


Preview text:
Group assignment presentation 2
Exercise 1: Demand and supply of fridge are shown in the table below:
Price ($/unit) 100 120 140 160 180 200
Quantity Demanded (units) 1000 900 800 700 600 500
Quantity supplied (units) 300 400 500 600 700 800
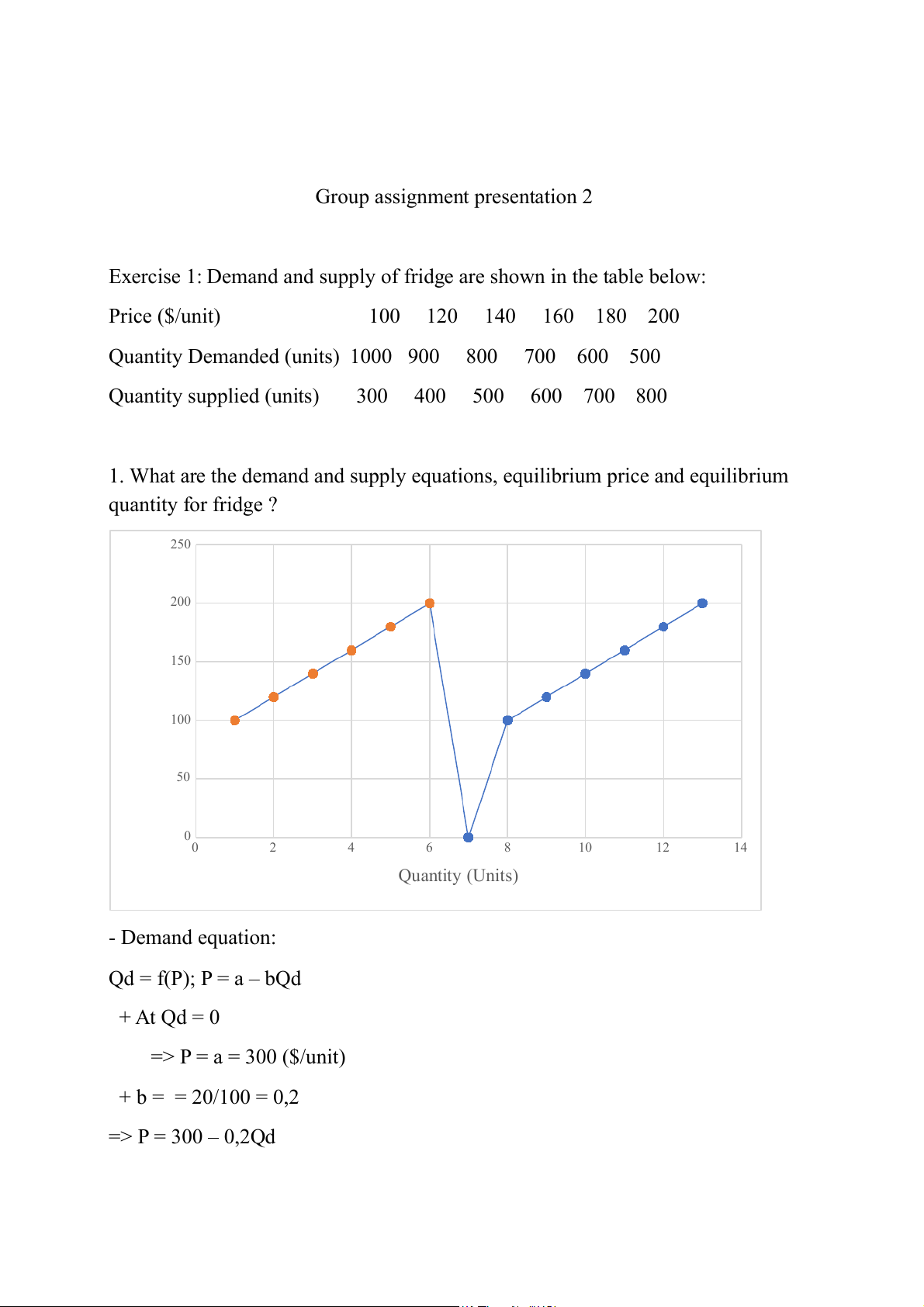
1. What are the demand and supply equations, equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity for fridge ? 250 200 ) it 150 ($/un 100 rice P 50 00 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Quantity (Units) - Demand equation: Qd = f(P); P = a – bQd + At Qd = 0 => P = a = 300 ($/unit) + b = = 20/100 = 0,2 => P = 300 – 0,2Qd - Supply equation: Qs = f(P); P = c + dQs + At Qs = 0 => P = c = 40 ($/unit) + d = = 20/100 = 0,2 => P = 40 + 0,2Qs
The equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity can be found if:
300 – 0,2Qd = 40 + 0,2Qs (Qd = Qs = Qe) => 0.4Qe = 260
=> Qe = 650 (units) Pe = 170 ($/unit)
