to raise the price due to demand
pressure Price tends to increase to return to Assignment
In market, there 100 sellers and 80 buyers. Individual supply and demand functions are the same as
P=q2 and } P= 6400 . q2
1. What are market demand and market supply?
2. What are market prices and market quantity at the equilibrium? Solution:
1.Adapting the horizontal summation method to develop the market demand and market supply function.
Hint: We need to transform the function into the form: Q=f(P)
(S): P=q2→ q =√ P (the single supply function) s
Because there are 100 sellers in the market, the market supply function is given as: Q =q +q s s ,1
s ,2 +…+q ,100 s Q = = s 100∗q 100 √P s
(D)P= 6400 → q = 80 D (the single demand function) q2 √P
Because there are 80 buyers in the market, the market demand function is given as
→ Q =80∗q = 6400 D D √ P
2. What are market prices and market quantity at the equilibrium?
In the equilibrium, we have Q =Q → 100 √P=6400 → P¿=64 → Q¿=100∗√ 64=800 D s √ P
Analyse the change in the market equilibrium:
How to predict the changes in price and quantity due to shocks, external factors 3-step Analysis: -
Step 1: Based on the information we collected, you must indicate that shocks will affect the demand or supply or both -
Step 2: The effects are negative or positive -
Step 3: using the figure to make simulation to show changes in price and quantity. -
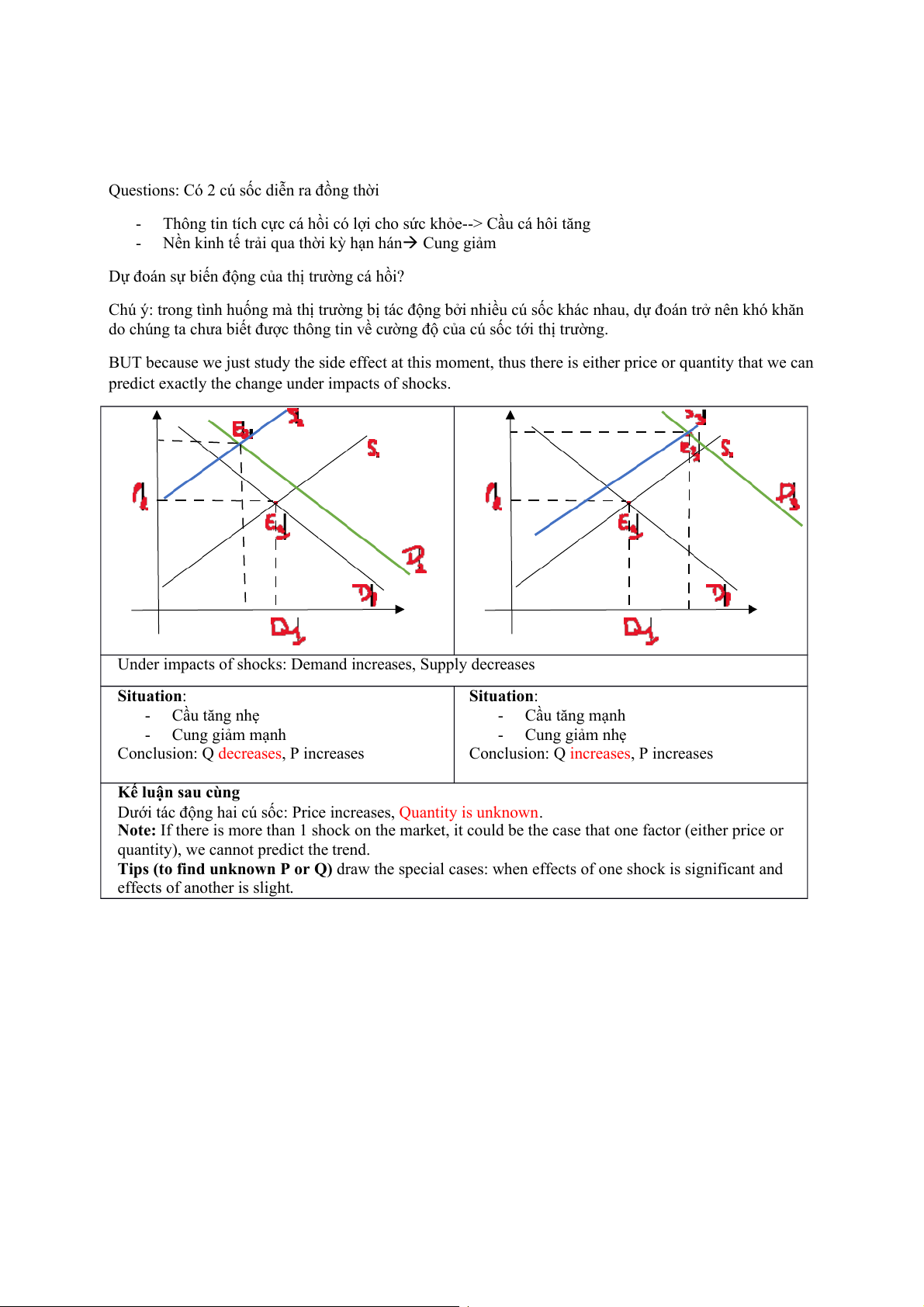
E.g., you want to focus on analysing the salmon market.
In one day, you see the news from Bloomberg that states the salmon is good for the health. What happen to salmon market? Solution: 3-step Analysis: Step 1: Demand change Step 2: Positive effect Step 3:
Demand shifts to the right hand side from D1 to D2 - New equilibrium point: E1 E2 -
