






Preview text:
Midterm Exam #1 10 February 2002 Econ sections 1 & 4
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1) In every economic system, choices must be made because resources
A) are limited, and so are human desires and wants.
B) are unlimited, and so are human desires and wants.
C) are unlimited, but human desires and wants are limited.
D) are limited, but human desires and wants are unlimited.
2) A normative statement concerns A) a value judgment. B) what is incorrect. C) what is provable. D) what is correct.
3) An example of a question that might be explored in microeconomics is to determine
A) savings by the household sector.
B) why the U.S. economy has grown more rapidly than the Japanese economy.
C) employment at General Motors.
D) the total employment within the U.S. economy.
4) The problem of "scarcity" applies
A) only in economic systems that are just beginning to develop because specialized resources are scarce.
B) only in industrially developed countries because resources are scarce in these countries.
C) to all economic systems, regardless of their level of development.
D) only in underdeveloped countries because there are few productive resources in these countries.
5) The level of consumption that people enjoy, on the average, is A) standard of living. B) entrepreneurship. C) cost of living. D) scarcity.
6) When an economist refers to choices made "at the margin" the economist is referring to
A) decisions based on the marginal benefits and marginal costs of small changes in a particular activity.
B) an individual's all-or-nothing choice concerning a specific good or activity.
C) an individual's margin account with a stockbroker that allows part of a stock purchase to be made with borrowed money. D) all of the above Production possibilities possibility Pizza Soda (per hour) (cases per hour) A 0 100 B 1 95 C 2 80 D 3 60 E 4 35 F 5 0
7) In the above table, the production of 3 pizzas and 80 cases of soda is
A) feasible but would involve unemployed or misallocated resources.
B) possible only if the economy produces with maximum efficiency.
C) impossible unless more resources become available or technology improves.
D) possible only if there is inflation.
8) Suppose a scientific breakthrough made free solar power available in unlimited quantities in the United
States. The effect of this invention would be to move the
A) U.S. production possibilities frontier outward.
B) U.S. production possibilities frontier inward.
C) United States inside its production possibilities frontier.
D) United States beyond its production possibilities frontier.
9) In the figure above, both Joe and Jill initially produce at point . If Joe and Jill realize that they each
possess a comparative advantage, which outcome can we expect?
A) Joe will specialize in shirts, and Jill will specialize in pants.
B) Joe will specialize in pants, and Jill will specialize in shirts.
C) Joe and Jill each will be able to consume more than 2 shirts and 2 pairs of pants.
D) Both answers B and C are true.
10) Throughout the 1990s, the price of four-wheel drive vehicles rose and each year more were purchased. This experience suggests that
A) there must have been rightward shifts in the demand curve for four-wheel drive vehicles.
B) there must have movements leftward along the supply curve of four-wheel drive vehicles.
C) there must have been tremendous technological advances in the way four-wheel drive vehicles are produced. D) none of the above
11) Consider the market for soft drinks shown in the figure above. Suppose the economy is at point .
What would result in a movement to point ?
A) a decrease in the relative price of a soft drink.
B) an increase in the price of bottled water.
C) an increase in the opportunity cost of soft drinks.
D) a decrease in the price of bottled water.
12) If the money price of wheat increases and no other prices change,
A) the relative price of wheat is unaffected.
B) the demand for wheat will increase too.
C) the relative price of wheat will fall.
D) the opportunity cost of wheat rises.
13) Suppose Frosty Pops cereal is an inferior good. An increase in income
A) has no impact on the demand for Frosty Pops.
B) leads to a decrease in the demand for Frosty Pops. C) has no income effect.
D) leads to an increase in the demand for Frosty Pops.
14) If a 20 percent increase in the price of a used car results in a 10 percent decrease in the quantity of used
cars demanded, then the price elasticity of demand equals A) 1.0. B) 2.0. C) 0.5. D) 10.0.
15) Suppose inter-city bus travel is a substitute for transportation by train. Which of the following could then be true?
A) The cross elasticity between bus and train travel could equal 0.65.
B) The cross elasticity between bus and train travel could equal 1.25.
C) The cross elasticity between bus and train travel could equal 1.0.
