










Preview text:
From the 2014 Administration
This Exam is provided by the College Board for AP Exam preparation.
Teachers are permitted to download the materials and make copies to
use with their students in a classroom setting only. To maintain the
security of this exam, teachers should collect all materials after their
administration and keep them in a secure location. Ex E ams m ay n o n t be po p s o te t d on s ch c oo o l o l r personal we bs b it i es e , n or electronically y redistributed fo f r a ny re r a e s a o s n o .
n Further distribution of these materials
outside of the secure College Board site disadvantages teachers who
rely on uncirculated questions for classroom testing. Any a dditional
distribution is in violation of the College Board’s copyright policies and
may result in the termination of Exam access for your school as well
as the removal of access to other o
nline services such as the AP
Teacher Community and Online Score Reports. St S u t dent t An A swer S he h et f or r th t e Mu M lt l ip i le-Cho h ice Se S ctio i n
Use this section to capture student responses. (Note that the following
answer sheet is a sample, and may differ from one used in an actual exam.) R E r 0 1 2 3 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E 4 5 6 7 8 9 e ID a e d E IN V E H Y L L ra O D 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 T 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E G N R O g P C IR V th A . O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 l B T E 9 r in o P G ay F L e o D N 0 1 2 3 t in g O E E n E R D sch t ye th lo h 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 T ar A th th pr ay ug ep ct ov ec R o o th th 2 ig A Jan Feb M A M Jun Jul A S O N D U R N 9 10 11 1 N h n G 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 o . D . C T M K N E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 L K O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 O B 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 . r E E e E u IC R 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 C th N yo O O E N B in e ive H 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 d M O e th ce -C U te E LY re 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 list L N e ica L N d d t to IP R n e a t) IA 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 T O U co in L A m e w l R a O le U g ck, E E Y a u rt. e k 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 l N o S lle R o try E o n t P t yo p b o . M te F D A u ch ity ta o IV co n a e re a o S N S C S C E T e e m IS d th re a E C R th tu e N T L T 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E O g g e I B H n S sco g try P T T A R lle n si P P lle te u m n M R E E M 2 E U A co A o ity o 1 2 3 ta 4 5 A E U 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 O C C S C a A P 1 D R X T IM T O T O x tio S T E c M E E . E 6 7 8 9 0 E Y 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A 11 C R D E 1 L L G L E e O O O E S P O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 L C C 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 P M O O L E H S H G A m E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 O C O P E C 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 T C S A L A ay . C L . S (fro D D 0 1 2 3 O J 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 M M C A X th 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 n . E o D M 0 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 N R O Y l) E a 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 B 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 H IT n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 D R N P R M E L tio 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 U U 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B A C p N E M N E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 P D U 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 (O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 IO S O R A N T L E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 R C E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 IA B U A N N C M O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 R O 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 R H E U T . Y P T . S N 9 C 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 I. A IN L 8 7 6 5 4 Y I I J L e e A B C D E F G H K N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z 3 L M M W ts, 2 th n N 2 g n re A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 1 a ervices B O tio ill seal th P letin p d S I p J L – n IL A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z d O m a ard C s. I w te ts o n n I n N A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – 2 e e B ra d E estio tu lleg A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – G u W S o P rs n e after co P : 1 y C tte e tio . 2 F I J L T Z – n ice q r A e A B C D E G H K M N O P Q R S U V W X Y d c o b o y tim fo u O L tio 2 C d p tin ved A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – e te W O N rm le-ch lle ro a t 1 o R u p D E F e ltip irs A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – e 1 u e at an n B 4 S F reap F U e m yo -1 3 p — A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – : an 1 e 0 een rm ith m A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – o F 9 see th e 2 a th ave b s w t N n s. in A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – 8 n W ed irs tio e else to n estio l F I u tlin ly if I h A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – 7 n lica W o u a p o g p n e a l A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 6 w ese q L e ) Y g e L k res as o lle N u b c A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 5 ill allo ss th ter, etc.) o u a a . r co O ced p u I r E iscu M J L – e 4 ro m A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z yo t P S b re, I w p n A t d r L n m o d U r o X A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – u 3 sco e, co a e e L P e N ill n p b d E O tim p I J n y A F T Z – 2 Y r., II. A B C D E G H K L M N O P Q R S U V W X Y O licies an ed tu tio I w o d ill a m R H f m , J c d S s A B C D E F H I J K L N P R S T U V X Y Z – C e 1 ’s p G M O Q it w u E e W S S ity o s , an V m h a ram : ., exten I J L e N p A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – e so g E m o m ro a P e valid T tro a d P (fro I J – s (e.g F L T Z l n A B C D E G H K M N O P Q R S U V X Y th W N P A s A rs n a d o m to g A p tte xa an e A I atio A B C D E F H J K L N P R S T U V X Y Z – r le e G M O Q W E th E d u o L R it a asked m yo A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – n m W e exam en ree to m t 15 IS ig A h O S H f th ag irs A B C D E F H I J K L N P R S T U V X Y Z – T d IS F G M O Q W T acco ilities. E g H E M G E 8 rity o klet w f an A B C D E F H I J K L N P R S T U V X Y Z – o isab — G O Q T E t M W IN H 9 o M e D E S 8 are o R A I A S testin e m I 3 T a A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z – e secu g ith U W M U R ice b e N 7 E T A E th o aw G sin L 7 ts w A h t N L I X u A s A B E F J K L P S T V X Y Z – a C D G H M N O Q R U W IN W tain g en N P E S le-ch . I am S G K n in d P N ain d tu IG l L I M r E a A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z – A T A m ltip u clu r S g O . S e . L e . A To m sectio in fo I J L C A B L A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z H w 4 s 1 n 0 A 2 99735-00657• UNLWEB114 Q3779/1-4 PAGE 2
COMPLETE THIS AREA AT EACH EXAM (IF APPLICABLE)
O. SURVEY QUESTIONS — Answer the survey questions in the AP Student Pack. Do not put responses to exam questions in this section. 1 A B C D E F G H I 4 A B C D E F G H I 7 A B C D E F G H I 2 A B C D E F G H I 5 A B C D E F G H I 8 A B C D E F G H I 3 A B C D E F G H I 6 A B C D E F G H I 9 A B C D E F G H I
P. LANGUAGE — Do not complete this section unless instructed to do so.
If this answer sheet is for the French Language and Culture, German Language and Culture, Italian Language and Culture, Spanish Language
and Culture, or Spanish Literature and Culture Exam, please answer the following questions. Your responses will not affect your score.
1. Have you lived or studied for one month or more in a country where the language of the
2. Do you regularly speak or hear the language at home?
exam you are now taking is spoken? Yes No Yes No QUESTIONS 1–75
Indicate your answers to the exam questions in this section (pages 2 and 3). Mark only one response per question.
If a question has only four answer options, do not mark option E. Answers written in the multiple-choice booklet will not be scored.
