



















Preview text:
Analytical Chemistry 1 Lecture'8
Complexation'reactions'and'titration Instructor:*Nguyen*ThaoTrang Outlines • Complex formation • Organic complexing agents
• Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) titration 2 Complex)formation
phức chất trong dung dịch
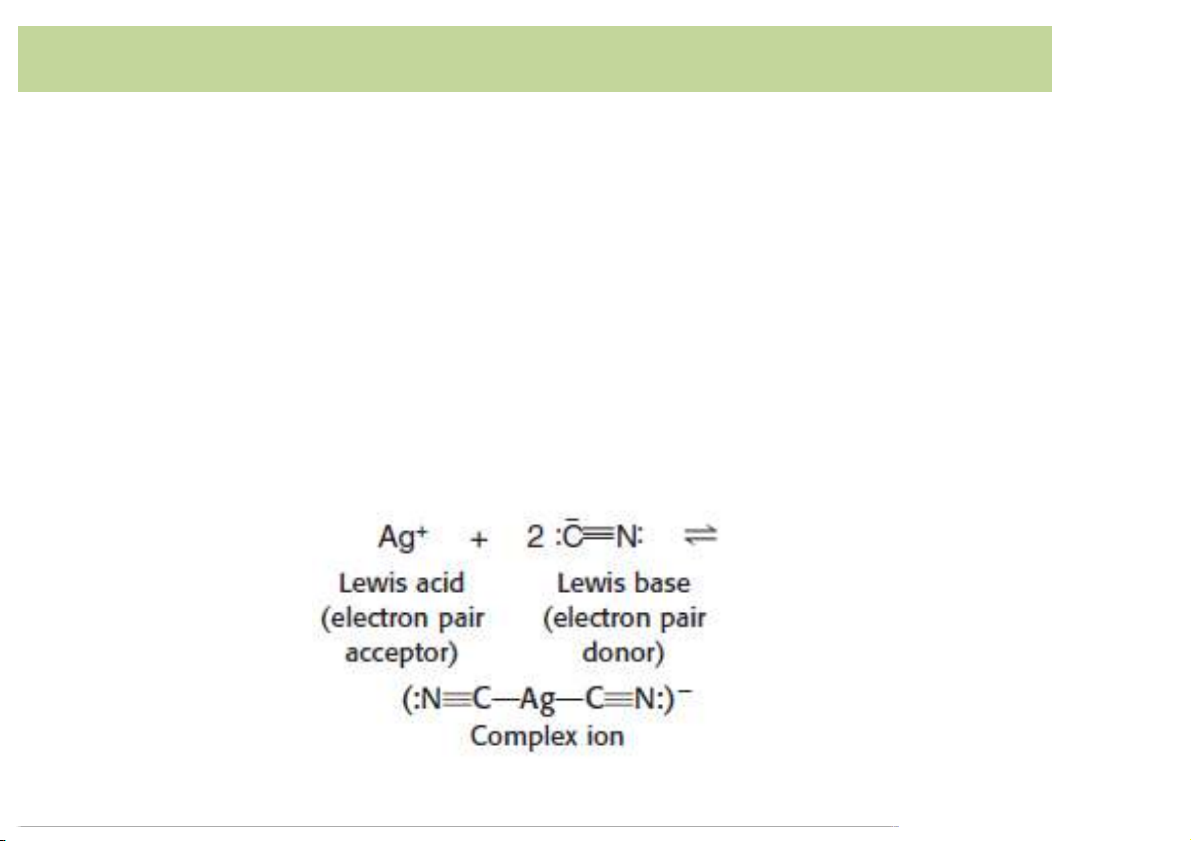
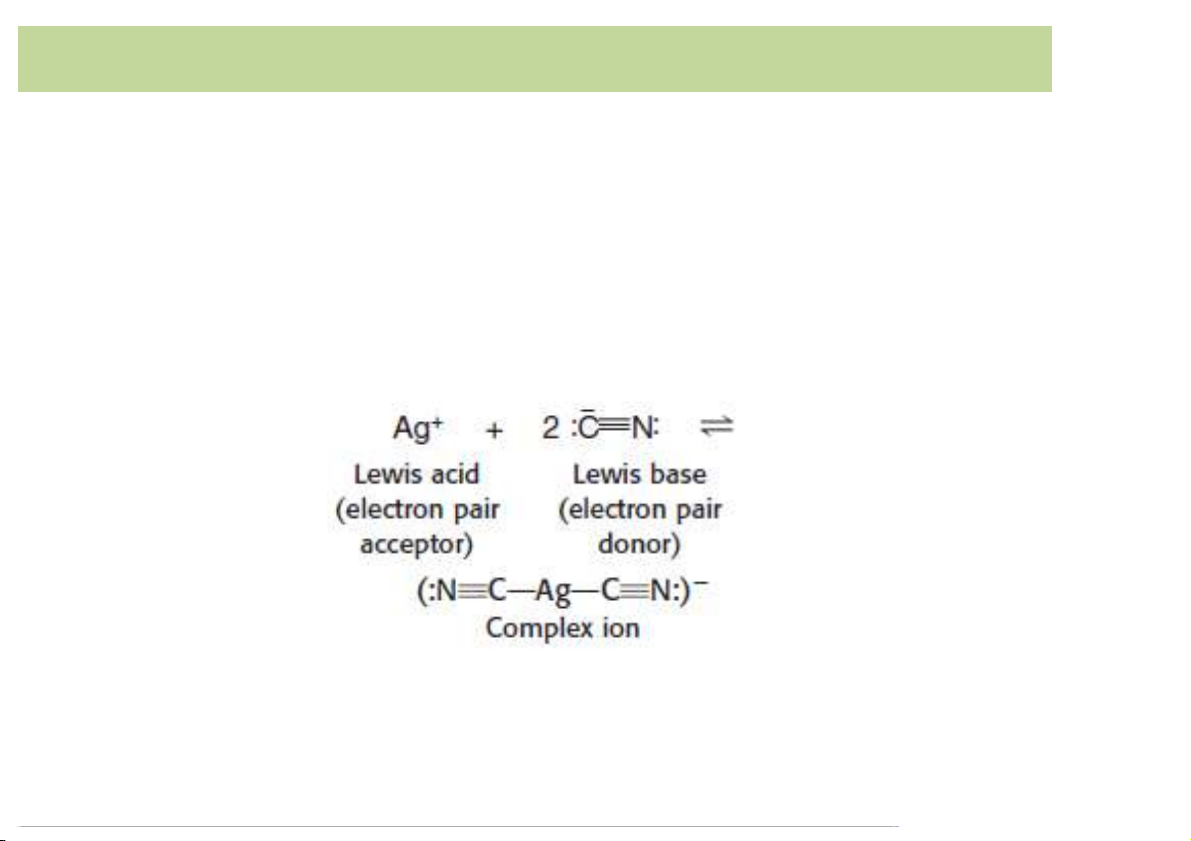
• Many metal cations (Lewis acid) form complexes in
solutionwithsubstances,calledligands,containinga
pairofunsharedelectrons(Lewisbase). sở hữu
• A ligand is a molecule (or ion) which possesses at