D) All of the above could be true.
16) If the price of a burger decreases by 5 percent and as a result the quantity of burgers demanded
increases by 8 percent, the price elasticity of demand equals A) 0.40. B) 0.625. C) 0.60. D) 1.60.
17) The relative price of a good . I.
shows the number of dollars' worth of other goods and services that must be given up to
obtain one more unit of the good. II.
is the same value as the money price. A) I and II B) II only C) neither I nor II D) I only
18) Suppose that Hot Dog House produces hot dogs for $0.25 each. If the Hot Dog House can sell hot dogs
for $0.50 each, then definitely
A) the Hot Dog House will allow consumers to earn a consumer surplus.
B) the Hot Dog House will raise the price of hot dogs.
C) the Hot Dog House can earn a producer surplus.
D) there will be no producer surplus.
19) Consider the market for soft drinks. If we produce one more bottle of soft drinks,
A) the price of soft drinks must rise.
B) we cannot be acting efficiently.
C) we must move away from market equilibrium. D) we incur a marginal cost.
20) A normal good is defined as a good for which
A) the demand curve is perfectly price elastic.
B) the demand curve shifts leftward as income increases.
C) the demand curve slopes downward to the right.
D) the demand curve shifts rightward as income increases.
21) ________ is the difference between the value placed on the good and the price paid for it. A) Shortage B) Producer surplus C) Consumer surplus D) Surplus
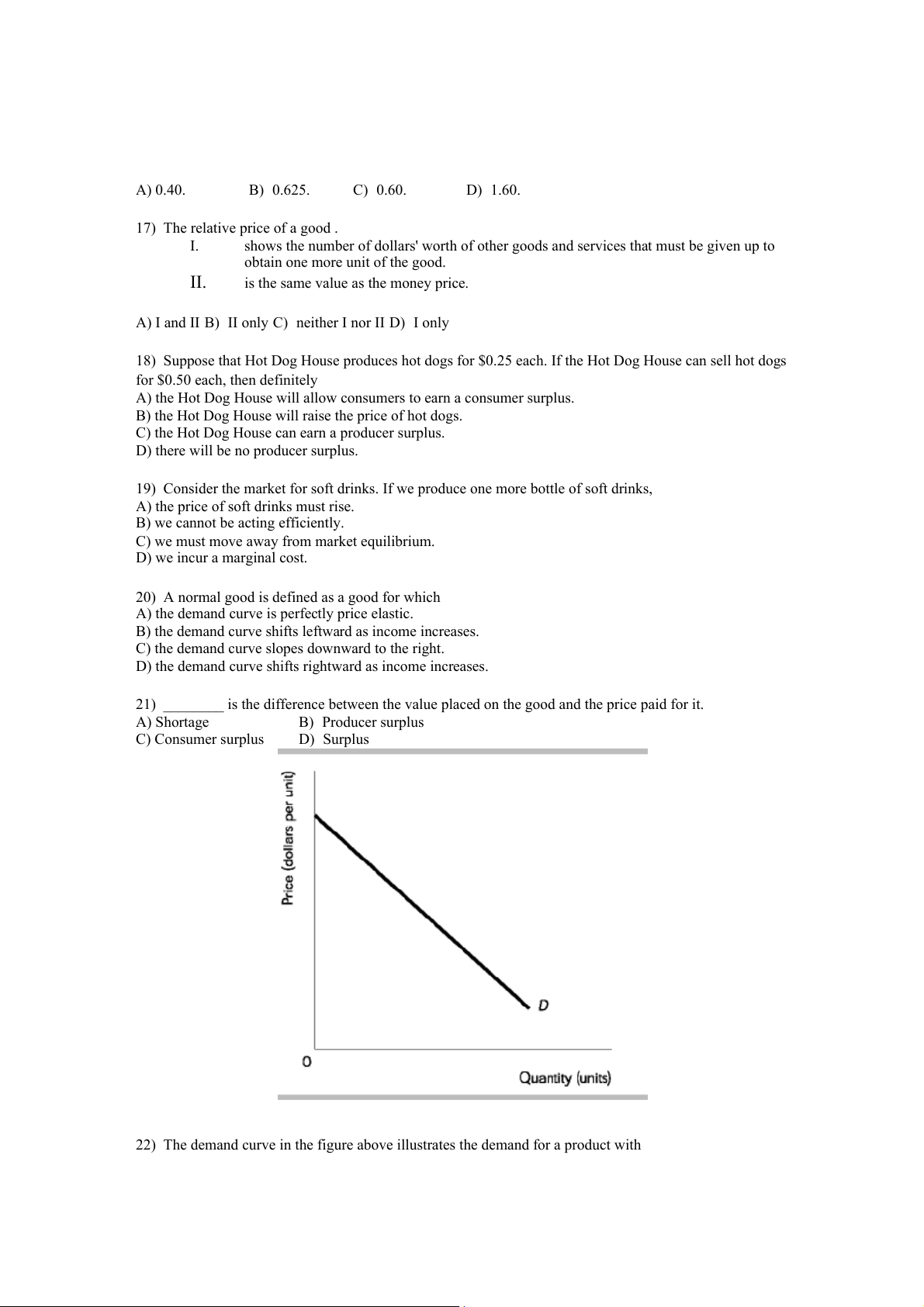
22) The demand curve in the figure above illustrates the demand for a product with
A) zero price elasticity of demand at all prices.
