


Preview text:
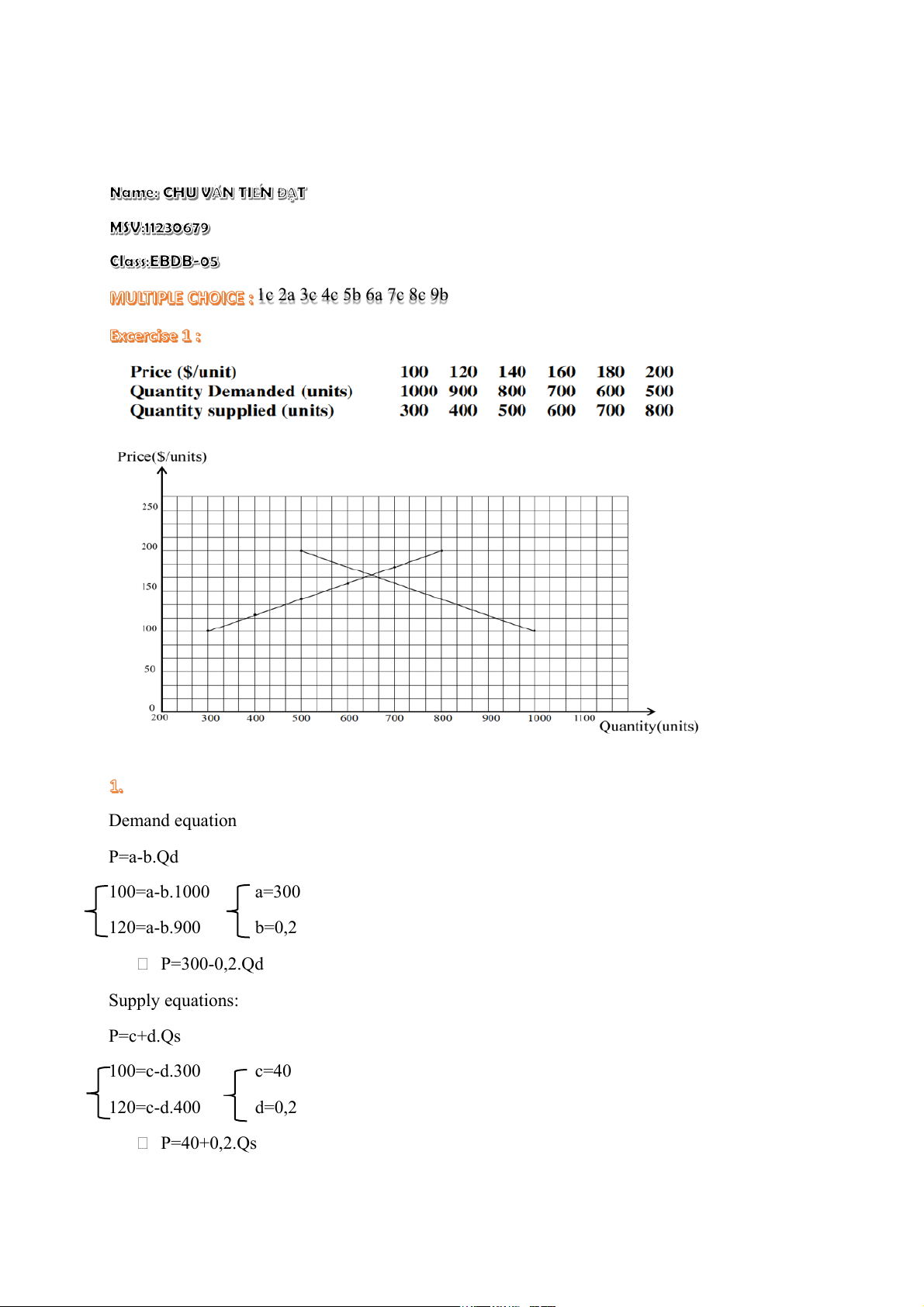
1c 2a 3c 4c 5b 6a 7c 8c 9b Demand equation P=a-b.Qd 100=a-b.1000 a=300 120=a-b.900 b=0,2 P=300-0,2.Qd Supply equations: P=c+d.Qs 100=c-d.300 c=40 120=c-d.400 d=0,2 P=40+0,2.Qs
Equilibrium price and Equilibrium quantity for fridge: Pe=300-0,2.Qd=40 +0,2.Qs Qd=Qs=Qe 300-0,2.Qe =40+0,2.Qs Qe=650 ($/units) Pe=300-0,2.650=170
+ At price of $200: The quantity demanded for fridge is 500 units and the quantity supplied is
800 units. It means there are 300 fridges in surplus.
+ At price of $100: The quantity demanded for fridge is 1000 units and the quantity supplied is
300 units. It means there are 700 fridges in shortage.
If electricity prices increase, demand will definitely decrease. Because electricity is the factor
directly related to the product. Moreover, people who are hesitant to buy the product will not
buy it anymore. This is non-price factor.
