
Preview text:
Problem 1:
Given: A consumer has $60 to spend on two goods 𝑋and 𝑌. Prices: 𝑝𝑋 = $3per
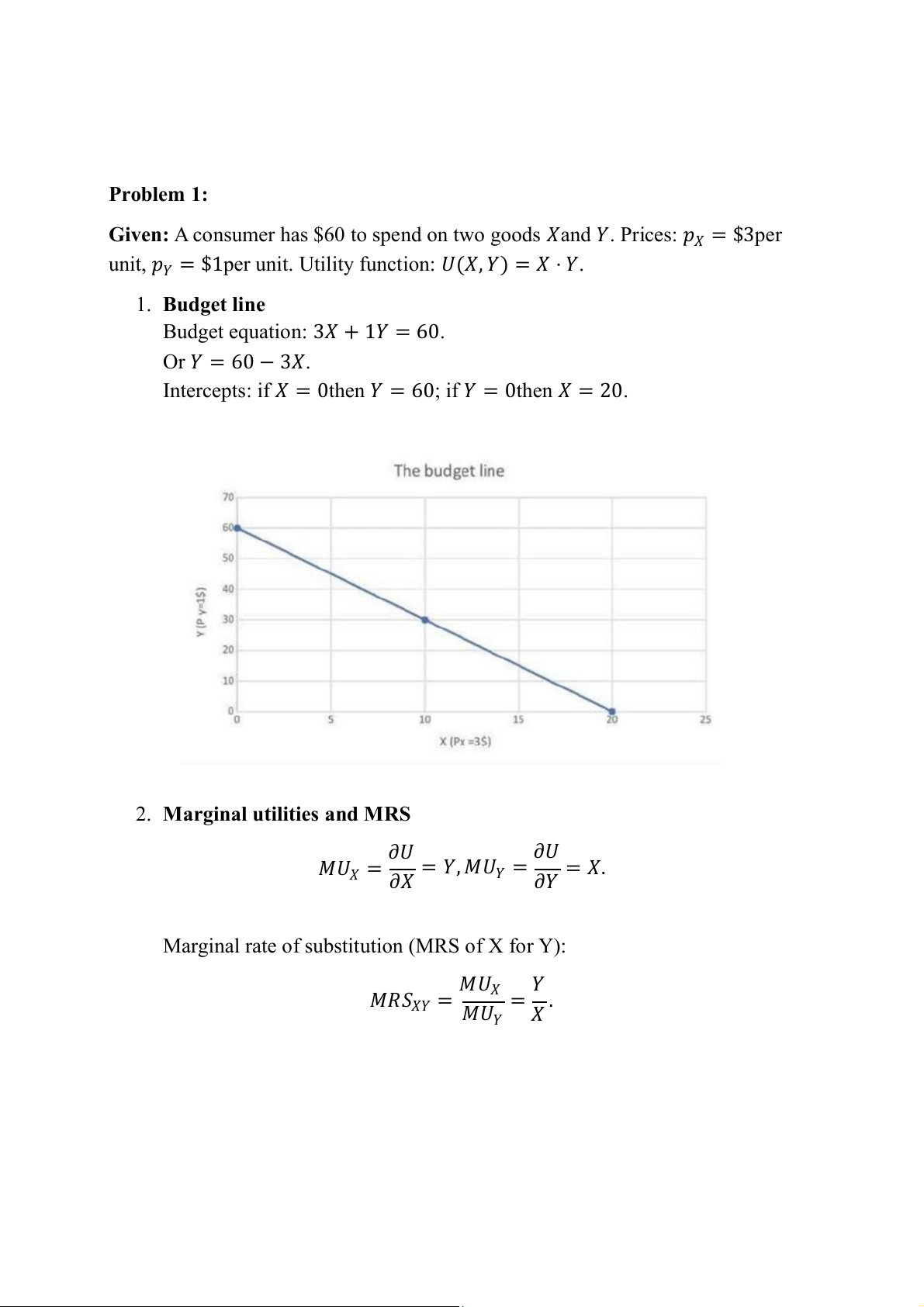
unit, 𝑝𝑌 = $1per unit. Utility function: 𝑈(𝑋, 𝑌) = 𝑋 ⋅ 𝑌. 1. Budget line
Budget equation: 3𝑋 + 1𝑌 = 60. Or 𝑌 = 60 − 3𝑋.
Intercepts: if 𝑋 = 0then 𝑌 = 6 ; 0 if 𝑌 = 0then 𝑋 = 20. 2. Marginal utilities and MRS ∂𝑈 ∂𝑈 𝑀𝑈 = 𝑌, 𝑀𝑈 𝑋 = = 𝑋. ∂𝑋 𝑌 = ∂𝑌
Marginal rate of substitution (MRS of X for Y): 𝑀𝑈𝑋 𝑌 𝑀𝑅𝑆𝑋𝑌 = = . 𝑀𝑈𝑌 𝑋 3. Utility maximization 𝑝 3
Interior first-order condition: 𝑀𝑅𝑆 𝑋 𝑋𝑌 = = = 3. 𝑝𝑌 1 𝑌
So = 3 ⇒ 𝑌 = 3𝑋. Substitute into budget: 𝑋
3𝑋 + 3𝑋 = 60 ⇒ 6𝑋 = 60 ⇒ 𝑋∗ = 10. Then 𝑌∗ = 3 ⋅ 10 = 30. Problem 2:
Given: Monthly budget = 1,000,000 VND. Meat 𝑋price 𝑝𝑋 = 20,000VND/kg.