B) unit price elasticity of demand at all prices.
C) a price elasticity of demand that is different at all prices.
D) infinite price elasticity of demand.
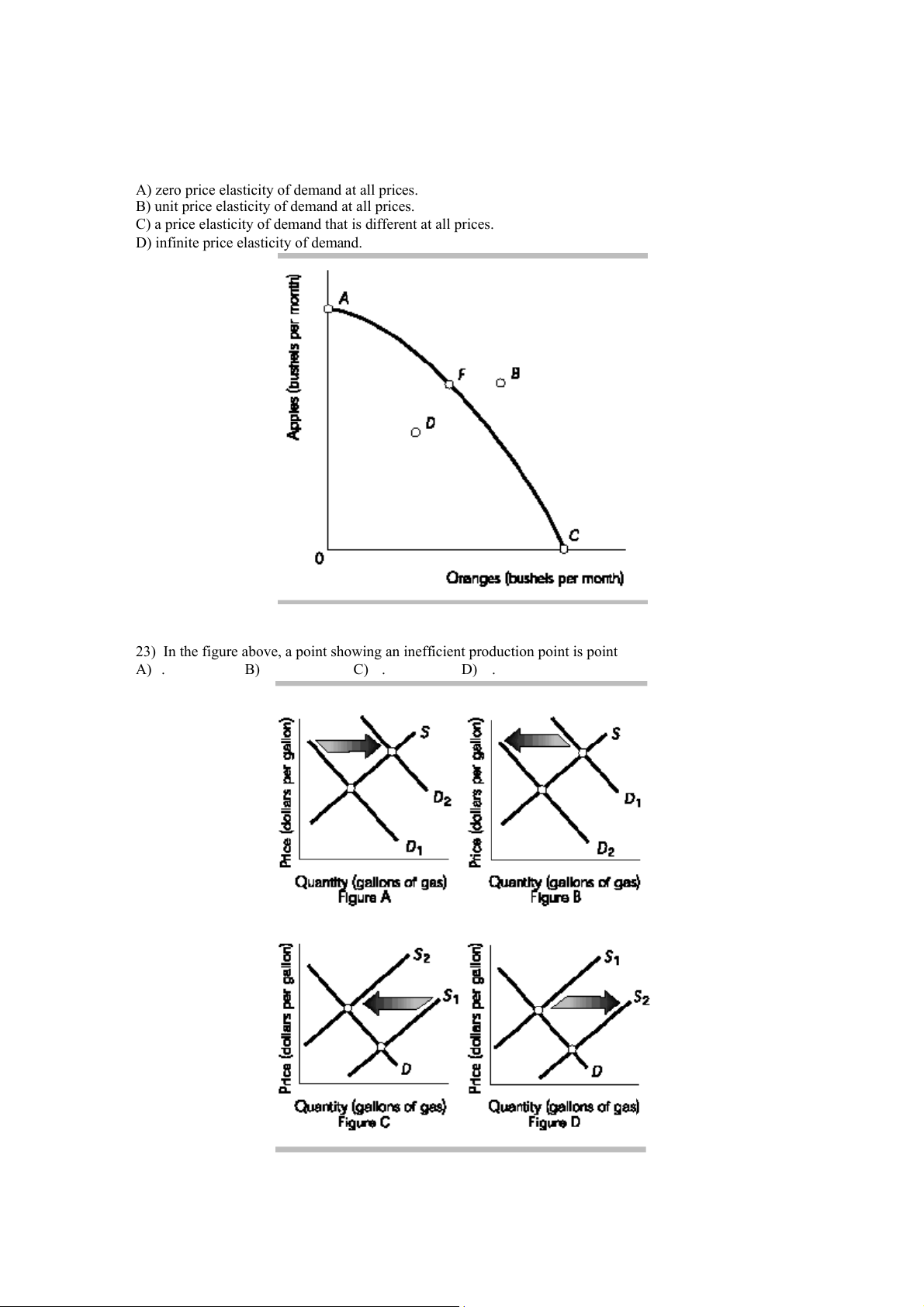
23) In the figure above, a point showing an inefficient production point is point A) . B) C) . D) .
