









































Preview text:
Analytical Chemistry 1 Lecture5 Acid-Base,+pH+and+Buffer Instructor:-Nguyen-ThaoTrang Semester-I 2019-2020 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Acid:
– Acid*is*a*substance*that*can*release*proton*or*hydrogen*ion*when* dissolved* in*water. HCl H+ +*Cl-
– Must*have*H*in*formula.* The*general*formula* is*HnX.
– Monoprotic:-one-acidic-proton- • HNO3 Nitric*acid • HClHydrochloric*acid • HBr Hydrobromicacid • CH3COOH*Acetic*acid 2 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Acid:
– Diprotic:-two-acidic-protons • H2SO4 Sulfuric*acid • H2SO3 Sulfurous*acid
– Triprotic:-three-acidic-protons
• H3PO4 Orthophosphoricacid*(Phosphoric*acid) Base:
– Any*substance*that*dissociates* in*H2O*to*give*OH- ions. NaOH Na+ +*OH-
– The*general*formula*is*M(OH)n:*NaOH,*KOH,*Ca(OH)2,*Mg(OH 2 ) ,* Al(OH)3 3 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Strength*of*Acid/Base:
– Acids*and*bases*are*commonly*classified*as*strong*or*weak,*depending*
on*whether*they*react*nearly*“completely”*or*only*“partially”*to* produce*H+ or*OH-. – Example:*
• In*a*6*M*solution*of*HCl,*99.996%*HClmolecules*reacts*with*water*to*form
H+*and*Cl- à HClis*a*strong-acid.
• Acetic*acid*is*a*weak*acid*as*1%*CH3COOH*reacts*with*water*to*form*H and*CH -
3COO à CH3COOH*is* a*weak-acid.
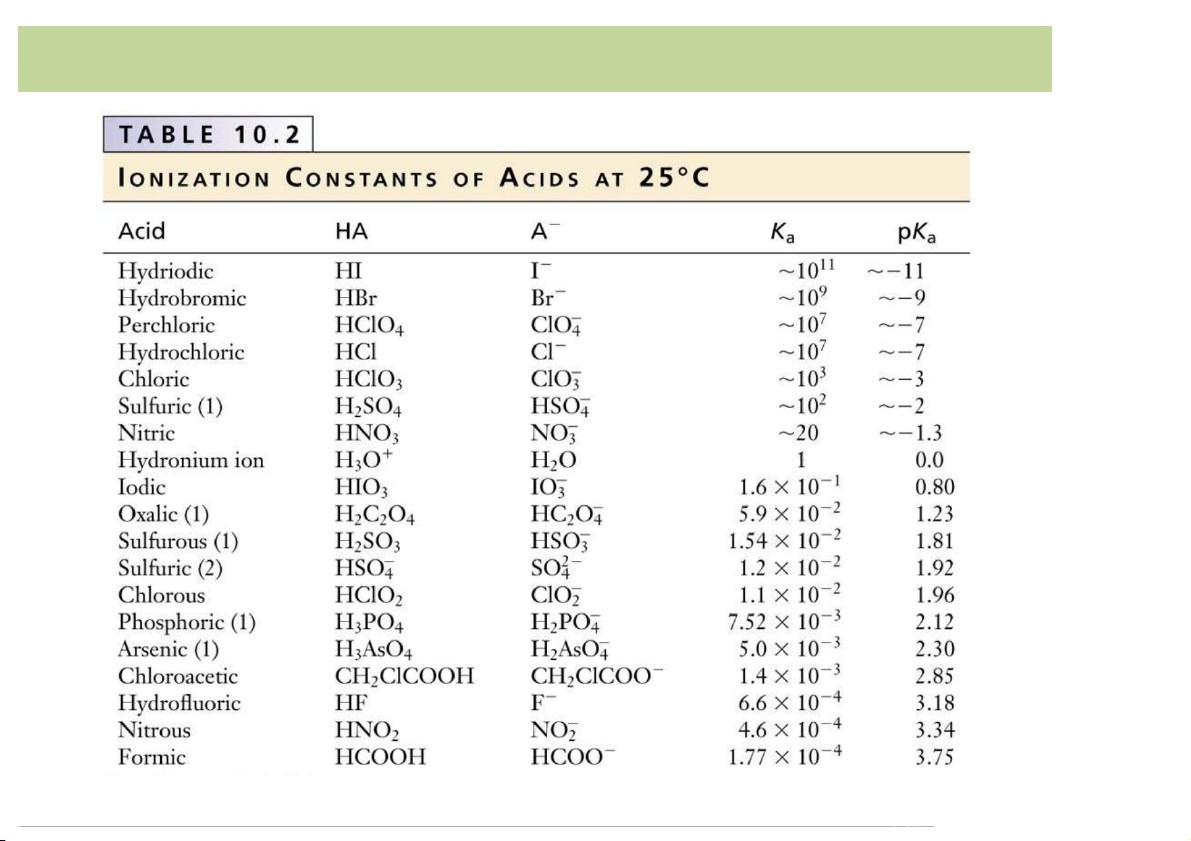
– Equilibrium*constant*or*dissociation*constant*Ka (acid)*or*Kb (base)*
reveals*if*an*acid/base*is*strong*or*weak. 4 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Strength*of*Acid/Base: – Example: CH +
3COOH*(aq)*****=****CH3COO- (a ) q **+****H (a ) q [CH K 3COO-]**[H+] a = [CH3COOH]* =**1.76*x*10-5
pKa (*=*negative*of*log10*Ka)*can*also*be*used:*
pKa =**- log10(1.76*x*10-5)**=**4.75 5 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Strength*of*Acid/Base: – Example: NH +* - 4OH*(aq)*****=****NH4 (a ) q **+****OH (aq) [NH +]**[OH-] K 4 b = [NH4OH]* =**1.76*x*10-5
