

Preview text:
NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM
CENTER FOR ADVANCED EDUCATIONAL
Independence – Freedom – Happiness PROGRAMS SYLLABUS 1. MODULE PROFILE Course Name: MICROECONOMICS 1 Course Code: Credit: 3 Class:
Program: Advanced Educational Program
2. LECTURER’S INFORMATION Ful name: TO TRUNG THANH Tittle: Professor, PhD Address: Room 214, Building A1 Phone number: Email: thanhtt@neu.edu.vn Faculty/ Institute: Economics 3. COURSE PREREQUISITES Mathematics 4. COURSE OBJECTIVES
The main objective of the course is to improve economic literacy as wel as critical thinking
and problem solving skil s to explain and predict economic issues. After the course, students are able to:
• Understand how markets and businesses run.
• Understand how individuals, firms and the government make economic decisions
and interact, given the resource scarcity.
• Understand how economic relationships might affect market agents.
• Understand how the government policies affect individuals, firms and society.
Improve skil s of analytical thinking, problem solving, writing ability and team work 1 | P a g e 5. COURSE CONTENT/DESCRIPTION
Economics is the study of how society manages its scarce resources. Economics has been
divided into the subcategories of microeconomics and macroeconomics. While
macroeconomics studies aggregate issues related to national and international economic
activities, this course - microeconomics - focuses on the behavior of individual economic
agents. Microeconomics studies how households (or individuals), business (or firms,
enterprises) and the government make decisions, given the resource scarcity. It also studies
the interactions among those market members and how these interactions have impacts on
their economic benefits and the economy. Because most of these activities occur in the
