


Preview text:
Overview of economics 1. Why? 2. Methods? 3. Principles (10) I.WHY
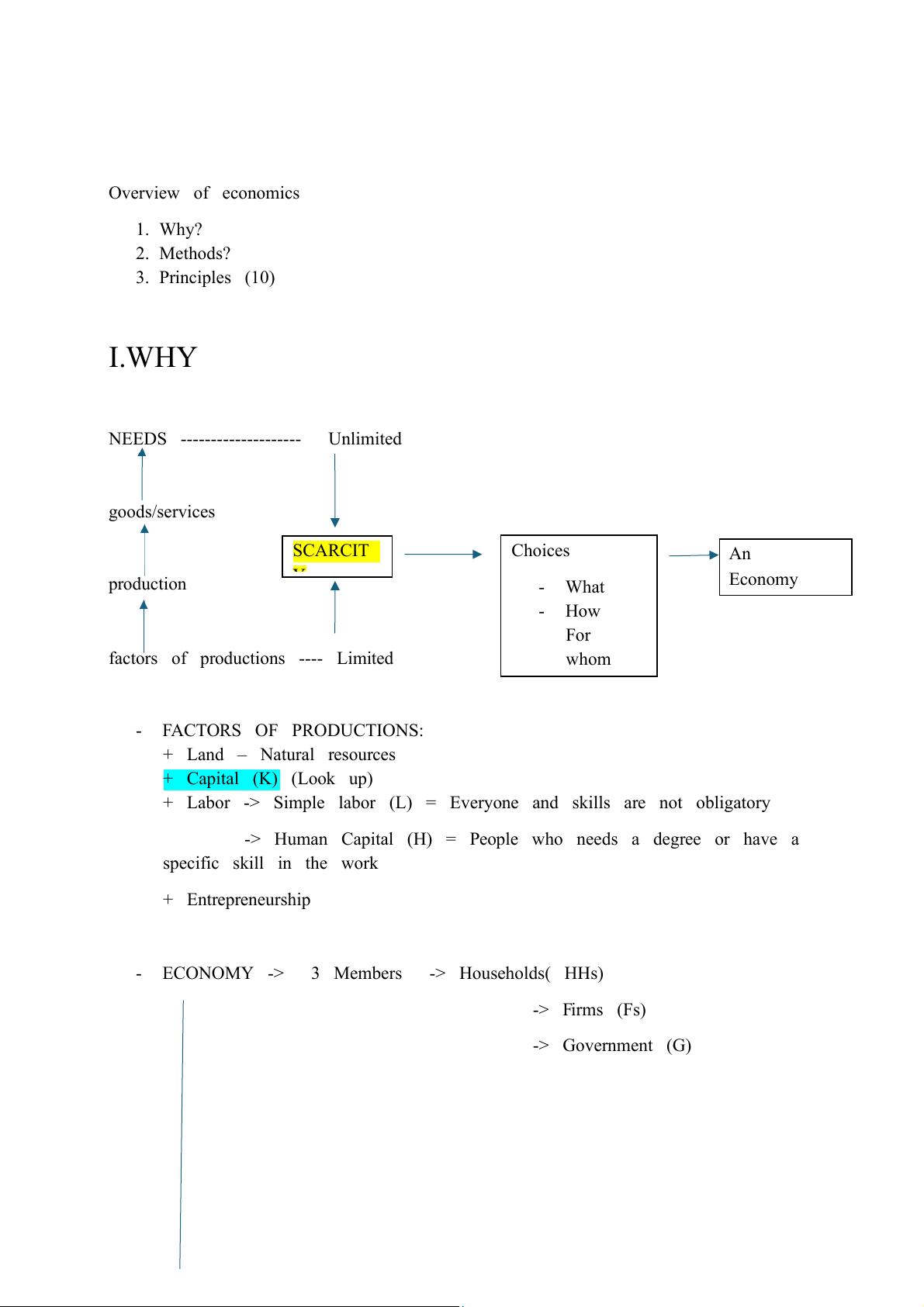
NEEDS -------------------- Unlimited goods/services SCARCIT Choices An production Y - What Economy - How For
factors of productions ---- Limited whom - FACTORS OF PRODUCTIONS: + Land – Natural resources + Capital (K) (Look up)
+ Labor -> Simple labor (L) = Everyone and skills are not obligatory
-> Human Capital (H) = People who needs a degree or have a specific skill in the work + Entrepreneurship -
ECONOMY -> 3 Members -> Households( HHs) -> Firms (Fs) -> Government (G) -> 3 systems:
+ A command ( Usually from G and they decide everything)
Ex: Vietnam = Centrally planned economy ( Disadv: Need a huge in4)
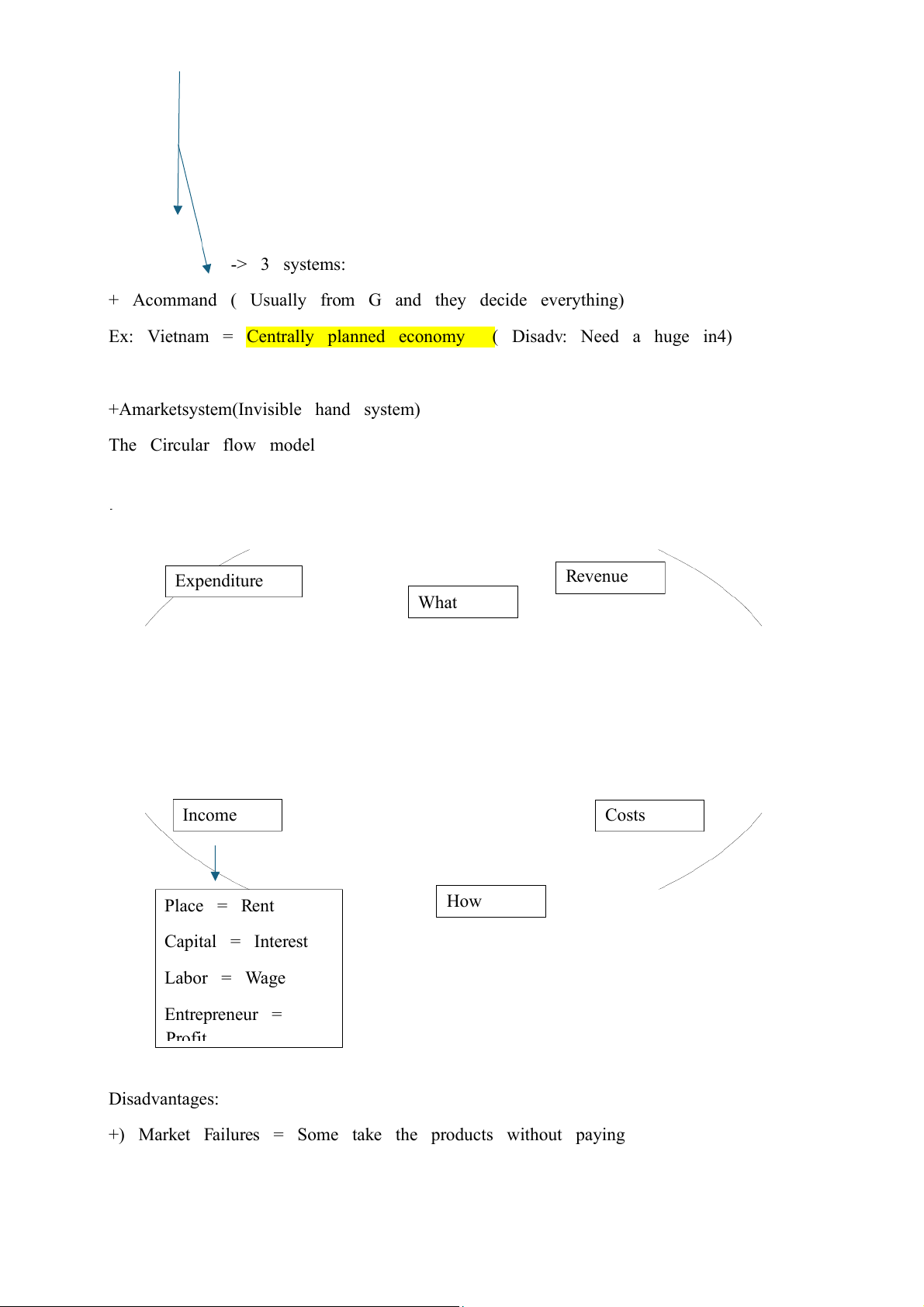
+ A market system (Invisible hand system) The Circular flow model ar G se kF pro r e m Htaao vi ctd nr H dc mo fu k S /er s ct isoo Fs Revenue Expenditure What Income Costs How Place = Rent Capital = Interest Labor = Wage Entrepreneur = Profit Disadvantages:
+) Market Failures = Some take the products without paying
Ex: Fireworks -> People could film -> The image spread out -> Everyone can see without paying
+ A mixed economy = A combine of both command and market economy
Economics: Study how our society ALLOCATES scarce resources to alternative uses
Microeconomy = How each member makes decision Their – Interactions H F G HsS
HHs >< Fs = Market Failure then G comes in to solve Normative vs Positive
Normative = Petrol gas is too high = Subjective = Have the world should be