least one position atwhich itcan attach itselfto a metalion. 3 Complex)formation • Monodentate (unidentat ) e : ligand binds to a metal
ionthroughonly oneatom(onetoothedligand).
– Ex. CN- isa monodentateasitbindsto themetal throughonlytheC atom. 4 Complex)formation
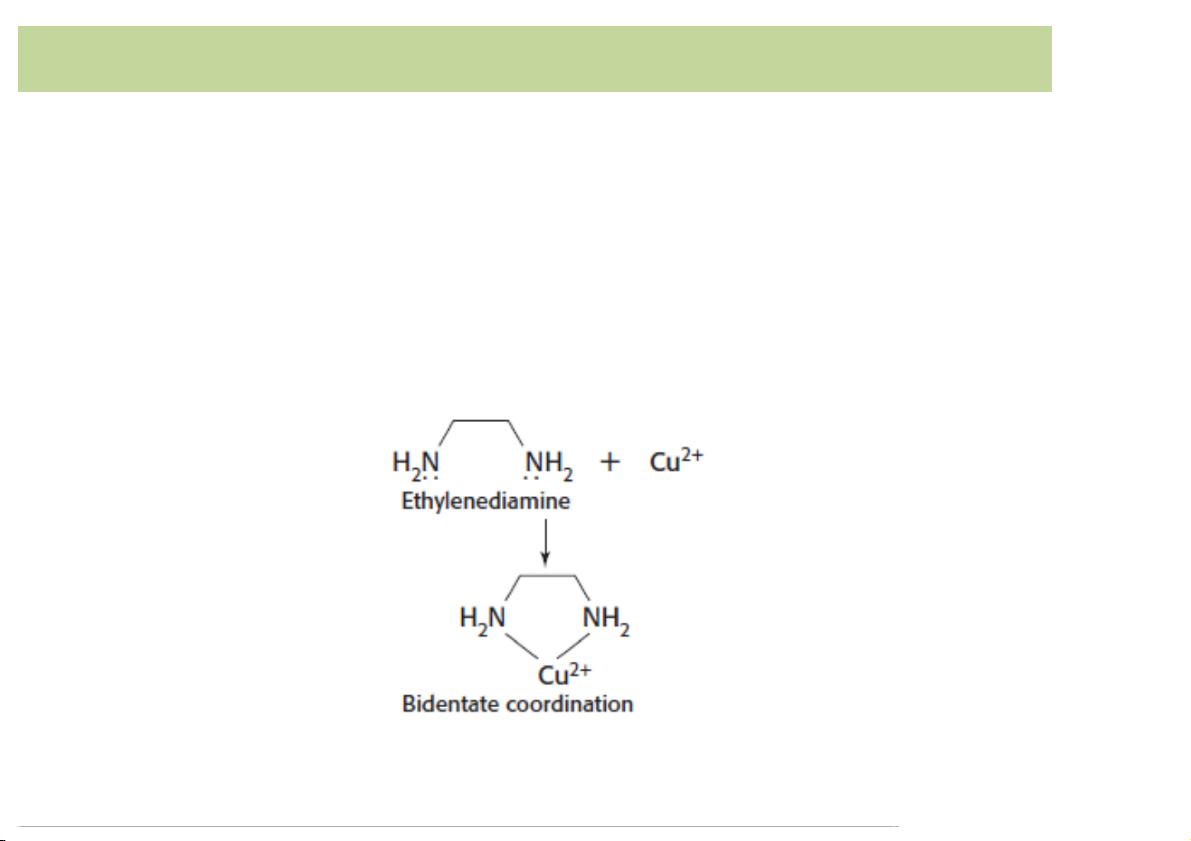
• Multidentate: ligandattachestoa metalionthrough
morethanoneligandatom(manytoothedligandor chelatingligand)
– Ex. Ethylenediamine is a bidentate as it binds to themetalthroughtwoN atoms. 5 Complexation)equilibria
• Complexationreactions)involve)a)metal-ion)M)
reacting)with)a)ligand)L)to)form)a)complex)ML: M'+'L'⇌ ML AddingmoreL:
ML)+)L)⇌ ML2,)K1*=[ML2]/[ML][L];
