


Preview text:
MICROECONOMICS Individual Assignment Name: Nguyen Thi Kieu Trang Class: EBBA 16.2
Exercise 1: Demand and supply of fridge are shown in the table below: Price ($/unit) 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity Demanded (units) 1000 900 800 700 600 500 Quantity Supplied (units) 300 400 500 600 700 800
1. What are the demand and supply equations, equilibrium price and
equilibrium quantity for fridge ?
DEMAND FUNCTION: P = a – bQd
Based on the data table, we have set of equations: 100=a-1000b 120=a-900b a=300, b=0,2 DEMAND EQUATION: P=300-0,2Qd SUPPLY FUNCTION: P=c+dQs
Based on the data table, we have set of equations: 100=c+300d 120=c+400d c=40, d=0,2 SUPPLY EQUATION: P=40+0,2Qs
We have equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity for fridge must be satisfied:
Qd=Qs (300-P)/0,2 = (P-40)/0,2 => P=170 Qd=Qs=650 Equilibrium price = 170$
Equilibrium quantity = 650 units
2. What are the surplus and shortage of fridge at the price of $200 and $110 ? At $200: Quantity Demanded: 500 Quantity Supplied: 800 Surplus = 800 - 500 = 300 At $110: Quantity Demanded: 950 Quantity Supplied: 350 Shortage = 950 – 350 = 600
3. Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, what happened for demand for fridge
if price of electricity increase? Given that quantity demanded for fridge change
300 units at each price level, what are new equilibrium price and new
equilibrium quantity for fridge?
Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, if price of electricity increase, demand for
fridge will drecrease. The price of electricity is considered as non-price factor,
cause we need electricity to run fridge.
Suppose quantity demanded for fridge change 300 units at each price level:
+ If there’s an addition of 300 units in demand at each level of price, we have the new data table: Price ($/unit) 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity Demanded (units) 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 Quantity Supplied (units) 300 400 500 600 700 800
New Demand equation: P=360–0,2Qd
Supply equation (constant): P=40+0,2Qs
=> The new equilibrium and quantity are $200/unit and 800 units respectively.
+ If there’s a decrease of 300 units in demand at each level of price, we have the new data table: Price ($/unit) 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity Demanded (units) 700 600 500 400 300 200 Quantity Supplied (units) 300 400 500 600 700 800
New Demand equation: P=240–0,2Qd
Supply equation (constant): P=40+0,2Qs
=> The new equilibrium and quantity are $140/unit and 500 units respectively.
4. Suppose government imposes a tax of $ 10 per one units of fridge sold, what
are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge?
Supply equation: P= 40 +0,2.Qs => Qs= 5P - 200 (*)
When the government imposes a tax of 10 per one unit of fridge sold: (*)=> Qs’= 5.(P-10) -200
Demand equation: P= 300 - 0,2.Qd => Qd= 1500 - 5P
At the point of equilibrium price: Qs=Qd ⇔ 5.(P-10) - 200 = 1500 -5P => P= 175$, Q=625 units
5. Suppose government supports for the sellers the amount of $ 10 per one units
of fridge sold, what are new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity for fridge?
Supply equation: P= 40 +0,2.Qs => Qs= 5P - 200 (*)
When the government imposes a tax of 10 per one unit of fridge sold: (*)=> Qs’= 5.(P+10) -200
Demand equation: P= 300 - 0,2.Qd => Qd= 1500 - 5P
At the point of equilibrium price: Qs=Qd ⇔ 5.(P+10) - 200 = 1500 -5P => P= 165$, Q=675 units
Exercise 2: With the aid of diagrams, show how each of the following events
affects the supply and/or demand curve for motorcycles. In each case, show and
state the effect on the equilibrium price and quantity.
1. An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates
Their demand of motorcycles will decrease because the customers have less money than they used to.
=> Effect of the increase of Vietnamese income tax rates cause the shift of the D curve to the left.
=> In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the left
hand side of the old equilibrium price and quantity 2. An increase in the price of steel - The supply of motor cycle will decrease 3. because the price of input resources rises. The manufacturers will reduce the 4. amount of motor cycle producers to stay their profit. 5. An increase in the price of steel - The supply of motor cycle will decrease 6. because the price of input resources rises. The manufacturers will reduce the 7. amount of motor cycle producers to stay their profit.
2. An increase in the price of steel
The supply of motor cycle will decrease because the price of input resources rises.
The manufacturers will reduce the amount of motor cycle producers to stay their profit.