Positive = If Pgas is high, Taxi fare is high = Objective = Describe the world as it is Why do we cares? Bcs of the role of an economy
If you’re a researcher, you will work with positive statements
If you’re a consultant or politician, you will work with normative statements II.Methods
- Step 1: Observe -> Q + What is it? + Why does it happen? + What happens next?
- Step 2: Models/Theories -> A
+ A model simplifies the real world by making assumptions
keeping the core issues/ get rid of unrelated in4
Ex: Adam Smith -> Why nations trade
1st theories = Absolute Advantage theory (Exporter have lower cost than Importer) Assumption: + 2 countries VN vs Brazil + 1 product: Football + 1 input + difference in tech Vietnam Brazil Tech Tech < Tech Cost Cost > Cost Product Pfootball > Pfootball Importer Exporter
Brazil has lower costs = Abs Adv
- Step 3: Test Models 1St way: Testing assumption 2nd way: Testing prediction
If your model cannot explain the future or current situation -> Wrong H-O model Assume + 2 countries: VN vs US + 2 inputs: K & L
+ 2 products: L-intensive & K-intensive + No diff in tech + Diff in K/L
VN has less K/L than US -> Vietnam is L-abundant, and US is K- abundant
-> Vietnam L is relatively cheaper, and US K is relatively cheaper L- K- intensi intensi ve ve -> III. Principals - What do we care?
+ Causal – Effect relationship
If A increase -> B increase or else, cateris paribus = keep
other things being equal (obligatory)
Ex: Income increase then more ip consumed ?
Only be answered when other things are equal ( No effects
from expectancy, prs, … ) -> cateris paribus USE ECONOMETRICS




