




Preview text:
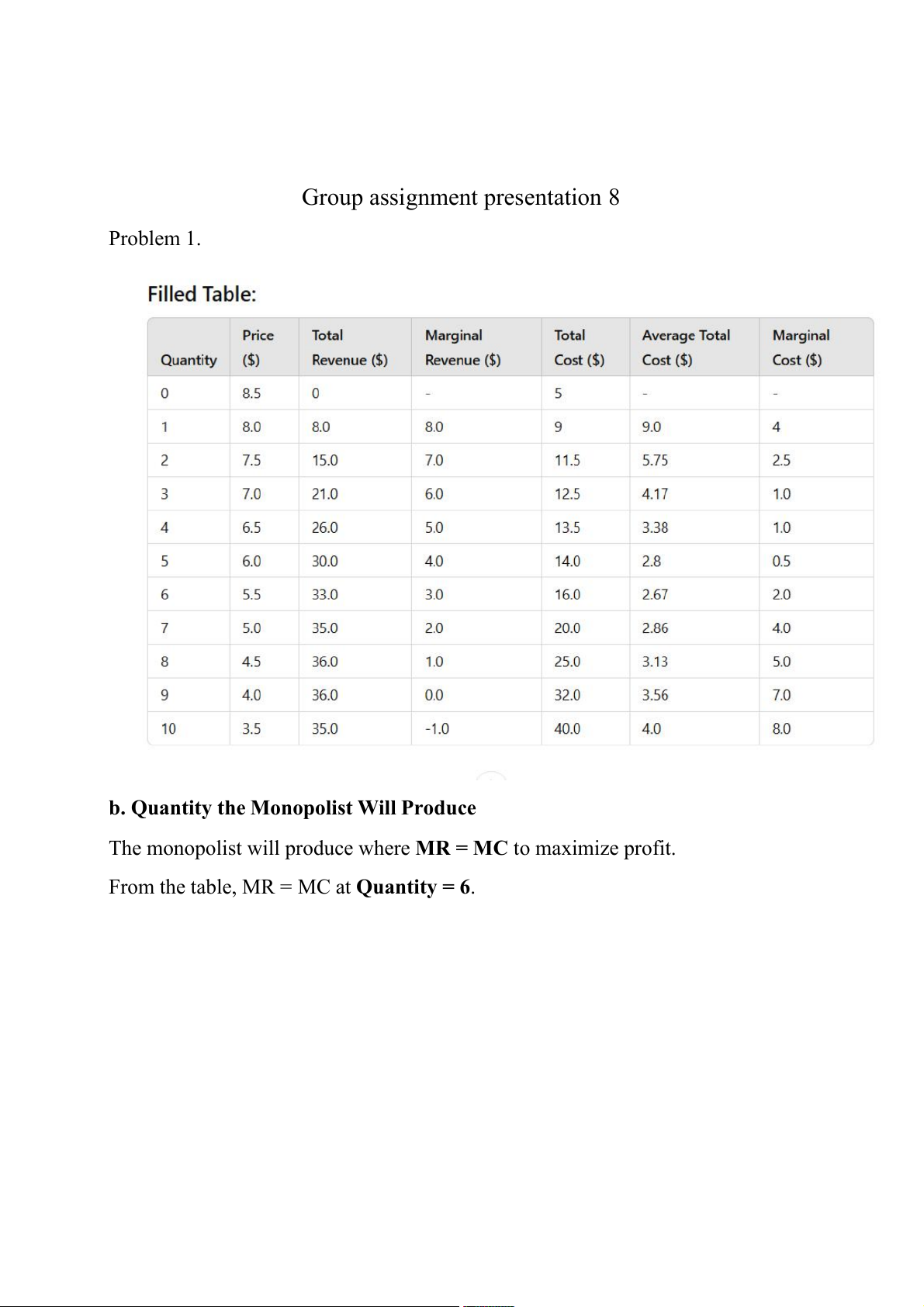
Group assignment presentation 8 Problem 1.
b. Quantity the Monopolist Will Produce
The monopolist will produce where MR = MC to maximize profit.
From the table, MR = MC at Quantity = 6. Total Revenue = 33.0 Total Cost = 16.0
Thus, Profit = 33.0 - 16.0 = 17.0. Problem 2 Given data: Demand function: P=100−Q
Total cost function: TC=500+4Q+Q^2
Part (a): Is this firm a perfectly competitive firm?
No, this firm is not perfectly competitive. The demand function P=100−QP
indicates that the firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve, which means it
has some control over the price (price-maker), a characteristic of monopoly or
imperfect competition, not perfect competition.
Part (b): Maximizing Total Revenue
Total Revenue (TR) is calculated as:
TR=P×Q=(100−Q)×Q=100Q−Q^2
To maximize Total Revenue, we need to take the derivative of TR with respect to Q,
set it to zero, and solve for Q:
Substitute Q=50 back into the demand function to find the price: P=100−50=50 The maximum Total Revenue is: Answer:
Quantity that maximizes Total Revenue, Q=50 Price at this quantity, P=50 Maximum Total Revenue = 2500 Part (c): Profit Maximization
Profit is maximized where Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC). Answer:
Profit-maximizing Quantity, Q=24 Price at this quantity, P=76 Maximum Profit = 652
Part (d): Effect of a Per-Unit Tax of $8




