
Preview text:
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND FINAL EXAMINATION TRAINING Advanced Education Program NATIONAL ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY Date of exam: 25/02/2021
------------------------------------------------
Subject: Principles of Microeconomics FACULTY OF ECONOMICS (Time Allowance: 90 minutes) DEPARTMENT OF MICROECONOMICS
Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions
1. When the government implements programs such as progressive income tax rates, which of the following is likely to occur? a.
equality is increased and efficiency is increased. b.
equality is increased and efficiency is decreased. c.
equality is decreased and efficiency is increased. d.
equality is decreased and efficiency is decreased.
2. You have driven 1,000 miles on a vacation and then you notice that you are only 50 miles from an
attraction you hadn’t known about, but would really like to see. In computing the opportunity cost of
visiting this attraction you had not planned to visit, you should include a.
both the cost of driving the first 1,000 and the next 50 miles. b.
the cost of driving the first 1,000 miles, but not the cost of driving the next 50. c.
the cost of driving the next 50 miles, but not the cost of driving the first 1,000. d.
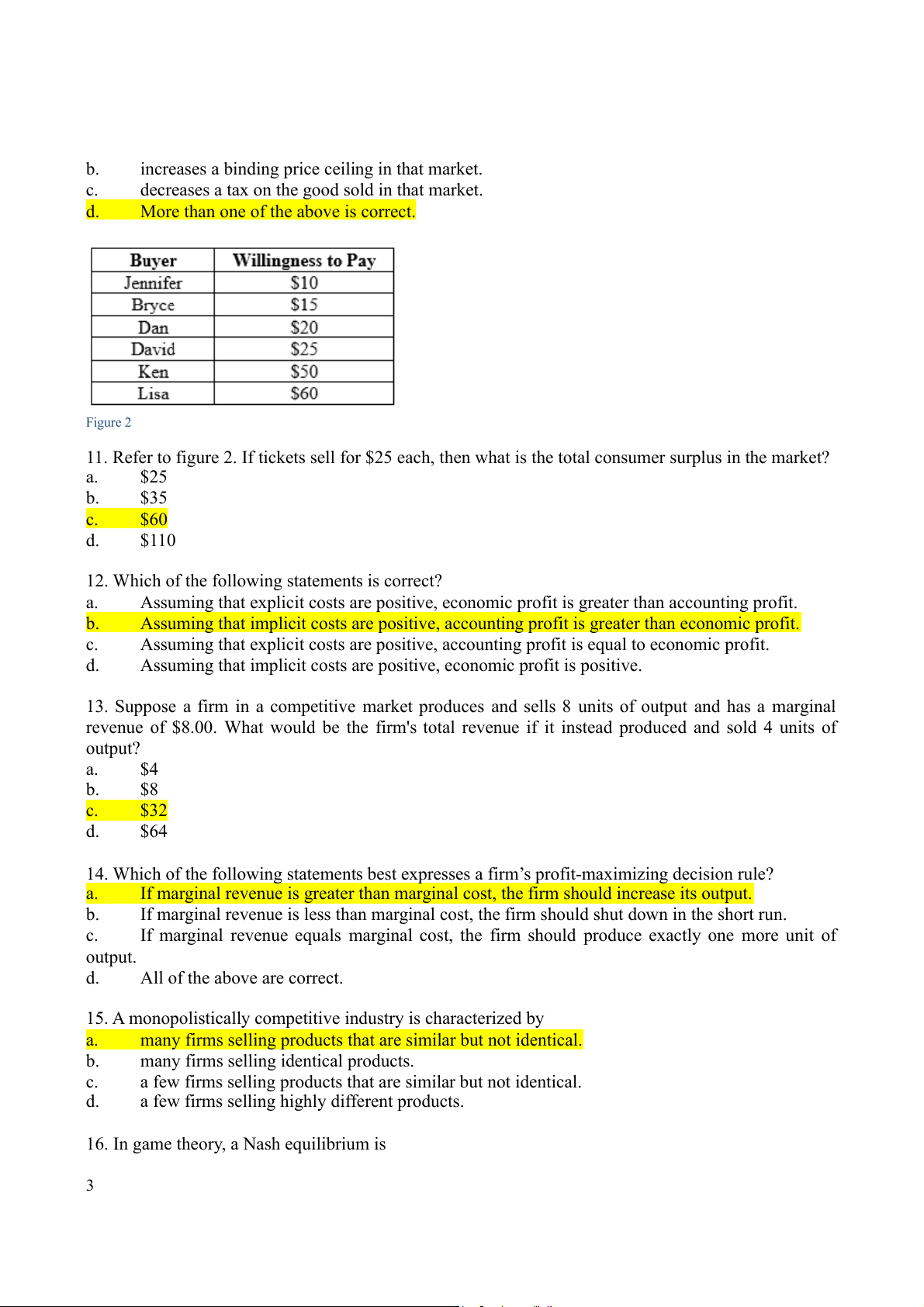
neither the cost of driving the first 1,000 miles nor the cost of driving the next 50 miles. Figure 1
3. Refer to figure 1. Efficient production is represented by which point(s)? 1 a. A, B b. A, B, C c. A, B, D d. C
4. When each person specializes in producing the good in which he or she has a comparative
advantage, total production in the economy a. falls. b. stays the same. c. rises. d.
may fall, rise, or stay the same.
