




Preview text:
National Economics University ********* COURSE MICROECONOMICS Midterm Examination Instructor: Vu Ngoc Xuan Name: Nguyen Quynh Thu Student ID: 11194967
Class: POHE - Commercial Business Administration K61 Midterm Examination
Part 1: Multiple- Choice question. For each question, choose the best answer.
1. The Vietnam economy relies
a. exclusively on the market mechanism
b. exclusively on the market mechanism in a mixed economy
c. exclusively on the command mechanism
d. equally on market and command mechanisms in a mixed economy
e. extensively on the command mechanism in a mixed economy
2. Which of the following is a normative statement?
a. Pollution is an example of an external cost.
b. Pollution makes people worse off.
c. Firms that pollute should be forced to shut down.
d. Pollution imposes opportunity costs on others. e. None of the above.
3. If both demand and supply increase, then equilibrium price
a. will rise and quantity wil increase
b. will fall and quantity will increase
c. could rise or fall or unchanged and quantity will increase
d. will rise and quantity could either increase or decrease
e. will fall and quantity could either increase or decrease
4. In perfect competition, ___________________.
a. only firms know their competitors' prices
b. firms in the industry have advantages over firms that plan to enter the industry
c. there are many firms that sel similar products
d. there are no restrictions on entry into the industry e. None of above
5. In perfect competition, each firm ____________________________
a. faces a perfectly inelastic demand for its product
b. can influence the price that it charges c. produces as much as it can d. is a price taker e. None of above
6. Normal profit is ____________________________.
a. equal to total revenue minus marginal cost
b. equal to total revenue minus total cost
c. equal to economic profit minus total cost
d. included in the firm's total cost e. None of above
7. A competitive firm's total revenue minus its total cost equals its __________. a. profit b. normal profit c. opportunity cost d. economic profit e. None of above
8. In the short run, the competitive firms ___________ but in the long run, firms make ___________.
a. make positive economic profits; positive economic profits
b. can incur economic losses; positive economic profits
c. make economic losses; positive economic profits
d. can incur economic losses; zero economic profit e. None of above
9. In perfect competition, the firm's marginal revenue ________________________.
a. is less than the market price
b. exceeds the price it charges c. equals its normal profit d. equals the market price e. None of above
10. When a competitive firm produces the profit-maximizing output and it is at its
shutdown point, the firm's ______________________.
a. marginal revenue equals its average fixed cost
b. total revenue is less than its total variable cost
c. marginal cost is less than its average variable cost
d. total revenue equals its total variable cost e. None of above Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Answer D C C D D B B B D E
Part 2: True/False and Explain, draw graph if necessity
1. The principle of diminishing marginal utility means that as consumption of a good
increase, total utility increase but at a decreasing rate. Answer: FALSE
Acording to the principles of diminishing marginal utility that as consumption of a good
increase, total utility decrease but decrease at a slow rate.
2. Consumer surplus for relatively cheap goods like water wil be relatively low. Answer: TRUE
Water is an available and relatively cheap good so consumers will only be willing to spend
a cheap price to purchase water, which leads to surplus be relatively low.