pKb (*=*negative*of*log10*Kb)*can*also*be*used:*
pKb =**- log10(1.76*x*10-5)**=**4.75 6 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Strength*of*Acid/Base: stronger
– The*strongerthe*acid,*the*larger-the-Ka (the*smaller*the*pKa): HNO -
2 (aq)*****=***NO2 (aq)**+****H+ (aq)******************** Ka =*4 pKa =*3.34 CH +
3COOH*(aq)*****=****CH3COO- (a )
q **+****H (aq)* ***********Ka =*1. pKa =*4.75
HCN*(aq)*****=***CN- (aq)**+****H+ (aq)*************************** pKa =*9.21 weaker 7 Acid-Base*Definition 8 Acid-Base*Definition 9 Acid-Base*Definition
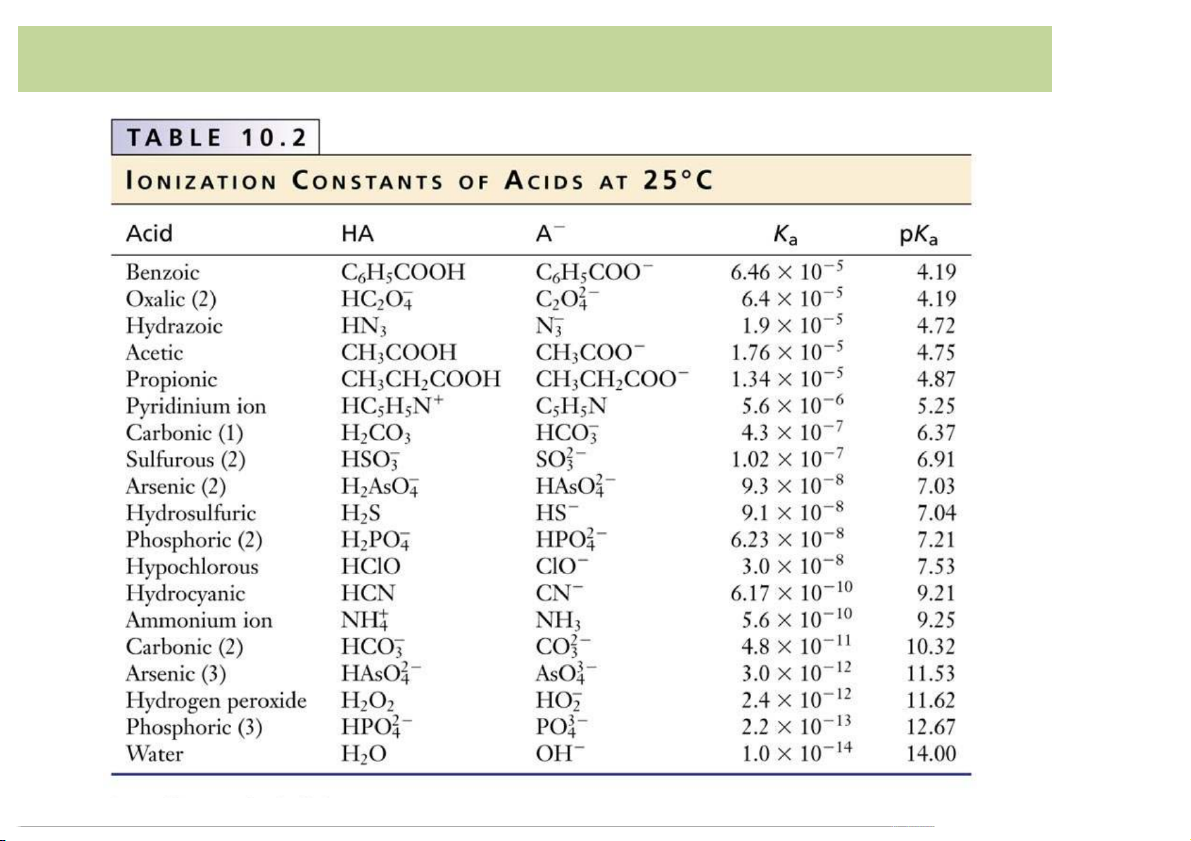
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Strength*of*Acid/Base:
– The*strongerthe*base,*the*larger-the-Kb (the*smaller*the*pKb): stronger PO 3- 2-
4 (aq)**+**H2O*(l)***=***HPO4 (aq)**+****OH- (aq)********Kb =*4.5*x pKb =**1.34 NH +