24) The above figures show the market for gasoline. Which figure(s) shows the effect of a decision by the
OPEC countries in the Middle East to export less oil to the rest of the world? A) Figure D B) Figure B C) Figure C D) Figures B and C
25) The income elasticity of demand is ________ for a normal good and ________ for an inferior good. A) negative; negative B) positive; negative C) positive; positive D) negative; positive
26) The "law of supply" states that, other things remaining the same,
A) firms will produce more of a good the less it costs to produce it.
B) firms will produce more of a good the higher its price.
C) firms will produce less of a good as the required resources become scarcer.
D) firms will produce less of a good the more it costs to produce it.
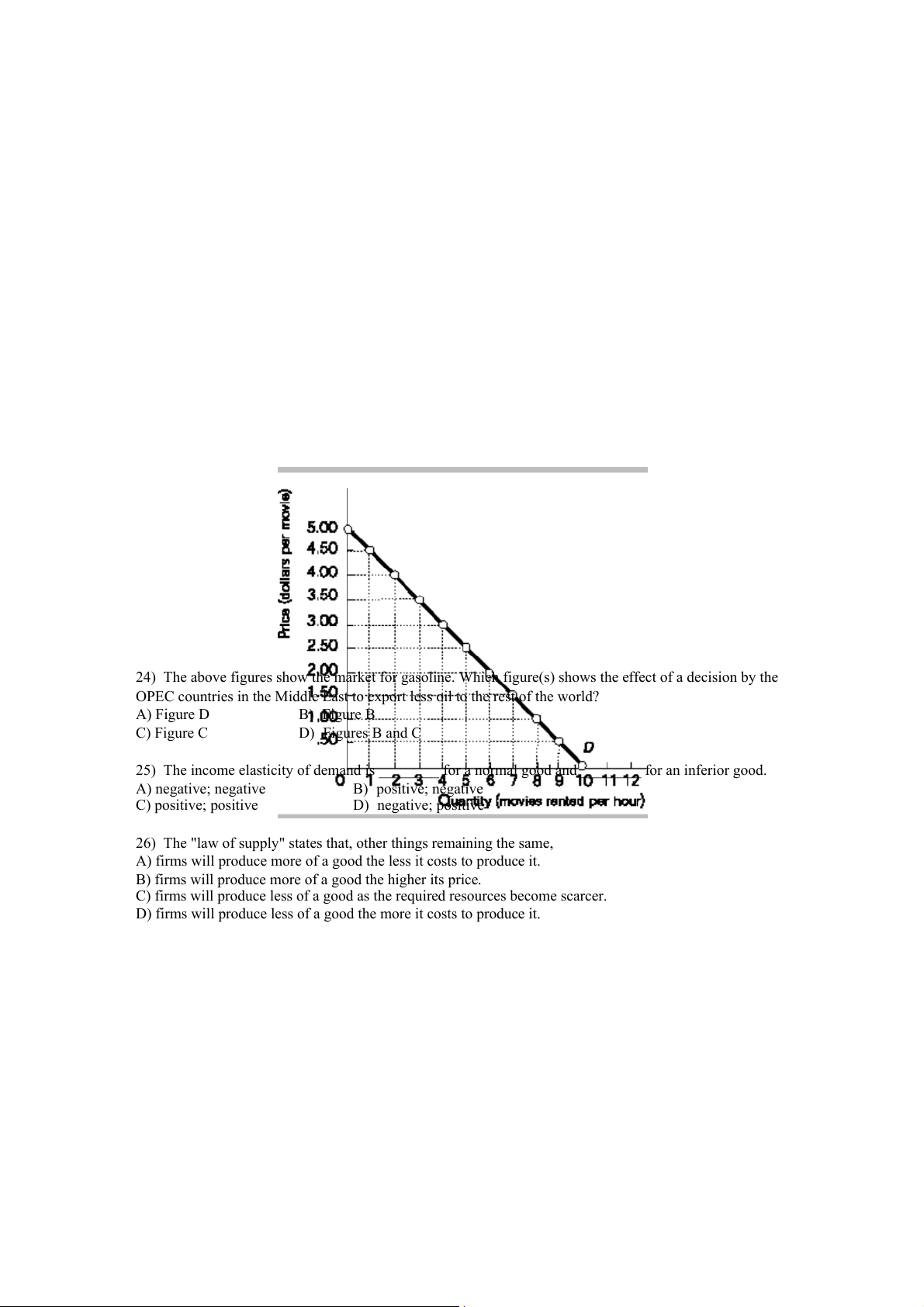
27) The above figure shows the demand curve for movie rentals from Blockbuster. If Blockbuster lowered
its price from $4.00 to $3.50, which of the following would happen?
A) Total revenue would increase because demand is elastic.
B) Total revenue would increase because demand is inelastic.
C) Total revenue would decrease because demand is elastic.
D) Total revenue would decrease because demand is inelastic.
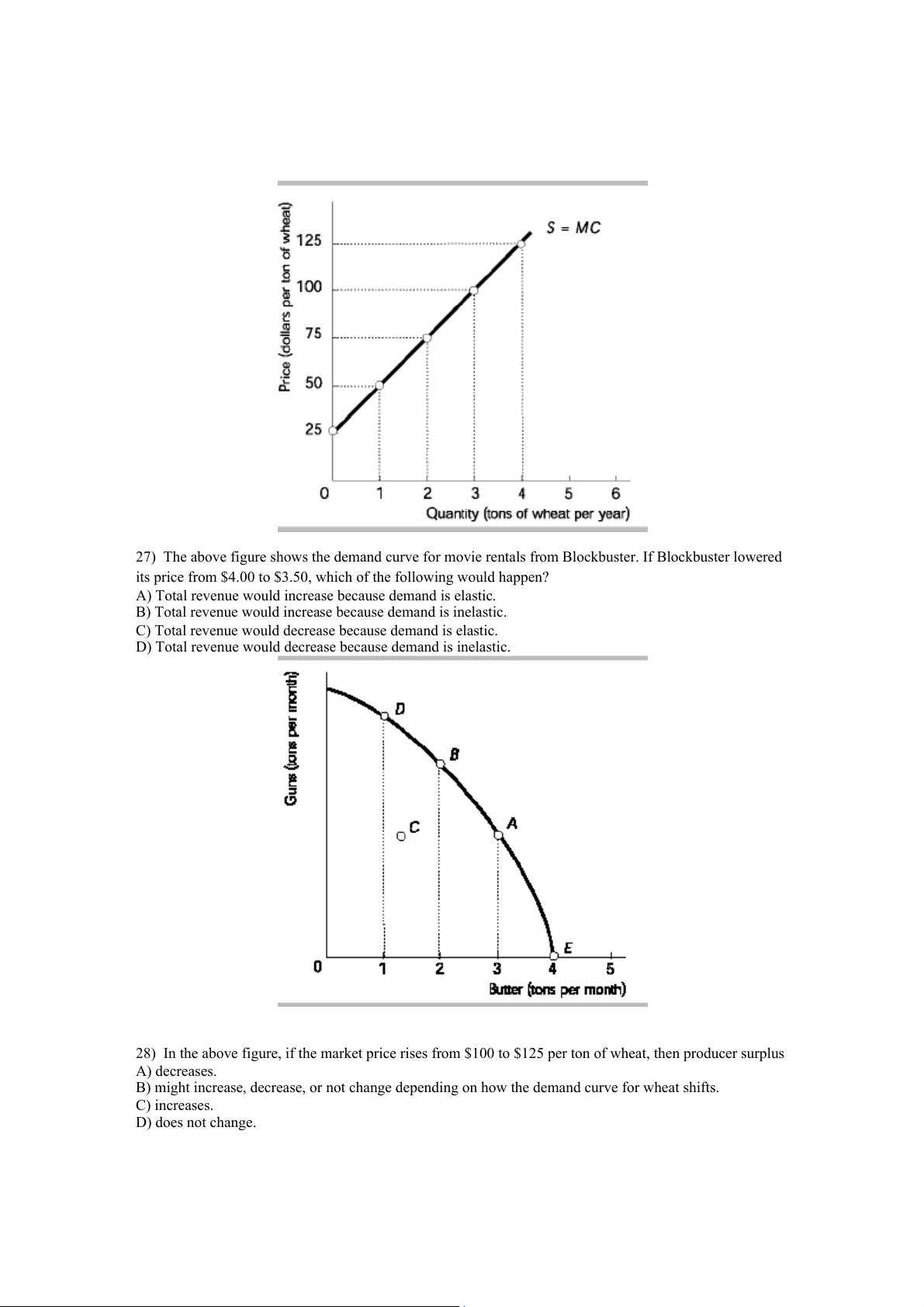
28) In the above figure, if the market price rises from $100 to $125 per ton of wheat, then producer surplus A) decreases.
B) might increase, decrease, or not change depending on how the demand curve for wheat shifts. C) increases. D) does not change.