ML2 +)L)⇌ ML3,)K2*=[ML3]/[L][ML ] 2 ; ...
MLn-1+)L)⇌ MLn,)Kn=[MLn]/[L][MLn-1]; 6 Complexation)equilibria
• The)equilibria)can)be)expressed)as)sum)of)individual) steps:)
M)+)L)⇌ ML,)β1*=[ML]/([M][L])=*K1
M)+)2L)⇌ ML2,)β2*=[ML2]/([M][L]2)=*K1 K2 ...
M)+)nL)⇌ MLn,)βn=[MLn]/([M][L]n)=K1 K2*...Kn
inwhichβn istheoverallformationconstant 7 Complexation)equilibria • Fraction'of'each'species: TotalconcentrationofthemetalM: CM = [M]+ [ML + ] [ML2]+ [ML3]+...+ [MLn]
= [M]+β1 [M][L]+β2 [M][L]2 +β3 [M][L]3 +...βn[M][L]n àFractionofeachspecies: M 𝛼" = C" [M]
= [M])+)β1 [M][L])+)β [M][L]2)+)β3 [M][L]3)+...)βn [M] * 2* * * 1
= 1)+)β1 [L])+)β2 [L]2)+)β [L]3)+...)Β [L]n * * 3* n* 8 Complexation)equilibria • Fraction)of)each)species: TotalconcentrationofthemetalM: CM = [M]+ [ML + ] [ML2]+ [ML3]+...+ [MLn]
= [M]+β1 [M][L]+β2 [M][L]2 +β3 [M][L]3 +...βn[M][L]n àFractionofeachspecies: ML 𝛼"*= C" β [M][L] = 1*
[M])+)β1 [M][L])+)β [M][L]2)+)β3 [M][L]3)+...)βn [M] * 2* * * β [L] = 1*
1)+)β1 [L])+)β2 [L]2)+)β [L]3)+...)Β [L]n * * 3* n* 9 Organic complexing agents
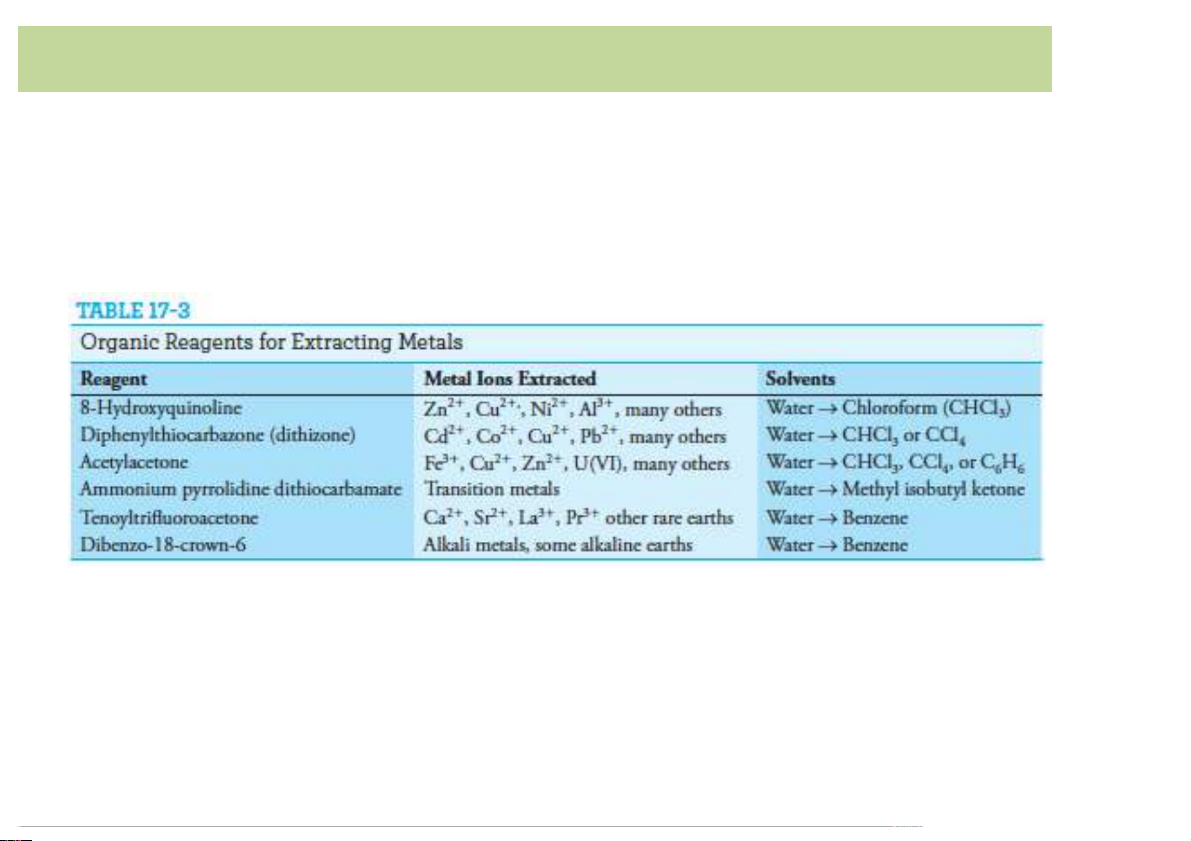
• Manyorganicreagentsareusefulinconvertingmetalionsinto
theformthatcanbeextractedfromwaterintoanimmiscible organicphase.