Price increases--> Quantity supplied also increases - Quantity increases - -
Questions: Có 2 cú sốc diễn ra đồng thời -
Thông tin tích cực cá hồi có lợi cho sức khỏe--> Cầu cá hôi tăng -
Nền kinh tế trải qua thời kỳ hạn hán Cung giảm
Dự đoán sự biến động của thị trường cá hồi?
Chú ý: trong tình huống mà thị trường bị tác động bởi nhiều cú sốc khác nhau, dự đoán trở nên khó khăn
do chúng ta chưa biết được thông tin về cường độ của cú sốc tới thị trường.
BUT because we just study the side effect at this moment, thus there is either price or quantity that we can
predict exactly the change under impacts of shocks.
Under impacts of shocks: Demand increases, Supply decreases Situation: Situation: - Cầu tăng nhẹ - Cầu tăng mạnh - Cung giảm mạnh - Cung giảm nhẹ
Conclusion: Q decreases, P increases
Conclusion: Q increases, P increases Kế luận sau cùng
Dưới tác động hai cú sốc: Price increases, Quantity is unknown.
Note: If there is more than 1 shock on the market, it could be the case that one factor (either price or
quantity), we cannot predict the trend.
Tips (to find unknown P or Q) draw the special cases: when effects of one shock is significant and effects of another is slight. III.The government policy
3.1. Tax and Subsidy Policy Một số điểm lưu ý: -
Có hai loại đánh thuế/trợ cấp o
Quantity tax (Thuế sản lượng): chính phủ đánh thuế t cho mỗi đơn vị sản phẩm:
t/product Tổng số tiền thuế phải trả của doanh nghiệp phụ thuộc vào số lượng hàng hóa
mà doanh nghiệp sản xuất. o
Lump-sum tax (thuế cố định): CP đánh một mức thuế cố định (T) bất kể sản xuất bao
nhiêu sản phẩm, các doanh nghiệp sẽ phải trả một mức thuế như nhau. -
Thuế/trợ cấp có thể được đánh lên cả người bán và người mua.
Note: We analyse the impacts of quantity tax imposed on either sellers or buyers.
