


























Preview text:
Analytical Chemistry 1 Lecture 6 Acid-Base*Titrations
Instructor:-Nguyen-Thao Trang Acid-base*titration
• Write*balanced*chemical*equation*between*titrant*and* analyte.
• Calculate*composition*and*pH*after*each*addition*of*titrant.
• Construct*a*graph*of*pH*versus*titrant*added. 2
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid: H+ +**OH- →**H2O
– The equilibrium constant: K = 1/K -14 14 w = 1/10 = 10
– Reaction goes to completion
– At equivalence point (end point):
moles*of*titrant*=*moles*of*analyte
(V*titrant)(M* titrant)*=*(V*analyte)(M* analyte) Volume,*L
Molar*concentration,**M*or*mol/L 3
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid
3 regions of titration curve exists:
– Before the equivalence point: pH is determined by excess OH- in the solution.
– At the equivalence point: pH is determined by dissociation of water (H+ ≈ OH-).
– After the equivalence point: pH is determined by excess H+ in the solution. 4
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl
First*calculate*the*volume*of*HCl needed*to*reach*the* equivalence*point
(V*titrant)(M* titrant)*=*(V*analyte)(M* analyte)
(V*HCl)(C*HCl)*=*(V*NaOH)(C*NaOH)*
(V*HCl)(0.100*M)*=*(50.00*mL)(0.100*M) à Volume*HCl =*50.00*mL 5
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl Before*the*equivalence*point
– Initial amount of analyte (NaOH) = 50.00 mL x 0.100 M = 5.00 mmol
– After adding 1.00 mL of HCl:
• mmol H+ added = mmol OH- consumed
• mmol H+ = (1.00 mL)(0.100 M) = 0.100 mmol
àmmol OH- remaining = 5.00 – 0.100 = 4.90 mmol
• Total volume = 50.00 mL + 1.00 mL = 51.00 mL
