



Preview text:
Quiz 13 (Chapter 15)
1. Consider a many-worker economy with two goods. With access to international trade, a country
can consume the greatest amount of both goods by producing at the point where the…
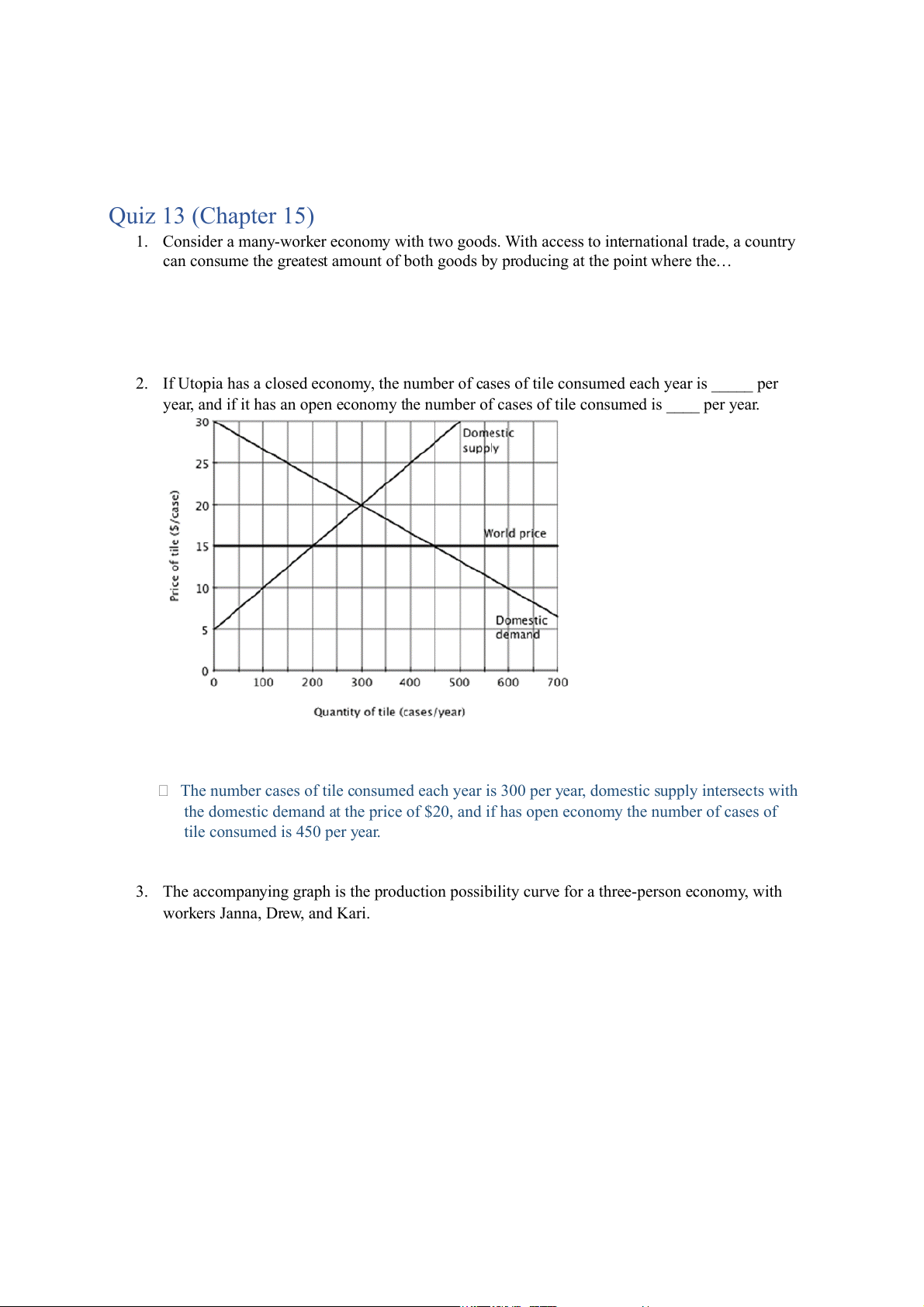
2. If Utopia has a closed economy, the number of cases of tile consumed each year is _____ per
year, and if it has an open economy the number of cases of tile consumed is ____ per year.