markets, this course also focuses on how the markets work. . 7. DETAILED CLASS SCHEDULE
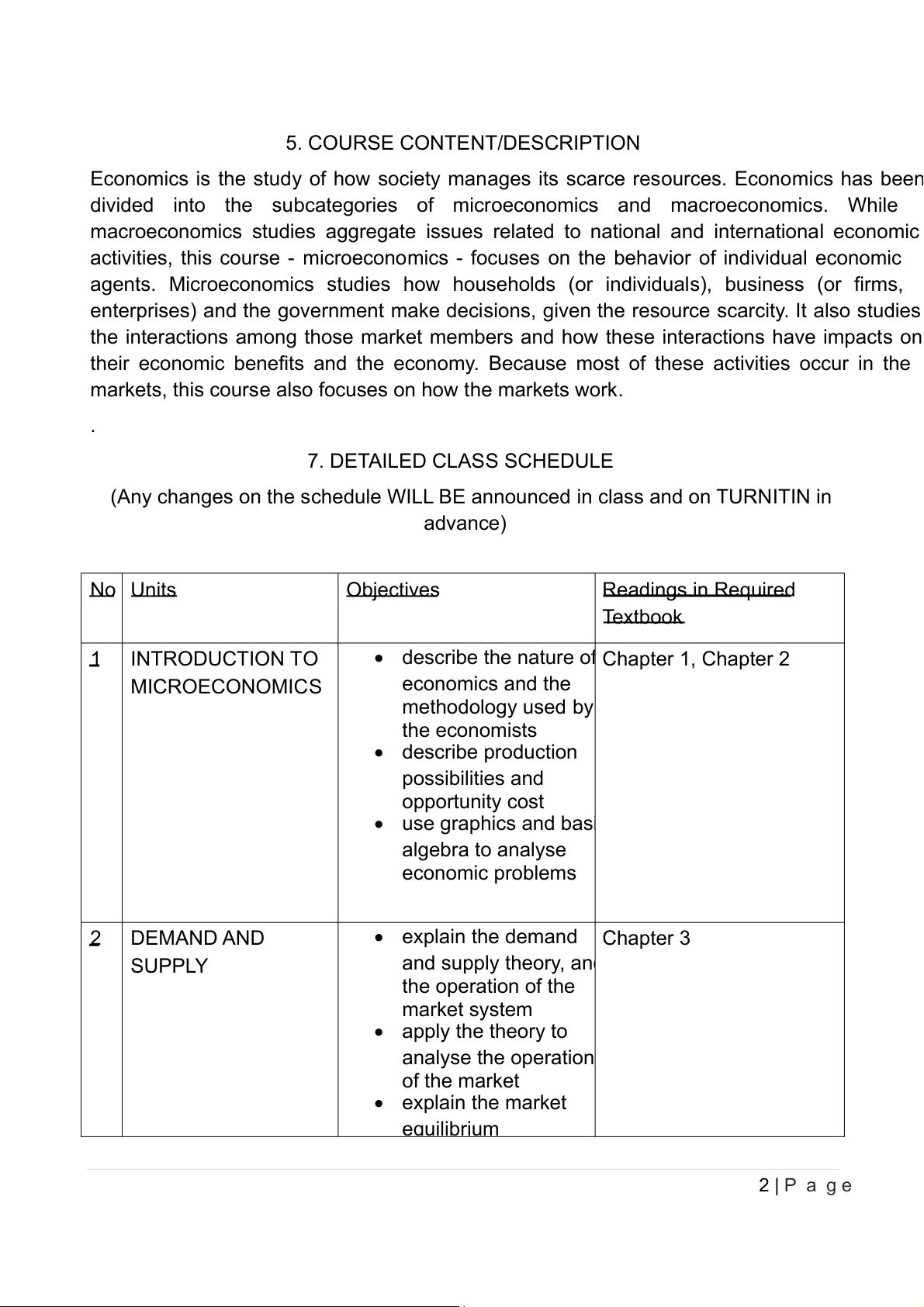
(Any changes on the schedule WILL BE announced in class and on TURNITIN in advance) No Units Objectives Readings in Required Textbook 1 INTRODUCTION TO
• describe the nature of Chapter 1, Chapter 2 MICROECONOMICS economics and the methodology used by the economists • describe production possibilities and opportunity cost • use graphics and basi algebra to analyse economic problems 2 DEMAND AND • explain the demand Chapter 3 SUPPLY and supply theory, and the operation of the market system • apply the theory to analyse the operation of the market • explain the market equilibrium 2 | P a g e 3 ELASTICITY
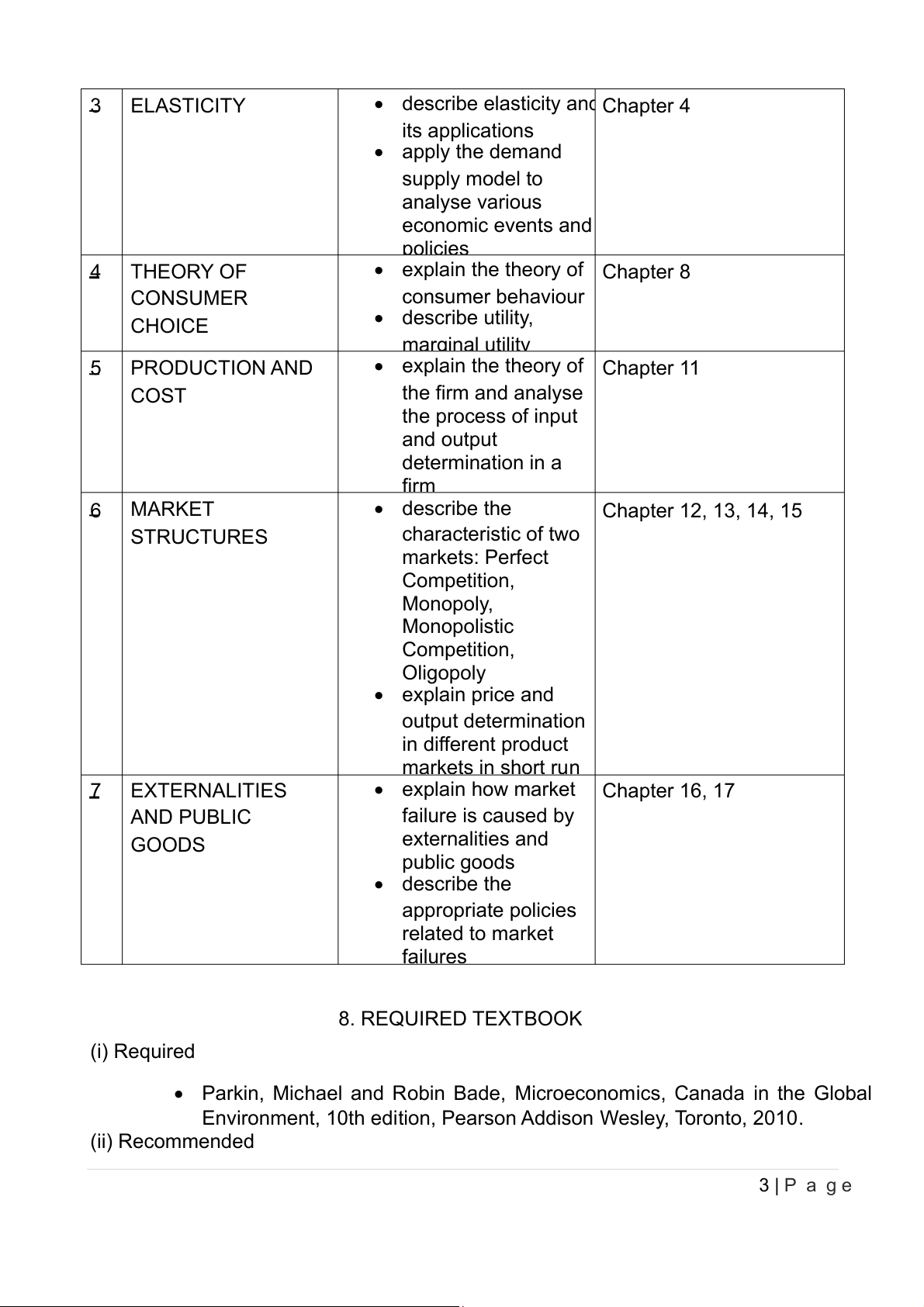
• describe elasticity and Chapter 4 its applications • apply the demand supply model to analyse various economic events and policies 4 THEORY OF
• explain the theory of Chapter 8 CONSUMER consumer behaviour CHOICE • describe utility, marginal utility 5 PRODUCTION AND
• explain the theory of Chapter 11 COST the firm and analyse the process of input and output determination in a firm 6 MARKET • describe the Chapter 12, 13, 14, 15 STRUCTURES characteristic of two markets: Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly • explain price and output determination in different product markets in short run 7 EXTERNALITIES • explain how market Chapter 16, 17 AND PUBLIC failure is caused by GOODS externalities and public goods • describe the appropriate policies related to market failures 8. REQUIRED TEXTBOOK (i) Required
• Parkin, Michael and Robin Bade, Microeconomics, Canada in the Global
Environment, 10th edition, Pearson Addison Wesley, Toronto, 2010. (i ) Recommended 3 | P a g e
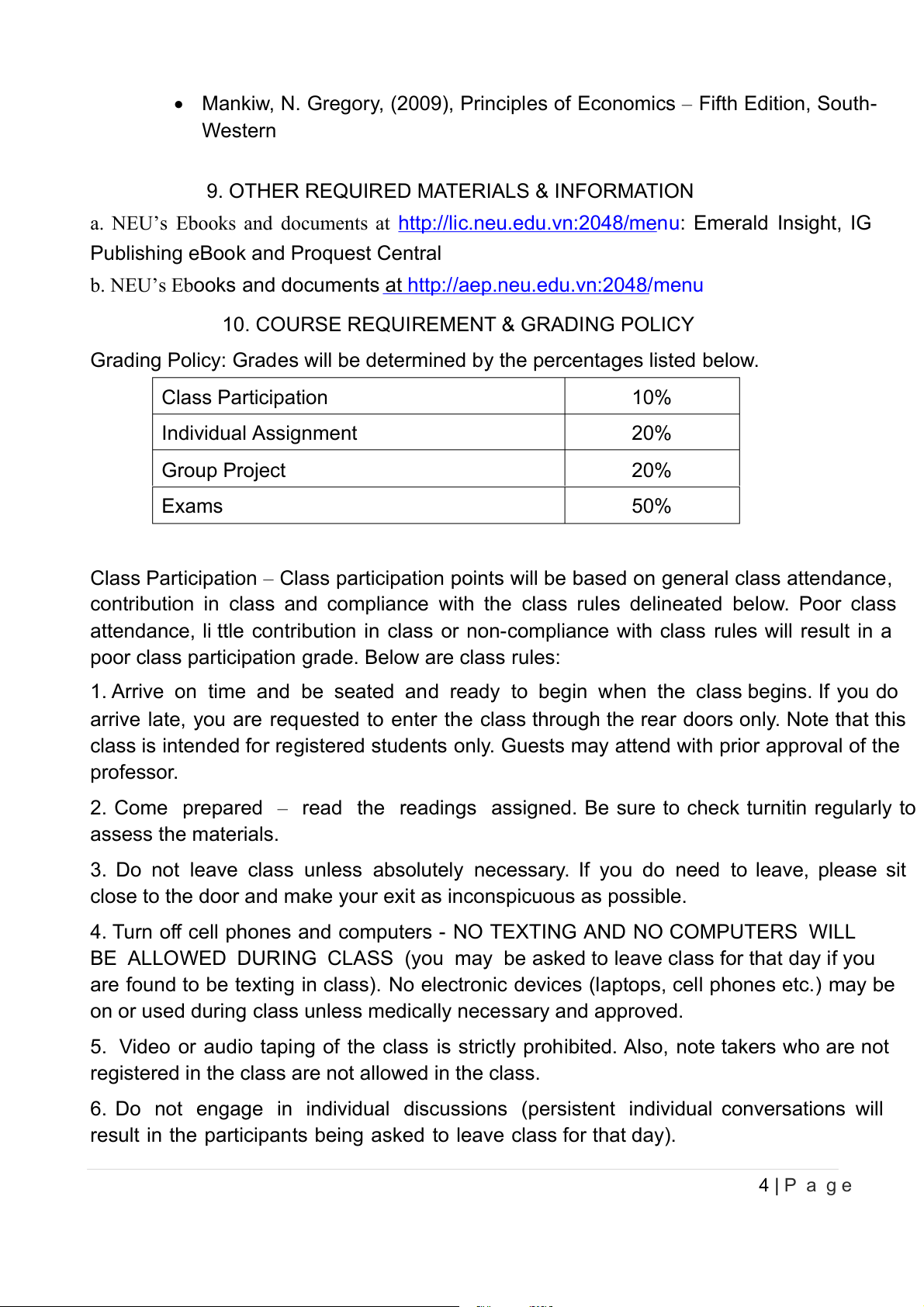