2. What are the surplus and shortage of fridge at the price of $ 200 and $ 110 ?
- At the price of $200, the firm produces 800 units when cosumers’s demand is only 500 units
The surplus of fridge: 800 – 500 = 300 (units)
- At the price of $110, the quantity of demand is 950 units and the quantity of supply is 350 units
The surplus of fridge: 950 – 350 = 600 (units)
3. Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, what happened for demand for fridge
if price of electricity increase? Given that quantity demanded for fridge change
300 units at each price level, what are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge?
- Electricity is a complementary good (non-price factor) since we need it to run
fridge. As a result, when the price of electricity increase, the quantity demanded for fridge will be reduced.
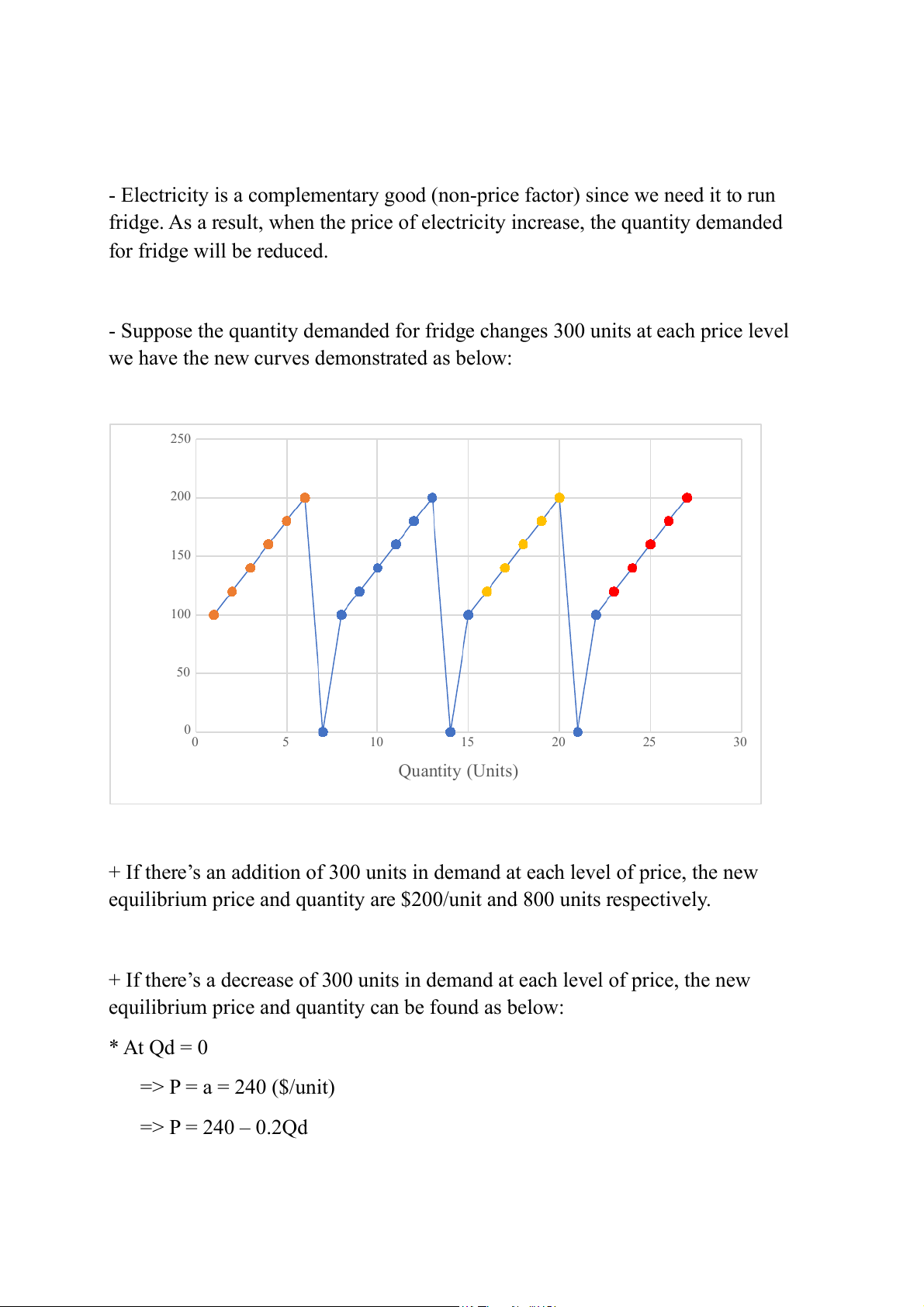
- Suppose the quantity demanded for fridge changes 300 units at each price level
we have the new curves demonstrated as below: 250 200 ) it 150 ($/un 100 rice P 50 00 5 10 15 20 25 30 Quantity (Units)
+ If there’s an addition of 300 units in demand at each level of price, the new