5. The term price takers refers to buyers and sellers in a. perfectly competitive markets. b. monopolistic markets. c.
markets that are regulated by the government. d.
markets in which buyers cannot buy all they want and/or sellers cannot sell all they want.
6. The demand curve for hot dogs a.
shifts when the price of hot dogs changes because the price of hot dogs is measured on the vertical axis of the graph. b.
shifts when the price of hot dogs changes because the quantity demanded of hot dogs is
measured on the horizontal axis of the graph. c.
does not shift when the price of hot dogs changes because the price of hot dogs is measured on
the vertical axis of the graph. d.
does not shift when the price of hot dogs changes because the quantity demanded of hot dogs is
measured on the horizontal axis of the graph.
7. An advance in production technology will a.
increase a firm's costs and increase its supply. b.
increase a firm’s costs and decrease its supply. c.
decrease a firm’s costs and increase its supply. d.
decrease a firm’s costs and decrease its supply.
8. Goods with many close substitutes tend to have a. more elastic demands. b. less elastic demands. c.
price elasticities of demand that are unit elastic. d.
income elasticities of demand that are negative.
9. If a price ceiling is not binding, then a.
the equilibrium price is above the price ceiling. b.
the equilibrium price is below the price ceiling. c.
it has no legal enforcement mechanism. d.
More than one of the above is correct.
10. The quantity sold in a market will increase if the government a.
decreases a binding price floor in that market. 2 b.
increases a binding price ceiling in that market. c.
decreases a tax on the good sold in that market. d.
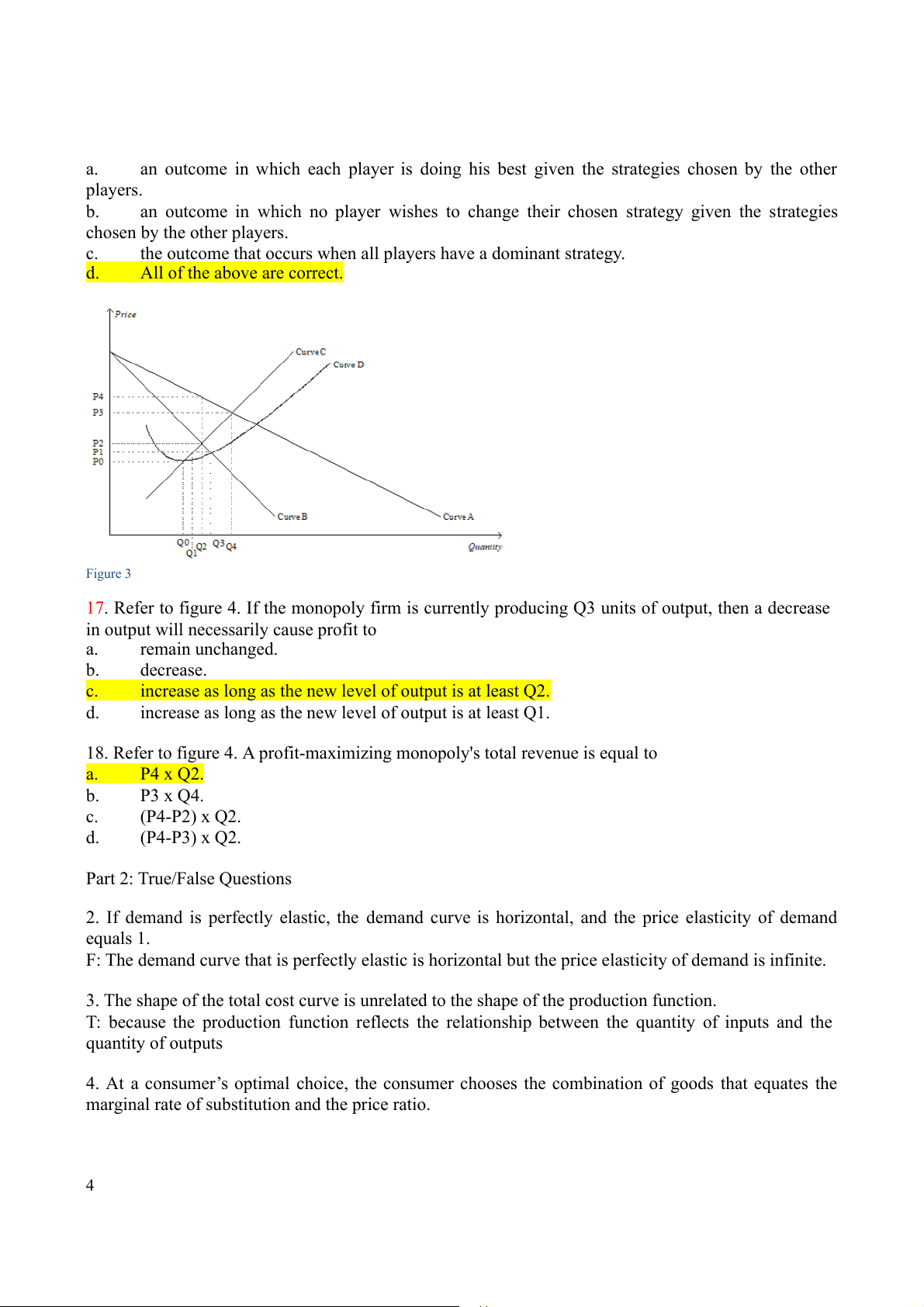
More than one of the above is correct. Figure 2
11. Refer to figure 2. If tickets sell for $25 each, then what is the total consumer surplus in the market? a. $25 b. $35 c. $60 d. $110
12. Which of the following statements is correct? a.
Assuming that explicit costs are positive, economic profit is greater than accounting profit. b.
Assuming that implicit costs are positive, accounting profit is greater than economic profit. c.