29) The country whose production possibilities frontier is illustrated above is currently at position on the
production possibilities frontier. If it wishes to move to position , it will
A) have to employ all currently unemployed resources to accomplish this.
B) be able to make the desired switch only if there is a significant improvement in the technological base available to the nation.
C) incur an opportunity cost of having to give up some butter in order to make the additional amount of guns desired.
D) find this change impossible to achieve given the resources it currently possesses.
30) Which of the following is an investment in human capital?
A) a medical student's internship
B) a mechanic attends a training workshop on a new type of engine C) Johnny learns how to read
D) the purchase of a personal computer
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'A' on answer sheet if the statement is true and 'B' if the statement is false.
31) If a country operates on its , it achieves production efficiency.
32) If the demand for cigarettes decreases after the U.S. Surgeon General publicizes five new diseases
associated with smoking, this is conclusive evidence that the demand for cigarettes is elastic.
33) An increase in technology will shift the good's supply curve rightward.
34) When I buy an $8.00 movie ticket rather than two paperback books, the opportunity cost of going to
the movie is the $8.00 I spend.
35) The larger the portion of a person's total budget spent on a good, the more inelastic the demand for the good.
ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided below.
36) What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for shredded wheat if (a) the
producer purchases and applies a "crunch enhancer" food additive to shredded wheat and (2) consumers
begin to eat more shredded wheat because they like the way the crunch enhancer keeps it crisper longer in milk?
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) D 2) A 3) C 4) C 5) A 6) A 7) C 8) A 9) D 10) A 11) B 12) D 13) B 14) C 15) D 16) D 17) D 18) C 19) D 20) D 21) C 22) C 23) D 24) C 25) B 26) B 27) A 28) C 29) C 30) D
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'A' on answer sheet if the statement is true and 'B' if the statement is false. 31) TRUE 32) FALSE 33) TRUE 34) FALSE 35) FALSE
ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided below.
36) The supply curve shifts leftward because the purchase and application of the crunch enhancer creates
one more cost of production. The demand curve shifts rightward because tastes and preferences for
shredded wheat have improved. Both shifts cause the equilibrium price of shredded wheat to increase.
Whether the equilibrium quantity increases or decreases depends on whether the demand curve shift is
greater than the supply curve shift, or vice versa.