The number cases of tile consumed each year is 300 per year, domestic supply intersects with
the domestic demand at the price of $20, and if has open economy the number of cases of
tile consumed is 450 per year.
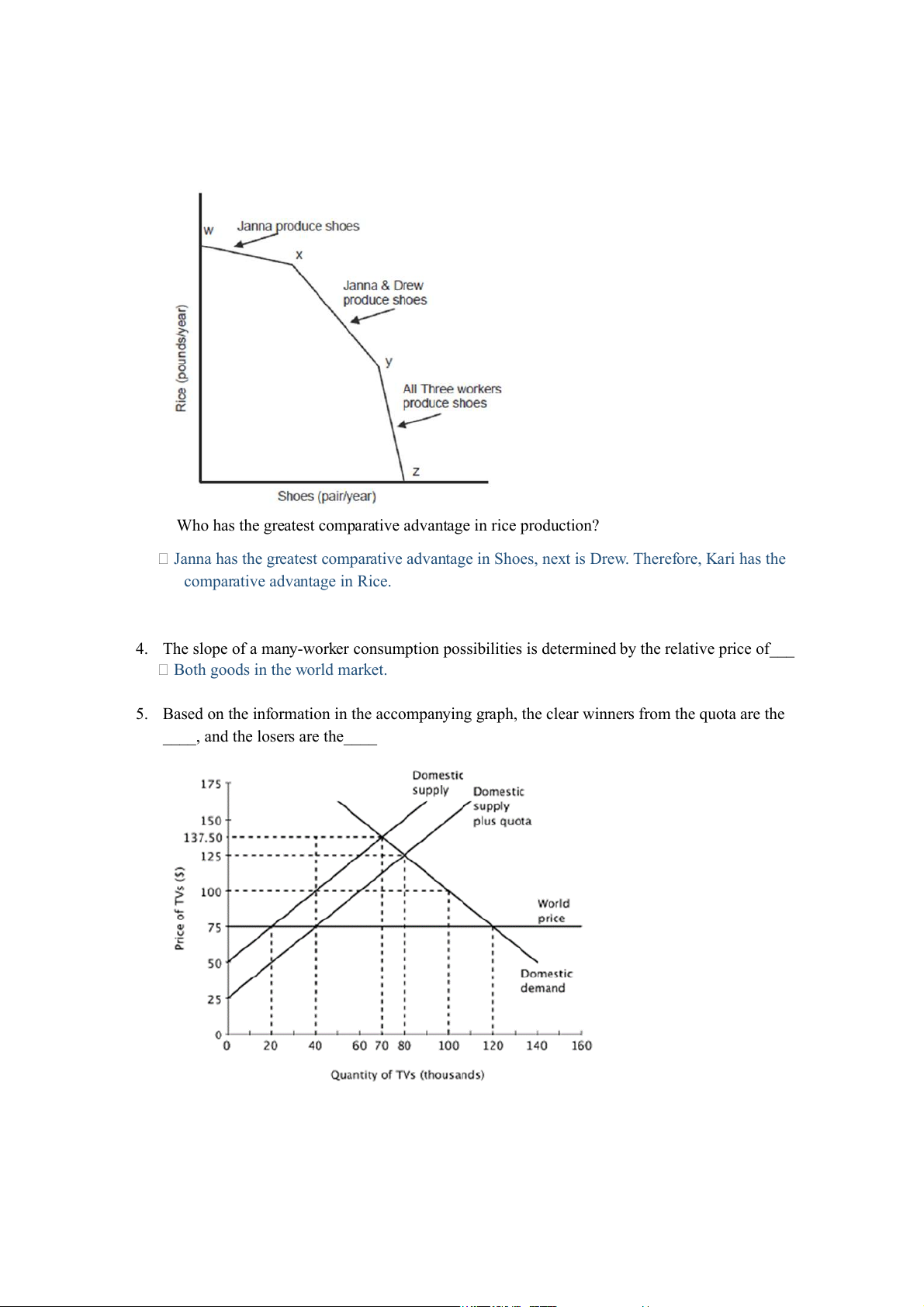
3. The accompanying graph is the production possibility curve for a three-person economy, with workers Janna, Drew, and Kari.
