
Preview text:
SECTION 1. PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS I. DEFINITION
Scarcity is the condition that arises because wants exceed the ability of resources to satisfy them.
Economics: studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments and
the entire societies make as they cope with scarcity, the incentives
that influence those choices, and the arrangements that coordinate them. 1. Factors of production Land: natural resources
Labor: work time and work effort that people devote to producing goods and services
Capital: tools, instruments, machines, buildings, other items
Entrepreneurship: human resources that organizes labor, land and capital 2. Rational choice
Benefit is the gain or pleasure that something brings.
Marginal cost is the cost of a one-unit increase in an activity.
Marginal benefit is the what you gain when you get one more unit of something.
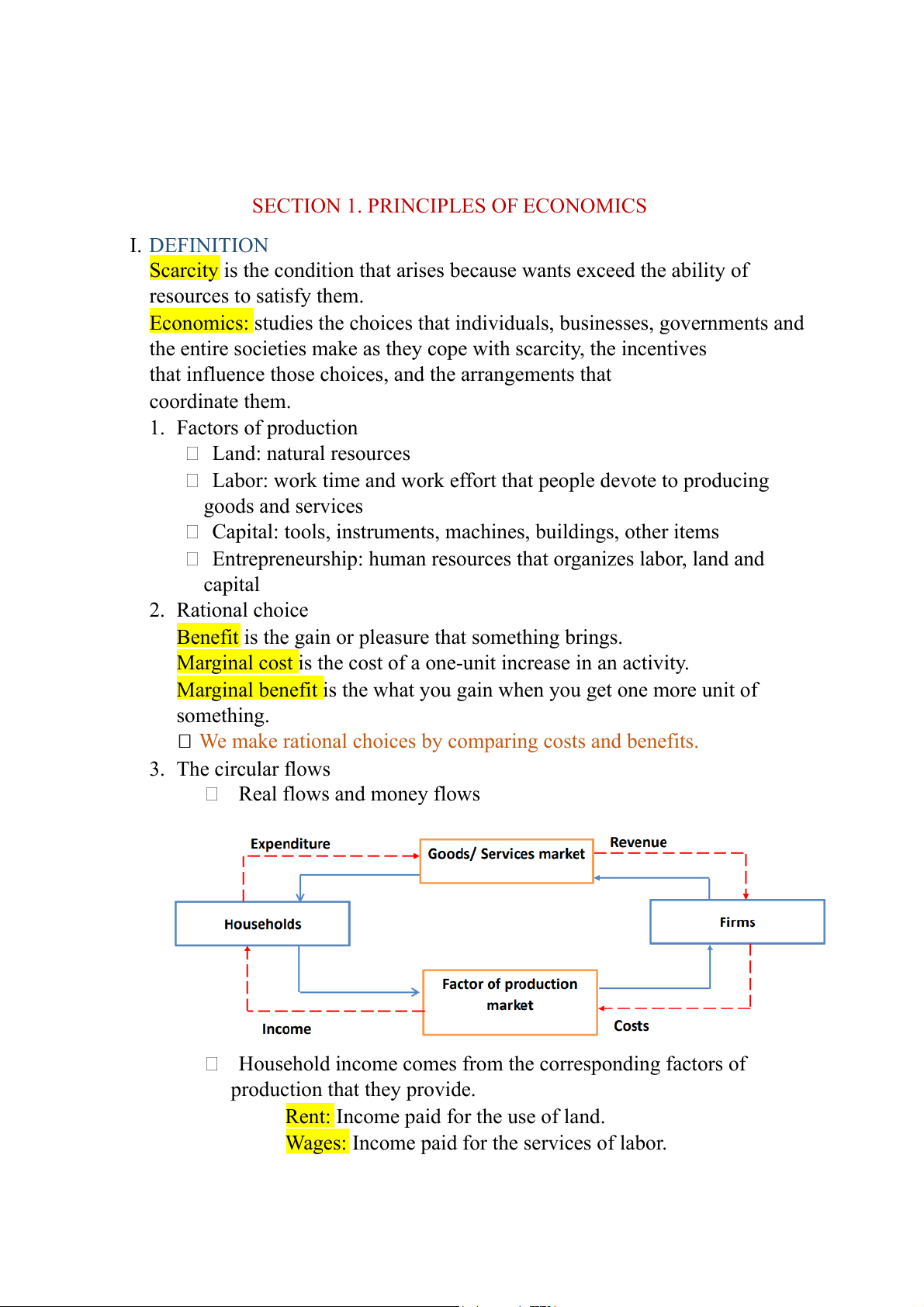
We make rational choices by comparing and costs benefits. 3. The circular flows Real flows and money flows
Household income comes from the corresponding factors of production that they provide.
Rent: Income paid for the use of land.