• Many organic complexing reagents are widely used in
spectrophotometricdetermination ofmetal ionsduetothe
formationofcoloredorUVabsorbedmetal-ligandcomplexes. 10
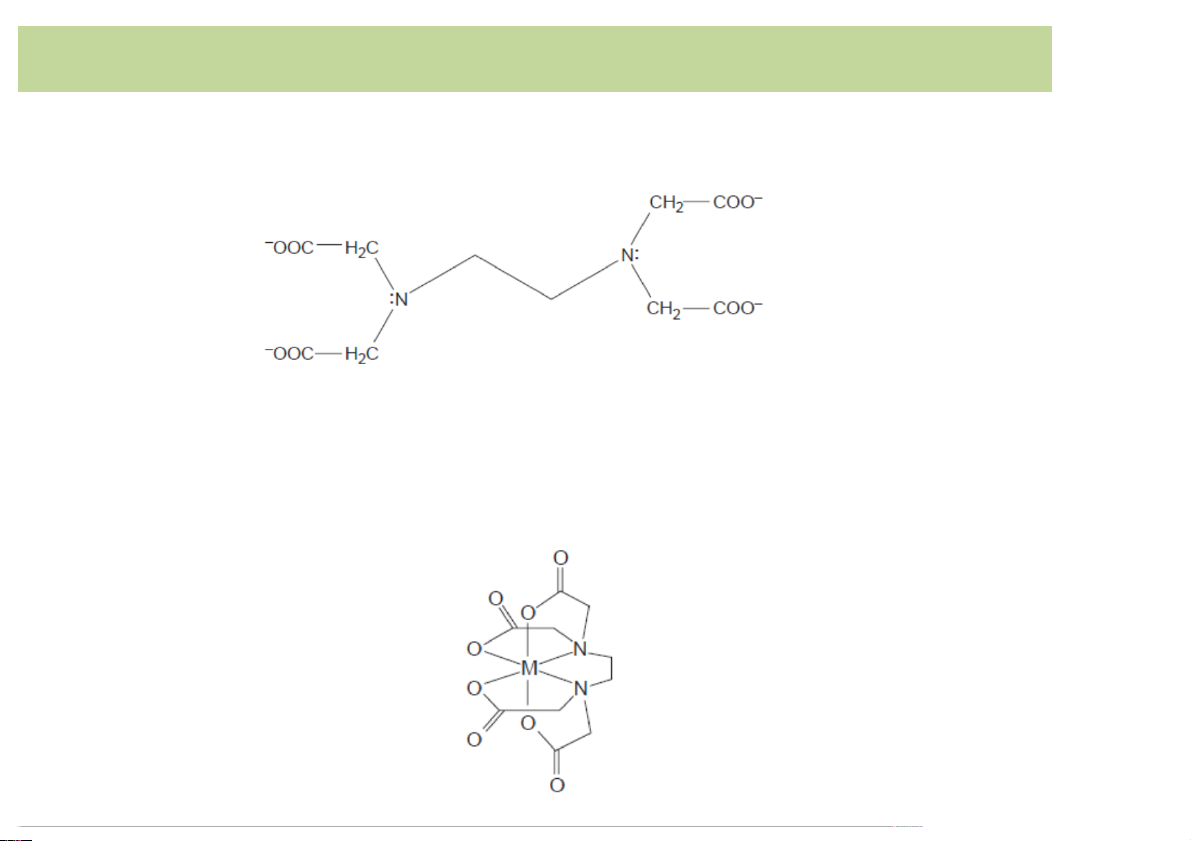
EDTA,)a)common)multidentateligand
• Ethylenediaminetetraaceticacid)(EDTA))is)an)aminocarboxylic acid.
• EDTA)has)6)binding)sites)(4)carboxylate)groups)and)2)amino)
groups),)providing)6)pairs)of)electrons)à EDTA)forms)a)cage-
like)structure)around)the)metal)ion)in)metal–ligand)complex: 11
EDTA,)a)common)multidentateligand
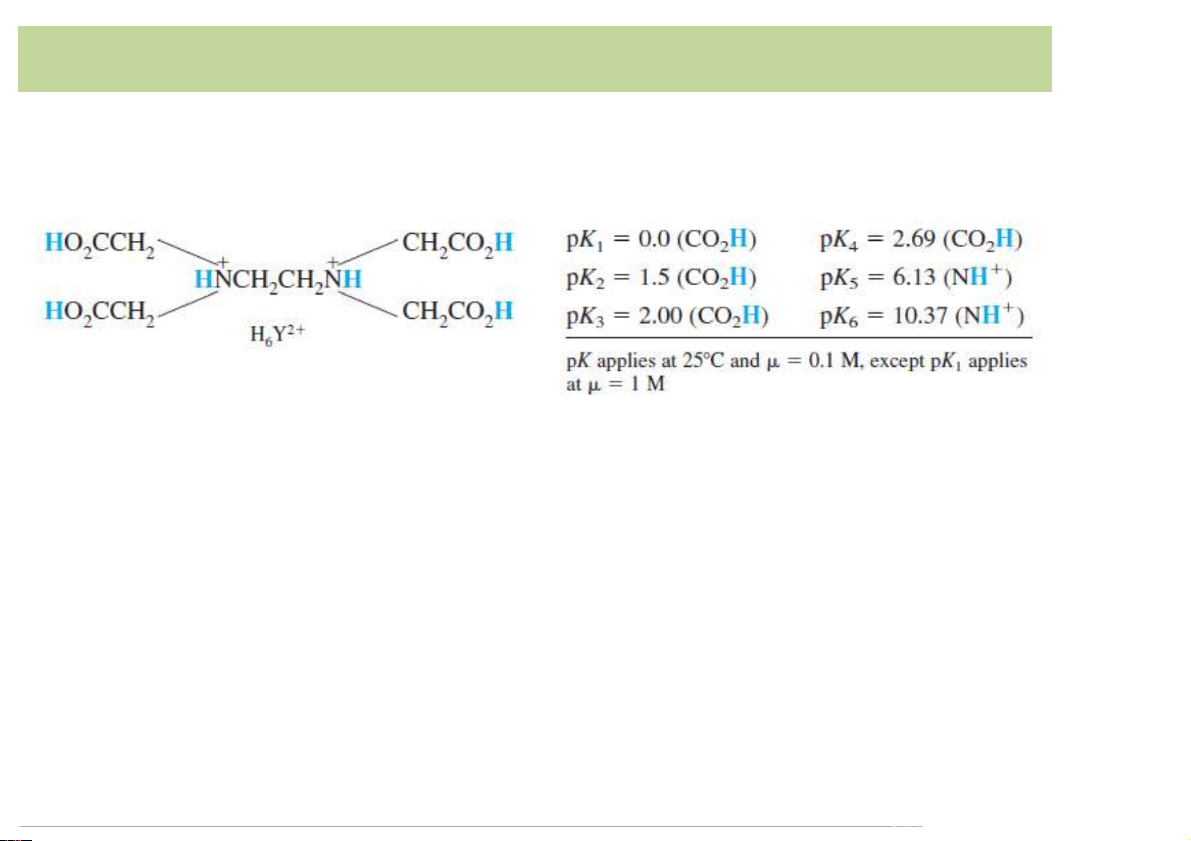
• Acid-base)properties:)hexaproticacid,)designated)H6Y2+.