4OH*(aq)*****=***NH4 (aq)**+****OH- (aq)********************Kb = pKb =**4.74 weaker 10 Acid-Base*Definition
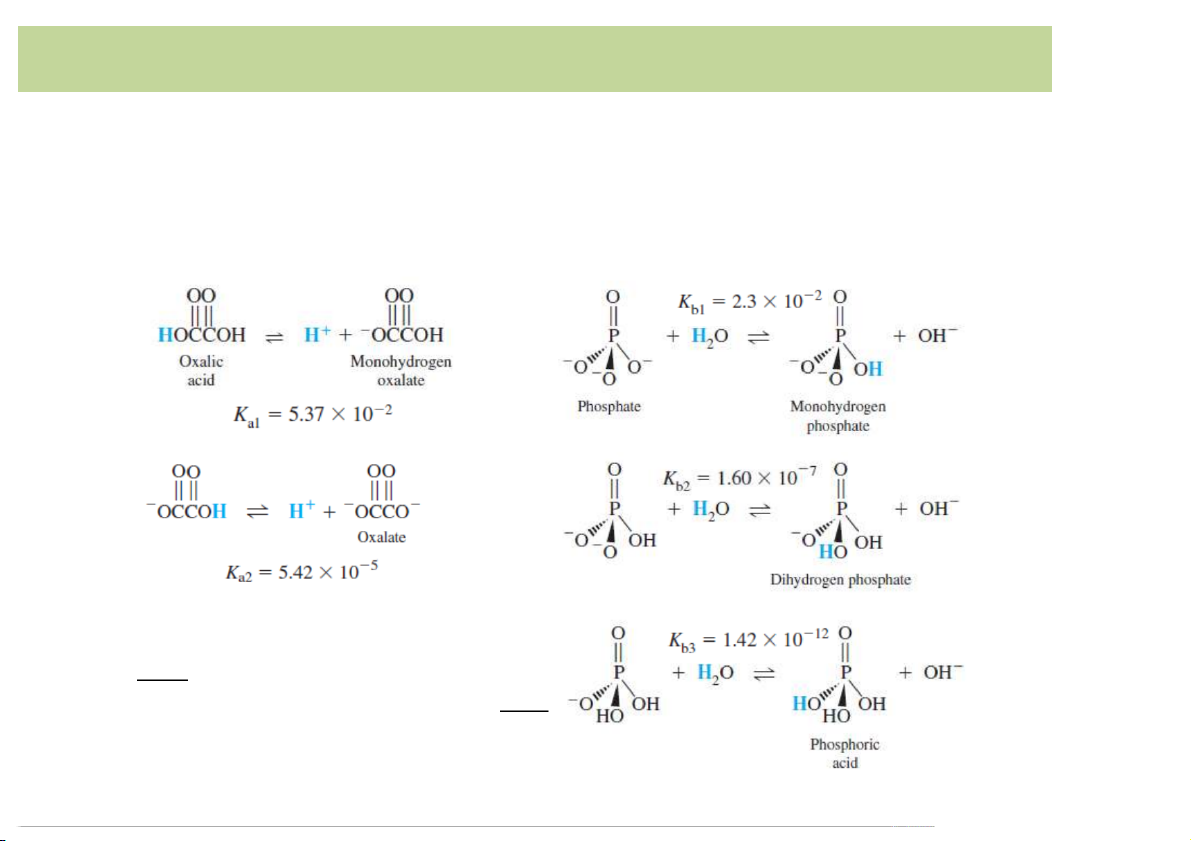
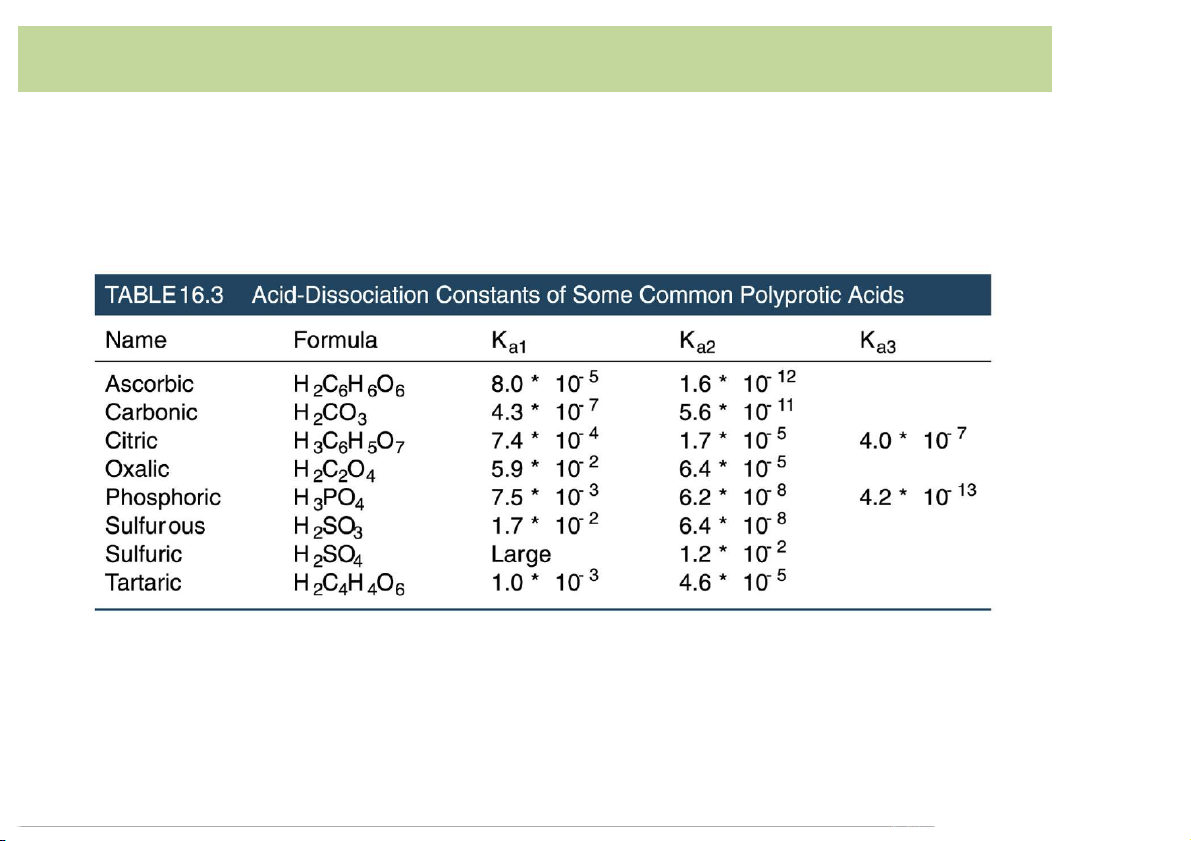
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884):
Strength*of*PolyproticAcid/Base:
– Example:*oxalic*acid*is*diprotic*and*phosphate*is*tribasic:
Ka1(or*K1)*refers-to-the-acidic-species-with- the-mostprotons.
Kb1*refers-to-the-basic-species-with-the-least number-of-protons. 11 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884):
Strength*of*PolyproticAcid/Base: 12 Acid-Base*Definition
• Definition*of*Arrehnius(Sweden,*1884): Limitations:
– Many*substances*dissolve*in*water*to*give*acidic*or*basic*solutions*but*
do*not*have*the*classical*acid*or*base*formulas.
– Example:*A*solution*of*K2O*in*H2O*is*identical*with*a*solution*of*KOH
H2O.*However*,*according*to*the*Arrhenius* system*K2O*cannot*be*