Assuming that explicit costs are positive, accounting profit is equal to economic profit. d.
Assuming that implicit costs are positive, economic profit is positive.
13. Suppose a firm in a competitive market produces and sells 8 units of output and has a marginal
revenue of $8.00. What would be the firm's total revenue if it instead produced and sold 4 units of output? a. $4 b. $8 c. $32 d. $64
14. Which of the following statements best expresses a firm’s profit-maximizing decision rule? a.
If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, the firm should increase its output. b.
If marginal revenue is less than marginal cost, the firm should shut down in the short run. c.
If marginal revenue equals marginal cost, the firm should produce exactly one more unit of output. d. All of the above are correct.
15. A monopolistically competitive industry is characterized by a.
many firms selling products that are similar but not identical. b.
many firms selling identical products. c.
a few firms selling products that are similar but not identical. d.
a few firms selling highly different products.
16. In game theory, a Nash equilibrium is 3 a.
an outcome in which each player is doing his best given the strategies chosen by the other players. b.
an outcome in which no player wishes to change their chosen strategy given the strategies chosen by the other players. c.
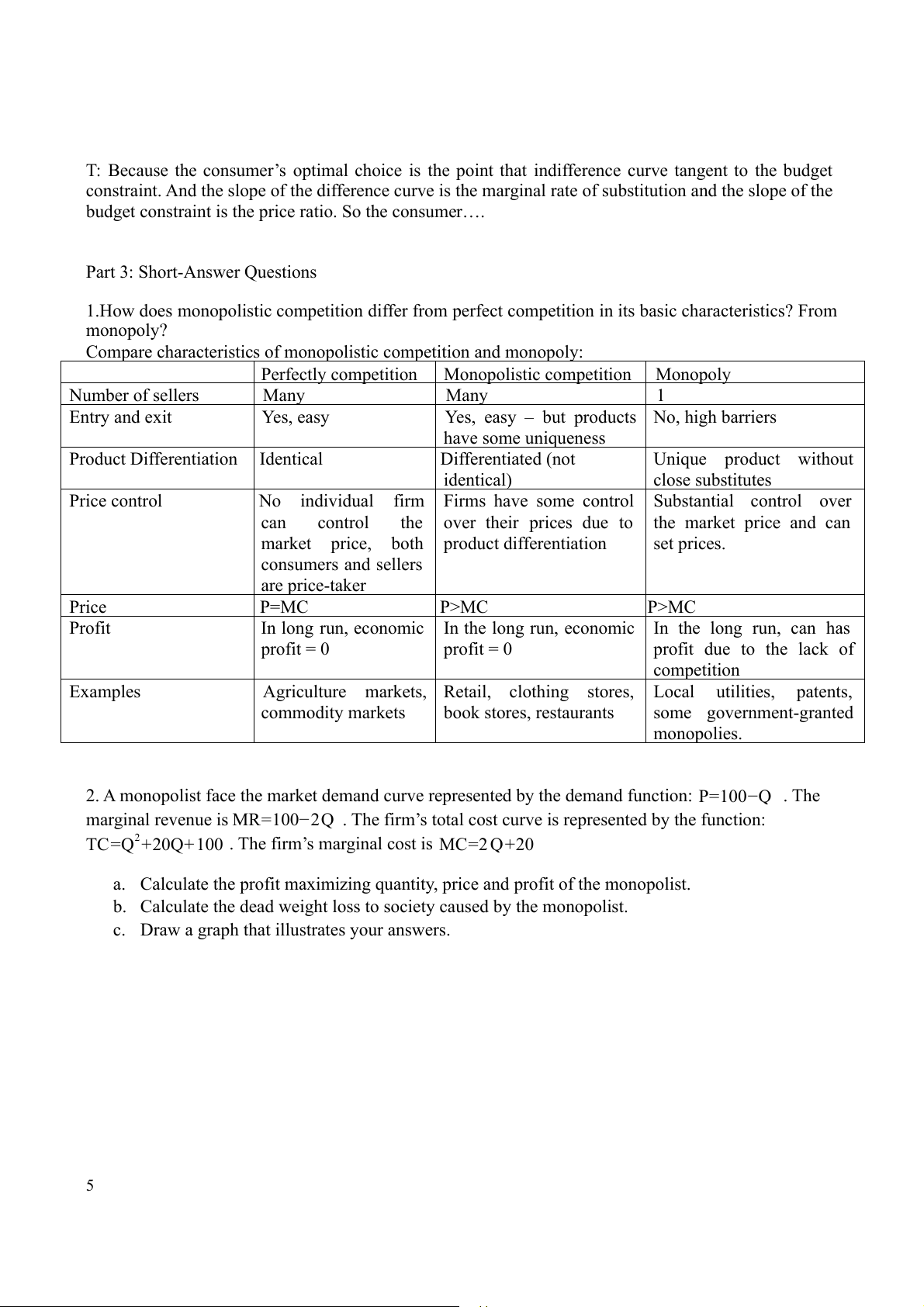
the outcome that occurs when all players have a dominant strategy. d. All of the above are correct. Figure 3 17. Refer to figure 4. If
the monopoly firm is currently producing Q3 units of output, then a decrease
in output will necessarily cause profit to a. remain unchanged. b. decrease. c.
increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q2. d.
increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q1.
18. Refer to figure 4. A profit-maximizing monopoly's total revenue is equal to a. P4 x Q2. b. P3 x Q4. c. (P4-P2) x Q2. d. (P4-P3) x Q2. Part 2: True/False Questions
2. If demand is perfectly elastic, the demand curve is horizontal, and the price elasticity of demand equals 1.
