

Preview text:
INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT
NAME: LE THI NGOC MAI STUDENT CODE: 11224036 CLASS: E-BBA 14.1
Group assignment presentation 9 Problem 1:
A monopoly has a demand function of P=15-Q ($) and total cost function of TC= 7Q ($)
a. What is price and optimal quantity that gives the firm maximum profit? Using
Lerner indicator (L) to identify market power of this firm? P=15-Q => MR= 15-2Q TC=7Q => MC=(TC)’ = 7 To maximum profit: MR=MC 15-2Q=7 Q= 4 => P= 15-4=$11 P −MC 11 7 − 4 L= = = P 11 11
b. What is price and optimal quantity for society (for perfect competitive market)?
Identify dead-weight loss (DL) created by this firm?
For perfect competitive market: P= MR= 15-Q MC = (TC)’ = 7
For a perfectly competitive market, we get optimal price and quantity when: MR=MC Q=8 => P=$7 (8−4 )(11−7) DL=S =8 ABC= 2
Problem 2: A monopolist has demand function of P= 100-Q and cost functions of AVC= Q+4; FC=200
a. What is optimal output level that maximizes profit? What is that maximum profit? P= 100-Q => MR=100-2Q AVC= Q+4 => VC= Q2+4Q
TC= VC+ FC = Q2+4Q+200 => MC= (TC)’ = 2Q+4 To maximize profit: MR=MC 100-2Q= 2Q+4 Q= 24
P= 100-24= $76, AVC= 24+4 =$28 Therefore, πmax = TR-TC= $952
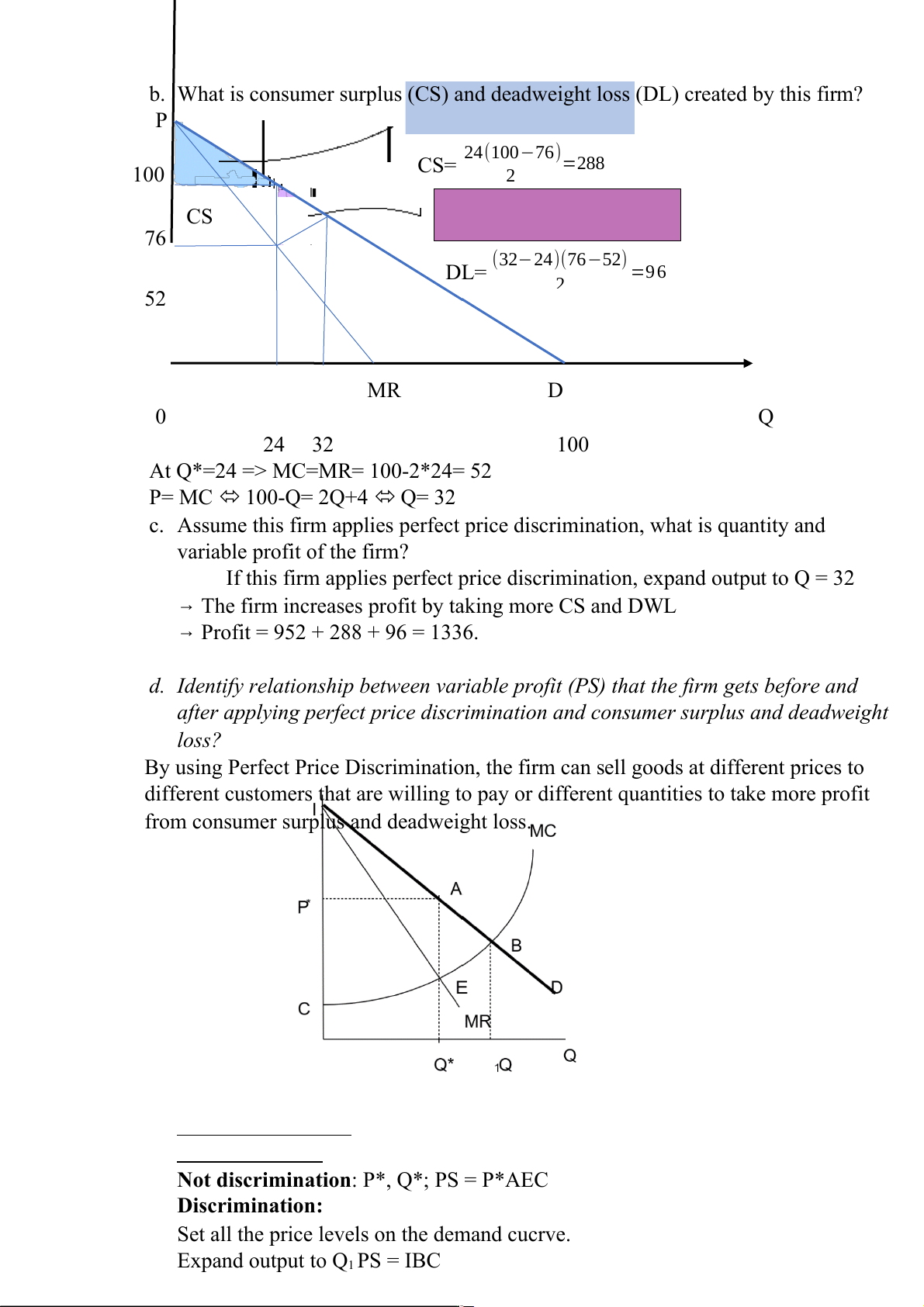
b. What is consumer surplus (CS) and deadweight loss (DL) created by this firm? P 24 100 76 ( − )=288 100 CS= 2 CS 76 (32−24)(76−52) DL= =9 6 2 52 MR D 0 Q 24 32 100
At Q*=24 => MC=MR= 100-2*24= 52 P= MC 100-Q= 2Q+4 Q= 32
c. Assume this firm applies perfect price discrimination, what is quantity and variable profit of the firm?
If this firm applies perfect price discrimination, expand output to Q = 32
→ The firm increases profit by taking more CS and DWL
→ Profit = 952 + 288 + 96 = 1336.
d. Identify relationship between variable profit (PS) that the firm gets before and
after applying perfect price discrimination and consumer surplus and deadweight loss?
By using Perfect Price Discrimination, the firm can sell goods at different prices to
different customers that are willing to pay or different quantities to take more profit
from consumer surplus and deadweight loss.
Not discrimination: P*, Q*; PS = P*AEC Discrimination:
Set all the price levels on the demand cucrve. Expand output to Q1 PS = IBC
So, by perfect price Discrimination, a firm increases profit by taking more CS and DWL