You must use a No. 2 pencil and marks must be complete. Do not use a mechanical pencil. It A C D EXAMPLES OF COMPLETE MARK
is very important that you fill in the entire circle darkly and completely. If you change your response,
INCOMPLETE MARKS A B C D
erase as completely as possible. Incomplete marks or erasures may affect your score. 1 A B C D E 26 A B C D E 51 A B C D E 2 A B C D E 27 A B C D E 52 A B C D E 3 A B C D E 28 A B C D E 53 A B C D E 4 A B C D E 29 A B C D E 54 A B C D E 5 A B C D E 30 A B C D E 55 A B C D E 6 A B C D E 31 A B C D E 56 A B C D E 7 A B C D E 32 A B C D E 57 A B C D E 8 A B C D E 33 A B C D E 58 A B C D E 9 A B C D E 34 A B C D E 59 A B C D E 10 A B C D E 35 A B C D E 60 A B C D E 11 A B C D E 36 A B C D E 61 A B C D E 12 A B C D E 37 A B C D E 62 A B C D E 13 A B C D E 38 A B C D E 63 A B C D E 14 A B C D E 39 A B C D E 64 A B C D E 15 A B C D E 40 A B C D E 65 A B C D E 16 A B C D E 41 A B C D E 66 A B C D E 17 A B C D E 42 A B C D E 67 A B C D E 18 A B C D E 43 A B C D E 68 A B C D E 19 A B C D E 44 A B C D E 69 A B C D E 20 A B C D E 45 A B C D E 70 A B C D E 21 A B C D E 46 A B C D E 71 A B C D E 22 A B C D E 47 A B C D E 72 A B C D E 23 A B C D E 48 A B C D E 73 A B C D E 24 A B C D E 49 A B C D E 74 A B C D E 25 A B C D E 50 A B C D E 75 A B C D E
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA PAGE 3 QUESTIONS 76–120
Be sure each mark is dark and completely fills the circle. If a question has only four answer options, do not mark option E. 76 A B C D E 91 A B C D E 106 A B C D E 77 A B C D E 92 A B C D E 107 A B C D E 78 A B C D E 93 A B C D E 108 A B C D E 79 A B C D E 94 A B C D E 109 A B C D E 80 A B C D E 95 A B C D E 110 A B C D E 81 A B C D E 96 A B C D E 111 A B C D E 82 A B C D E 97 A B C D E 112 A B C D E 83 A B C D E 98 A B C D E 113 A B C D E 84 A B C D E 99 A B C D E 114 A B C D E 85 A B C D E 100 A B C D E 115 A B C D E 86 A B C D E 101 A B C D E 116 A B C D E 87 A B C D E 102 A B C D E 117 A B C D E 88 A B C D E 103 A B C D E 118 A B C D E 89 A B C D E 104 A B C D E 119 A B C D E 90 A B C D E 105 A B C D E 120 A B C D E
For Students Taking AP Biology
Write your answer in the boxes at the top of the griddable area and fill in the corresponding circles.
Mark only one circle in any column. You will receive credit only if the circles are filled in correctly. 121 122 123 124 125 126 / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / – . . . . . – . . . . . – . . . . . – . . . . . – . . . . . – . . . . . 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 ETS USE ONLY R W O R W O SELECTED MEDIA EXAMS OTHER EXAMS PT02 TOTAL PT03
Subscore (if applicable) PT04
Subscore (if applicable) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Exam 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Exam 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
© 2013 The College Board. College Board, AP, Student Search Service and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board.
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA ® . l to e o 4 E id y f e u o a o l a s t U E IC tin V u o e n m o ia c h n O g r le e G R s y n c o le Y a e n e l sch re m a ly a u g d iva e a g A E n r ll c O n re n ra rm fi u s e u M n u re a rica g o P S g fo o wi D e L q l g e H d l d ro io e in n y v E r la Isl m E o a C r e p a ly re , we . e o r d n n G c A V r d fi a fessi e o R ip to s p e o th tive a ro h n p p o tio A g n E a o a ci e A itie u d ic N U n e a a tin l m sch ssi d rs tio n s n rv a u a L ? m N o e -ye r-ye r p o E la a e G a g a rica o lo d o u o fe to r a rm T r P n N d n e r L ro l C S o rm rtu s s fo N S n sa sk l ip te a T h c fo o we is A e o m o IO o e r fo E la n o l d r tw a r p st p u s a r la rica T o sch r tra g o u o N s p e r in A o e o o L e d d le h r in n th tin lle o ? u B t th n A o a r A m te r’s r P E n u l o H lish lish th rica ig a ra a lik n in u E C ss a te s m g g o o e ca lo o D a o u yo W o sch h A L e co g a s n n’t a te e g e IC n n b n C n U e m e sch e ci e e u IP U tio e t y yo o a Y X F O E E a A A n exi d n d Z T a H ia ic, h g s tio in D m si m ch m e a d ip E N A c ld d n rm u id n ra o ig u o sso a o ra /R n a . S lle u u v K r M E q u o o fo rtic . S . W Y In a frica ica L G S H B S A B S G U d a ro / Co re e W in If y p p W n o IT si r A n isp R A e an V , A o T her di IC rica ca r H r e n rto e ite e N ot uar a ck xi M Femal e G N Y 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 e th h th E m si la u R H A A B M P O W O R / T T A e an N E 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 her al di U D . E . P Fat M uar O O X Y G C C 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 r) e b A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / m u N A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / try n . u t ID o n n E A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / C m e D d lu o O A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / tu t c C W a L (S A I J L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / R th T A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z S IE rid O A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / IF t g o P T n R N A B C D E F o G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / O W E ; d IP ID ox Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 T b k N n A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z E la D b A B C D E F U G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V a W X Y Z T g r rto e in e v A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V . S W X Y Z T A I V Y u ico A E P th a V W W W W P R A A A O ce S n le vi y A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z . ro b d s r P s e A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Y H K R A I C D N X T A d o re N O O O P R S S T T U V vi te d d ro ta A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z p S r a s u o A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z I N O S T C D E H J M V y ace . M M M M M N N N N N N N in sp E e A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z c e C a p th N s A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z I S Y A A D E in a H IA ID IL IN K K L M M M O ss te A B E F I J K L P S T V X Y Z re Y C D G H M N O Q R U a W d L ic d d N A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z K L R Z A O T C E L A r a . In A A A A C C C D D F G u n O E m A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z T f yo A lu Y A o T E IT S r o e r c C A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z R e d A p A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ain le m IS irc I re c J L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / s H A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z e e T n o A B E F I J K L P S T V X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / E C D G H M N O Q R U W ly fill in a rint th T n , p o I / E A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Q d L m ity ill in an C P A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / Ite . F R M k c m I a J / d in O A B C D E F G H K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 e d Ite C t P rd n vi in a e e A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / e o d ro p th tu B s circl e in S ) A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / e g s P e tc. ace lle o lici r A A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / o u r, e sp C o e e e p y b A B C D E F e G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V fill in th W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / th n th m m e g th u t in tin ith fro I L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / fi n . s t n A B C D E F G H J K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z t w ts n n o n, th ra n e n ce tio A B C D E F G H I J K L re M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / s ca n a ia u re g rtm a v P a oe a rd d re p A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / d u o n b s yo b cc , a ss , yo a a e s a a ts A B C D E F G H I J K L N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / re s e ss n m M W s d e a il in d rcl d re dre a d ci t n A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / r a d m tu d e u ny S a re a r e P e ail a A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / u If yo m m r A th r, st yo e e I / r e fo b A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 u se Us u tin m yo u lle A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V to W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / g in n u S t n Y d o B e S I / E L vi 4 re A B C D E F G H J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 E ID N ro issi -13 R p st S O rm 1 e I J L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / y 0 D T e d A B C D E F G H K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z S B p 2 D u U E cl A B C D E F T A G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / O S G (in S TA S S T F I J L T Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / IN S E S A B C D E G H K M N O P Q R S U V W X Y N R E D IL E R E D A B A C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / D D W U IT D D M T N A R A A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / S U T IL U E R E A O E A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 / O H ss M R T . Y re T . F d d . E Q S A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 R A T Sec S ti t on o I: I Mu M lt l ip i le- l Ch C oi o ce Q uestio i ns
This is the multiple-choice section of the 2014 AP exam.
