Preview text:
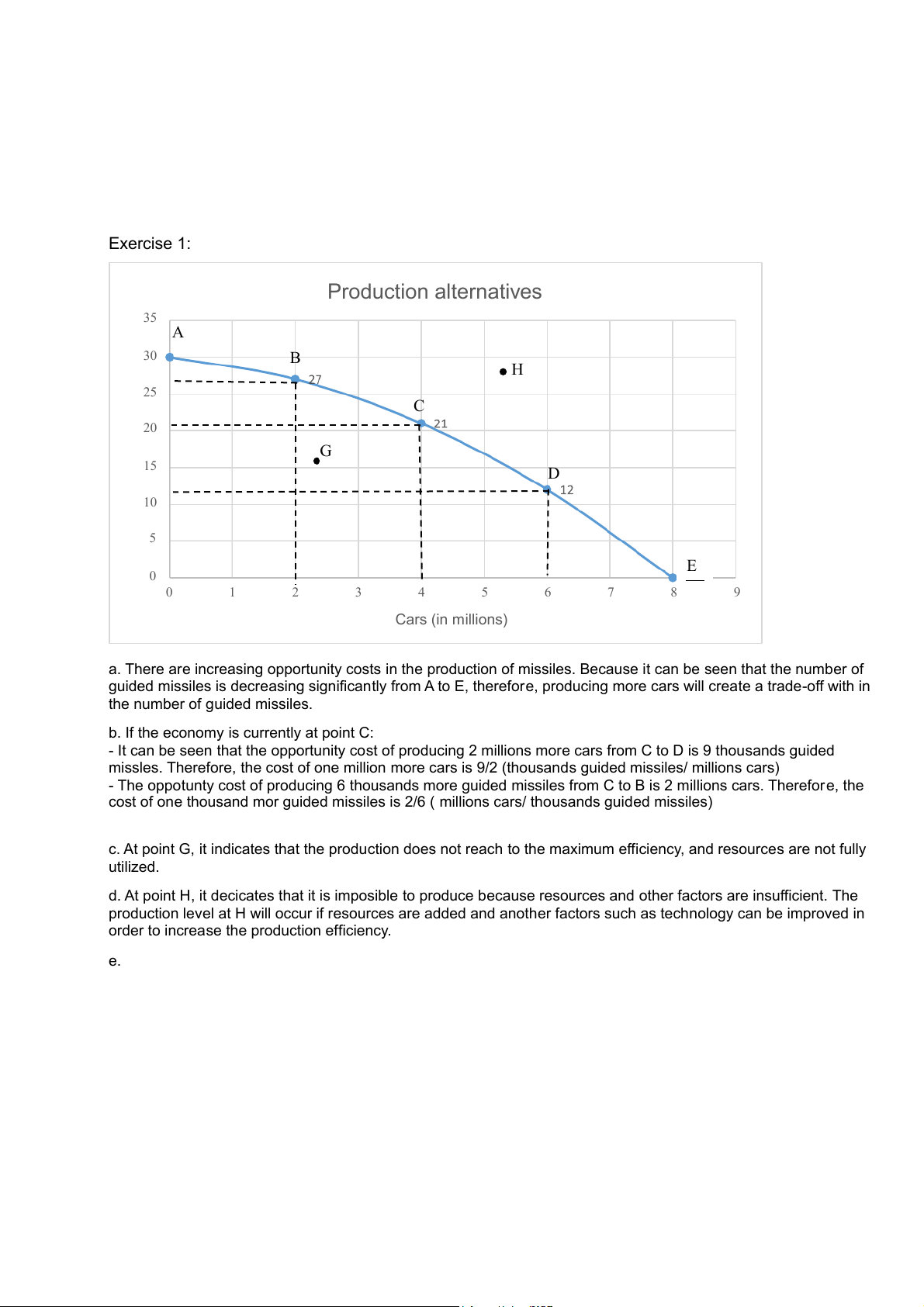
Exercise 1: Production alternatives 35 A ) 30 B H 25 C thousands 20 es(in G 15 D 10 Guided missil 5 E 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Cars (in mil ions)
a. There are increasing opportunity costs i
n the production of missiles. Because it can be seen that the number of
guided missiles is decreasing significantly from A to E, therefore, producing more cars wil create a trade-off with in
the number of guided missiles.
b. If the economy is currently at point C:
- It can be seen that the opportunity cost of producing 2 mil ions more cars from C to D is 9 thousands guided
missles. Therefore, the cost of one mil ion more cars is 9/2 (thousands guided missiles/ mil ions cars)
- The oppotunty cost of producing 6 thousands more guided missiles from C to B is 2 mil ions cars. Therefore, the
cost of one thousand mor guided missiles is 2/6 ( mil ions cars/ thousands guided missiles)
c. At point G, it indicates that the production does not reach to the maximum efficiency, and resources are not ful y utilized.