• Mankiw, N. Gregory, (2009), Principles of Economics – Fifth Edition, South- Western
9. OTHER REQUIRED MATERIALS & INFORMATION
a. NEU’s Ebooks and documents at http://lic.neu.edu.vn:2048/menu: Emerald Insight, IG
Publishing eBook and Proquest Central
b. NEU’s Ebooks and documents at http://aep.neu.edu.vn:2048/menu
10. COURSE REQUIREMENT & GRADING POLICY
Grading Policy: Grades wil be determined by the percentages listed below. Class Participation 10% Individual Assignment 20% Group Project 20% Exams 50%
Class Participation – Class participation points wil be based on general class attendance,
contribution in class and compliance with the class rules delineated below. Poor class
attendance, li ttle contribution in class or non-compliance with class rules wil result in a
poor class participation grade. Below are class rules:
1. Arrive on time and be seated and ready t
o begin when the class begins. If you do
arrive late, you are requested to enter the class through the rear doors only. Note that this
class is intended for registered students only. Guests ma
y attend with prior approval of the professor.
2. Come prepared – read the readings assigned. Be sure to check turnitin regularly to assess the materials.
3. Do not leave class unless absolutely necessary. If you do need to leave, please sit
close to the door and make your exit as inconspicuous as possible.
4. Turn off cel phones and computers - NO TEXTING AND NO COMPUTERS WILL
BE ALLOWED DURING CLASS (you may be asked to leave class for that day if you
are found to be texting in class). No electronic devices (laptops, cell phones etc.) may be
on or used during class unless medical y necessary and approved.
5. Video or audio taping of the class i
s strictly prohibited. Also, note takers who are not
registered in the class are not al owed in the class.