It includes cover material and other administrative instructions
to help familiarize students with the mechanics of the exam.
(Note that future exams may differ in look from the following content.)
AP® Microeconomics Exam
SECTION I: Multiple Choice 2014
DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Instructions
Section I of this exam contains 60 multiple-choice questions. Fil in only the circles for Total Time
numbers 1 through 60 on your answer sheet. 1 hour, 10 minutes Number of Questions
Indicate al of your answers to the multiple-choice questions on the answer sheet. No 60
credit wil be given for anything written in this exam booklet, but you may use the booklet Percent of Total Score
for notes or scratch work. After you have decided which of the suggested answers is best, 66.67%
completely fil in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet. Give only one answer to Writing Instrument
each question. If you change an answer, be sure that the previous mark is erased Pencil required
completely. Here is a sample question and answer.
Use your time ef ectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not
spend too much time on any one question. Go on to other questions and come back to
the ones you have not answered if you have time. It is not expected that everyone wil
know the answers to al of the multiple-choice questions.
Your total score on the multiple-choice section is based only on the number of questions
answered correctly. Points are not deducted for incorrect answers or unanswered questions. Form I Form Code 4JBP6-S 34
The inclusion of source material in this exam is not intended as an
endorsement by the College Board or ETS of the content, ideas, or
values expressed in the material. The material has been selected by
the economics faculty who serve on the AP Microeconomics
Development Committee. In their judgment, the material printed
here reflects various aspects of the course of study on which this
exam is based and is therefore appropriate to use to measure the
skills and knowledge of this course. -2- MICROECONOMICS Section I Time—70 minutes 60 Questions
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or
completions. Select the one that is best in each case and then fill in the corresponding circle on the answer sheet.
1. Improvements in technology for producing all
4. Assume that ice cream is a normal good. If the goods must result in
price of ice cream decreases, the substitution
(A) an inward shift in the production possibilities
effect and the income effect will lead to which of curve
the following changes in ice cream consumption?
(B) an outward shift in the production possibilities Substitution Effect Income Effect curve (A) Increase Decrease
(C) a flatter production possibilities curve
(D) a steeper production possibilities curve (B) Increase Increase
(E) greater unemployment of labor (C) Increase No change (D) Decrease Increase
2. The quantity of peanuts supplied increased from (E) Decrease No change
40 tons per week to 60 tons per week when the
price of peanuts increased from $4 per ton to
5. Short-run marginal costs eventually increase because of the effects of
$5 per ton. The price elasticity of supply for
peanuts over this price range is
(A) increasing marginal product (A) elastic
(B) diminishing marginal product (B) inelastic (C) diseconomies of scale (D) economies of scale (C) unit elastic (D) perfectly elastic (E) increasing fixed costs (E) perfectly inelastic
6. If a government eliminated an effective price floor
3. Which of the following best describes
in a market, all of the following would occur the law of demand? EXCEPT:
(A) The price of a good increases when
(A) The surplus would be eliminated. (B) The price would decrease.
the demand for the good increases.
(B) The price of a good decreases when
(C) The quantity supplied would decrease.
the supply of the good decreases.
(D) The quantity demanded would increase.
(E) The supply of the good would increase.
(C) When the price of a good increases, its demand decreases.
(D) When the price of a good decreases,
its quantity demanded increases.
(E) Demand creates its own supply.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -3-
7. Which of the following must be true if a firm is
experiencing economies of scale? (A) All costs are explicit.
(B) Long-run average total cost decreases as the firm’s output increases.
(C) Economic profits decrease as the firm’s output increases.
(D) Long-run average total cost remains constant
as the firm’s output decreases.
(E) Proportionate increases in inputs result in
less-than-proportionate increases in output.