F: The demand curve that is perfectly elastic is horizontal but the price elasticity of demand is infinite.
3. The shape of the total cost curve is unrelated to the shape of the production function.
T: because the production function reflects the relationship between the quantity of inputs and the quantity of outputs
4. At a consumer’s optimal choice, the consumer chooses the combination of goods that equates the
marginal rate of substitution and the price ratio. 4
T: Because the consumer’s optimal choice is the point that indifference curve tangent to the budget
constraint. And the slope of the difference curve is the marginal rate of substitution and the slope of the
budget constraint is the price ratio. So the consumer…. Part 3: Short-Answer Questions
1.How does monopolistic competition differ from perfect competition in its basic characteristics? From monopoly?
Compare characteristics of monopolistic competition and monopoly: Perfectly competition Monopolistic competition Monopoly Number of sellers Many Many 1 Entry and exit Yes, easy
Yes, easy – but products No, high barriers have some uniqueness Product Differentiation Identical Differentiated (not Unique product without identical) close substitutes Price control
No individual firm Firms have some control Substantial control over can control the over their prices due to the market price and can market price, both product differentiation set prices. consumers and sellers are price-taker Price P=MC P>MC P>MC Profit
In long run, economic In the long run, economic In the long run, can has profit = 0 profit = 0 profit due to the lack of competition Examples
Agriculture markets, Retail, clothing stores, Local utilities, patents, commodity markets book stores, restaurants some government-granted monopolies.
2. A monopolist face the market demand curve represented by the demand function: P=100−Q . The
marginal revenue is MR=100−2Q . The firm’s total cost curve is represented by the function:
TC=Q2+20Q+100 . The firm’s marginal cost is MC=2 Q+20
a. Calculate the profit maximizing quantity, price and profit of the monopolist.
b. Calculate the dead weight loss to society caused by the monopolist.
c. Draw a graph that illustrates your answers. 5