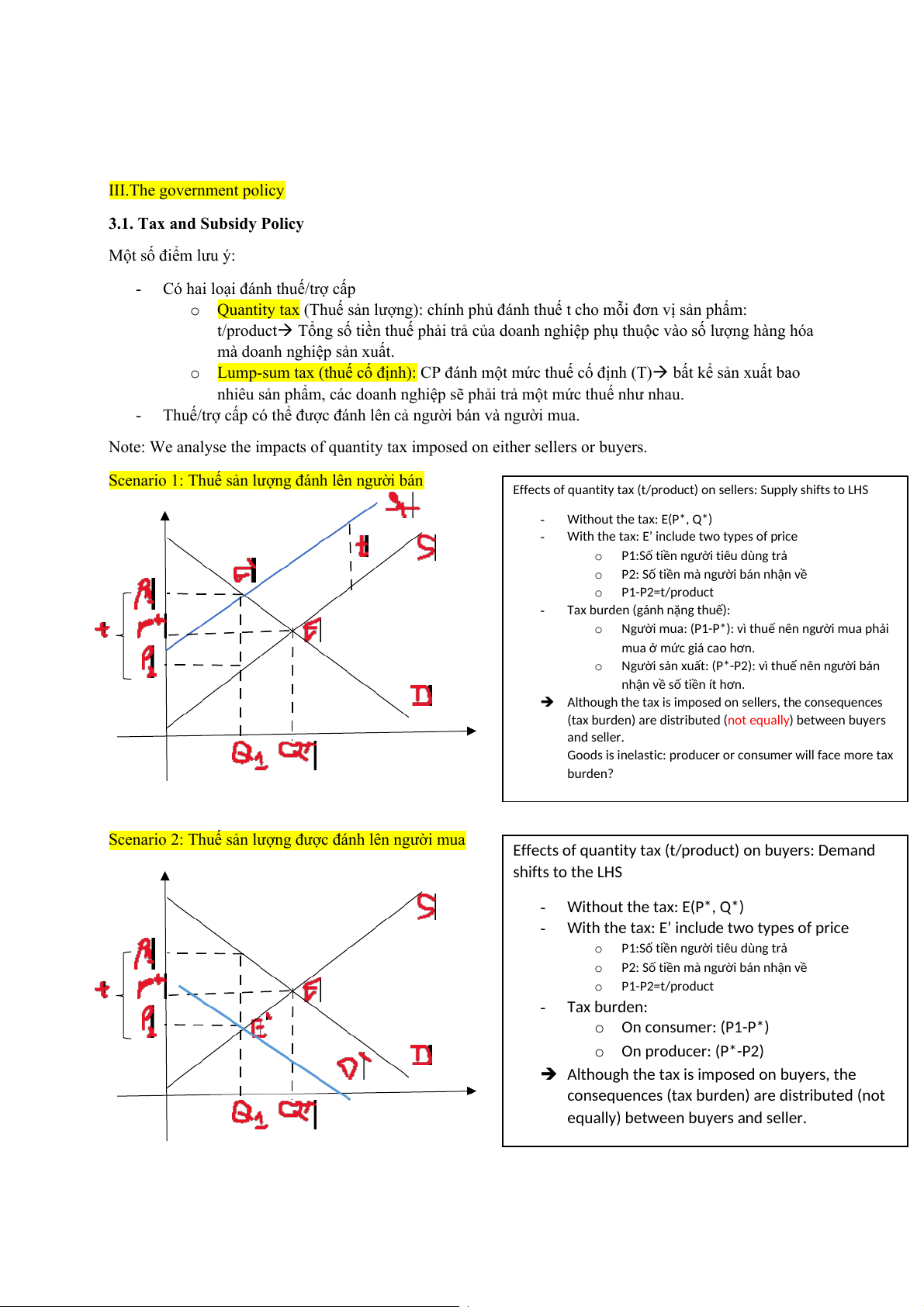
Scenario 1: Thuế sản lượng đánh lên người bán
Effects of quantity tax (t/product) on sellers: Supply shifts to LHS - Without the tax: E(P*, Q*) -
With the tax: E’ include two types of price o
P1:Số tiền người tiêu dùng trả o
P2: Số tiền mà người bán nhận về o P1-P2=t/product -
Tax burden (gánh nặng thuế): o
Người mua: (P1-P*): vì thuế nên người mua phải mua ở mức giá cao hơn. o
Người sản xuất: (P*-P2): vì thuế nên người bán
nhận về số tiền ít hơn.