Who has the greatest comparative advantage in rice production?
Janna has the greatest comparative advantage in Shoes, next is Drew. Therefore, Kari has the
comparative advantage in Rice.
4. The slope of a many-worker consumption possibilities is determined by the relative price of___
Both goods in the world market.
5. Based on the information in the accompanying graph, the clear winners from the quota are the
____, and the losers are the____
Because the quota increases the domestic price of TVs, producers are better off, and consumers are worse off.
6. If Utopia opened itself to trade it would
a. Import 250 cases of tile per year.
b. Export 450 cases of tile per year.
c. Export 100 cases of tile per year.
d. Import 150 cases of tile per year.
In an open economy: the domestic price becomes the world price => $15 per case.
+, At $15, domestic demand is 450 cases and domestic supply is 200 cases per year.
Implying Utopia will import 250 cases per year.
7. The demand for microwaves in a certain country is given by: D = 8,000 – 30P, where P is the price
of a microwave. Supply by domestic microwave producers is S = 4,000 + 10P. If this economy
opens to trade while the world price of a microwave is $50, and the government imposes a tariff
of $30 per microwave, then the tariff revenue collected by the government will be __$24.000___
World price of a microwave is $50, the government imposes a tariff of $30 per microwave. The demand for microwaves:
D = 8,000 – 30P (P is price of a microwave) 8,000 – 30(50 + 30) = 5,600
The domestic quantity supplied is: S = 4,000 + 10P 4,000 + 10 (30 +50) = 4,800
Demand > Supply => Import: 5,600 – 4,800 = 800 microwaves
The tariff revenue collected by the government will be: $30 x 800 = $24.000
8. Tamara can produce either 5,000 pounds of cheese or 20 cars per year. Jamal can produce either
5,000 pounds of cheese or 10 cars per year. By the principle of comparative advantage, Jamal
should specialize in producing______ Cheese
9. What is the domestic price of sugar in a closed economy?
In a closed economy, the domestic price is determined by the intersection of domestic supply and domestic demand $3,000 per ton
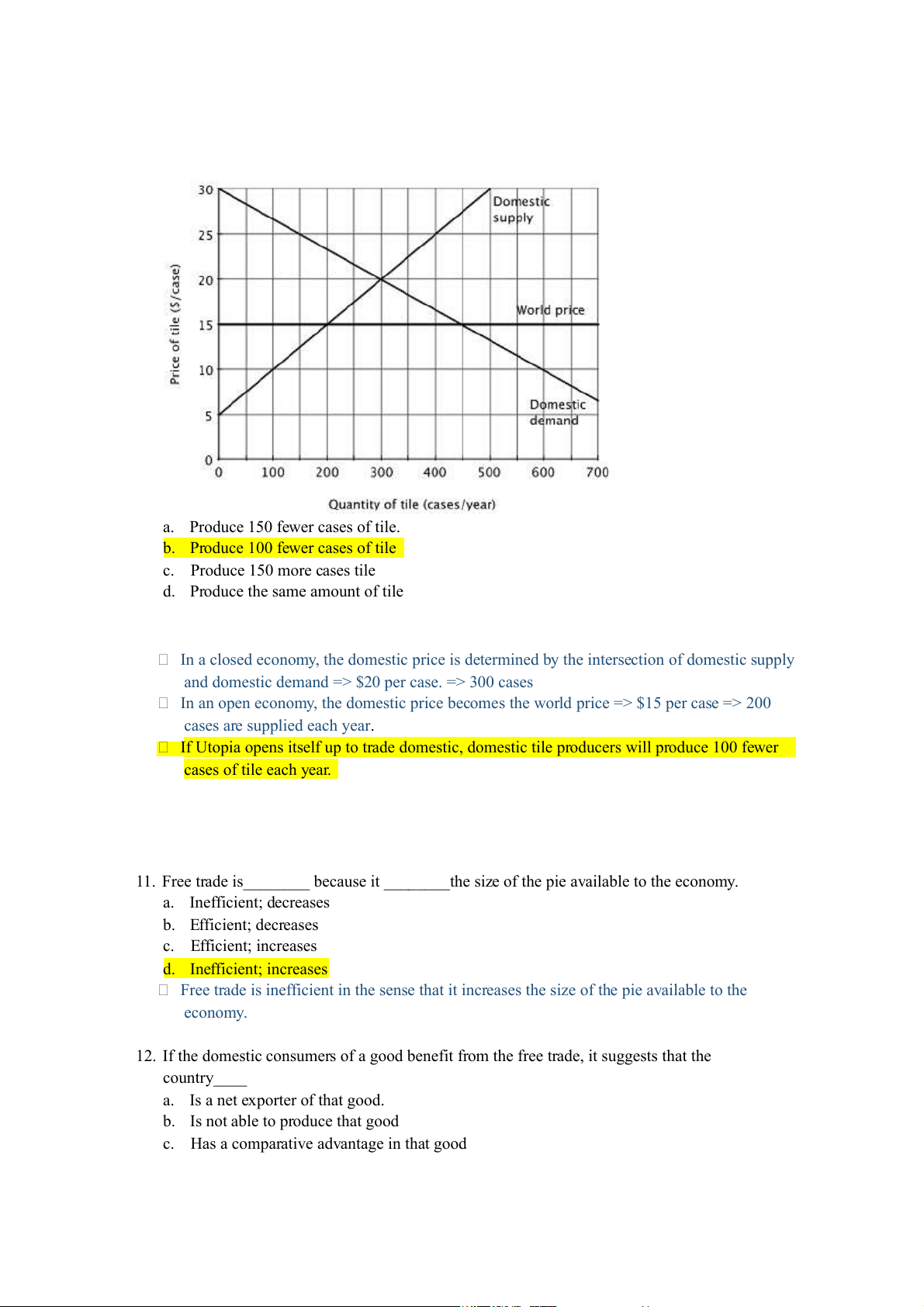
10. Relative to a closed economy, if Utopia opened itself to trade, domestic tile producers would:
a. Produce 150 fewer cases of tile.
