
Preview text:
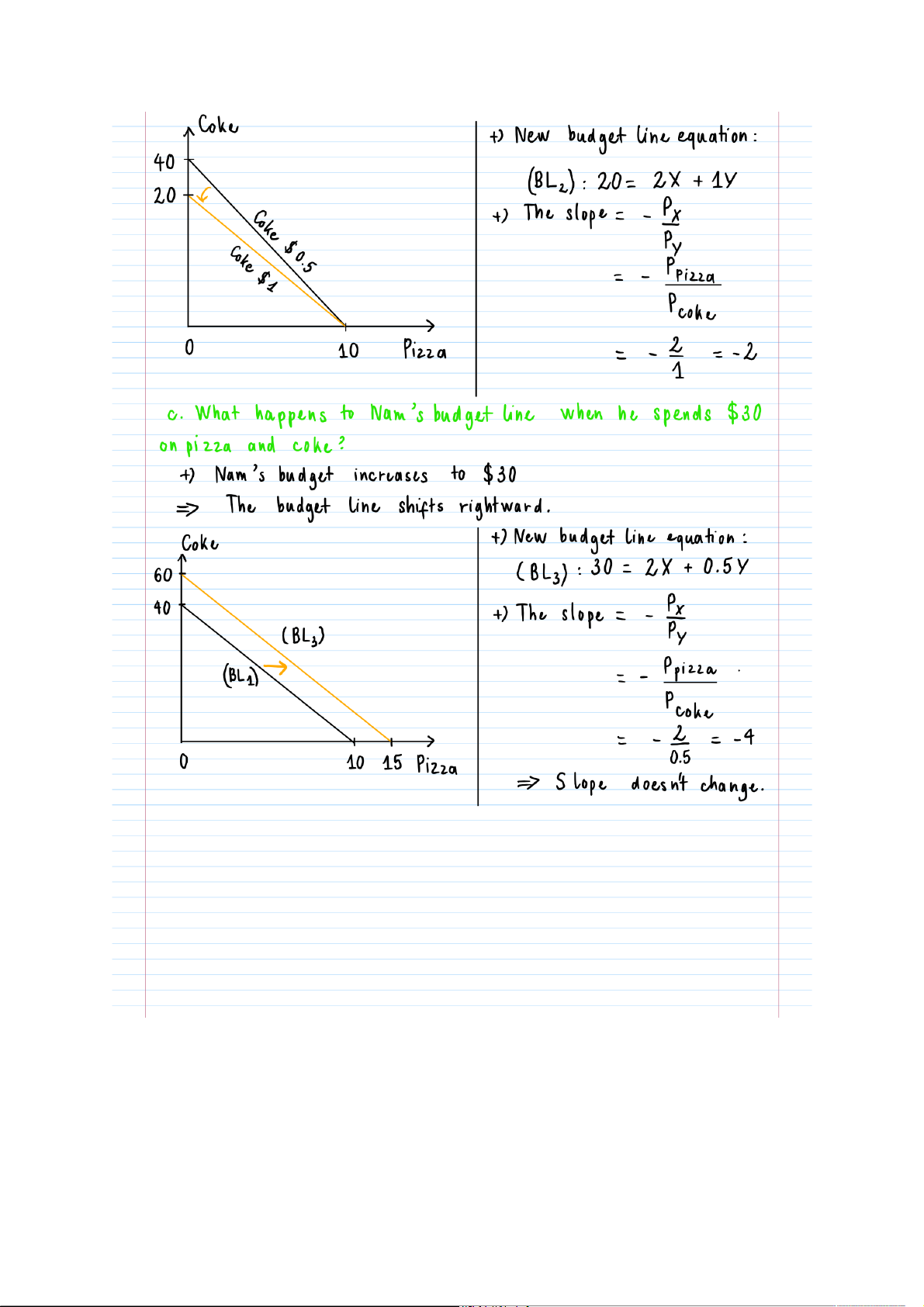
PROBLEM SOLVING SECTION 6 Ex1:
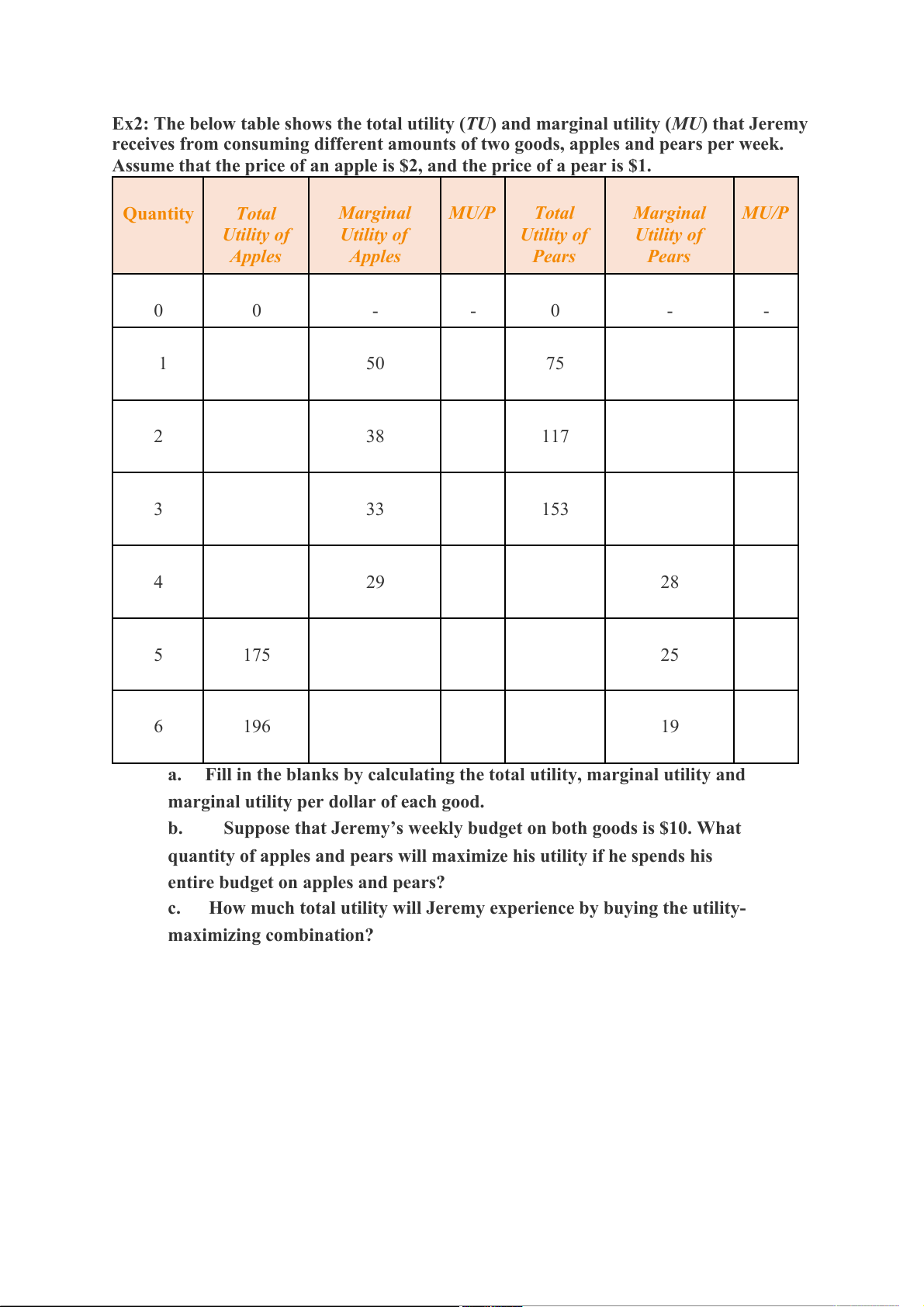
Ex2: The below table shows the total utility (TU) and marginal utility ( ) that Jeremy MU
receives from consuming different amounts of two goods, apples and pears per week.
Assume that the price of an apple is $2, and the price of a pear is $1. Quantity Total Marginal MU/P Total Marginal MU/P Utility of Utility of Utility of Utility of Apples Apples Pears Pears 0 0 - - 0 - - 1 50 75 2 38 117 3 33 153 4 29 28 5 175 25 6 196 19
a. Fill in the blanks by calculating the total utility, marginal utility and
marginal utility per dollar of each good. b.
Suppose that Jeremy’s weekly budget on both goods is $10. What
quantity of apples and pears will maximize his utility if he spends his
entire budget on apples and pears?