8. Compared to a perfectly competitive industry
with the same demand and cost curves, a
monopoly’s price and output will be which
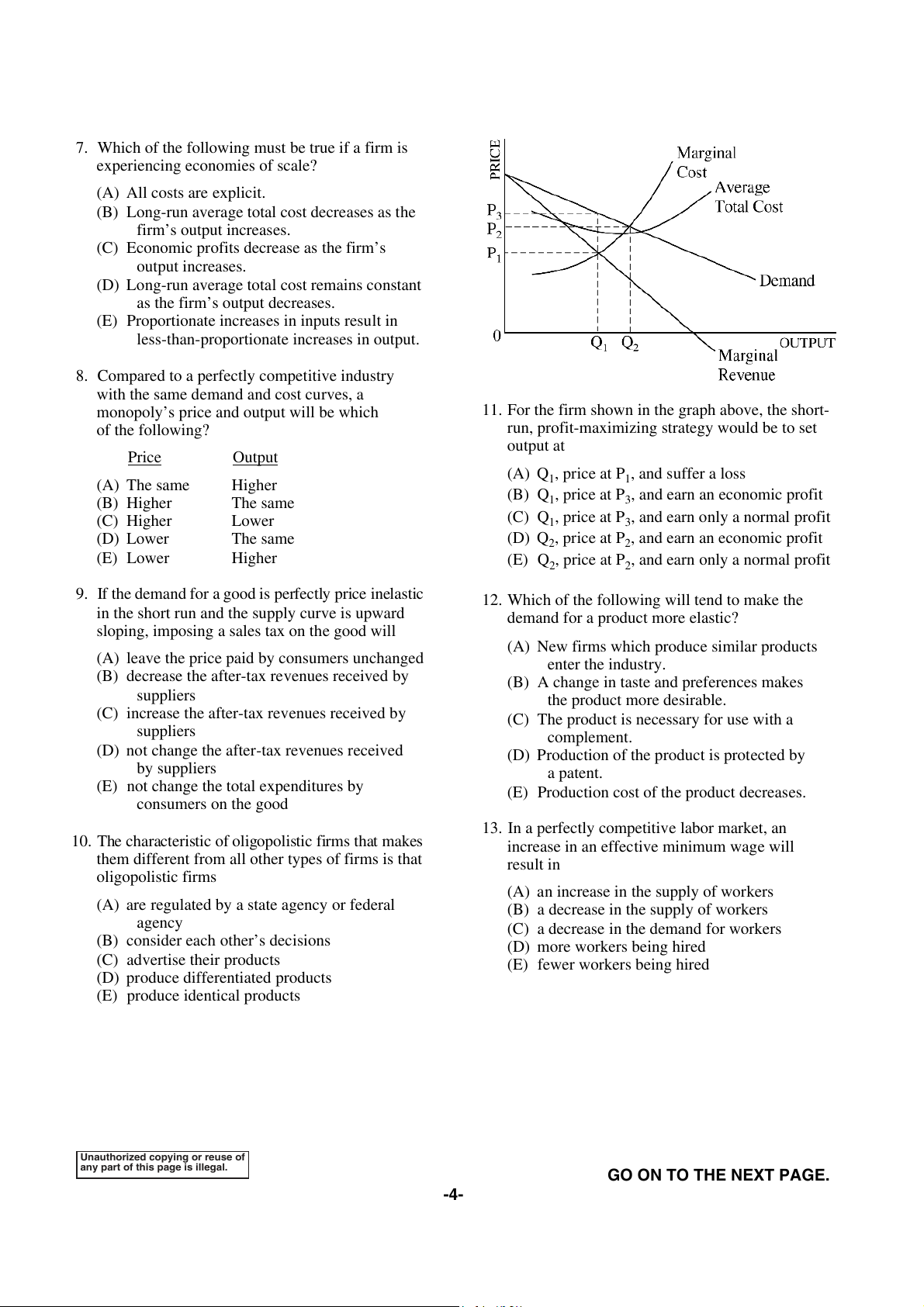
11. For the firm shown in the graph above, the short- of the following?
run, profit-maximizing strategy would be to set output at Price Output (A) Q (A) The same Higher
1, price at P , and suffer a loss 1 (B) Higher The same
(B) Q1, price at P3, and earn an economic profit (C) Higher Lower
(C) Q1, price at P , and earn only a normal profit 3 (D) Lower The same
(D) Q2, price at P2, and earn an economic profit (E) Lower Higher
(E) Q2, price at P , and earn only a normal profit 2
9. If the demand for a good is perfectly price inelastic
12. Which of the following will tend to make the
in the short run and the supply curve is upward
demand for a product more elastic?
sloping, imposing a sales tax on the good will
(A) New firms which produce similar products
(A) leave the price paid by consumers unchanged enter the industry.
(B) decrease the after-tax revenues received by
(B) A change in taste and preferences makes suppliers the product more desirable.
(C) increase the after-tax revenues received by
(C) The product is necessary for use with a suppliers complement.
(D) not change the after-tax revenues received
(D) Production of the product is protected by by suppliers a patent.
(E) not change the total expenditures by
(E) Production cost of the product decreases. consumers on the good
13. In a perfectly competitive labor market, an
10. The characteristic of oligopolistic firms that makes
increase in an effective minimum wage will
them different from all other types of firms is that result in oligopolistic firms
(A) an increase in the supply of workers
(A) are regulated by a state agency or federal
(B) a decrease in the supply of workers agency
(C) a decrease in the demand for workers
(B) consider each other’s decisions (D) more workers being hired (C) advertise their products (E) fewer workers being hired
(D) produce differentiated products
(E) produce identical products
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -4-
14. Which of the following taxes contributes most
17. Which of the following is true in a capitalist
to decreasing inequality in the distribution of economy? income?
(A) The factors of production are collectively (A) Progressive income taxes owned. (B) Sales taxes
(B) The factors of production are distributed (C) Proportional income taxes according to needs. (D) Excise taxes
(C) The prices of goods and services are usually
(E) Import tariffs on necessities determined by the government.
(D) The prices of goods and services are set so
15. A free-rider problem arises when a good is
that an equitable distribution of private (A) nonrival property is achieved. (B) nondepletable
(E) Prices serve as incentives for factors of (C) nonexcludable
production to move to the markets
(D) produced in a competitive market where they are most valued.
(E) produced in a monopolistic market
18. A city transit authority increases the price of sub-
way and bus tickets from $1.25 to $1.50. If the
demand for these tickets is price inelastic, the
number of people riding buses and subways and
the city’s revenues will most likely change in which of the following ways? Number of People Riding City’s Revenues (A) Increase Increase (B) Decrease Increase (C) Decrease Decrease (D) Decrease Remain constant (E) Remain constant Increase
16. According to the production possibilities curve
above, which of the following is true?
19. The difference between what consumers are
(A) The opportunity cost of producing another
willing to pay for units of a good and the price
unit of good Y in terms of good X
consumers actually pay for units of the good is
increases as more of good Y is produced. called
(B) The opportunity cost of producing another (A) marginal utility
unit of good Y in terms of good X (B) producer surplus
decreases as more of good Y is produced. (C) consumer surplus
(C) The opportunity cost of producing another (D) economic rent
unit of good X in terms of good Y (E) a positive externality
increases as more of good X is produced.
(D) The opportunity cost of producing another
unit of good X in terms of good Y
decreases as more of good X is produced.
(E) The opportunity cost of producing another unit
of either good remains constant as the
production of the other good increases.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -5-
20. Which of the following is true if consuming one
23. At 100 units of output, a firm’s total cost is
unit of a good yields 100 utils and consuming the
$10,000. If the firm’s total fixed cost is $4,000,
second unit of the good increases satisfaction by
its average variable cost is equal to 20 utils? (A) $140
(A) The marginal utility of the first unit is 20. (B) $100
(B) The marginal utility of the second unit is 80. (C) $60
(C) The marginal utility of the second unit is 120. (D) $40
(D) The total utility of consuming two units (E) $0 is 120.
(E) The total utility of consuming one unit is
24. Which of the following statements correctly
greater than the total utility of consuming
identifies a difference between perfect two units.
competition and monopolistic competition?
(A) In perfect competition there are no barriers
21. If a new tax on capital increases a firm’s fixed
cost of production, which of the following will
to entry, but there are strong barriers in occur in the short run? monopolistic competition.
(B) In perfect competition there are many firms,
(A) Marginal cost will increase.
but in monopolistic competition there are
(B) Average variable cost will increase. only a few firms.
(C) Average total cost will increase.
(C) In perfect competition the firms all sell
(D) The profit-maximizing level of output will
products that are exactly the same, but in increase.
monopolistic competition each firm sells
(E) The profit-maximizing level of output will
a slightly differentiated product. decrease.
(D) In perfect competition firms maximize profit
by selling the quantity where marginal
revenue equals marginal cost, but in
monopolistic competition firms maximize
• The marginal product of labor equals
profit by selling the quantity where 250 units of output.
marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost.