Although the tax is imposed on sellers, the consequences (tax burden) are distributed ( ) between buyers not equally and seller.
Goods is inelastic: producer or consumer will face more tax burden?
Scenario 2: Thuế sản lượng được đánh lên người mua
Effects of quantity tax (t/product) on buyers: Demand shifts to the LHS - Without the tax: E(P*, Q*) -
With the tax: E’ include two types of price o
P1:Số tiền người tiêu dùng trả o
P2: Số tiền mà người bán nhận về o P1-P2=t/product - Tax burden: o On consumer: (P1-P*) o On producer: (P*-P2)
Although the tax is imposed on buyers, the
consequences (tax burden) are distributed (not
equally) between buyers and seller.
Remarks: Bất kể thuế được đánh lên ai, thì cả thị trường đều bị tác động thuế. 3.2. Kiểm soát giá. E.g.,
Price control for the pork market in Vietnam
During the Covid-19 pandemic, the price of mark increased substantially, the gov need to control for the price of mark.
(1) Understanding; (2) Policy Objectives; (3) Effectiveness (4) Consequences; (5) Further discussion Content
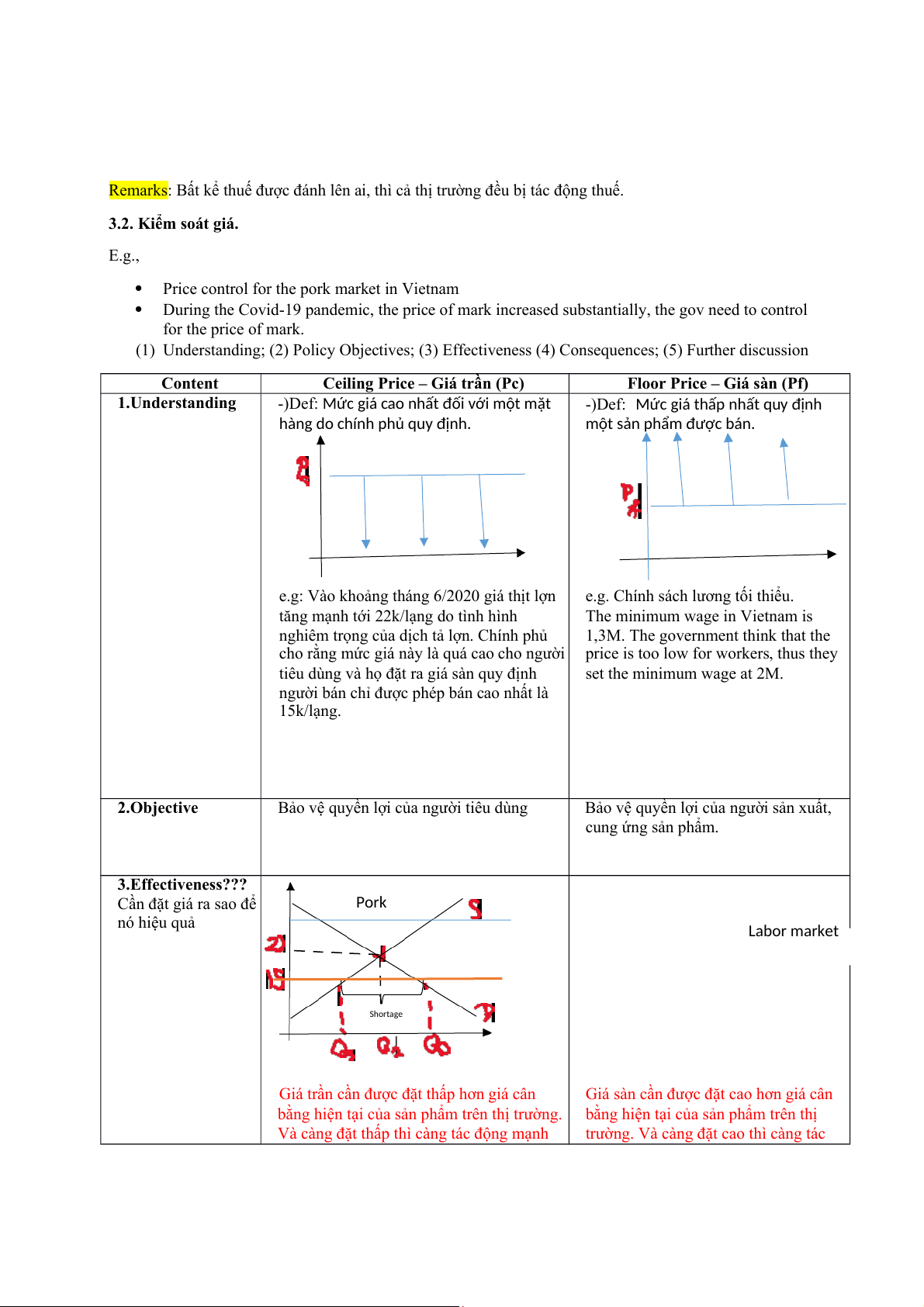
Ceiling Price – Giá trần (Pc)
Floor Price – Giá sàn (Pf) 1.Understanding
-)Def: Mức giá cao nhất đối với một mặt
-)Def: Mức giá thấp nhất quy định
hàng do chính phủ quy định.
một sản phẩm được bán.
e.g: Vào khoảng tháng 6/2020 giá thịt lợn
e.g. Chính sách lương tối thiểu.
tăng mạnh tới 22k/lạng do tình hình
The minimum wage in Vietnam is
nghiêm trọng của dịch tả lợn. Chính phủ
1,3M. The government think that the
cho rằng mức giá này là quá cao cho người price is too low for workers, thus they
tiêu dùng và họ đặt ra giá sàn quy định set the minimum wage at 2M.