6. Do not engage in individua l discussions (persistent individual conversations wil result i
n the participants being asked t o leave class for that day). 4 | P a g e
7. Participate by contributing comments and questions during the discussions. The
instructor wil cal on students during the class if participants do not volunteer.
8. Please use common courtesy and polite manners in class, during discussions and i n any
emails or communication related to the class in a business-like tone. 9. Keep item
s you bring to a class minimal. For instance ,noisy newspapers and food with
odors are not acceptable. Smal snacks are al owed and any additional materials should be kept i n your backpack.
10. I have no tolerance for acts of academic dishonesty (such matters may be treated as listed below). To be fair t
o al students, grade changes or additional extra credit opportunities wil not
be considered. The only discussions on grades will be verification of the grade. The
professor wil not tolerate requests to increase grades or any excuses regarding grades.
The system of an option final exam provides for any “second chances” for any issues arising during the semester. Communication:
Studies show that students who engage in one-on-one discussions with the instructor
about the course receive better grades. I, therefore, encourage your discussion with me.
You can communicate during office hours, email or i
n class discussions. You also are
welcome to make separate appointments. I wil be available before and after class, but
only for short questions. I also encourage feedback on the classes, lectures, teaching and
reading material. We enhance the class every semester and your thoughts are valuable in the process.
CENTER FOR ADVANCED EDUCATIONAL Hanoi, / / 2019 PROGRAMS Lecturer Signed 5 | P a g e