• The marginal product of capital equals
(E) In perfect competition there are few 750 units of output.
consumers, but in monopolistic competition
• The price of labor is $50 per person. there are many consumers.
• The price of capital is $100 per unit.
22. Given the information above, which of the
25. The most profitable level of output for any firm
following is true for a firm buying its labor and
operating in the short run is the level of output at
capital inputs in a perfectly competitive market? which
(A) The firm is producing its current level of
(A) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by
output with the least-cost combination of the highest amount labor and capital.
(B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost
(B) The firm is maximizing profits with its
(C) price exceeds average cost by the highest
current combination of inputs. amount
(C) The firm’s level of output will remain the (D) price equals average cost
same if 1 unit of capital is substituted for
(E) price equals marginal cost 2 units of labor.
(D) The firm’s input costs will decrease if 2 units
of labor are substituted for 1 unit of capital.
(E) The firm can reduce the cost of its current
level of output by laying off workers and employing more capital.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -6-
26. For an unregulated monopolist, the profit- Number of Workers Parts per Week
maximizing quantity will always be 0 0
(A) in the elastic region of the demand curve 1 100
(B) where marginal revenue equals price
(C) where price equals average total cost 2 190
(D) where price equals marginal cost 3 270
(E) where the marginal cost curve intersects the 4 340 demand curve 5 400
27. If a per-unit tax is imposed on a monopolist, how 6 450
will the monopolist’s marginal cost curve, output, 7 480
and the price paid by consumers be affected?
29. The table above describes the production function Marginal Cost Output Price
of an auto parts manufacturer. Assume that the (A) Shift down Increase Decrease
firm can hire as many workers as it wants at the (B) Shift down Decrease Decrease
market wage rate of $600 per week per worker (C) No shift Decrease Decrease
and sell as many auto parts as it wants at the price (D) Shift up Decrease Increase
of $10 per part. To maximize profits, the firm (E) Shift up Increase Increase should hire (A) 0 workers
28. The demand curve for labor for a monopolist that (B) 1 worker
faces a perfectly competitive factor market is (C) 3 workers called the (D) 5 workers (A) average product curve (E) 7 workers (B) marginal product curve (C) marginal revenue curve
30. Monopolistically competitive firms are considered
(D) marginal revenue product curve
inefficient in allocating society’s resources for
(E) value of the average product curve
which of the following reasons?
(A) In equilibrium, the marginal benefit exceeds
the price charged by the firms.
(B) In equilibrium, the marginal benefit exceeds
the marginal cost of production.
(C) In equilibrium, the marginal revenue of the
firm is not equal to its marginal cost.
(D) In long-run equilibrium, the firm is earning economic profits.
(E) Firms exhibit significant market power and
therefore the number of firms in the industry is strictly limited.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -7-
31. As a factor of production, capital refers to the
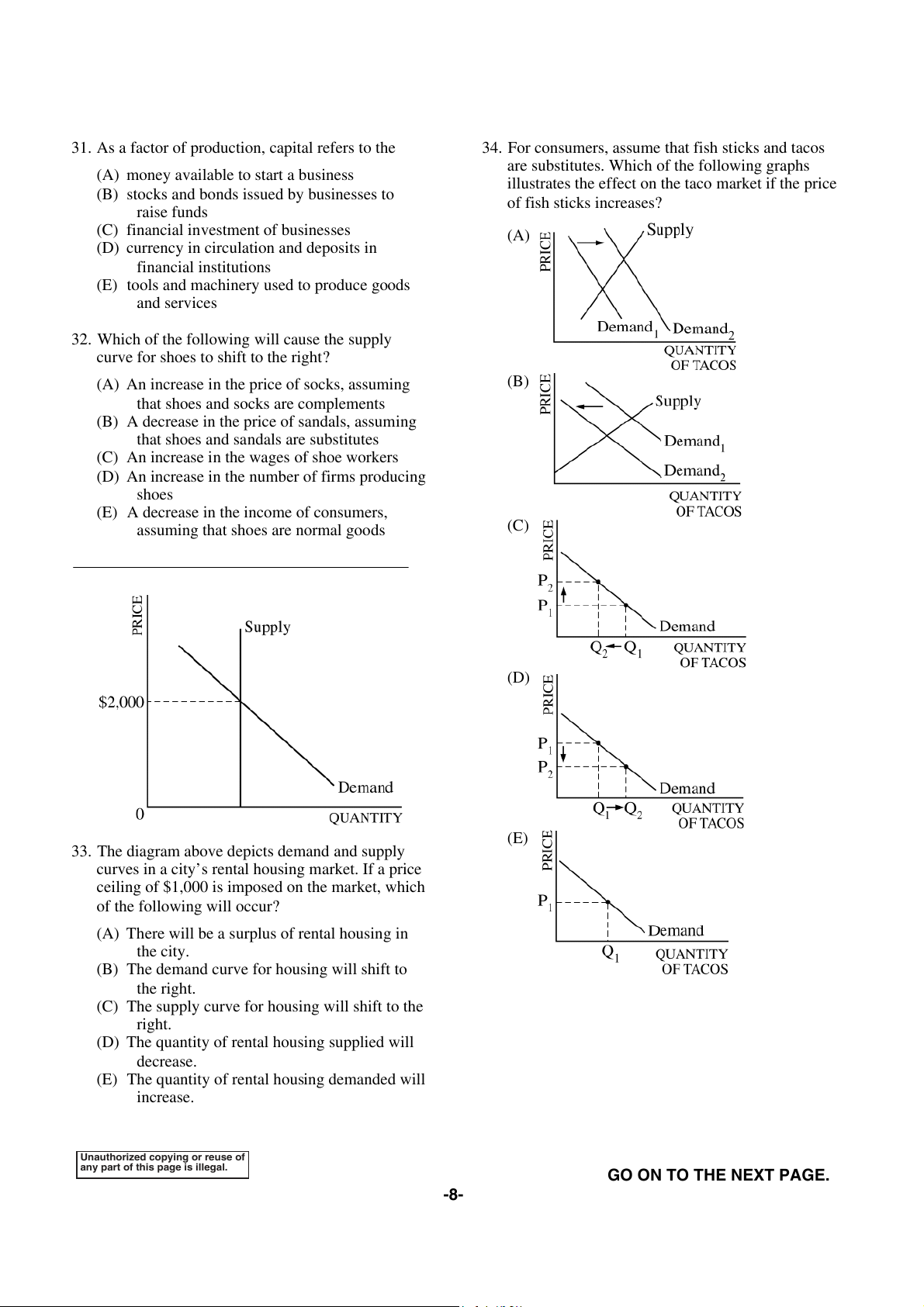
34. For consumers, assume that fish sticks and tacos
(A) money available to start a business
are substitutes. Which of the following graphs
illustrates the effect on the taco market if the price
(B) stocks and bonds issued by businesses to raise funds of fish sticks increases?
(C) financial investment of businesses (A)
(D) currency in circulation and deposits in financial institutions
(E) tools and machinery used to produce goods and services
32. Which of the following will cause the supply
curve for shoes to shift to the right?