• Neutral)acid)is)tetraprotic,)with)the)formula)H4Y. 12
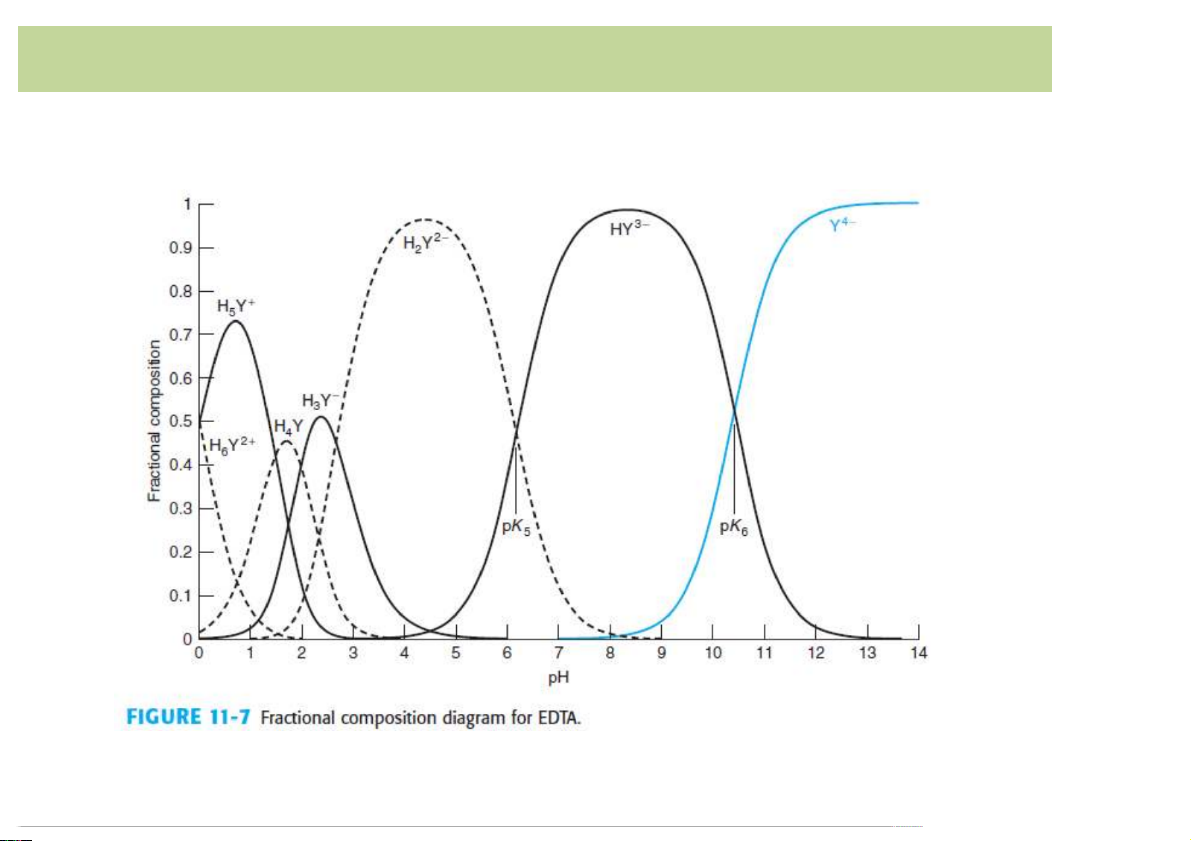
EDTA,)a)common)multidentateligand • Fraction)of)EDTA: 13
Complexes)of)EDTA)and)Metal)ions
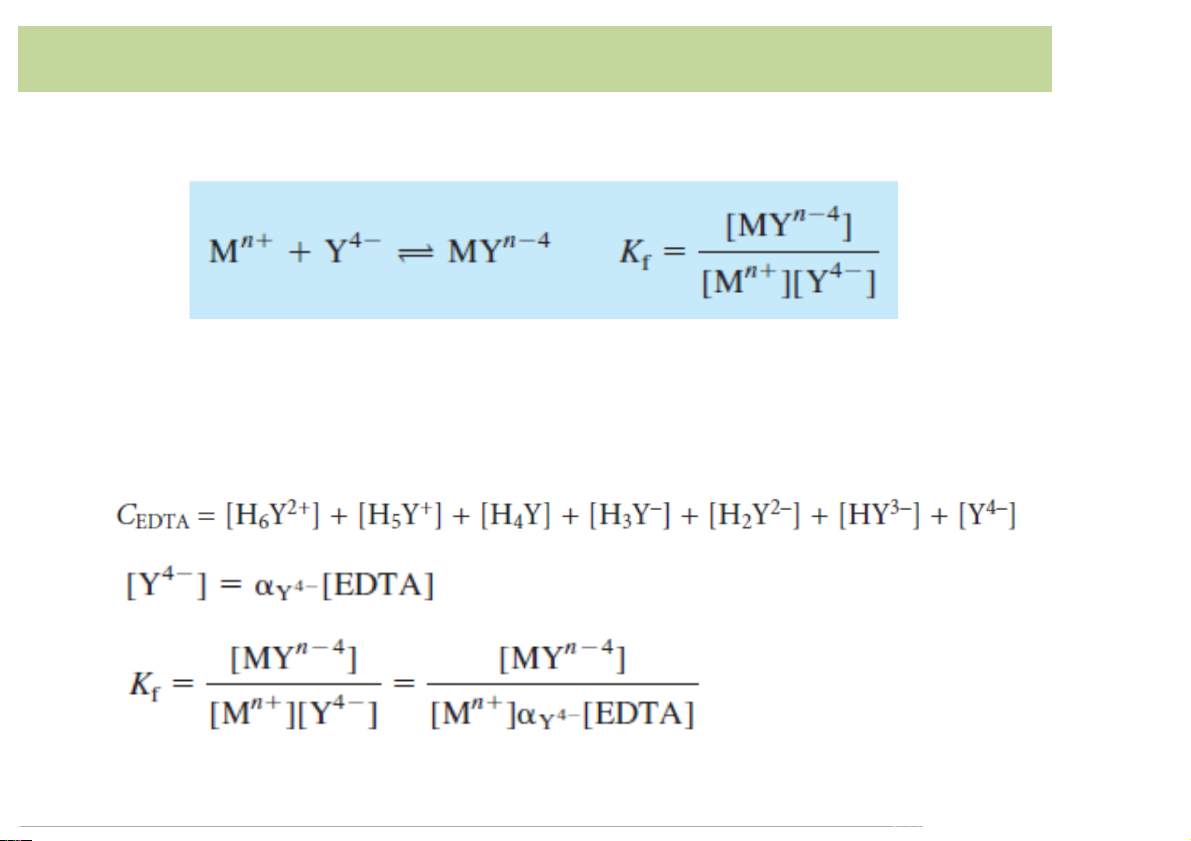
• EDTA)complex:)Y4-forms)a)complex)with)a)metal)ion)Mn+:
• Kf is)defined)as)a)formation*constant*or)stability)constant
• At)any)pH:)the)analytical)concentration)of)EDTA)is)given)by: 14
Complexes)of)EDTA)and)Metal)ions
• Conditional formation constant or effective formation constant:
• This conditional formation constant can be applied for a
complex formation between a metal ion and all forms of uncomplexedEDTA:
à Thebasicequationincomplexometrictitration
• If𝐾′. is large,wecanconsiderthereactiontobecompleteat eachpointinthetitration. 15
Complexes)of)EDTA)and)Metal)ions • Computing∝012: ∝312 𝐾 = 4𝐾5𝐾6𝐾7
[𝐻9]7+;𝐾4[𝐻9]6+;𝐾4𝐾5[𝐻9]5 +𝐾4𝐾5𝐾6[𝐻9]+ 𝐾4𝐾5𝐾6𝐾7 whereK1,K2,K3 an K
d 4 arethe4 dissociationconstantsforH4Y. 16
Complexes)of)EDTA)and)Metal)ions 17
Complexes)of)EDTA)and)Metal)ions 18
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Complexometrictitration:)Plot)of)pM(=)-log[Mn+]) 19
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Complexometrictitration:)Plot)of)pM(=)-log[Mn+])
• Before the equivalence point: - Excess Mn+ in solution
- Dissociation of the MYn-4 complex is negligible à [Mn+]free = [Mn+]excess 20
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Complexometrictitration:)Plot)of)pM(=)-log[Mn+]) • At the equivalence point: - No free Mn+ in solution
- Dissociation of the MYn-4 complex: à [Mn+]free = [EDTA]free
• After the equivalence point: - Free EDTA in solution 21
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Ex.'Titration'of'50.00'mL'of'Ca2+'0.0400'M'with'EDTA'solution'
of'0.0800'M'(buffered'to'pH'10.0) Ca2++)EDTA)à CaY2- • 𝐾′ < 10.65 10) . =𝛼07 .K? =)(0.30) 1 ( 0 ) 1 = .34) x)10 à large!