equilibrium price and quantity are $200/unit and 800 units respectively.
+ If there’s a decrease of 300 units in demand at each level of price, the new
equilibrium price and quantity can be found as below: * At Qd = 0 => P = a = 240 ($/unit) => P = 240 – 0.2Qd
P = 40 + 0.2Qs (Supply is constant)
Pe = 240 – 0.2Qd = 40 + 0.2Qs (Qd = Qs = Qe) => 0.4Qe = 200
Qe = 500 (units), Pe = 140 ($/unit)
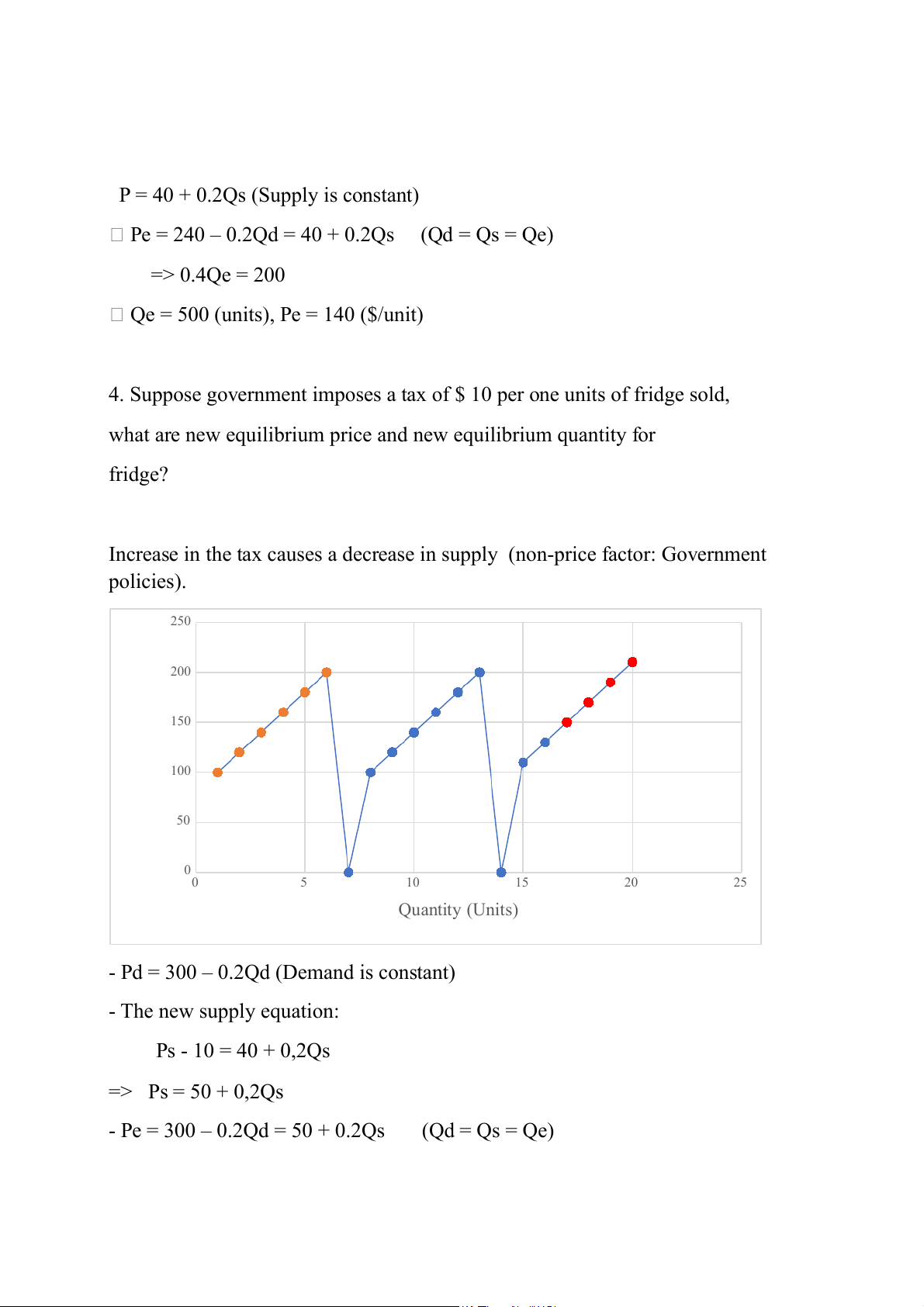
4. Suppose government imposes a tax of $ 10 per one units of fridge sold,
what are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge?
Increase in the tax causes a decrease in supply (non-price factor: Government policies). 250 200 ) it 150 ($/un 100 rice P 50 00 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity (Units)
- Pd = 300 – 0.2Qd (Demand is constant) - The new supply equation: Ps - 10 = 40 + 0,2Qs => Ps = 50 + 0,2Qs
- Pe = 300 – 0.2Qd = 50 + 0.2Qs (Qd = Qs = Qe) => 0.4Qe = 250
Qe = 625 (units) Pe = 175 ($/unit)
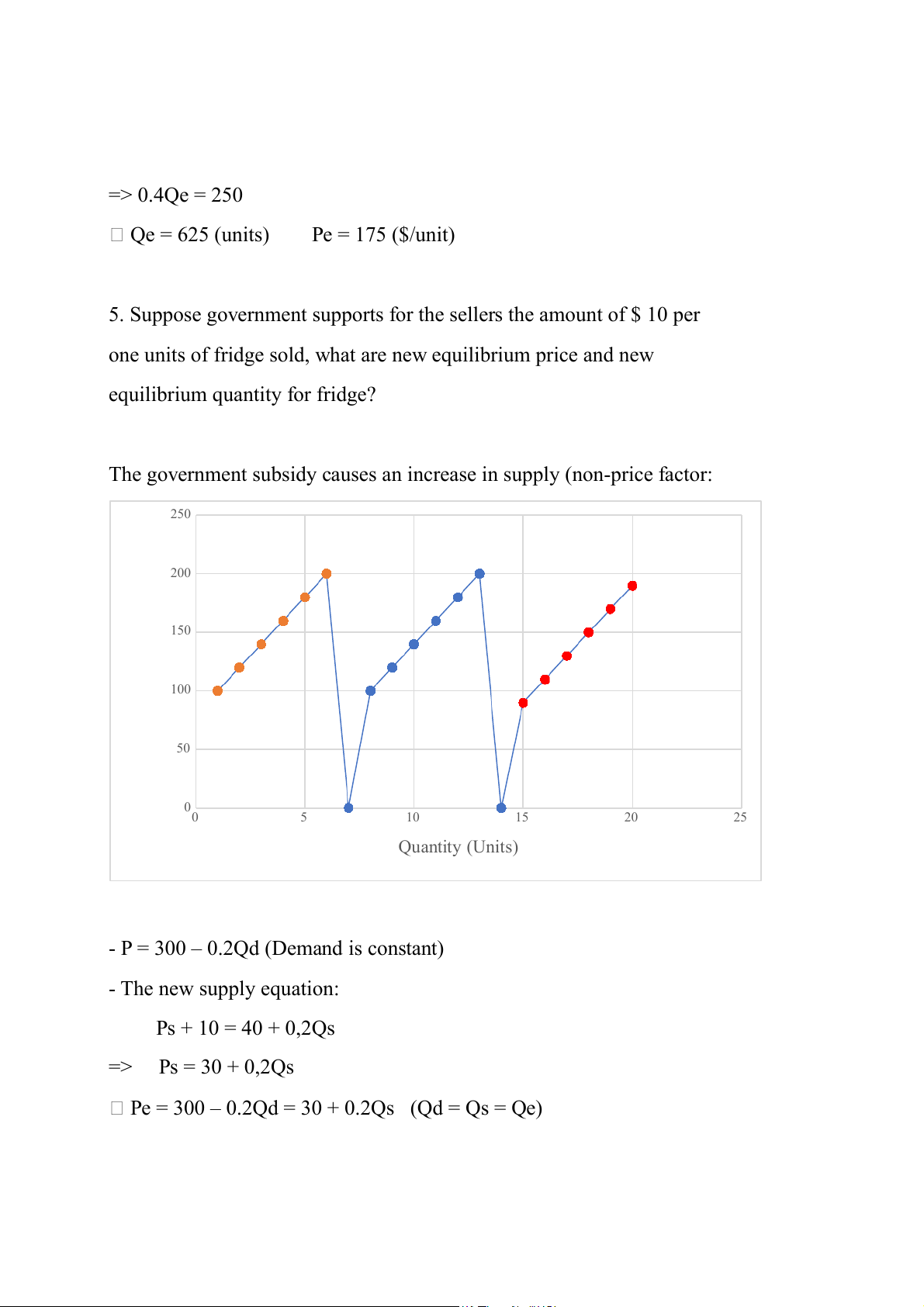
5. Suppose government supports for the sellers the amount of $ 10 per
one units of fridge sold, what are new equilibrium price and new
equilibrium quantity for fridge?