(A) An increase in the price of socks, assuming (B)
that shoes and socks are complements
(B) A decrease in the price of sandals, assuming
that shoes and sandals are substitutes
(C) An increase in the wages of shoe workers
(D) An increase in the number of firms producing shoes
(E) A decrease in the income of consumers,
assuming that shoes are normal goods (C) (D) (E)
33. The diagram above depicts demand and supply
curves in a city’s rental housing market. If a price
ceiling of $1,000 is imposed on the market, which of the following will occur?
(A) There will be a surplus of rental housing in the city.
(B) The demand curve for housing will shift to the right.
(C) The supply curve for housing will shift to the right.
(D) The quantity of rental housing supplied will decrease.
(E) The quantity of rental housing demanded will increase.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -8-
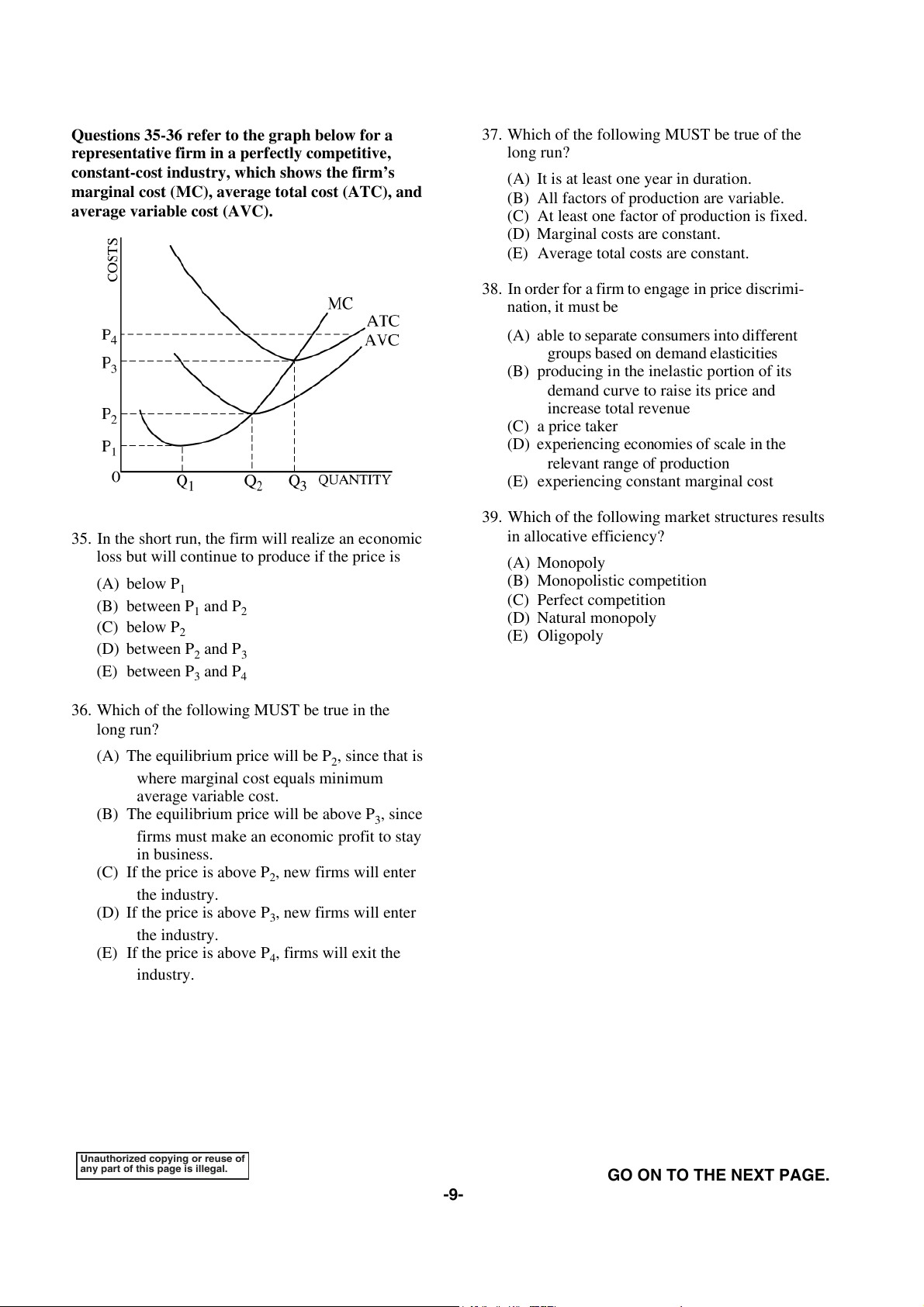
Questions 35-36 refer to the graph below for a
37. Which of the following MUST be true of the
representative firm in a perfectly competitive, long run?
constant-cost industry, which shows the firm’s
(A) It is at least one year in duration.
marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and
(B) All factors of production are variable.
average variable cost (AVC).
(C) At least one factor of production is fixed.
(D) Marginal costs are constant.
(E) Average total costs are constant.
38. In order for a firm to engage in price discrimi- nation, it must be
(A) able to separate consumers into different
groups based on demand elasticities
(B) producing in the inelastic portion of its
demand curve to raise its price and increase total revenue (C) a price taker
(D) experiencing economies of scale in the relevant range of production
(E) experiencing constant marginal cost
39. Which of the following market structures results
35. In the short run, the firm will realize an economic in allocative efficiency?
loss but will continue to produce if the price is (A) Monopoly (A) below P (B) Monopolistic competition 1 (B) between P and P (C) Perfect competition 1 2 (C) below P (D) Natural monopoly 2 (E) Oligopoly (D) between P2 and P 3 (E) between P3 and P4
36. Which of the following MUST be true in the long run?
(A) The equilibrium price will be P2, since that is
where marginal cost equals minimum average variable cost.
(B) The equilibrium price will be above P3, since
firms must make an economic profit to stay in business.
(C) If the price is above P2, new firms will enter the industry.
(D) If the price is above P3, new firms will enter the industry.