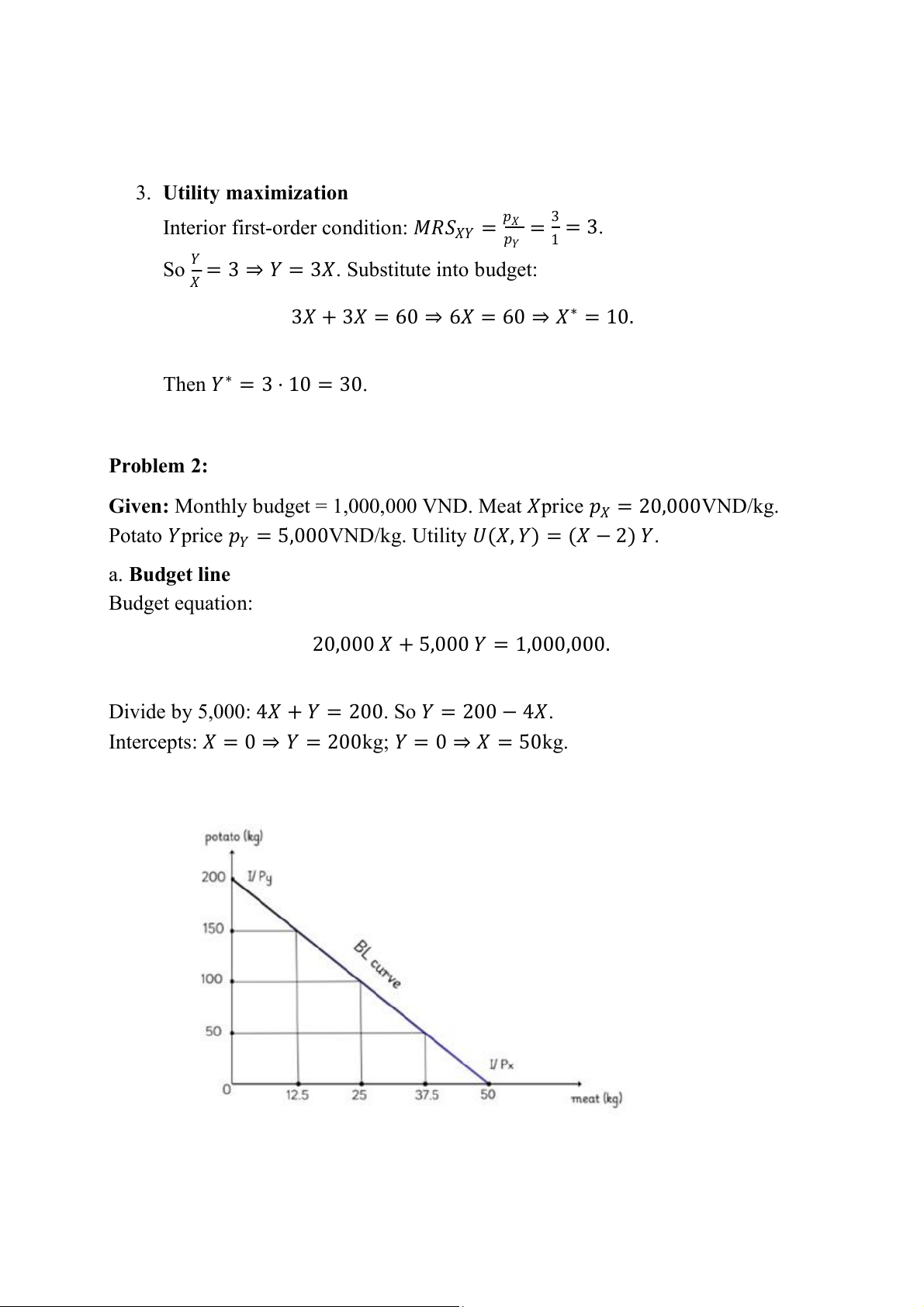
Potato 𝑌price 𝑝𝑌 = 5,000VND/kg. Utility 𝑈(𝑋, 𝑌) = (𝑋 − 2) 𝑌. a. Budget line Budget equation:
20,000 𝑋 + 5,000 𝑌 = 1,000,000.
Divide by 5,000: 4𝑋 + 𝑌 = 20 . 0 So 𝑌 = 200 − 4𝑋.
Intercepts: 𝑋 = 0 ⇒ 𝑌 = 200kg; 𝑌 = 0 ⇒ 𝑋 = 50kg.
b. Marginal utilities, MRS and optimum ∂𝑈 ∂𝑈 𝑀𝑈𝑋 = = 𝑌, 𝑀𝑈 = 𝑋 − 2. ∂𝑋 𝑌 = ∂𝑌 𝑀𝑈𝑋 𝑌 𝑀𝑅𝑆𝑋𝑌 = = . 𝑀𝑈𝑌 𝑋 − 2 𝑝 20,000 Set 𝑀𝑅𝑆 = 𝑋 = = 4. So 𝑝𝑌 5,000 𝑌
= 4 ⇒ 𝑌 = 4(𝑋 − 2) = 4𝑋 − 8. 𝑋 − 2
Substitute into budget 4𝑋 + 𝑌 = 200:
4𝑋 + (4𝑋 − 8) = 200 ⇒ 8𝑋 − 8 = 200 ⇒ 8𝑋 = 208 ⇒ 𝑋∗ = 26.
Then 𝑌∗ = 4(26 − 2) = 4 ⋅ 24 = 96.




