
Preview text:
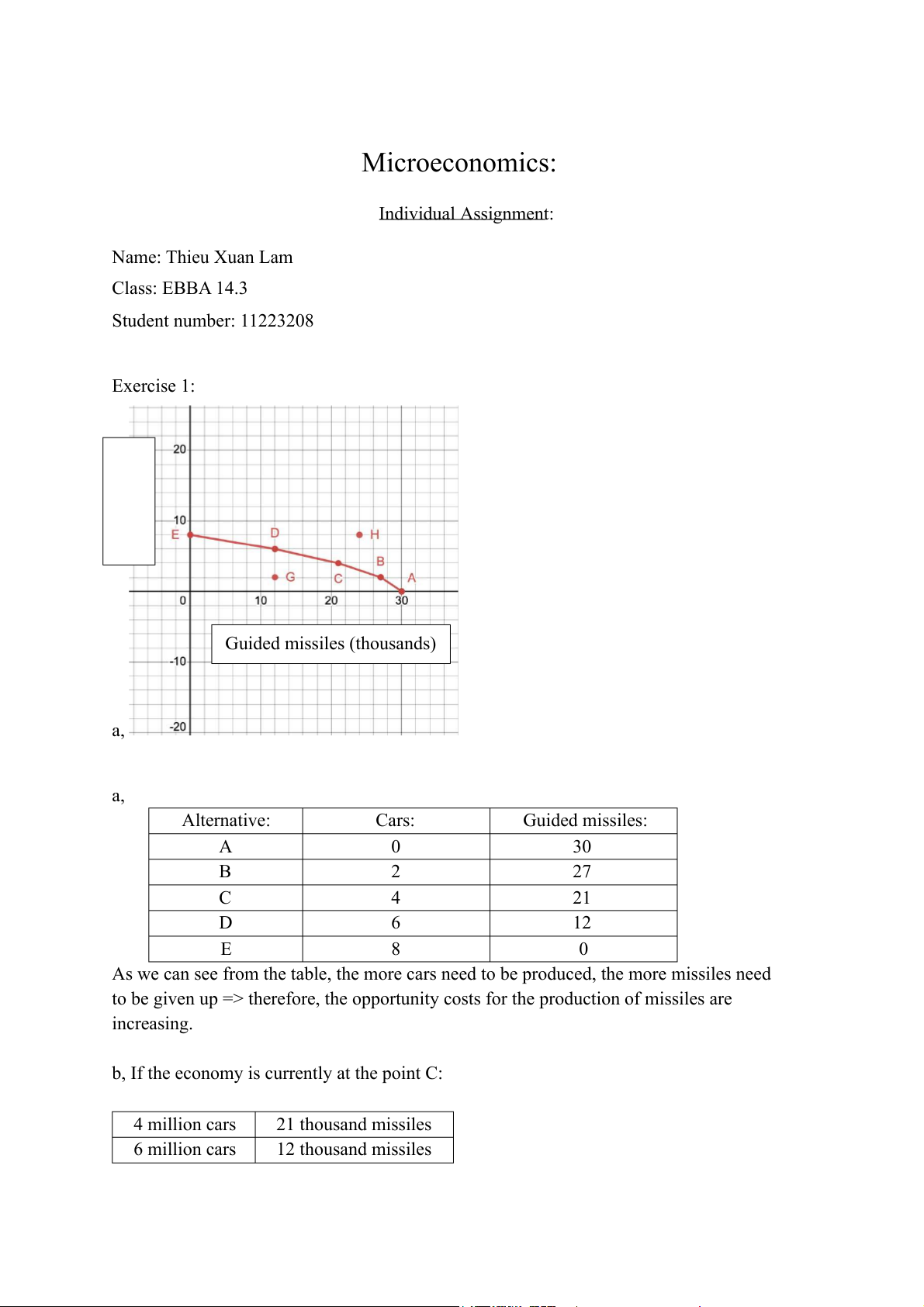
Microeconomics: Individual Assignment: Name: Thieu Xuan Lam Class: EBBA 14.3 Student number: 11223208 Exercise 1: Cars (milions) Guided missiles (thousands) a, a, Alternative: Cars: Guided missiles: A 0 30 B 2 27 C 4 21 D 6 12 E 8 0
As we can see from the table, the more cars need to be produced, the more missiles need
to be given up => therefore, the opportunity costs for the production of missiles are increasing.
b, If the economy is currently at the point C: 4 million cars 21 thousand missiles 6 million cars 12 thousand missiles
The opportunity cost of increasing output from point C to D is 9 thousand g ided missiles u
which means the opportunity cost of producing 2 milion more cars is 9 thousand guided missiles.
ð Therefore, the opportunity cost of producing 1 more milion car is 4.5 thousand guided missiles. 2 million cars 27 thousand missiles 4 million cars 21 thousand missiles
The opportunity cost if increasing output from point C to B is 2 million cars which means
the opportunity cost of producing 6 thousand more missiles is 2 million cars.