The government subsidy causes an increase in supply (non-price factor: 250 200 ) it 150 ($/un 100 rice P 50 00 5 10 15 20 25 Quantity (Units)
- P = 300 – 0.2Qd (Demand is constant) - The new supply equation: Ps + 10 = 40 + 0,2Qs => Ps = 30 + 0,2Qs
Pe = 300 – 0.2Qd = 30 + 0.2Qs (Qd = Qs = Qe) => 0.4Qe = 270
=> Qe = 675 (units), Pe = 165 ($/unit) Exercise 2:
With the aid of diagrams, show how each of the following events affects the
supply and/or demand curve for motor cycles. In each case, show and state the
effect on the equilibrium price and quantity.
1. An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates
- Their demand of motor cycle will decrease because the customers have less
money than they used to. They must make a choice and only buy things they really need.
- Effect of the increase of Vietnamese income tax rates causes the shift of the
Demand curve to the left. In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be
shifted to the left side of the old equilibrium price and quantity.
2. An increase in the price of steel
- The supply of motor cycle will decrease because the price of input resources
rises. The manufacturers will reduce the amount of motor cycle production to stay their profit.
- Effect of the increase of price of steel cause the shift of the Supply curve to the
left. In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the left side
of the old equilibrium price and quantity.
3. An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same time as
a recession hits the Vietnamese economy
- An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production helps the supply of
motor vehicle production increase so the price will fall. While at the same time, a
recession hits the Vietnamese economy make the demand fall and the price will drop even further.
Effect of this double event cause the shift of the S curve and the shift of the D
curve to the left. In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to
the right side of the old equilibrium price and quantity.
HOWEVER, in other cases there might be different trends, based on the actual
data. This means there is also 2 other case scenarios:
- Lower equilibrium price, higher quantity: When Qs increase more than Qd
- Lower equilibrium price, same quantity: When Qs and Qd increase/decrease at the same rate.