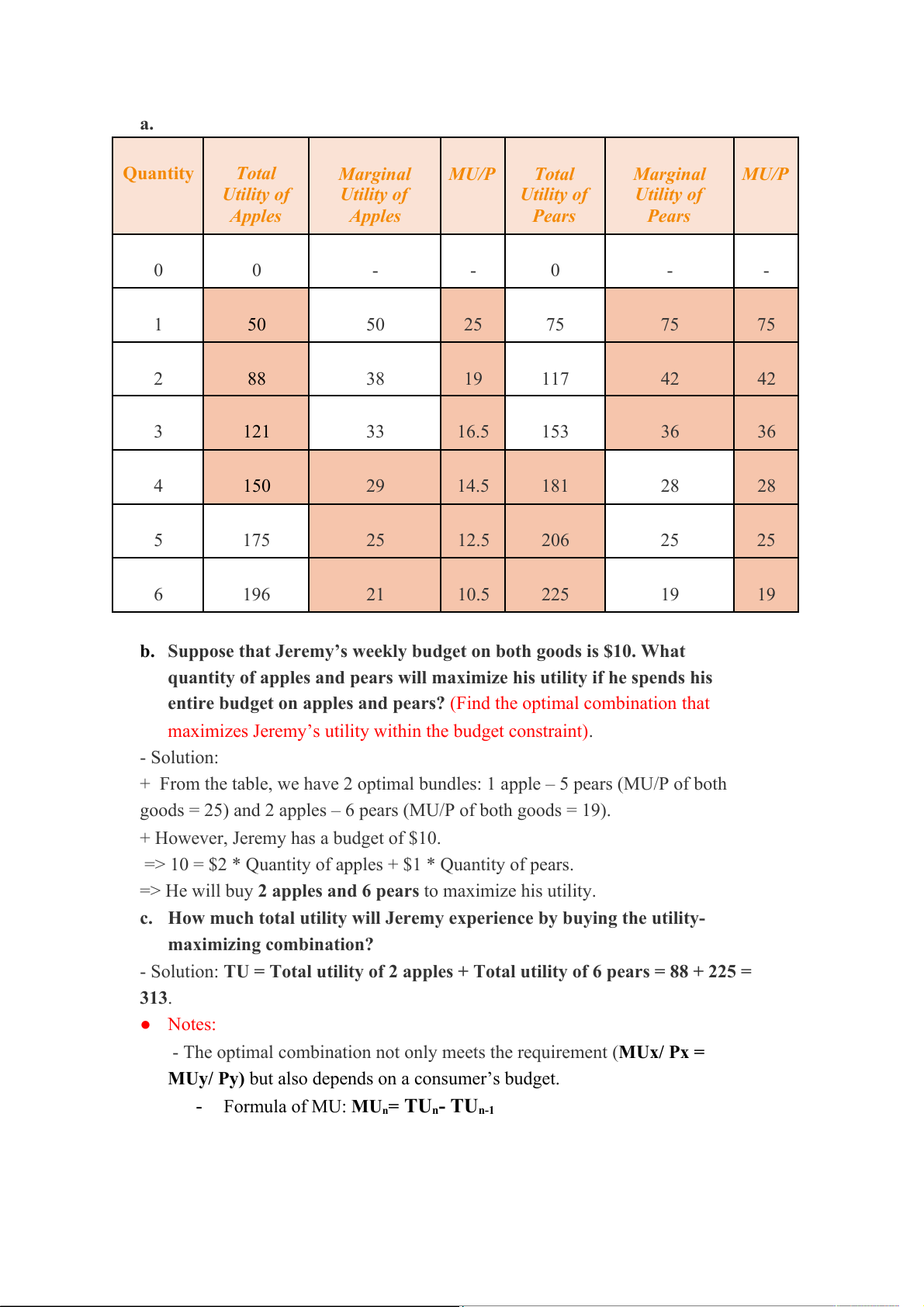
c. How much total utility will Jeremy experience by buying the utility- maximizing combination? a. Quantity Total Marginal MU/P Total Marginal MU/P Utility of Utility of Utility of Utility of Apples Apples Pears Pears 0 0 - - 0 - - 1 50 50 25 75 75 75 2 88 38 19 117 42 42 3 121 33 16.5 153 36 36 4 150 29 14.5 181 28 28 5 175 25 12.5 206 25 25 6 196 21 10.5 225 19 19
b. Suppose that Jeremy’s weekly budget on both goods is $10. What
quantity of apples and pears will maximize his utility if he spends his
entire budget on apples and pears? (Find the optimal combination that
maximizes Jeremy’s utility within the budget constraint). - Solution:
+ From the table, we have 2 optimal bundles: 1 apple – 5 pears (MU/P of both
goods = 25) and 2 apples – 6 pears (MU/P of both goods = 19).
+ However, Jeremy has a budget of $10.
=> 10 = $2 * Quantity of apples + $1 * Quantity of pears.
=> He will buy 2 apples and 6 pears to maximize his utility.
c. How much total utility will Jeremy experience by buying the utility- maximizing combination?
- Solution: TU = Total utility of 2 apples + Total utility of 6 pears = 88 + 225 = 313. ● Notes:
- The optimal combination not only meets the requirement (MUx/ Px =
MUy/ Py) but also depends on a consumer’s budget. -
Formula of MU: MUn= TUn- TUn-1




