







Preview text:
BASIC ECONOMICS
MID-TERM TEST – IBD 01 INSTRUCTIONS
1. The exam consists of four parts (i)
Part I: 20 multiple-choice questions (1.5 point each) (ii)
Part II: 4 true-false questions (5 points each) (iii)
Part III: 2 short questions (10 points each) (iv)
Part IV: 2 calculating exercises (15 points each)
2. Time allowed: 100 minutes.
3. Calculators are permitted. Books, notes, reference materials, etc. are prohibited.
4. Do all your work on the exam itself. Write clearly. Good luck!
Student Name: Phan Thuỷ Anh Class: I18S4 Student ID: 10220524
--------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
Part 1: Multiple-choice questions (1.5 points each) 1. A 6. C 11. C 16. D 2. D 7. A 12. B 17. C 3. A 8. C 13. C 18. A 4. B 9. A 14. D 19. B 5. D 10. A 15. D 20. D
Part 1: Multiple-choice questions (1.5 points each)
1. The overriding reason as to why households and societies face many decisions is that? A. resources are scarce.
B. goods and services are not scarce.
C. incomes fluctuate with business cycles.
D. people, by nature, tend to disagree.
2. During the summer you have made the decision to attend summer school, which
precludes you from working at your usual summer job in which you normally earn
$36,000 for the summer. Your tuition cost is $3,000, books and supplies cost
$10.000, and room and board cost$1,000. The opportunity cost of attending summer school is A. $36,000 B. $3,000 C. $14,000 D. $50,000
3. Which of the following is a macroeconomic issue?
A. how federal government budget deficits affect interest rates
B. the cause of a decline in the price of peanut butter
C. what determines the amount a firm will produce
D. how a rise in the price of sugar affects the market for sodas
4. Which of the following changes would not shift the demand curve for a good or service? A. a change in income
B. a change in the price of the good or service
C. a change in expectations about the future price of the good or service
D. a change in the price of a related good or service
5. Good X and good Y are substitutes. If the price of good Y increases, then the
A. demand for good X will decrease.
B. quantity demanded of good X will decrease.
C. demand for good X will increase.
D. quantity demanded of good X will increase. Figure 1 price 24 22 20 S 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 D 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 quantity
6. Refer to Figure 1. At a price of $6,
A. there would be a shortage and the law of supply and demand predicts that
the price will fall from $10 to a lower price
B. there would be a surplus and the law of supply and demand predicts that the
price will rise from $10 to a higher price
C. there would be an excess demand and the law of supply and demand
predicts that the price will rise from $6 to a higher price
D. there would be an excess supply and the law of supply and demand predicts
that the price will fall from $10 to a lower price
7. If the price elasticity of demand for tuna is 0.7, then a 1.5% increase in the
price of tuna will decrease the quantity demanded of tuna by
A. 1.05%, and tuna sellers' total revenue will increase as a result.
B. 1.05%, and tuna sellers' total revenue will decrease as a result.
C. 2.14%, and tuna sellers' total revenue will increase as a result.
D. 2.14%, and tuna sellers' total revenue will decrease as a result.
8. When her income increased from $10,000 to $20,000, Heather's consumption
of macaroni decreased from 10 pounds to 5 pounds and her consumption of
soy-burgers increased from 2 pounds to 4 pounds. We can conclude that for Heather,
a. macaroni and soy-burgers are both normal goods with income elasticities equal to 1.
b. macaroni is an inferior good and soy-burgers are normal goods; both have income elasticities of 1.
c. macaroni is an inferior good with an income elasticity of -1 and soy-burgers
are normal goods with an income elasticity of 1.
d. macaroni and soy-burgers are both inferior goods with income elasticities equal to -1.
9. Which of the following could be the cross-price elasticity of demand for two goods that are complements? A. -2.5 B. 0 C. 0.25 D. 2.5
10. Other things equal, the demand for a good tends to be more inelastic, the
A. fewer the available substitutes.
B. longer the time period considered.
C. more the good is considered a luxury good.
D. more narrowly defined is the market for the good.
11. If marginal cost is above average variable cost, then average variable cost A. is constant B. is falling C. is rising
D. may rise or fall depending on the size of fixed costs
12. A firm is producing 100 units with an average total cost of $60 and a
marginal cost of $40. If it were to increase production to 101 units, which of
the following must occur?
A. marginal cost would decrease.
B. marginal cost would increase.
C. average total cost would decrease.
D. average total cost would increase.
13. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a competitive market?
A. Buyers and sellers are price takers.
B. Each firm sells a virtually identical product. C. Free entry is limited.
D. Each firm chooses an output level that maximizes profits..
14. For a competitive firm,
A. total revenue equals average revenue.
B. total revenue equals marginal revenue.
C. total cost equals marginal revenue.
D. average revenue equals marginal revenue.
15. A firm will shut down in the short run if, for all positive levels of output,
A. its loss exceeds its fixed costs.
B. its total revenue is less than its variable costs.
C. the price of its product is less than its average variable cost.
D. All of the above are correct.
16. Competitive firms differ from monopolies in which of the following ways?
(i) Competitive firms do not have to worry about the price effect lowering their total revenue.