• Ve =)(50.00)mL)(0.0400)M)/(0.0800)M))=)25.00)mL
Before&the&equivalence&point:&VEDTA =&5.00&mL
• nEDTA) added=)nCa2+)reacted)=)(5.00)mL)(0.0800)M))=)0.400)mmol
• nCa2+)excess)=)nCa2+)initial)- nCa2+)reacted)=)(50.00)mL)(0.0400)M))- 0.400)=)1.60) mmol
à [Ca2+)excess])=)(1.60)mmol)/(50.00)+)5.00)mL))=)0.0291)M à pCa2+)=)1.54 22
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Ex.'Titration'of'50.00'mL'of'Ca2+'0.0400'M'with'EDTA'solution'
of'0.0800'M'(buffered'to'pH'10.0) Ca2++)EDTA)à CaY2-
At&the&equivalence&point:&VEDTA =&25.00&mL • nCaY2-produced =)2.00)mmol
• [CaY2-]produced =)2.00)mmol/(50.00)+)25.00))=)0.0267 CaY2-⇌ Ca2++)EDTA (0.0267 – x) x x
1/𝐾′. =)[Ca2+][EDTA])/)[CaY2-]
x2/(0.0267 – x) = 1/1.34.1010 à x = 1.4x10-6 M à pCa2+)=)5.85 23
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Ex.'Titration'of'50.00'mL'of'Ca2+'0.0400'M'with'EDTA'solution'
of'0.0800'M'(buffered'to'pH'10.0) Ca2++)EDTA)à CaY2-
After&the&equivalence&point:&VEDTA =&26.00&mL
• nEDTAexcess)=)(26.00-25.00)(0.0800)M)=)0.0800)mmol
• [EDTA]excess)=)0.0800)mmol/(50.00)+)26.00)mL))=)1.05)x)10-3M
• [CaY2-]produced =)2.00)mmol/(50.00)+)26.00))=)2.63)x)10-2M
𝐾′. =)[CaY2-]/[Ca2+][EDTA])=1.34 x 1010 à [Ca2+)])=)1.9)x 10-9 M à pCa2+)=)8.73 24 Complexometric titration curve The greater the Kf’, the more distinct the end point! 25
Indicators)in)complexometrictitration
• Metalindicators: arecompoundsthatchange colorwhenthey bindtoa metalion.
• Useful indicators must bind metal less strongly than EDTA does. 26
Indicators)in)complexometrictitration
• Example:)reaction)of)Mg2+with)EDTA)at)pH)10)with)Calmagite indicator.
• Any)excess)EDTA)from)titration)will)form)complex)with)a)metal)
that)binds)to)the)indicator,)and)thus,)releasing)free)indicator) à identify)the)endpoint. 27
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA
• Application: Using complexometric titration with EDTA to
determinetheconcentrationofCa2+andMg2+ presentintap water.
• A watersupplyisconsideredhardwhentheamountofCa+2,
Mg+2, and/orFe+3 ionsbecomestoohighforitsintendeduse.
Softwaterdoesnotcontainanysignificantamountsofthese ions.
• It isnot necessary to measure each ion contributingtothe
water hardness separately. Instead, all hard water ions are
determined collectively and reported as an "apparent
hardness" assumingthatallofthehardness isderivedfrom CaCO3. 28
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA • Procedure:
– A)1:1)complex)between)EDTA)and)Mg2+/Ca2+ (called)Mn+))is)formed)
when))EDTA)is)added) to)a)solution)of)Mg2+and)Ca2+):
– The)indicator)used:)EriochromeBlack)T)(EBT))has)3)ionizableprotons)
H3In)and)a)complex)between)EBT)and)Mg2+/Ca2+ has)a)smaller)𝐾′.
– At)pH)~)10,)free) EBT)(HIn2-))has)a)blue)color)and)complexedEBT)is)wine) red 29
Complexometrictitration)with)EDTA • Procedure:
– At)pH)10,)before)the)equivalent)point:)Mn+is)in)excess:
• A)complex)is)formed)between Mn+ and)EDTA.
• A)complex)is)formed)between)Mn+ and)EBT.) • Free)Mn+
à Solution)has)a)color)of)the)complexedEBT:)red
– At)the)equivalent) point:)all)Mn+)complexedwith)EDTA)and)EBT.
– After)the)equivalent) point:)EDTA)is)in)excess,)no)free)Mn+.
• EDTA)competes)with)EBT)for)Mn+.
• 𝐾′. (EDTA-Mn+)))>)𝐾′.()EBT-Mn+))à EBT)will)be)released)from)the) complex.
• Solution)has)a)color)of)the)free)EBT:)blue
– Transition)color:)red)to)light)blue) 30