ð Therefore, the opportunity cost of producing 1 more thousand missiles is 1/3 million cars.
c, Point G indicates the output of cars and missiles production are 2 million cars and 12
thousand guided missiles respectively, this means the economy at this point is inefficient
because if it produces 2 million cars, the most missiles can be produced is 27 thousand, and
if it produces 12 thousand guided missiles, the most cars can be produced is 6 million.
d, Point H indicates the output of cars and missiles production are 8 million cars and 24
thousand guided missiles respectively, this means the economic outputs which can only
result from growth of the availability of inputs to transform inputs into outputs, therefore
the point H indicates the impossible outcome with the fixed resource. e,
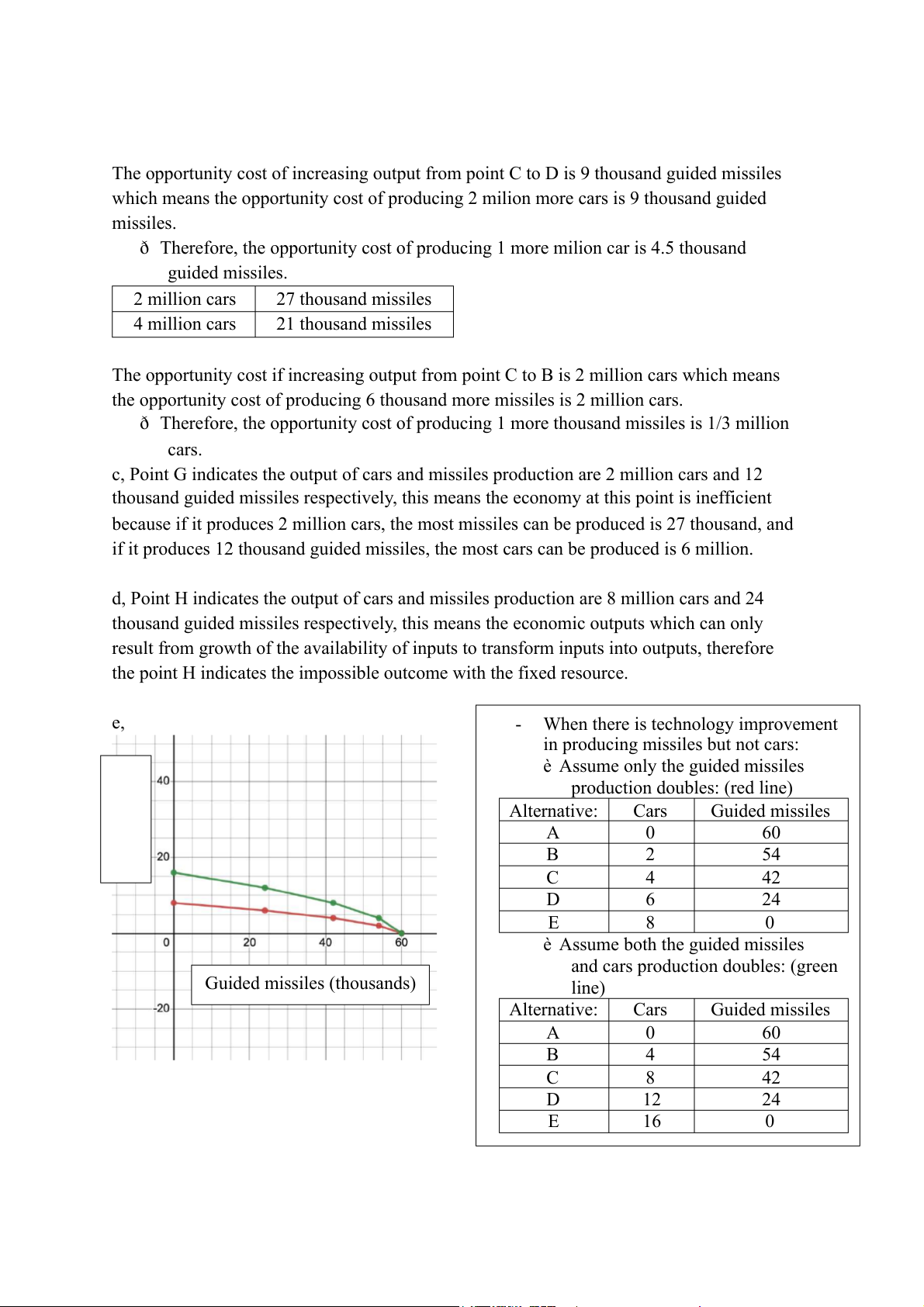
- When there is technology improvement
in producing missiles but not cars:
è Assume only the guided missiles
production doubles: (red line) Alternative: Cars Guided missiles A 0 60 B 2 54 Cars (milions) C 4 42 D 6 24 E 8 0
è Assume both the guided missiles
and cars production doubles: (green Guided missiles (thousands) line) Alternative: Cars Guided missiles A 0 60 B 4 54 C 8 42 D 12 24 E 16 0 Exercise 2: a, cloths (1000 set) wheat (tons) b,
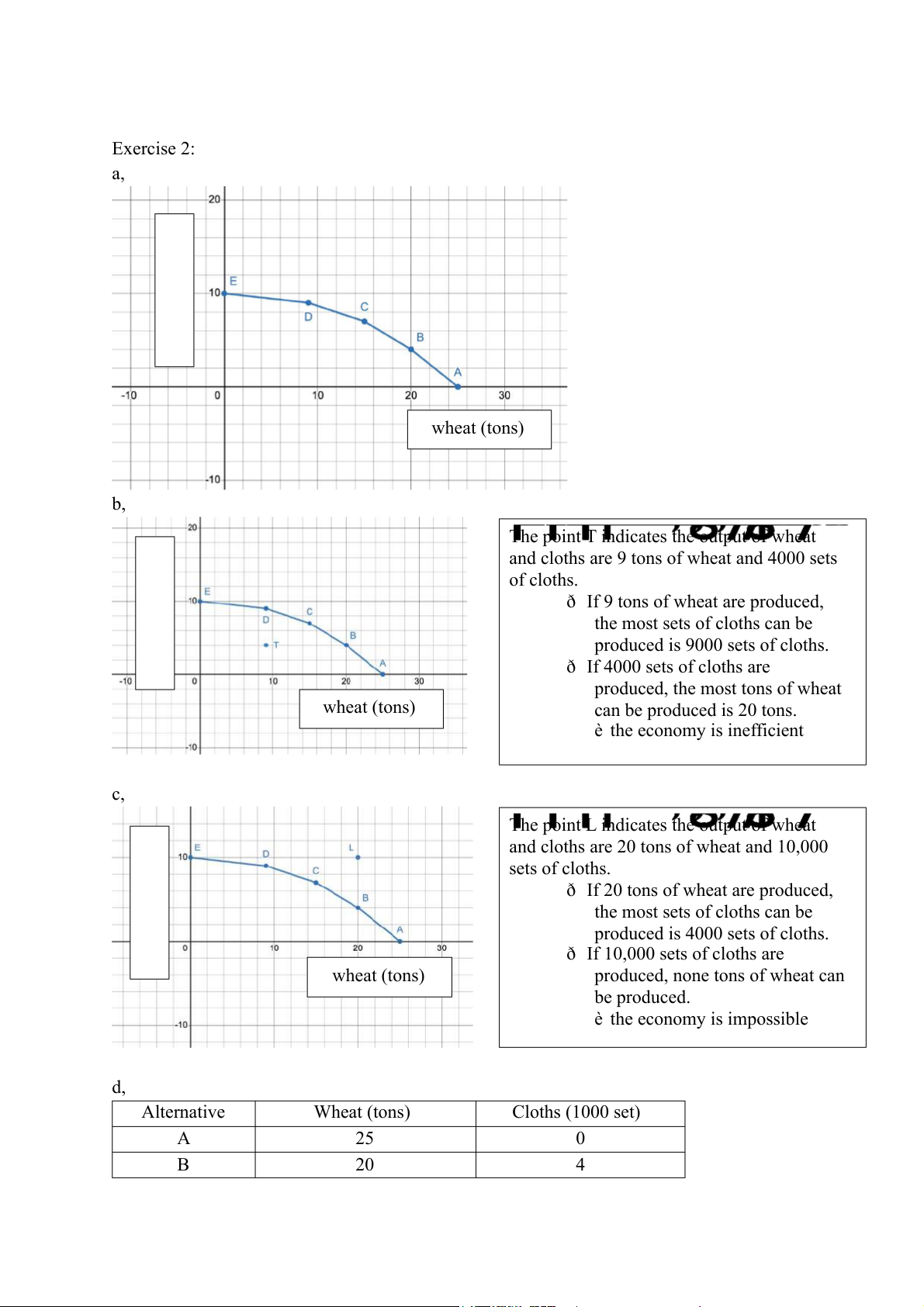
The point T indicates the output of wheat