(E) If the price is above P4, firms will exit the industry.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -9-
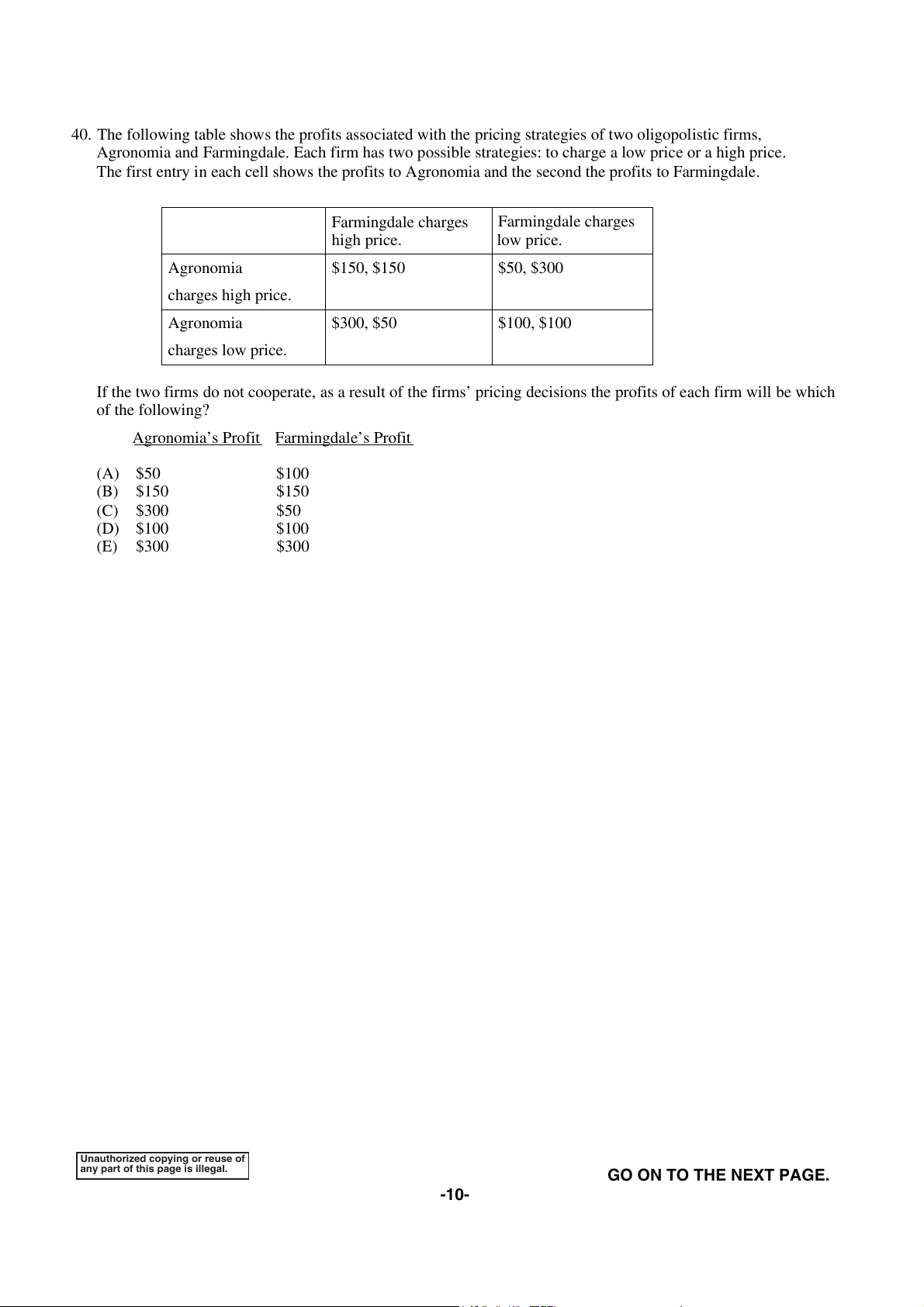
40. The following table shows the profits associated with the pricing strategies of two oligopolistic firms,
Agronomia and Farmingdale. Each firm has two possible strategies: to charge a low price or a high price.
The first entry in each cell shows the profits to Agronomia and the second the profits to Farmingdale. Farmingdale charges Farmingdale charges high price. low price. Agronomia $150, $150 $50, $300 charges high price. Agronomia $300, $50 $100, $100 charges low price.
If the two firms do not cooperate, as a result of the firms’ pricing decisions the profits of each firm will be which of the following?
Agronomia’s Profit Farmingdale’s Profit (A) $50 $100 (B) $150 $150 (C) $300 $50 (D) $100 $100 (E) $300 $300
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -10-
41. Which of the following will occur in a perfectly
43. Which of the following best defines a pure public
competitive labor market if Firm X’s demand for good? labor decreases?
(A) A good that is provided free of charge to the Equilibrium Employment public Market Wage Rate by Firm X
(B) A good that is provided by the government, (A) Increase Increase
whether or not a fee is charged (B) No change No change
(C) A good that is efficiently produced only by a (C) No change Decrease monopoly (D) Decrease Decrease
(D) A good whose benefits can be enjoyed by (E) Decrease No change
many consumers at the same time and from
which consumers cannot be excluded
(E) A good that by law must be available to all
consumers without discrimination on the
basis of sex, race, or religion
44. A perfectly competitive manufacturing industry
pollutes public water in its production process,
leaving the water unsuitable for use by the
surrounding communities. At the market
equilibrium output level, which of the following is true?
(A) Marginal private cost exceeds marginal social cost.
(B) Marginal private cost exceeds marginal private benefit.
(C) Marginal social cost exceeds marginal social benefit.
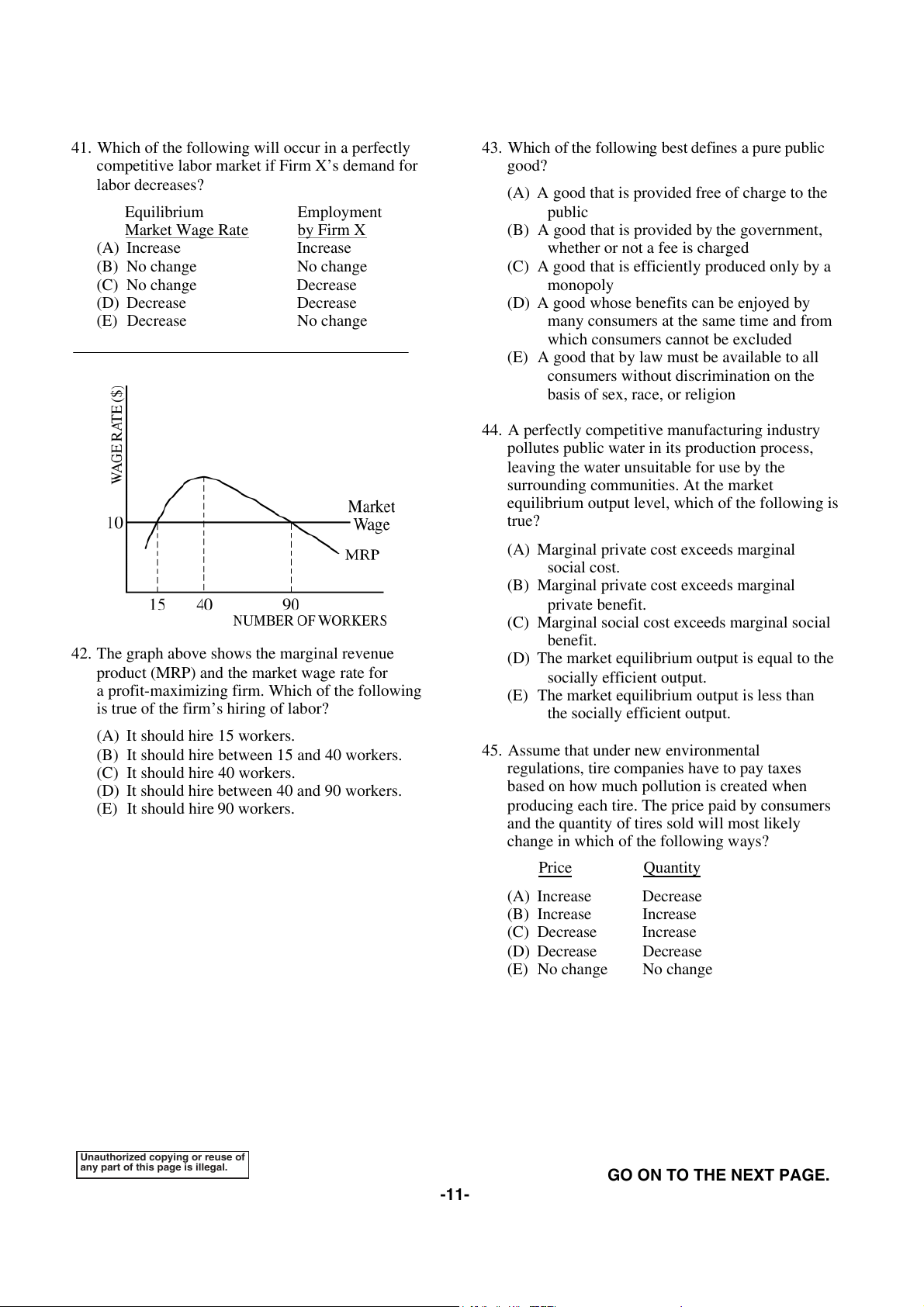
42. The graph above shows the marginal revenue
(D) The market equilibrium output is equal to the
product (MRP) and the market wage rate for socially efficient output.