(ii) Marginal revenue for a competitive firm equals price, while marginal revenue for a
monopoly is less than the price it is able to charge.
(iii) Monopolies must lower their price in order to sell more of their product, while competitive firms do not. A. and (ii) only B. (ii) and (iii) only C. (i) and (iii) only D. (i), (ii), and (iii)
17. An Italian company operates a pasta restaurant in the U.S. The value of the
output produced by this pasta restaurant is included in A. U.S. GNP and Italian GNP. B. U.S. GNP and Italian GDP. C. U.S. GDP and Italian GNP. D. U.S. GDP and Italian GDP
18. The local Chevrolet dealership has an increase in inventory of 25 cars in 2006.
In 2007, it sells all 25 cars. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. The value of the cars in inventory will be counted as part of 2006 GDP, and the
value of the cars sold in 2007 will not increase 2007 GDP.
B. The value of the cars in inventory will not affect 2006 GDP, and the value of
the cars sold in 2007 will increase 2007 GDP.
C. The value of the cars in inventory will be counted as part of 2006 GDP, and the
value of the cars sold in 2007 will increase 2007 GDP.
D. The value of the cars in inventory will not affect 2006 GDP, and the value of
the cars sold in 2007 will not increase 2007 GDP.
19. When an Egyptian firm purchases a cement mixer from Slovakia,
A. Egyptian investment does not change, Egyptian net exports decrease, Egyptian
GDP decreases, Slovakian net exports increase, and Slovakian GDP increases.
B. Egyptian investment increases, Egyptian net exports decrease, Egyptian GDP
is unaffected, Slovakian net exports increase, and Slovakian GDP increases.
C. Egyptian investment decreases, Egyptian net exports increase, Egyptian GDP
is unaffected, Slovakian net exports decrease, and Slovakian GDP decreases.
D. Egyptian investment increases, Egyptian net exports do not change, Egyptian
GDP increases, Slovakian net exports do not change, and Slovakian GDP is
20. An increase in the price of Irish whiskey regularly purchased by Americans will be reflected in
A. both the U.S. GDP deflator and the U.S. CPI.
B. neither the U.S. GDP deflator nor the U.S. CPI.
C. the U.S. GDP deflator, but not the U.S. CPI.
D. the U.S. CPI, but not the U.S. GDP deflator.
Part 2: True or False? Briefly explain. (5 points each)
1. GDP does not make adjustments for leisure time, environmental quality, or volunteer work TRUE
Because these things are difficult to measure and value accurately
2. In general, demand curves for necessities tend to be price elastic. FALSE
Demand curves for necessities tend to be price inelastic, because our survival depends on them
3. A government program that reduces land under cultivation hurts farmers but helps consumers. FALSE
Farmers and consumers are both harmed by a government initiative that
decreases the amount of land used for agriculture. Farmers would suffer
since they will have to produce fewer goods as a result of having less farming area.
4. An increase in nominal U.S. GDP necessarily implies that the United States is
producing a larger output of goods and services. FALSE
Growing nominal GDP from year to year can indicate an increase in prices
rather than an increase in the quantity of goods and services produced
because it is calculated in current prices.
Part 3: Short answers (10 points each)
1. If a firm faces an elastic demand for its product, what policy on price for a firm to
increase the total revenue? (Hint: based on elasticity to explain)
Based on elasticity, we have to decrease the price in order to increase the total
revenue if there is an elastic demand for products.
2. Which is likely to have the larger effect on the CPI, a 2 percent increase in the
price of food or a 3 percent increase in the price of diamond rings? Explain.
Given that food makes up a higher share of the market basket than diamond
rings does, the 2% increase in food prices will have a greater impact on the CPI.