classified*as*a*base*in*that*it*does*not*have*OH-’s*in*its*formula. 13 Acid-Base*definition
• Definition*of*Lowry*(England)*or*Bronstedworking*
independently*in*1923*(Bronsted-Lowry*definition):
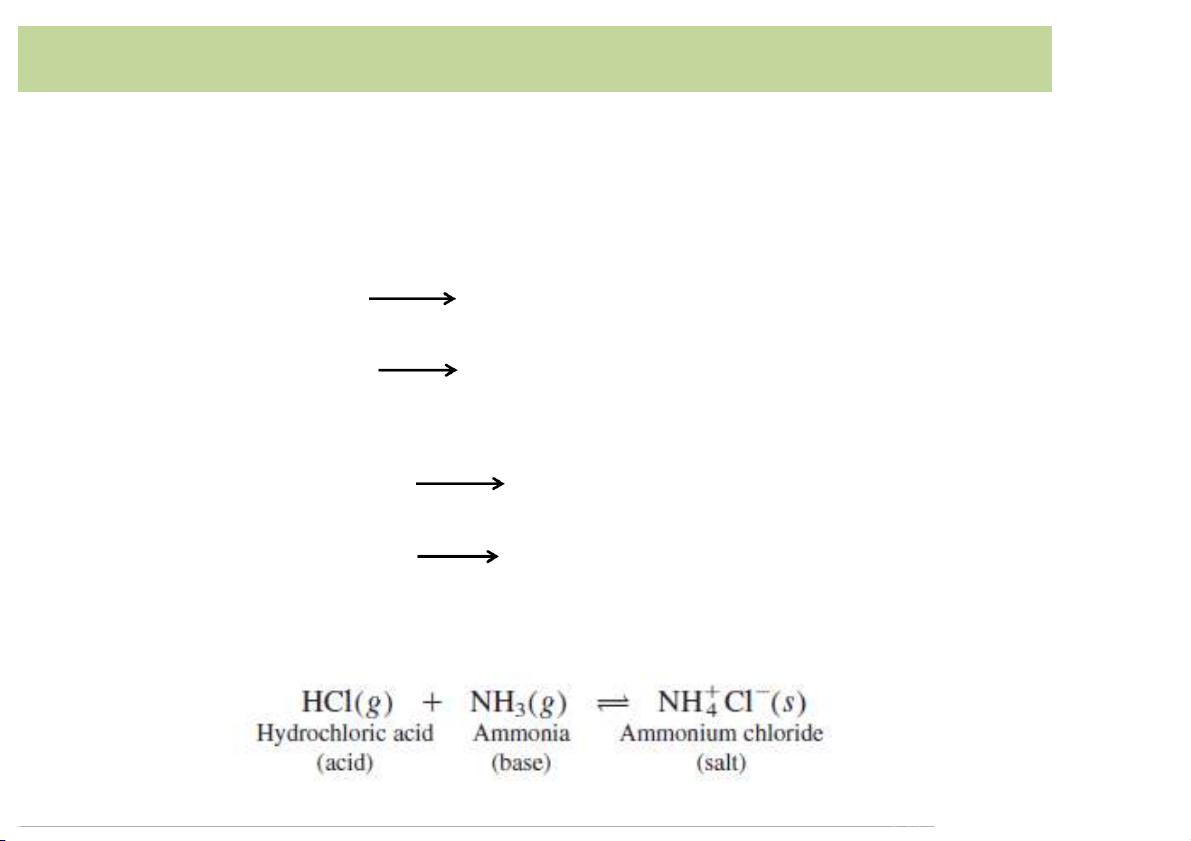
– Acid*is*a*material*that*donates*a*proton. HCl H+ +*Cl- NH + 4 NH3 +*H+
– Base*is*a*substance*that*accepts*a*proton. OH- +*H+ H2O** NH + 3 +*H+ NH4
– The*Bronsted–Lowry*definition*can*be*extended*to*gas*or*nonaqueous solvent: 14 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Acid:*must*have*a*H*in*its*formula.
– Base:*must*have*a*lone*pair*of*electrons*to*form*a*covalent*bond*with* H+ NH + 4 NH3 +*H+ (Acid) (Conjugate-base)
– The*product*formed*when*an*acid*gives*up*a*proton*is*a*potential*
proton*acceptor*and*is*called*the*conjugate-base-of*the*parent*acid. NH + 3 +*H+ NH4 (Base) (Conjugate-acid)
– The*product*formed*when*a*base**accepts*a*proton*is*a*potential*
proton*donator*and*is*called*the*conjugate-acid-of*the*parent*base. – NH + 4 /N 3
H :*a-conjugate-acid/base-pair. 15 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition: – General:
– Combination*of*2*reactions:*neutralization-reaction
• Direction-of-the-reaction-depends-on-which-acid-donates-proton-stronger-
or-which-base-accepts-proton-stronger. – Example: 16 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Proton*H+*does*not*exist*by*itself*in*water.**It*exists*in*the*form*of*H3
(a*proton*covalently*binds*to*a*water*molecule). – H +
5O2 cationis*another* simple*species.
– Hydroxyl*ion*OH- also*exists*in*the*form*of*H - 3O2 (OH-.H2O) 17 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Species*possess* both*acidic*and*basic*properties:*amphiprotic. – Example: • H - 2PO4 acts*as*a*base: • H - 2PO4 acts*as*an*acid:
– Amino*acids*are*amphiproticcompounds:*rearrange*to*form*
zwitterionicspecies*that*bears*both*a*positive*and*a*negative*charge.