• [OH-] = 4.90 mmol/51.00 mL = 0.0961 M
• pOH = - log(0.0961) = 1.017 à pH = 14.000 - 1.017 = 12.983 6
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl Before*the*equivalence*point
– Repeat calculations for all volumes added.
– Increments can be large initially but must be reduced just before and
just after the equivalence point (around 50.00 mL in this case).
– Sudden change in pH occurs near the equivalence point.
– Greatest slope at the equivalence point. 7
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl At*the*equivalence*point
– pH is determined by the dissociation of water: H2O**↔**H+ +**OH- x**********x Kw =*x2 =*1.0*x*10-14 à x*=*1.0*x*10-7 pH*=*7.00**(at*25*oC) 8
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl After*the*equivalence*point
– Excess H+ is present: After adding 51.00 mL of HCl
• Excess HCl present = 51.00 – 50.00 = 1.00 mL
• Excess H+ = (1.00 mL)(0.100 M) = 0.100 mmol
• Total volume of solution = 50.00 + 51.00 = 101.00 mL
• [H+] = 0.100 mmol/101.00 mL = 9.90 x 10-4 M
• pH = -log(9.90 x 10-4) = 3.004 9
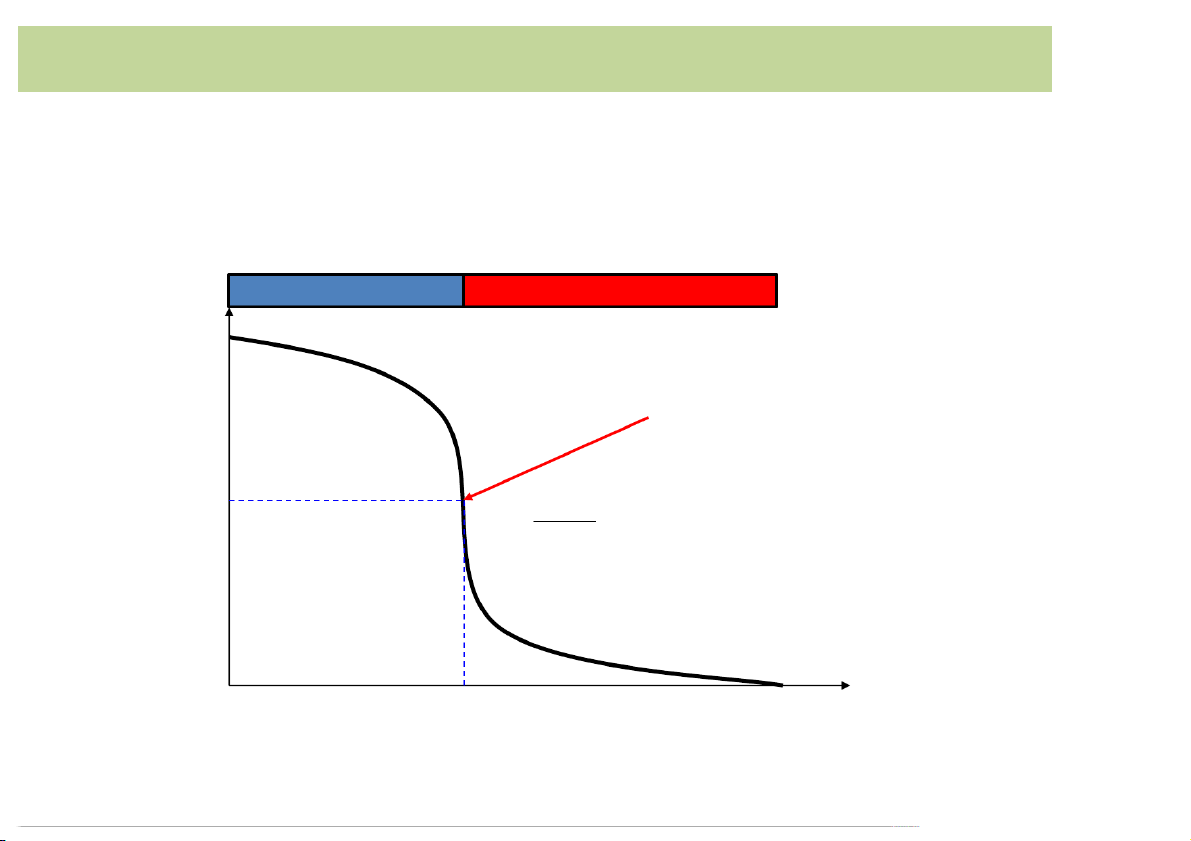
Titration*of*strong*base*with*strong*acid*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*base*with*a*strong*acid:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*NaOH with*0.100*M*HCl Titration*curve Excess*OH- Excess*H+ H Equivalence*point p
(maximum*slope*or*point*of*inflection) 7 𝑑"𝑝𝐻 =0 𝑑𝑉" 50.00
Volume*of*HCl*added*(mL) 10
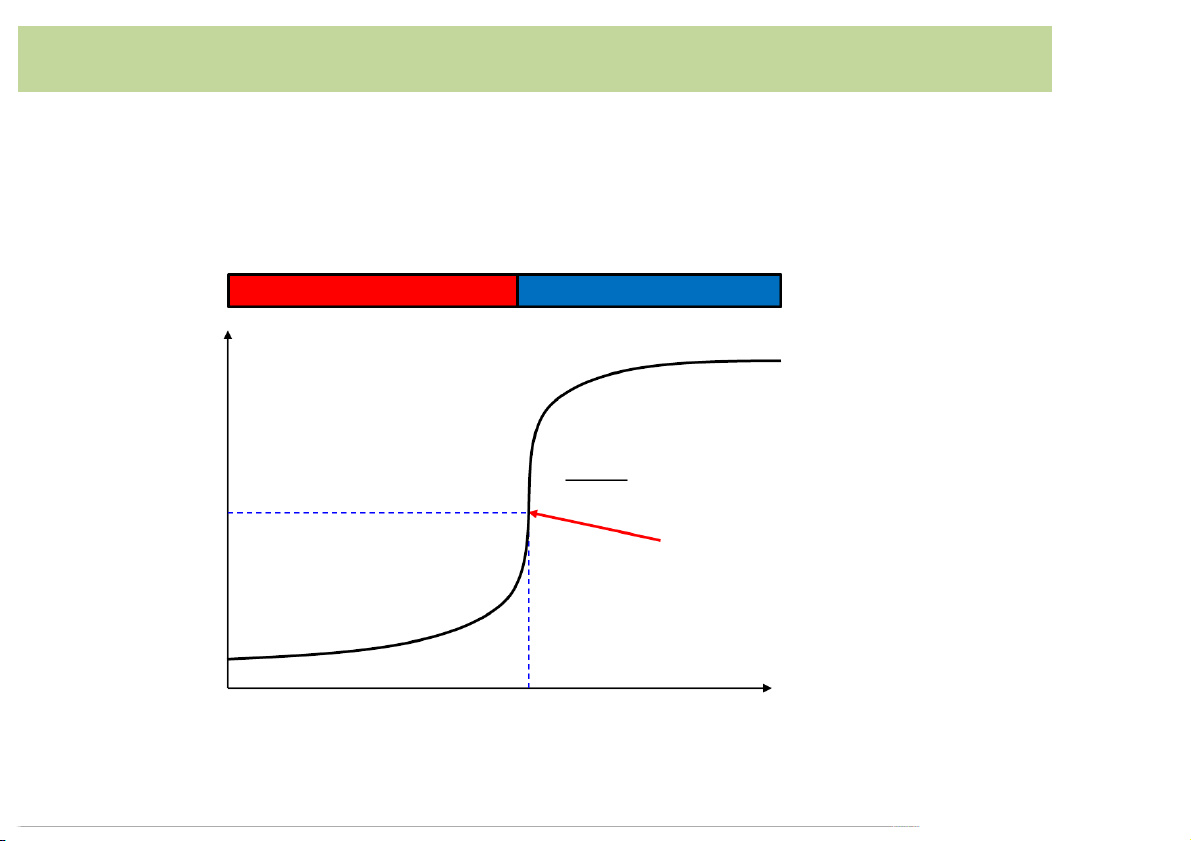
Titration*of*strong*acid*with*strong*base*
• Consider*titration*of*a*strong*acid*with*a*strong*base:*50.00*