người bán chỉ được phép bán cao nhất là 15k/lạng. 2.Objective
Bảo vệ quyền lợi của người tiêu dùng
Bảo vệ quyền lợi của người sản xuất, cung ứng sản phẩm. 3.Effectiveness???
Cần đặt giá ra sao để Pork nó hiệu quả Labor market Shortage
Giá trần cần được đặt thấp hơn giá cân
Giá sàn cần được đặt cao hơn giá cân
bằng hiện tại của sản phẩm trên thị trường.
bằng hiện tại của sản phẩm trên thị
Và càng đặt thấp thì càng tác động mạnh
trường. Và càng đặt cao thì càng tác tới thị trường.
động mạnh tới thị trường. 4.Consequences
Advantage: Khi áp dụng giá trần thì giá
Advantage: Khi áp dụng giá sàn thì giá
ngay lực tức giảm tới mục tiêu đặt ra.
ngay lập tức tăng tới mục tiêu đặt ra.
Disadvantages: Qd tăng trong khi Qs
Disadvantages: Qd giảm while Qs
giảm Shortage (Thiếu hụt)=Qd-Qs
tăng Surplus (Dư thừa)=Qs-Qd Consequences:
-)There is not enough goods in the market.
-)The consumers buy the lower-quality products. Discussion
What is the better solution to the pork
Minimum wage policy will decrease market?
the demand for employees, while labor -
Increase the supply of pork by
supply increases the unemployment importing the pork.
rate increases due to the minimum
Analyse this policy??? The price still wage policy. remained at the high price.
The unemployment happens mostly for
the basic workers (low skill, without
In spite of consequences, the gov should education…)
consider the ceiling price to protect the
consumers after the serious disasters like
drought… the price of goods increases dramatically. Recommendation
If the government solely impose the price control, the market will be negatively
affected. Therefore, the supporting policies need to consider together with the price control.