– H2O,*methanol,*ethanol*are*common*amphiproticsolvent. 18 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Autoprotolysis:* self-ionization*(autoionization)*to*form*a*pair*of*ionic* species
– The*extent*of*these*reactions*is*very*small.*The*autoprotolysisconstant-
(equilibrium*constants)*for*H3O+/OH- pair*is*1×10-14*M*at*25oC. 19 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Autoprotolysisconstant*for*H2O*has*the*special*symbol*Kw
– Kw =*1.01*×10-14*or*pKw =*14 – Kw depends*on*temperature 20 pH
• An*approximate*definition*of*pH+is*the*negative*logarithm*of* the*H*concentration.
• Relationship*between*pH*and*Kw 21 Acidity/basicity*of*a*solution
• Solution*is*acidic+if*[H+]*>*[OH-].
• Solution*is*basic+if*[H+]*<*[OH-].
• At*25oC,*an*acidic*solution*has*a*pH*below*7*and*a*basic* solution*has*a*pH*above*7.
• pH*generally*falls*in*the*range*0*to*14,*these*are*not*the*limi of*pH. 22 Acidity/basicity*of*a*solution • What*is*pH*of*pure*water?
– If*x*=*the*molarity*of*[H+]*,*** H + 2O** =**H +*OH- Kw =*[H+]*[OH-]***=****10-14 x********x x2 =*********10-14
Therefore,*****x*=*[H+]**=**[OH-]**=**10-7M in*pure*water*at*25°C. 23 Acidity/basicity*of*a*solution
• The*degree*of*acidity*or*basicity*of*a*solution*is*measured*on the*pH*scale [H+] pH***********pOH 1*M
0*************14 low*pH**or*high*pOH*is*strongly*acid 10-2M 2 12 10-4M 4 10 10-6M 6 8 pH**7*is*a*neutral*solution 10-8M 8 6 10-10M 10 4 10-12M 12 2 10-14M 14 0
high*pH**or*low*pOHis*strongly*base 24 Acidity/basicity*of*a*solution 25 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Relative*strength*of*acids/bases:* Strong-acids-will-yield-weak-conjugate-
bases-and-weak-acids-will-give-strong-conjugate-bases.- 26 Acid-Base*definition • Bronsted-Lowry*definition:
– Relationship*between* Ka and*Kb*for*a*conjugate*acid/base*pair:
– For*a*diprotic*acid*or*triproticacid: 27 Acid-Base*definition • Definition*of*J.N.*Lewis:
– Acid*is*a*substance*that*accepts*an*electron*pair*in*forming*a* coordinate*covalent*bond.
– A*Lewis*acid*must*have*a*fairly*low*energy*vacant,*or*easily*vacated* orbital. – Example:
• BF3 (vacant*2p*orbital*on*B)
• Ni2+(vacant*3d,*4s,*and*4p*orbitals)
• SO3 (the*S—O*π*bond*is*easily*broken)
– Acid*are*electrophiles*because*they*react*readily*with*electron*pair* donors. 28 Acid-Base*definition • Definition*of*J.N.*Lewis:
– Base*is*a*substance*that*donates*an*electron*pair*in*forming*a* coordinate*covalent*bond.
– A*Lewis*base*must*have*a*lone*pair*of*electrons*à the*same*as*a* Bronsted-Lowry*base. – Example: H .. .. .. .. 2- : N-H : O-H :S+: :O-H- .. : I..+++: .. H H hydroxide++++ iodide+++ ammonia+++++++++ water++++++++++++++s – The*base*is*a*nucleophile. 29 Acid-Base*definition • Definition*of*J.N.*Lewis:
– The*Lewis+definition generalizes*the*acid/base*concept:
• Every*Arrhenius* acid/base*is*also*a*Lewis*acid/base.
• Every*Bronstedacid/base*is*also*a*Lewis*acid/base. Least general definition Most general definition Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis
– Example:**A*strong*acid*reacts*with*a*strong*base H+(aq) + :OH-(aq) = H2O(l) Electron pair acceptor electron pair donor 30