mL*of*0.100*M*HCl with*0.100*M*NaOH Titration*curve Excess*H+ Excess*OH- H p 𝑑"𝑝𝐻 =0 𝑑𝑉" 7 Equivalence*point (maximum*slope*or*point* of*inflection) 50.00
Volume*of*NaOH*added*(mL) 11 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2
Equilibrium*constant*=*1/Kb =*1/*(Kw/Ka)*=*1.7*x*109* à so*large,*can*
assume* the*reaction* goes*to*completion.
Determine* volume*of*the*base*at*equivalence* point:* mmol HC2H3O2 ≈*mmol OH-
(V*NaOH)(0.100*M)*=*(50.00*mL)(0.0100*M) à Volume*NaOH =*5.00*mL 12 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 Before*adding*the*base
– pH is determined by equilibrium of weak acid: HA***↔***H+ +*A- F - x x x [x2 ] [x2 ] K = = a [F - x] [0.0100 - x] x*=*4.1*x*10-4 pH*=*3.39 13 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 Before*the*equivalence*point:
– By adding OH- a buffer solution of HA and A- is forme : d • After adding 0.100 mL OH-: HA + OH- → A- + H O 2 Initial**mmol
0.500* *******0.0100*** ****** ******0 Final***mmol 0.490* 0 0.0100 ⎛[A- ] ⎞ pH = pK + a lo ⎜ ⎜ g ⎝ [HA] ⎠ [ ⎛0.0100] ⎞ pH = 4.76 +log = 0 . 3 7 [ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ 0.490] ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ 14 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 Before*the*equivalence*point:
– By adding OH- a buffer solution of HA and A- is forme : d
• After adding 2.50 mL OH- (haft of the volume at equivalence point) HA + OH- → A- + H O 2 Initial**mmol
0.500* *******0.250**** ******* ****0 Final***mmol 0.250* 0 0.250 ⎛[A- ] ⎞ pH = pK + a lo ⎜ ⎜ g ⎝ [HA] ⎠ [ ⎛0.250] ⎞ pH = 4.76 lo + g = 4.76 [ ⎜0.250] ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ 15 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 At*the*equivalence*point: – Volume of OH- = 5.00 mL
