



Preview text:
final micro
Question 1: The economising problem is essentially one of deciding
how to make the best use of:
A. Virtually unlimited resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants.
B. Limited Resources, to satisfy virtually unlimited wants.
C. Unlimited resources, to satisfy limited wants.
D. Limited resources, to satisfy limited wants.
Question 2: The production possibilities curve is bowed out from the origin because:
A. of increasing opportunity cost.
B. economic resources are perfectly substitutable in the production of the two products. C. of underemployment.
D. equal quantities of both products are produced at each possible point on the curve.
Question 3: The construction of demand and supply curves assumes
that the primary variable that influences decision to produce and purchase goods is: A. Price B. Expectations C. Preferences D. Incomes
Question 4: If X is a normal good, a rise in income will shift the:
A. Supply curve for X to the left
B. Supply curve for X to the right
C. Demand curve for X to the left
D. Demand curve for X to the right
Question 5: If the price of K declines, the demand curve for the
complementary product J will: A. Shift to the left. B. Decrease C. Shift to the right D. remain unchanged
Question 6: If Vietnam Airlines increases its total revenue when it
discounts its price by 10% then
A. Its passengers’ demand is elastic
B. its passengers’ demand is inelastic
C. it should continue to decrease its price as demand elasticity for the service doesn’t change
D. it means the provider must be a monopolist
Question 7: If rice demand is inelastic, a good rice harvest will cause
the rice growers’ revenue to:
A. Increase because of the increase in the quantity that farmers can sell
B. Remain unchanged, because the increase in the quantity that can be sold
will be matched by an equal decrease in price.
C. Increase because of downward movement along the supply curve,
encouraging an increase in demand.
D. Decrease because of a percentage fall in price greater than the
percentage increase in quantity sold.
Question 8: The sellers’ tax incident would be higher if:
A. The price elasticity of demand is higher
B. The price elasticity of demand is lower.
C. The price elasticity of demand is perfectly elastic D. None of the above
Question 9: Suppose a firm’s output increase from 910 to 1170 units
when it increases its labor input from 63 to 64 workers. The marginal
product of the last worker is: A. 1070 B. 910 C. 260 D. 64
Question 10: If marginal cost is falling and is lower than average total cost then
A. average total cost is falling
B. average total cost is constant
C. average total cost is rising
D. average total cost is at a minimum
Question 11: A firm in a competitive market is producing at the level
of output that maximises profit. At this output level:
A. marginal revenue equals price
B. average revenue equals marginal cost
C. marginal revenue equals marginal cost D. All the above
Question 12: A firm will cease production in the short-run if it cannot:
A. cover its total costs at any level of output
B. cover its total fixed costs at any level of output
C. cover its total variable cost at any level of output
D. earn a normal profit at any level of output Question 13: Output Total cost 0 2000 10 3000 20 4000 30 4500
In a competitive market. A Firm has output and total cost data as shown above.
What is the level of average variable cost when the Firm produces 20 units of output? A. $100 B. $200 C. $2000 D. $1000
Question 14: If a firm doubles its output in the long run and its unit
costs of production decline, we can conclude that:
A. technological progress has occurred.
B. economies of scale are being realised.
C. the firm is encountering diminishing returns.
D. diseconomies of scale are being encountered.
Question 15: Which of the following is not characteristics of a purely competitive industry? A. A large number of sellers. B. Identical products.
C. Substantial barriers to entry. D. Relatively small firms.
Question 16: Consider the following relationship between cost and
output for a perfectly competitive firm: Total cost = $20 $30 $41 $54 Q = 3 4 5 6
If the market price of the firm’s output is $12, how many units of output should the firm produce: A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6
Question 17: Price will always be greater than marginal revenue for a monopolist because:
A. The firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve
B. The demand curve is about the ATC curve
C. Since no new firms can enter the market, the firm is not forced to lower price to increase quantity sold
D. The firm must lower price for all units sold in order to increase the quantity sold. dc
Question 18: Mutual interdependence’ means that each oligopolistic firm:
A. faces a perfectly elastic demand for its product.
B. must consider the reactions of its rivals when it determines its price policy.
C. produces a product identical to those of its rivals.
D. produces a product similar, but not identical, to the products of its rivals.
Question 19: If the four-firm concentration ratio for industry X is 80, this means that:
A. the four largest firms account for 80% of total sales.
B. each of the four largest firms accounts for 20% of total sales.
C. the four largest firms account for 20% of total sales.
D. The industry is monopolistically competitive.
Question 20: Under monopolistic competition, the differentiation of products implies that:
A. Individual firms face downward sloping demand curve
B. Both marginal cost and marginal revenue will increase as output increase
C. Individual firms will make economic profit even in the long run
D. Individual firms will produce at minimum average cost in the long run. True/False Section:
1. In attempting to maximize profits, a firm will always produce at
that output where total revenue is at a maximum.
