



Preview text:
Microeconomics Assignment Presentation 2 Team 8 Nguyen Quang Ha Exercise 1: 1)
The demand equation: P = a - bQd = 300 – 0.2Qd
The supply equation: P = c + dQs = 40 + 0.2Qs Equilibrium price: ($) Equilibrium quantity: Q= Qd = Qs = (units) 2) At the price of $200: - The Quantity Demanded: 500 units - The Quantity Supplied: 800 units The surplus is 300 units At the price of $110: - The Quantity Demanded: 950 units - The Quantity Supplied: 350 units The shortage is 600 units 3)
a) Suppose the supply of fridge is constant, I think if the price of electricity
increases, the demand of fridge will decrease. This increase is considered a non-
price factor (price of complementary goods), since we need electricity to run a fridge. b)
- Circumstances 1: Quantity Demanded increases by 300 units Prices 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 Demande d Quantity 300 400 500 600 700 800 Supplied
+ The new demand equation: P = a - bQd = 360 – 0.2Qd
+ The supply equation: P = c + dQs = 40 + 0.2Qs
The new equilibrium price: p= 200 ($)
The new equilibrium quantity: Q=800 (units)
- Circumstances 2: Quantity Demanded decreases by 300 units Prices 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity 700 600 500 400 300 200 Demande d Quantity 300 400 500 600 700 800 Supplied
+ The new demand equation: P = a - bQd = 240 – 0.2Qd
+ The supply equation: P = c + dQs = 40 + 0.2Qs
The new equilibrium price: p= 140 ($)
The new equilibrium quantity: Q= 500 (units) 4)
The Increase in the tax causes a decrease in supply – non-price factor (Government policies).
The new supply equation: Ps = c + dQs = 50 + 0.2Qs
The new equilibrium price: p= 175 ($)
The new equilibrium quantity: Q= 625 (units)
5) Government subsidy of $10/unit causes increase in supply –non-price factor (Government policies).
The new supply equation: Ps = c + dQs = 30 + 0.2Qs
The new equilibrium price: p= 165 ($)
The new equilibrium quantity: Q= 675 (units) Exercise 2:
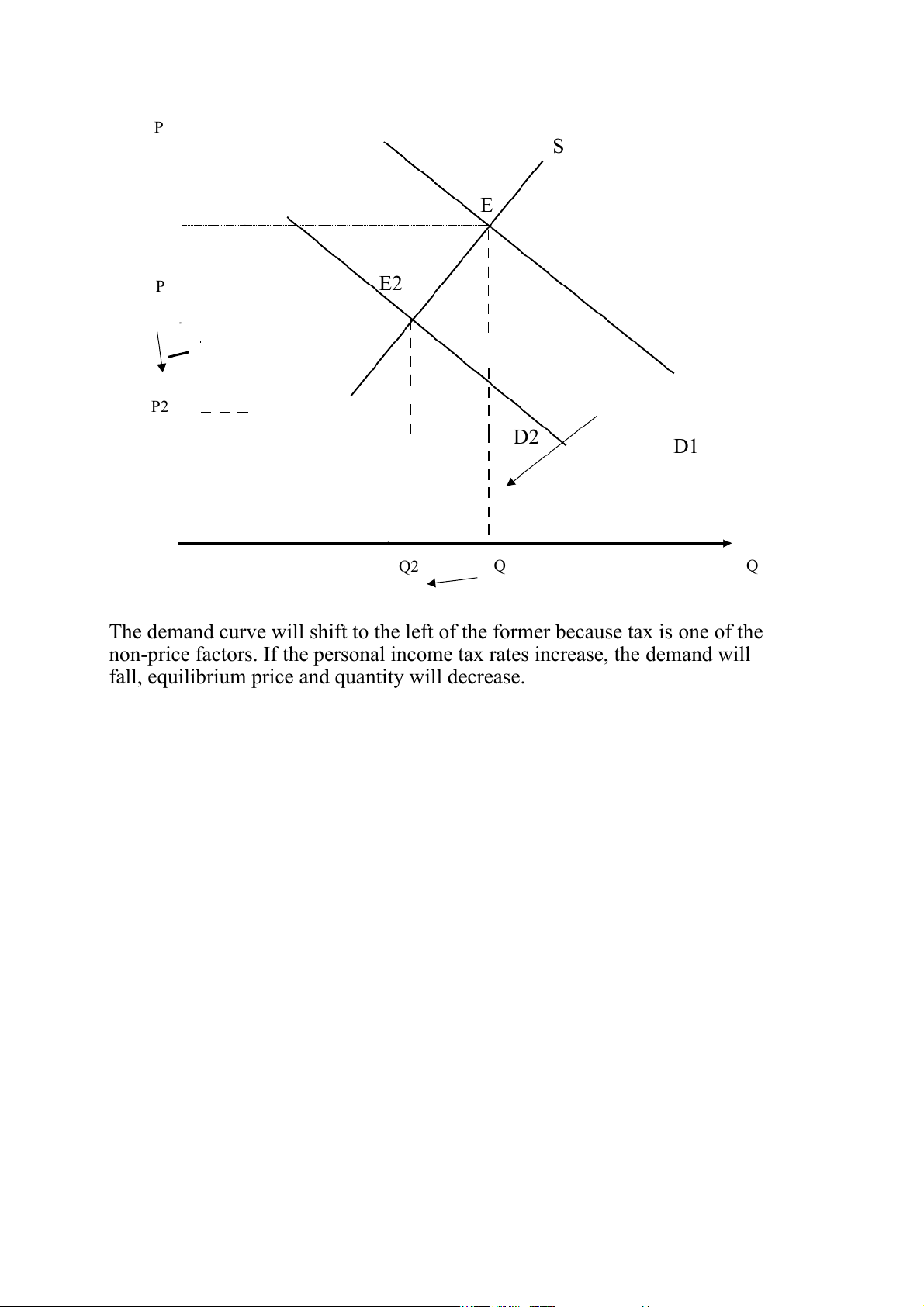
1) An increase in Vietnamese personal income tax rates: P S E P E2 P2 D2 D1 Q2 Q Q
The demand curve will shift to the left of the former because tax is one of the
non-price factors. If the personal income tax rates increase, the demand will
fall, equilibrium price and quantity will decrease.