Part 4: Calculating Exercises (15 points each)
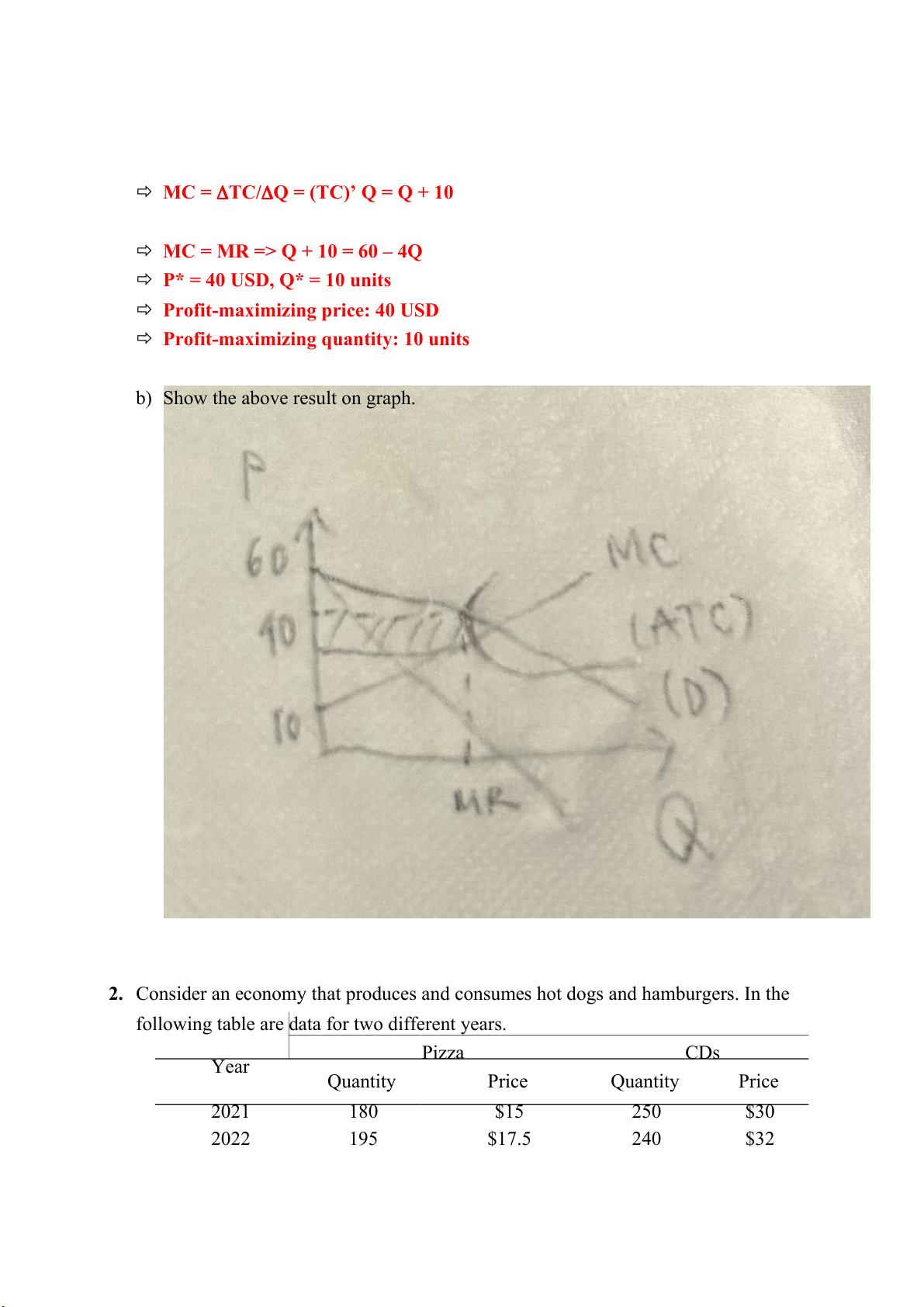
1. A monopolist is facing with the demand curve: (D) P = 60– 2Q
Where P is in USD and Q is in units
The firm’s total cost function is given by: TC = 0.5Q2 + 10Q + 10
a) Calculate P*, Q* and profits when this firm wants to maximize profit?
The monopolist can maximize its profit when the marginal cost equal to the
marginal revenue: MC = MR
TR = P x Q = (60 – 2Q) x Q = 60Q – 2Q2
MR = TR/Q = (TR)’ Q MR = 60 – 4Q
MC = TC/Q = (TC)’ Q = Q + 10
MC = MR => Q + 10 = 60 – 4Q
P* = 40 USD, Q* = 10 units
Profit-maximizing price: 40 USD
Profit-maximizing quantity: 10 units
b) Show the above result on graph.
2. Consider an economy that produces and consumes hot dogs and hamburgers. In the
following table are data for two different years. Pizza CDs Year Quantity Price Quantity Price 2021 180 $15 250 $30 2022 195 $17.5 240 $32
a) Using a method similar to the CPI, compute the percentage change in the overall
price level. Use 2021 as the base year and fix the basket at 150 pizza and 130 CDs.
The cost of the market basket in 2021 is: (150 x $15) + (130 x $30) = $6150
The cost of the market basket in 2022 is: (150 x $17.5) + (130 x $32) = $6785
CPI 2021 = $6150/$6150 x 100 = 100
CPI 2022 = $6785/$6150 x 100 = 110.325
b) Using a method similar to the GDP deflator, compute the percentage change in the
overall price level. Also use 2021 as the base year.
Nominal GDP for 2021 = 180 x $15 + 250 x $30 = $10200
Nominal GDP for 2022 = 195 x $17.5 + 240 x $32 = $11092.5
Real GDP for 2021 = 180 x $15 + 250 x $30 = $10200
Real GDP for 2022 = 195 x $15 + 240 x $30 = $10125
The GDP deflator for 2021 = $10200/$10200 x 100 = 100
The GDP deflator for 2022 = $11092.5/$10125 x 100 = 109.55
c) Is the inflation rate in 2022 the same using the two methods? Explain why or why not.
Inflation rate = (110.325 – 100)/100 x 100 = 10.325