False. Total Profit = Total Revenue – Total Cost. Because total profit depends
on 2 variables, so only total revenue is maximized is not enough. To maximize
profits, the firm must produce at the output where the distance between total
revenue and total cost is maximize.
2.True. Because when demand increases, and supply decrease simultaneously,
there will be shortage as demand exceeds supply, so the price will rise to eliminate that shortage. Section C:
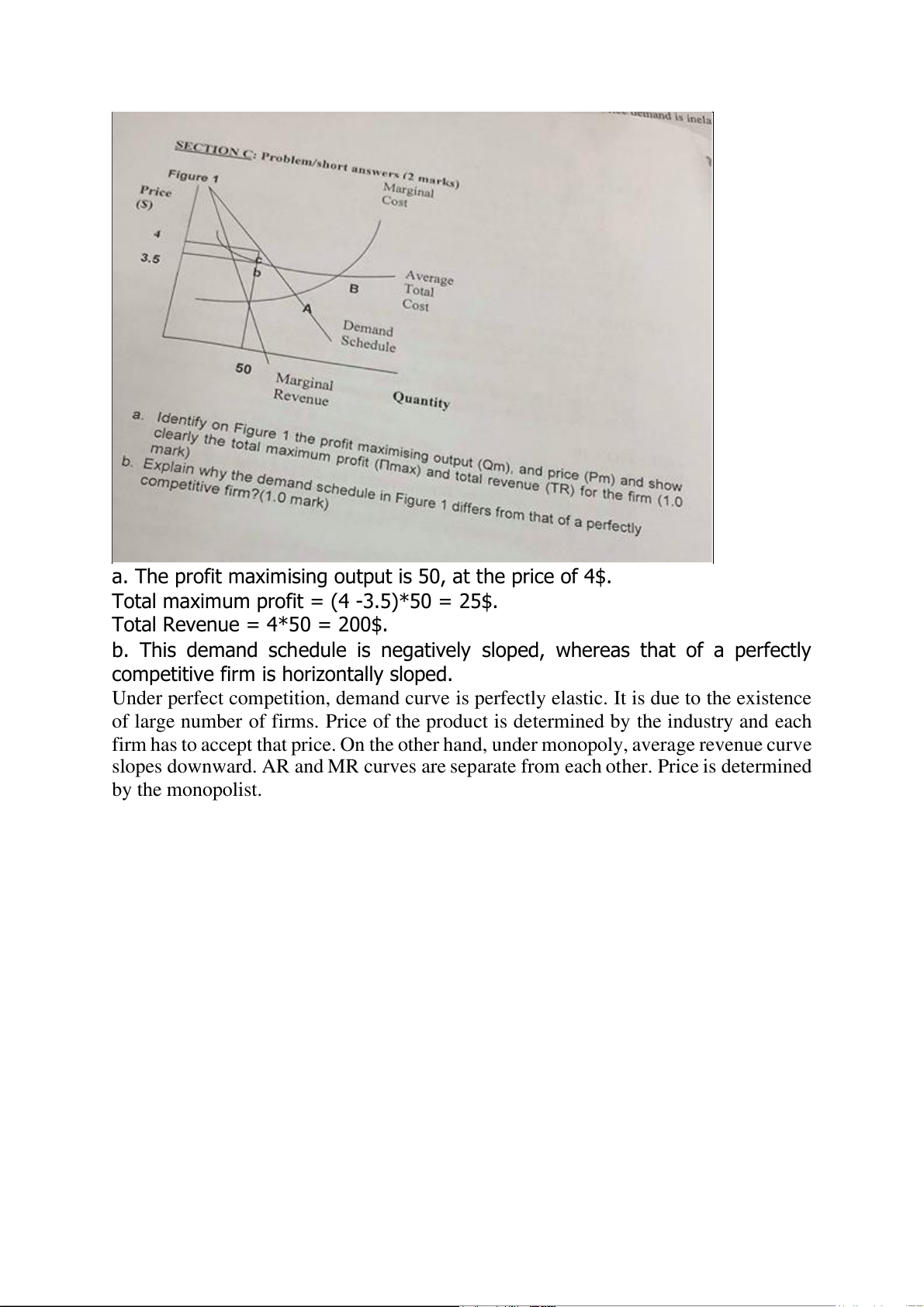
a. The profit maximising output is 50, at the price of 4$.
Total maximum profit = (4 -3.5)*50 = 25$. Total Revenue = 4*50 = 200$.
b. This demand schedule is negatively sloped, whereas that of a perfectly
competitive firm is horizontally sloped.
Under perfect competition, demand curve is perfectly elastic. It is due to the existence
of large number of firms. Price of the product is determined by the industry and each
firm has to accept that price. On the other hand, under monopoly, average revenue curve
slopes downward. AR and MR curves are separate from each other. Price is determined by the monopolist.




