


Preview text:
Le Bich Ngoc - 11230122 CLASS EBBA 15.2 Presentation assignment 9
Problem 1: A monopoly has a demand function of P=15-Q ($) and total cost function of TC= 7Q ($)
a. What is price and optimal quantity that gives the firm maximum
profit? Using Lerner indicator (L) to identify market power of this firm? We have:
TR=P . Q= (15−Q ) .Q=−Q2+15Q MR=−2 Q+15 We have: TC=7.Q dTC MC= =TC '=7 dQ Π = max ⟷ MR MC −2 Q+15=7 Q¿=4 P¿=11 P−MC 11−7 L= = 4 = 0,37 P 11 11
The price and optimal quantity that give firm profit maximization
are P*=11, Q*=4 and the market power of that firm is about 0,37
b. What is price and optimal quantity for society (for perfect competitive
market)? Identify dead-weight loss (DL) created by this firm? Le Bich Ngoc - 11230122 CLASS EBBA 15.2 Presentation assignment 9
We have a competitive market point which is the intersection of
the demand curve and the marginal cost curve. MC=7 = 15-Q Q=8 at P=7
The DWL equals to area of ABE so 1 1 DWL=S = . AE . BE= .4 .4=8 $ ABE 2 2
The price and optimal quantity for society are P=7, Q=8 and the dead-weight lost is 8$
Problem 2: A monopolist has demand function of P= 100-Q and cost functions of AVC= Q+4; FC=200
a. What is optimal output level that maximizes profit? What is that maximum profit? We have:
TR=P . Q=(100−Q).Q =100 Q−Q2 TR MR= =(TR)’=100−2 Q Q TC = VC + FC ¿ Q . AVC+FC ¿ Q .(Q+4 )+200 ¿ Q2+4 Q+20 0 MC =TCQ = (TC)’ = 2Q + 4
The firm gets maximized profit when: MR = MC 100 - 2Q = 2Q + 4. Q = 24. P = 76. With Q* = 24
TR−TC=100 . Q−Q2−(Q2+4 .Q+200)=952($)
The optimal output level to maximize profit is 24 The maximum profit is $952
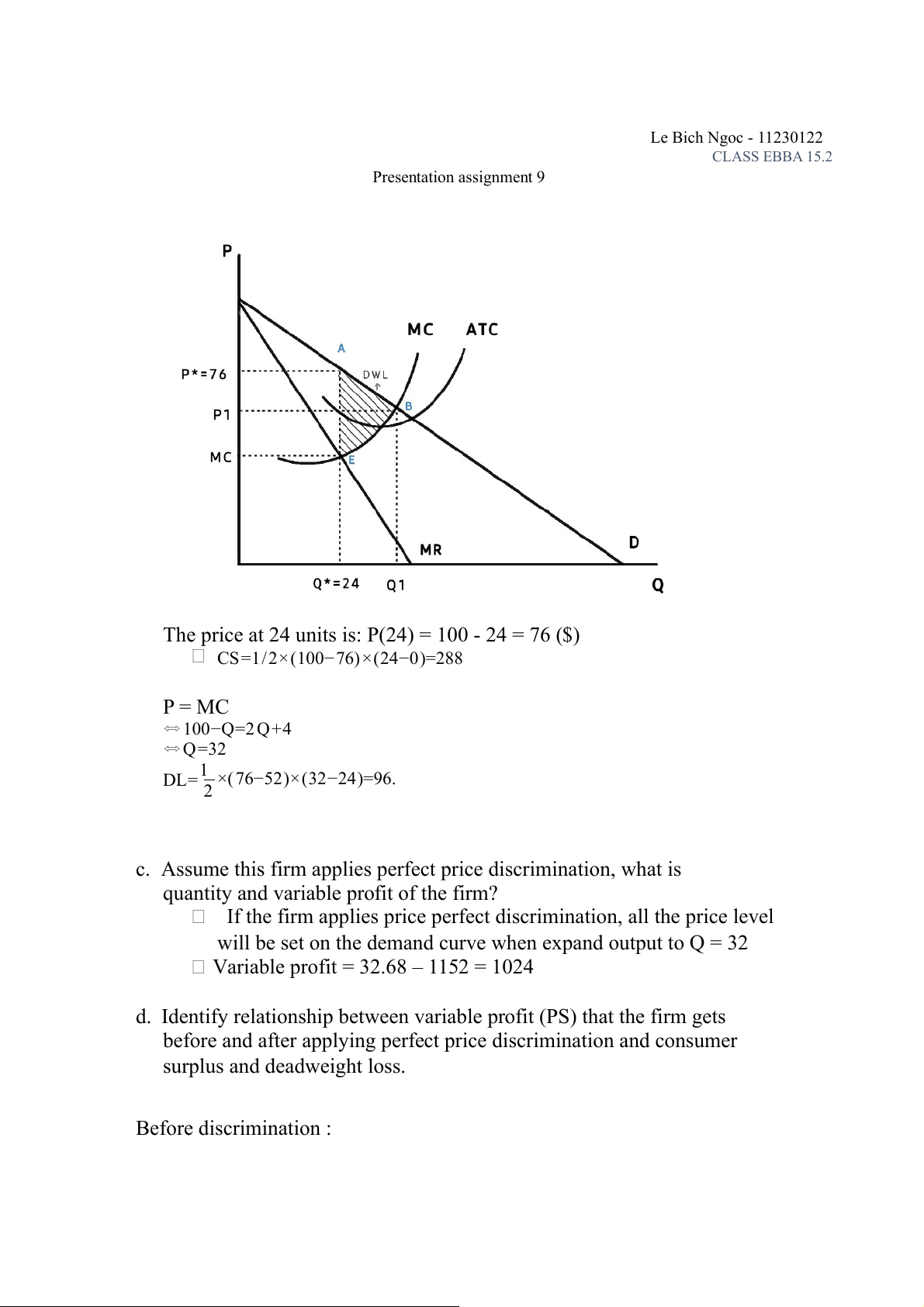
b. What is consumer surplus (CS) and deadweight loss (DL) created by this firm? Le Bich Ngoc - 11230122 CLASS EBBA 15.2 Presentation assignment 9
The price at 24 units is: P(24) = 100 - 24 = 76 ($)
CS=1/2×(100−76)×(24−0)=288 P = MC ⬄100−Q=2Q+4 ⬄Q=32 1 DL= ×(76−52)×(32−24)=96. 2
c. Assume this firm applies perfect price discrimination, what is
quantity and variable profit of the firm?
If the firm applies price perfect discrimination, all the price level
will be set on the demand curve when expand output to Q = 32
Variable profit = 32.68 – 1152 = 1024
d. Identify relationship between variable profit (PS) that the firm gets
before and after applying perfect price discrimination and consumer surplus and deadweight loss. Before discrimination : Le Bich Ngoc - 11230122 CLASS EBBA 15.2 Presentation assignment 9 PS=P∗AEC=¿ CS=288 $ DWL=96 $ After discrimination : Firm expand output to Q = 32
We got new PS = 1024$ , CS = 512$
By perfect price discrimination, firm increased profit by getting more CS and DWL