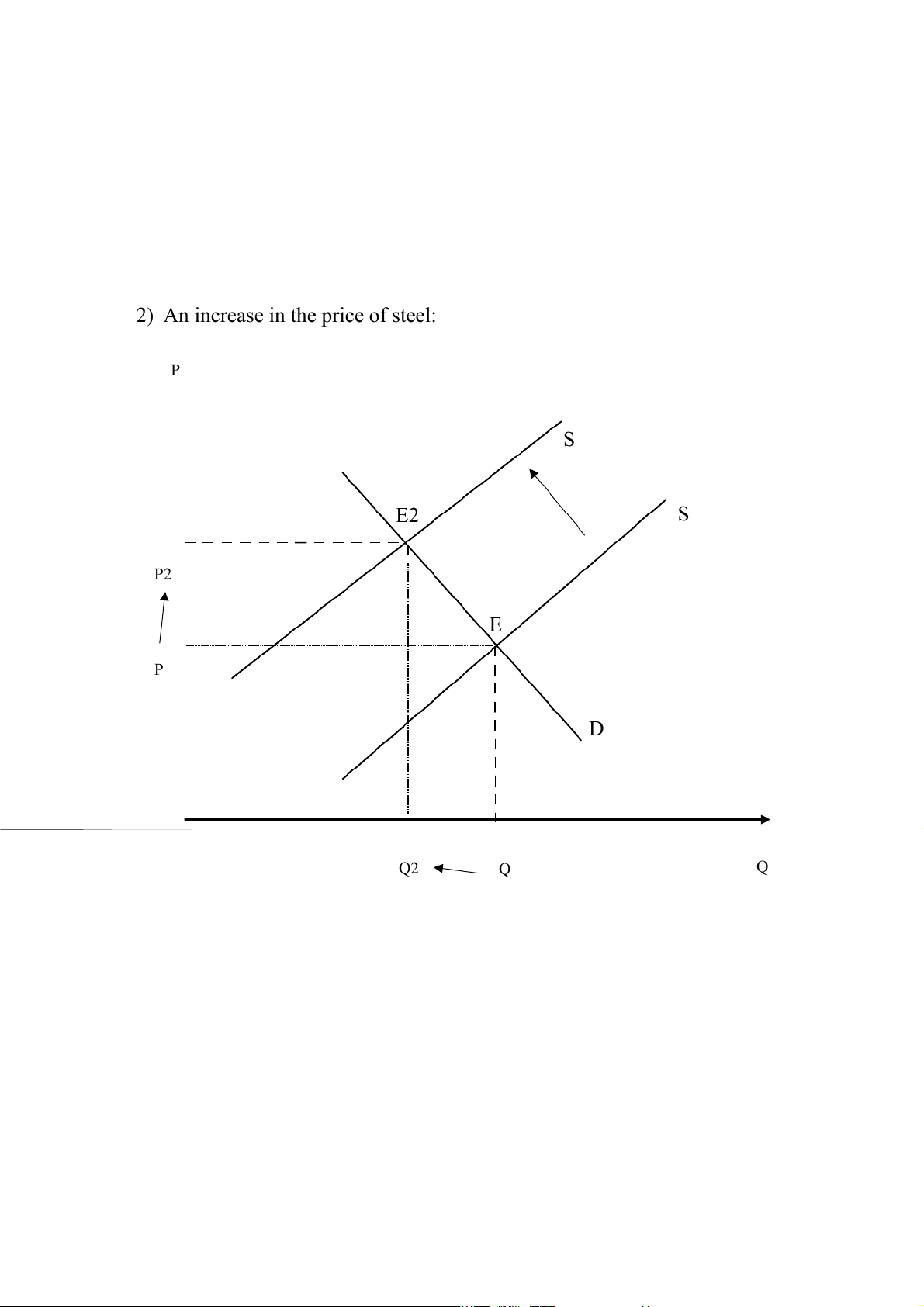
2) An increase in the price of steel: P S E2 S P2 E P D Q2 Q Q
The supply curve will shift to the left of the former because when the input price
increases, the supply price will increase, and the supply quantity will decrease.
This will cause an effect on the new equilibrium price and quantity.
3) An improvement in technology in motor vehicle production at the same time
as a recession hits the Vietnamese economy.
The improvement in technology in motor vehicle production helps increase the supply quantity.
However, there is a recession in the Vietnamese economy.
Therefore, the price needs to be decreased to balance with the market, and the demand will decrease.
The supply curve will shift to the right and the demand curve will shift to the left.
In this case, the equilibrium price and quantity move to the lower left of the former one. P S1 S2 E1 P S2’ E2 P2 E2’ D1 D2 Q2 Q2’ Q1 Q