If the quantity demanded for fridge increase 300 units at each price level: Demand equations: P=a-b.Qd 100=a-b.1300 a=360 120=a-b.1200 b=0,2 P=360-0,2.Qd Supply equation: P=c+d.Qs 100=c+d.300 c=40 120=c+d.400 d=0,2 P=40+0,2.Qs
Equilibrium price and Equilibrium quantity Pe=360-0,2.Qd=40+0,2.Qs Qd =Qs=Qe Qe=800 (units) Pe=360-0,2.800=200($/units) Demand equation: P=a-b.Qd 110=a-b.1000 a=310 130=a-b.900 b=0,2 P=310-0,2.Qd Supply equations: P=c+d.Qs 110=c+d.300 c=50 130=c+d.400 d=0,2 P=50+0,2.Qs
Equilibrium price and Equilibrium quantity Pe=50+0,2.Qd=310-0,2.Qs Qd=Qs=Qe Qe=650 (units) Pe=180 ($/units) Demand equation: P=a-b.Qd 90=a-b.1000 a=290 110=a-b.900 b=0,2 P=290-0,2.Qd Supply equations: P=c+d.Qs 90=c+d.300 c=30 110=c+d.400 d=0,2 P=30+0,2.Qs
Equilibrium price and Equilibrium quantity Pe=30+0,2.Qs=290-0,2.Qd Qd=Qs=Qe Qe=650 Pe=160
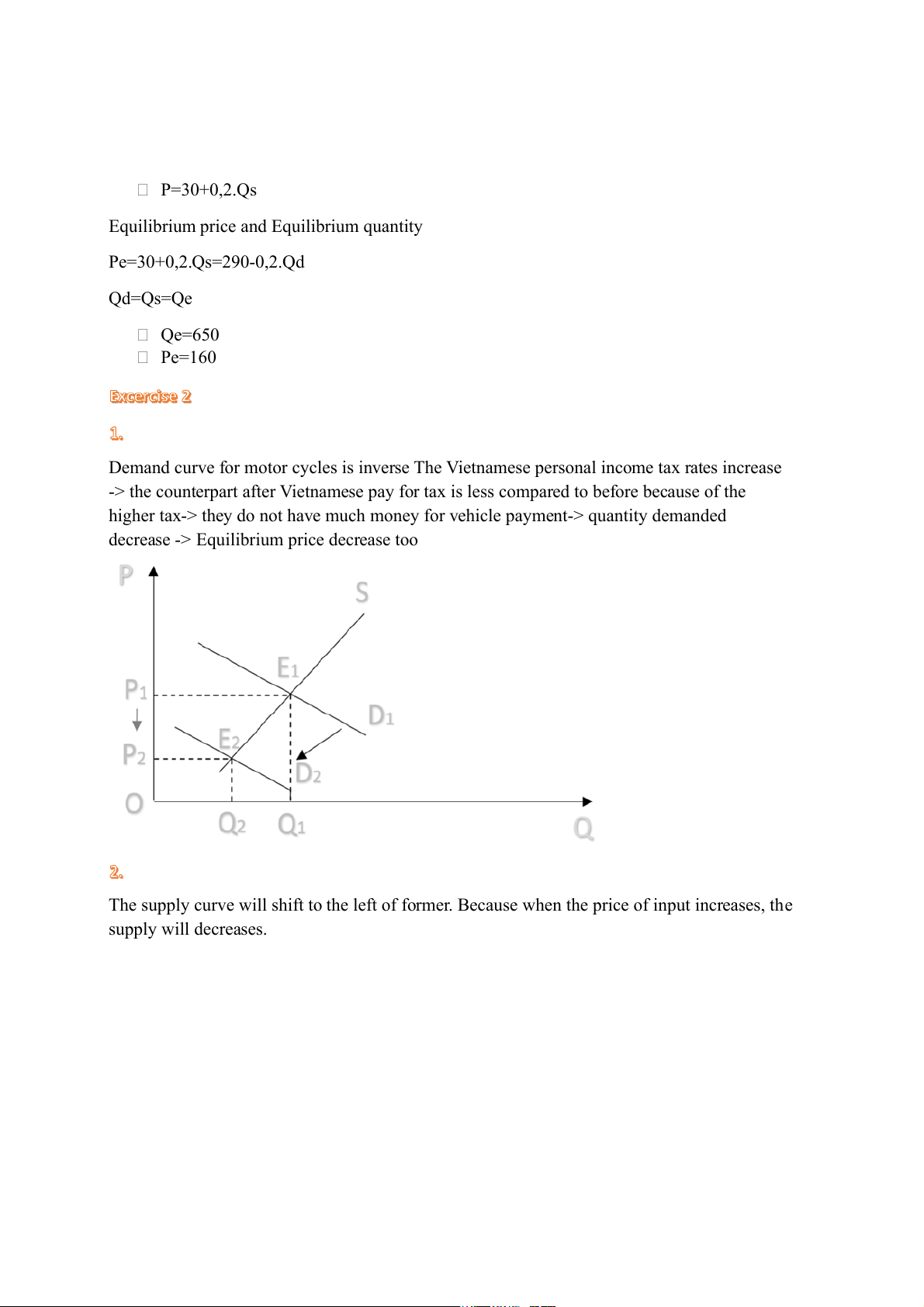
Demand curve for motor cycles is inverse The Vietnamese personal income tax rates increase
-> the counterpart after Vietnamese pay for tax is less compared to before because of the
higher tax-> they do not have much money for vehicle payment-> quantity demanded
decrease -> Equilibrium price decrease too
The supply curve will shift to the left of former. Because when the price of input increases, the supply will decreases.
Improvements in technology will boost supply quantity.
-However the price needs to be maintained or reduced, otherwise the quantity supplied will decrease.
-The supply curve will be shifted to the right and the demand curve will be shift to the left.
-Both the new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity move down to the lower left of the formal one.