d. At point H, it decicates that it is imposible to produce because resources and other factors are insufficient. The
production level at H wil occur if resources are added and another factors such as technology can be improved in
order to increase the production efficiency. e. -
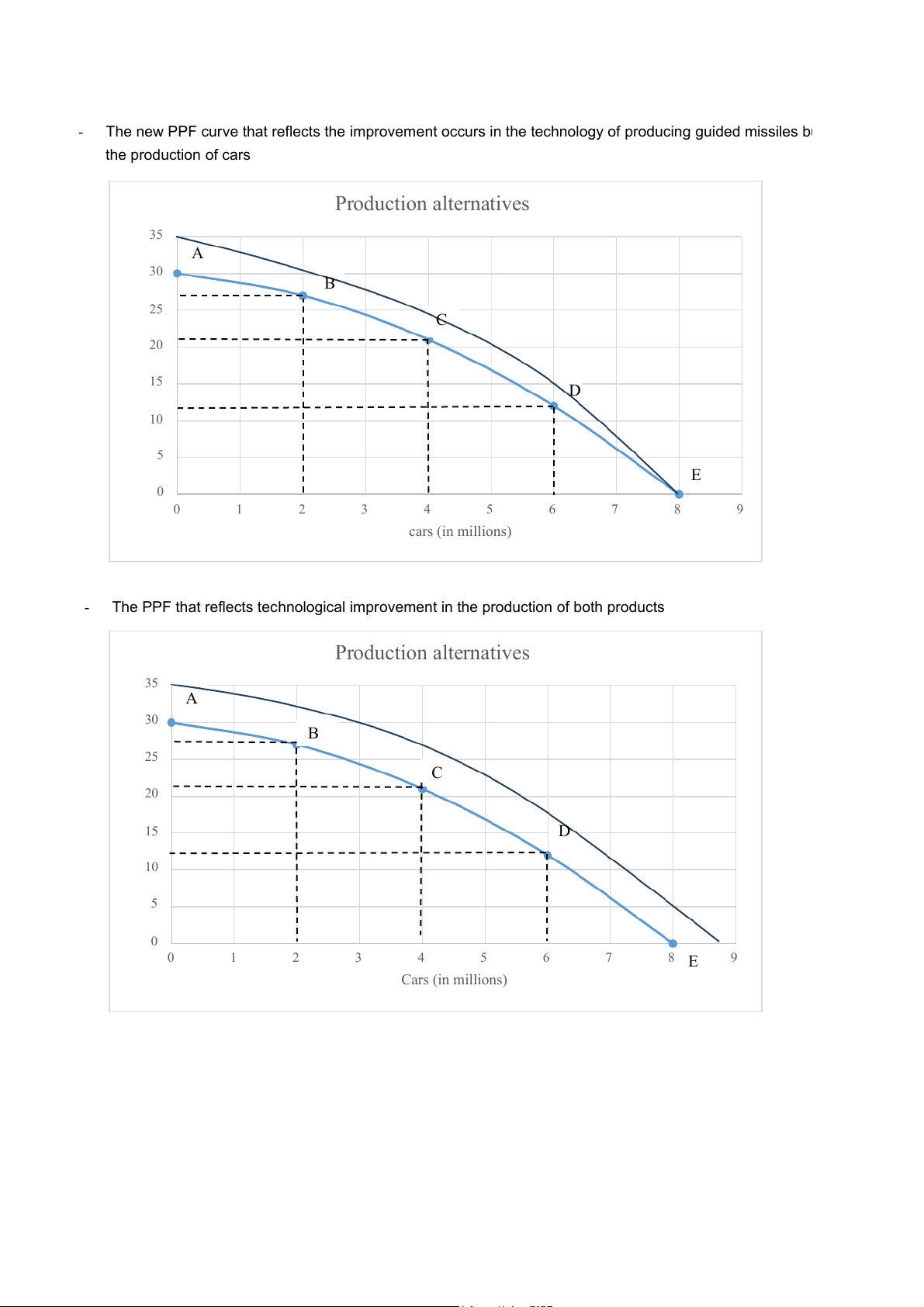
The new PPF curve that reflects the improvement occurs in the technology of producing guided missiles bu the production of cars Production alternatives 35 A 30 B 25 C 20 15 issiles(in thousands) D 10 uided m G 5 E 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 cars (in millions)
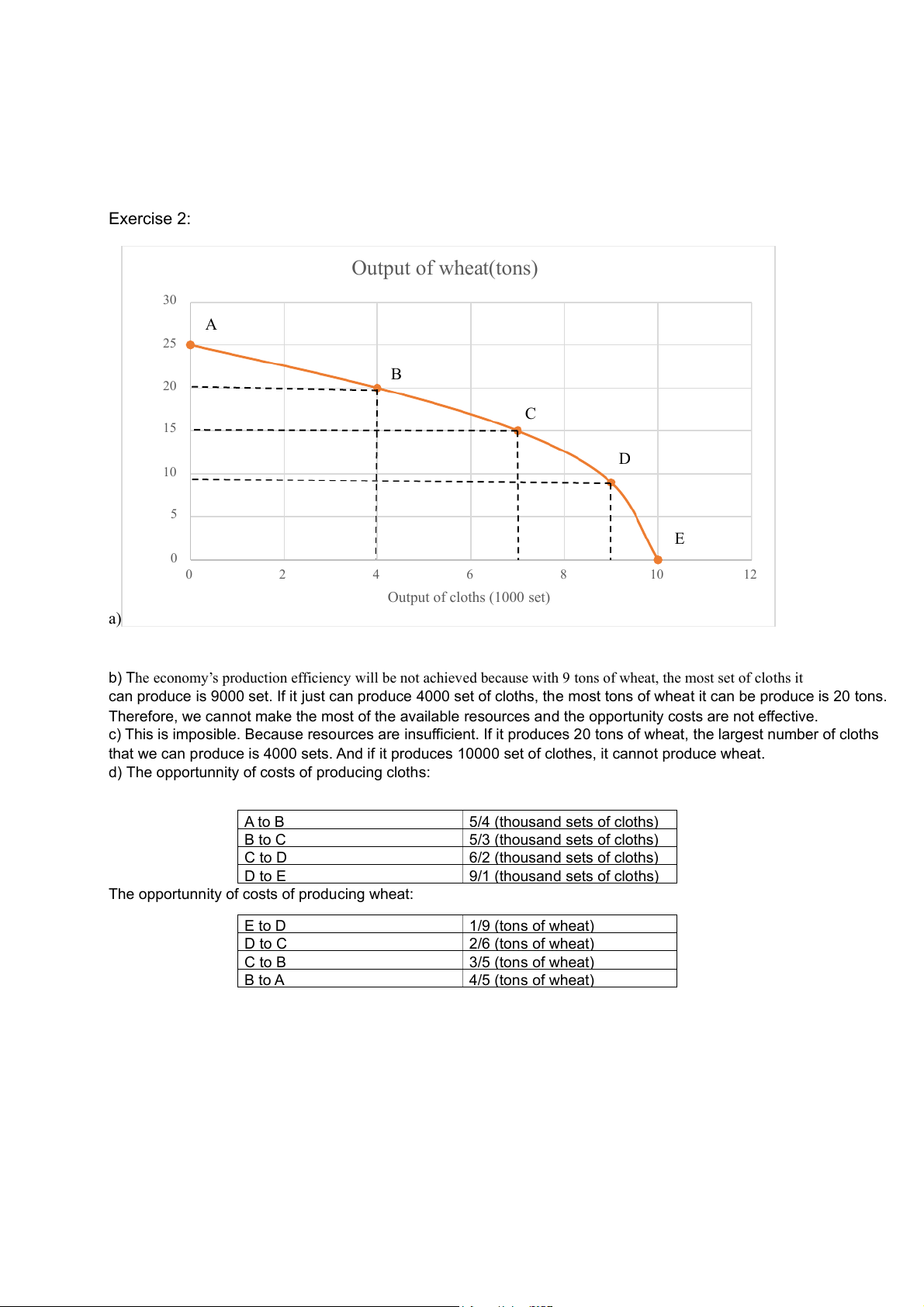
- The PPF that reflects technological improvement in the production of both products Production alternatives 35 A 30 B 25 C 20 15 D issiles(in thousands) 10 uided m G 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E Cars (in millions) Exercise 2: Output of wheat(tons) 30 A 25 B 20 C heat (tons) 15 D 10 utput of w O 5 E 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Output of cloths (1000 set) a)
b) The economy’s production efficiency will be not achieved because with 9 tons of wheat, the most set of cloths it
can produce is 9000 set. If it just can produce 4000 set of cloths, the most tons of wheat it can be produce is 20 tons.
Therefore, we cannot make the most of the available resources and the opportunity costs are not effective.
c) This is imposible. Because resources are insufficient. If it produces 20 tons of wheat, the largest number of cloths
that we can produce is 4000 sets. And if it produces 10000 set of clothes, it cannot produce wheat.
d) The opportunnity of costs of producing cloths: A to B 5/4 (thousand sets of cloths) B to C 5/3 (thousand sets of cloths) C to D 6/2 (thousand sets of cloths) D to E 9/1 (thousand sets of cloths)
The opportunnity of costs of producing wheat: E to D 1/9 (tons of wheat) D to C 2/6 (tons of wheat) C to B 3/5 (tons of wheat) B to A 4/5 (tons of wheat)