a profit-maximizing firm. Which of the following
(E) The market equilibrium output is less than
is true of the firm’s hiring of labor?
the socially efficient output.
(A) It should hire 15 workers.
(B) It should hire between 15 and 40 workers.
45. Assume that under new environmental
(C) It should hire 40 workers.
regulations, tire companies have to pay taxes
(D) It should hire between 40 and 90 workers.
based on how much pollution is created when
(E) It should hire 90 workers.
producing each tire. The price paid by consumers
and the quantity of tires sold will most likely
change in which of the following ways? Price Quantity (A) Increase Decrease (B) Increase Increase (C) Decrease Increase (D) Decrease Decrease (E) No change No change
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -11-
46. The market for goldfish is perfectly competitive.
49. An entrepreneur has earned enough total revenue
From year 1 to year 2, both the price and the
to cover her accounting costs, but economic losses
quantity of goldfish sold increase. This is most
are being incurred. What must be true? likely caused by
(A) Her accounting costs are larger than her (A) an increase in the supply economic costs. (B) a decrease in the supply
(B) Her accounting profits are less than her (C) an increase in the demand implicit costs. (D) a decrease in the demand
(C) Her accounting profits are greater than
(E) a decrease in both the demand and the supply her economic costs.
(D) Her economic losses are less than her total
47. Using the same amount of time and resources, fixed costs.
Jack can assemble either 10 bikes or 5 computers,
(E) Her implicit costs are less than her
whereas Sam can assemble either 5 bikes or 5 accounting costs.
computers. Based on the data, which of the
following statements is correct?
50. If nations specialize according to their
(A) Sam has an absolute advantage in assembling
comparative advantage and engage in bikes.
international trade with each other, each
(B) Sam has an absolute advantage in assembling nation can computers.
(A) produce outside its production possibilities
(C) Sam has a comparative advantage in curve assembling bikes.
(B) consume outside its production possibilities
(D) Jack has a comparative advantage in curve assembling bikes.
(C) shift its production possibilities curve to the
(E) Jack has a comparative advantage in right
assembling both bikes and computers.
(D) become more self-sufficient (E) produce more of all goods
48. Given an increase in the price of material K—
which is an input used to produce good X— and
51. When total physical product is at its maximum,
an increase in the price of good Y— which is a
marginal physical product must be
substitute for good X—which of the following will definitely occur? (A) greater than one (B) equal to one
(A) The equilibrium price of good X will (C) equal to zero decrease. (D) less than zero
(B) The equilibrium price of good X will (E) constant increase.
(C) The equilibrium quantity of good X will be unaffected.
(D) The equilibrium quantity of good X will increase.
(E) The equilibrium quantity of good X will decrease.
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -12-
52. Garcia is currently spending his entire lunch
56. Which of the following is true of a monopolisti-
budget on 3 sodas and 4 hot dogs. At his current
cally competitive firm in long-run equilibrium?
level of consumption, Garcia’s marginal utility for
(A) Price equals marginal cost and average total
sodas is 5 utils and his marginal utility for hot
dogs is 10 utils. In order to maximize his total cost. utility, Garcia should
(B) Price equals average total cost but is greater than marginal cost.
(A) consume more sodas and fewer hot dogs
(C) Price equals marginal cost and is greater than regardless of the prices average total cost.
(B) consume more hot dogs and fewer sodas
(D) The firm makes no attempt to differentiate its regardless of the prices products.
(C) maintain his current level of consumption
(E) The firm earns positive economic profits by
of sodas and hot dogs regardless of the
producing at minimum average cost. prices
(D) maintain his current level of consumption
57. Assume that firms sell their output in a perfectly
if the price of a soda is $1 and the price
competitive product market and hire labor in a of a hot dog is $2
perfectly competitive labor market. If all other
(E) maintain his current level of consumption
factors remain constant, an increase in the demand
if the price of a soda is $2 and the price
for the firms’ product will result in which of the of a hot dog is $1
following changes in the labor market?
53. As output of a firm increases, the difference
(A) Firms will move down along the demand
curve for labor and hire more workers.
between the firm’s average total cost and its
average variable cost gets smaller because the
(B) The supply curve for labor will shift to the firm’s right.
(C) The demand curve for labor will shift to the (A) total cost is increasing right.
(B) marginal cost is increasing
(D) The supply curve for labor will shift to the left.
(C) average fixed cost is decreasing
(E) The demand curve for labor will shift to the
(D) marginal product of labor is decreasing left.
(E) long-run average total cost is decreasing
58. A profit-maximizing firm will continue to hire
54. In a perfectly competitive market, a change in workers until the
which of the following could cause a shift in the supply curve?
(A) marginal factor cost of labor is equal to the
marginal revenue product of labor (A) The incomes of consumers
(B) marginal factor cost of labor is equal to the (B) The number of buyers
price of the good produced using labor (C) Technology
(C) marginal product of labor is equal to the (D) The price of the product
marginal revenue product of labor (E) Tastes and preferences
(D) marginal product of labor is equal to the marginal factor cost of labor
55. Productive efficiency occurs when a firm produces
(E) marginal product of labor is equal to the output at a level at which price of labor
(A) average total cost equals average revenue
(B) average total cost is at a minimum
(C) price exceeds average total cost
(D) price equals marginal cost
(E) marginal revenue exceeds average revenue
Unauthorized copying or reuse of
any part of this page is illegal.
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -13-