• mmol OH- = (5.00 mL)(0.100 M) = 0.500 mmol • HA is used up and [HA] = 0
• Only A- is present in solution à mmol A- = 0.500 mmol
• [A-] = (0.500 mmol)/(50.00 mL + 5.00 mL) = 0.00909 M (= F) A- + H2O ↔ HA + OH- F - x x x 2 [x ] K K w = = b 16 [F - x] Ka Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 At*the*equivalence*point: – Volume of OH- = 5.00 mL 2 [x ] Kw 1 − 0 K = = =5.8 1 × 0 b [F - x] Ka • x = [OH-] = 2.3 x 10-6
• pOH = 5.64 à pH = 14.00 – 5.64 = 8.36 • pH is greater than 7.00
• pH at equivalence point increases with decreasing strength of acid 17 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH HC2H O 3 2 +*OH- →*C2H3O - 2 +*H O 2 After*the*equivalence*point:
– pH is determined by the excess [OH-] (approximation) • After adding 5.10 mL OH-
• [OH-] = (0.10 mL)(0.100 M)/(50.00 mL + 5.10 mL) = 1.81 x 10-4
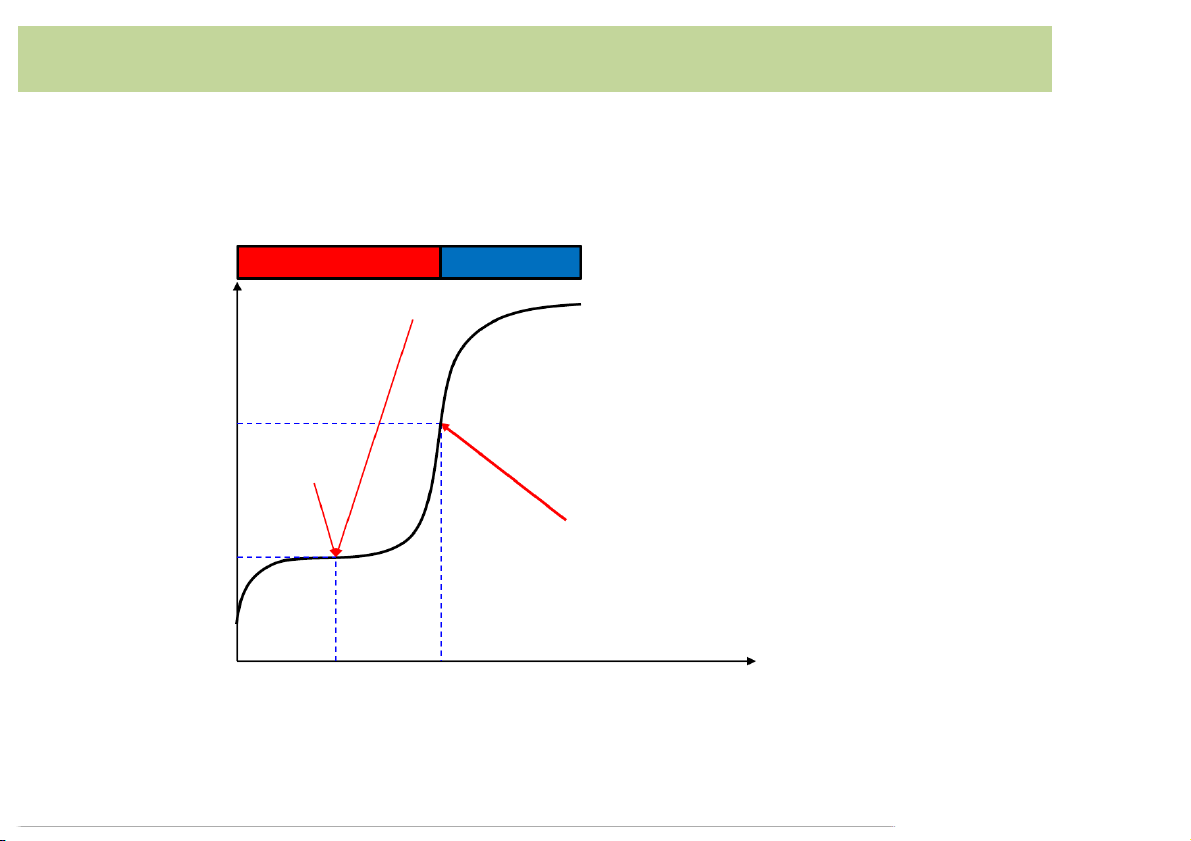
• pH = 14.00 – pOH = 14.00 – 3.74 = 10.26 18 Weak*acid-strong*base
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*acetic*acid*with*0.100*M* NaOH Buffer*region Excess*OH- Minimum*slope H p 8.36 pH*=*pKa Equivalence*point (maximum*slope*or*point* pKa of*inflection) 2.50 5.00
Volume*of*NaOH*added*(mL) 19 Strong*acid-weak*base
• The*reverse*of*weak*acid*and*strong*base: B**+**H+ →**BH+*
• Similarly*assume*reaction*goes*to*completion
• Consider*50.00*mL*of*0.0100*M*pyridine*with*0.100*M*HCl(Kb of*pyridine*=*1.6*x*10-9*)
– Determine volume of acid at equivalence point: • mmol pyridine ≈ mmol H+
• (V HCl)(0.100 M) = (50.00 mL)(0.010 M) à Volume HCl = 5.00 mL 20