and cloths are 9 tons of wheat and 4000 sets of cloths.
ð If 9 tons of wheat are produced,
the most sets of cloths can be
produced is 9000 sets of cloths. ð If 4000 sets of cloths are cloths (1000 set)
produced, the most tons of wheat wheat (tons) can be produced is 20 tons. è the economy is inefficient c,
The point L indicates the output of wheat
and cloths are 20 tons of wheat and 10,000 sets of cloths.
ð If 20 tons of wheat are produced,
the most sets of cloths can be
produced is 4000 sets of cloths.
ð If 10,000 sets of cloths are cloths (1000 set) wheat (tons)
produced, none tons of wheat can be produced. è the economy is impossible d, Alternative Wheat (tons) Cloths (1000 set) A 25 0 B 20 4
From point B to A, the opportunity cost of producing 5 more tons of wheat is 4 thousand set of cloths.
=>The opportunity cost of producing 1 more ton of wheat is 4/5= 0.8 thousand set of cloths.
=> From point A to B the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more set of cloths is 5/4= 1.25 tons of wheat. Alternative Wheat (tons) Cloths (1000 set) B 20 4 C 25 7
From point C to B, the opportunity cost of producing 5 more tons of wheat is 3 thousand set of cloths.
=>The opportunity cost of producing 1 more ton of wheat is 3/5 =0.6 thousand set of cloths.
=> From point B to C the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more set of cloths is 5/3 =1.6 tons of wheat.