Wages: Income paid for the services of labor.
Interest: Income paid for the use of capital.
Profit: Income paid for the entrepreneurship.
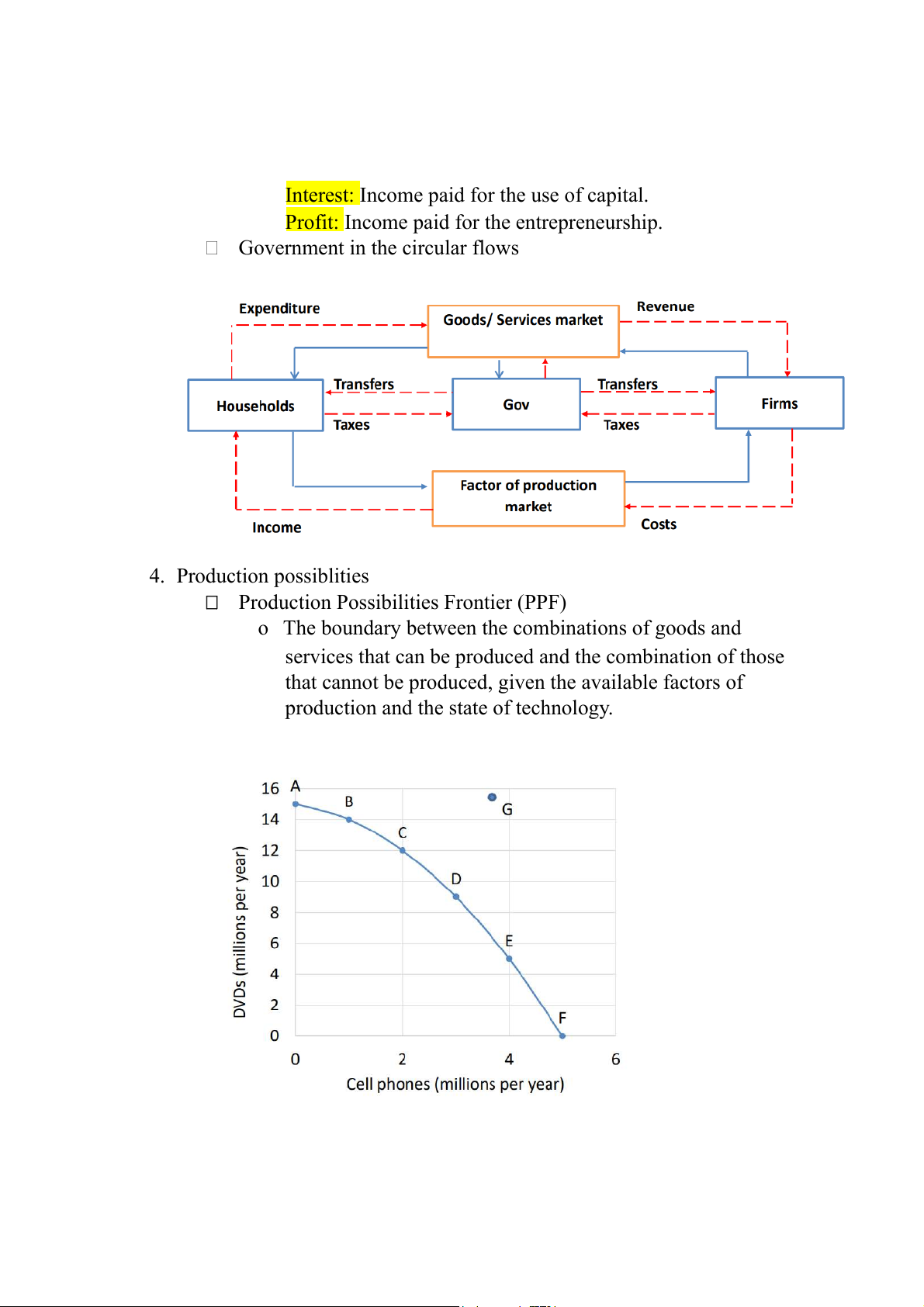
Government in the circular flows 4. Production possiblities
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
o The boundary between the combinations of goods and
services that can be produced and the combination of those
that cannot be produced, given the available factors of
production and the state of technology.
o The PPF puts three features of production possibilities in sharp focus:
- Attainable and unattainable combinations
- Efficient and inefficient production - Tradeoffs and free lunches 5. PPF and Opportunity Cost
Opportunity Cost (OC) The opportunity cost of a X is the decrease in the quantity of Y.
The law of increasing OC: The opportunity cost of producing a good
or service increases as more of the good or service are produced. Slope of the PPF and OC 6. Economic Growth Reasons for economic growth: - Technology innovation
- Increase in factors of production