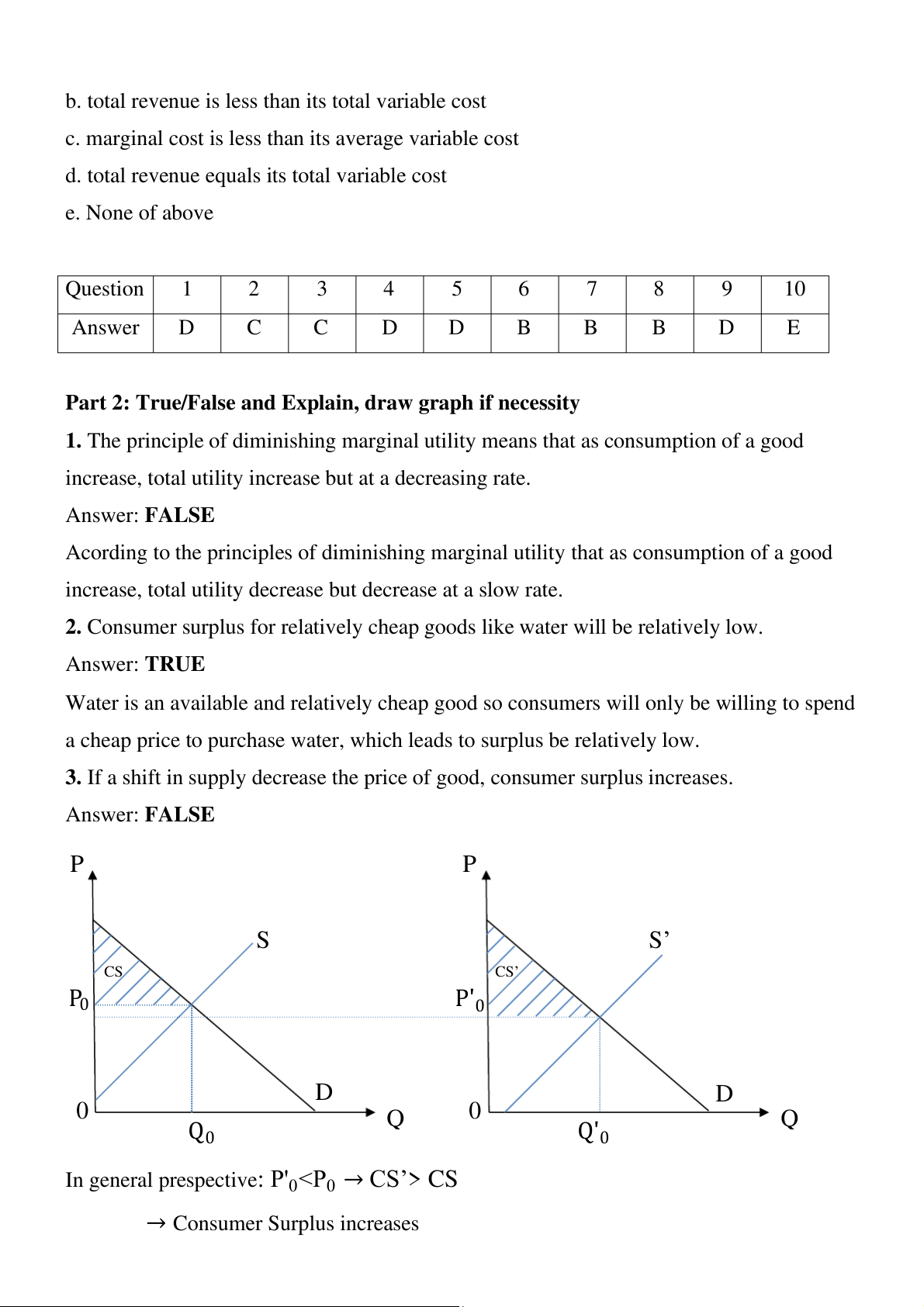
3. If a shift in supply decrease the price of good, consumer surplus increases. Answer: FALSE P P S S’ CS CS’ P0 P'0 D D 0 Q 0 Q Q 0 Q'0
In general prespective: P'
0 0 → CS’> CS
→ Consumer Surplus increases Part 3: Problems
The orange market has the supply and demand function as following: (S): P=4+Q (D): P=22-2Q
In which, Price unit: 1000 dong/kg Quantity unit: tons
1. Draw the demand and supply curve. Define the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity?
2. Define the Consumer surplus (CS) and Producer surplus (PS)?
3. Compute Total Revenue (TR) and Edp at the equilibrium point?
4. If the tax= 3.000 d/kg. Compute the new equilibrium price and quantity?
Asighment’s presentation 1.
• The demand and supply curve P 22 S CS 10 PS 4 D Q 0 6 • At the equilibrium point: P
s = PD → Q = 6 (tons); P = 10 (million/tons) 2. • Consumer surplus CS 1 = x 6 x 12 = 36 2 • Producer surplus PS 1 = x 6 x 6 = 18 2 3. 1 Q(D) = − x P + 11 2
At the equilibrium: P = 10, Q = 6 • Total Revenue TR = 10 x 6 = 60 ( million ) P 1 10 • Edp = Q'p x = − x = −0,83 Q 2 6 4. If t = 3000 d/kg
→ The supply curve after tax: P'S = PS + t = 7 + Q
• The new equilibrium price and quantity: 𝑃′ 𝑆 = 𝑃𝐷 <=> 7 + Q = 22 - 2Q <=> Q = 5 → P = 12