Effect of the increase of price of steel cause the shift of the S curve to the left.
In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity will be shifted to the left hand
side of the old equilibrium price and quantity.
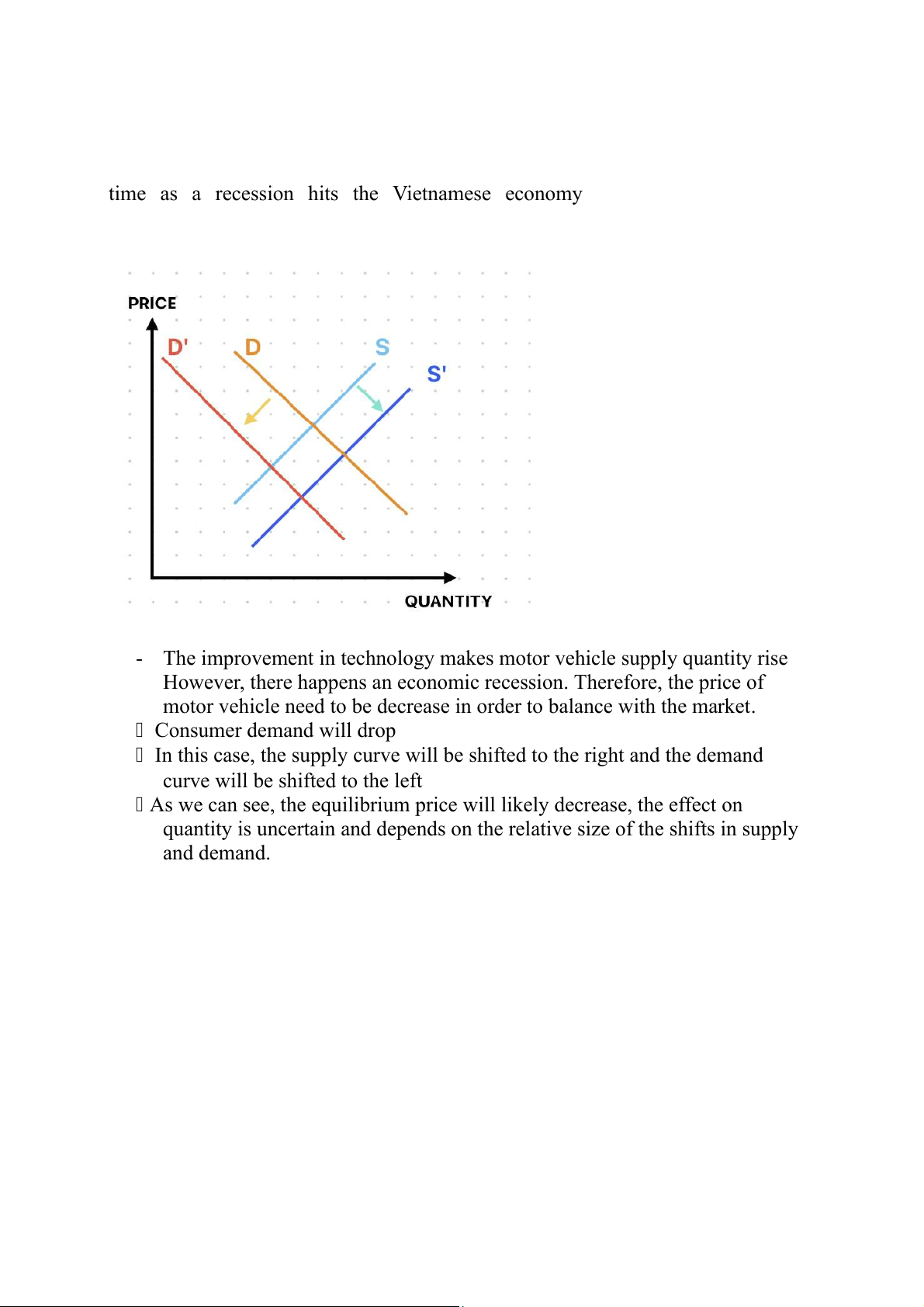
3. An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same
time as a recession hits the Vietnamese economy
- The improvement in technology makes motor vehicle supply quantity rise
However, there happens an economic recession. Therefore, the price of
motor vehicle need to be decrease in order to balance with the market. Consumer demand will drop
In this case, the supply curve will be shifted to the right and the demand
curve will be shifted to the left
As we can see, the equilibrium price will likely decrease, the effect on
quantity is uncertain and depends on the relative size of the shifts in supply and demand.