b. Produce 100 fewer cases of tile c. Produce 150 more cases tile
d. Produce the same amount of tile
In a closed economy, the domestic price is determined by the intersection of domestic supply
and domestic demand => $20 per case. => 300 cases
In an open economy, the domestic price becomes the world price => $15 per case => 200 cases are supplied each year.
If Utopia opens itself up to trade domestic, domestic tile producers will produce 100 fewer cases of tile each year.
11. Free trade is________ because it ________the size of the pie available to the economy. a. Inefficient; decreases b. Efficient; decreases c. Efficient; increases d. Inefficient; increases
Free trade is inefficient in the sense that it increases the size of the pie available to the economy.
12. If the domestic consumers of a good benefit from the free trade, it suggests that the country____
a. Is a net exporter of that good.
b. Is not able to produce that good
c. Has a comparative advantage in that good
d. Is a net importer of that good.
Free trade benefits the consumers of imported goods.
13. If the US consumption possibilities are greater than its production possibilities, then the US must have____ a. Autarky b. A closed economy c. An open economy d. Protectionism
In an open economy, a society’s consumption possibilities > its production possibilities.
14. If Fredonia has a closed economy, it ____ with other countries a. Does not negotiate b. Trades c. Does not trade
d. Prevents its citizens from traveling to other countries but trades
15. The demand for microwaves in a certain country is given by: D = 8,000 –30P, where P is the price
of a microwave. Supply by domestic microwave producers is: S = 4,000 + 10P. If this economy
opens to trade while the world price of a microwave is $50, how many microwaves will be imported or exported? a. 3,000 exported b. 2,000 imported c. 2,000 exported d. 1,000 imported D = 8,000 – 30.50 = 6,500 S = 4,000 + 10.50 = 4,500 Import 2,000
16. The demand for cars in a certain country is given by: D = 23,000 −P, where P is the price of a car.
Supply by domestic car producers is: S = 6,000 + 0.25P. If this economy is open to trade, and the
world price of a car is $6,000, how many cars will be imported? a. 14,000 b. 19,000 c. 11,750 d. 9,500 D = 23,000 – 6,000 = 17,000
S = 6,000 + 0.25 x 6,000 = 7,500
Import: 17,000 – 7,500 = 9,500
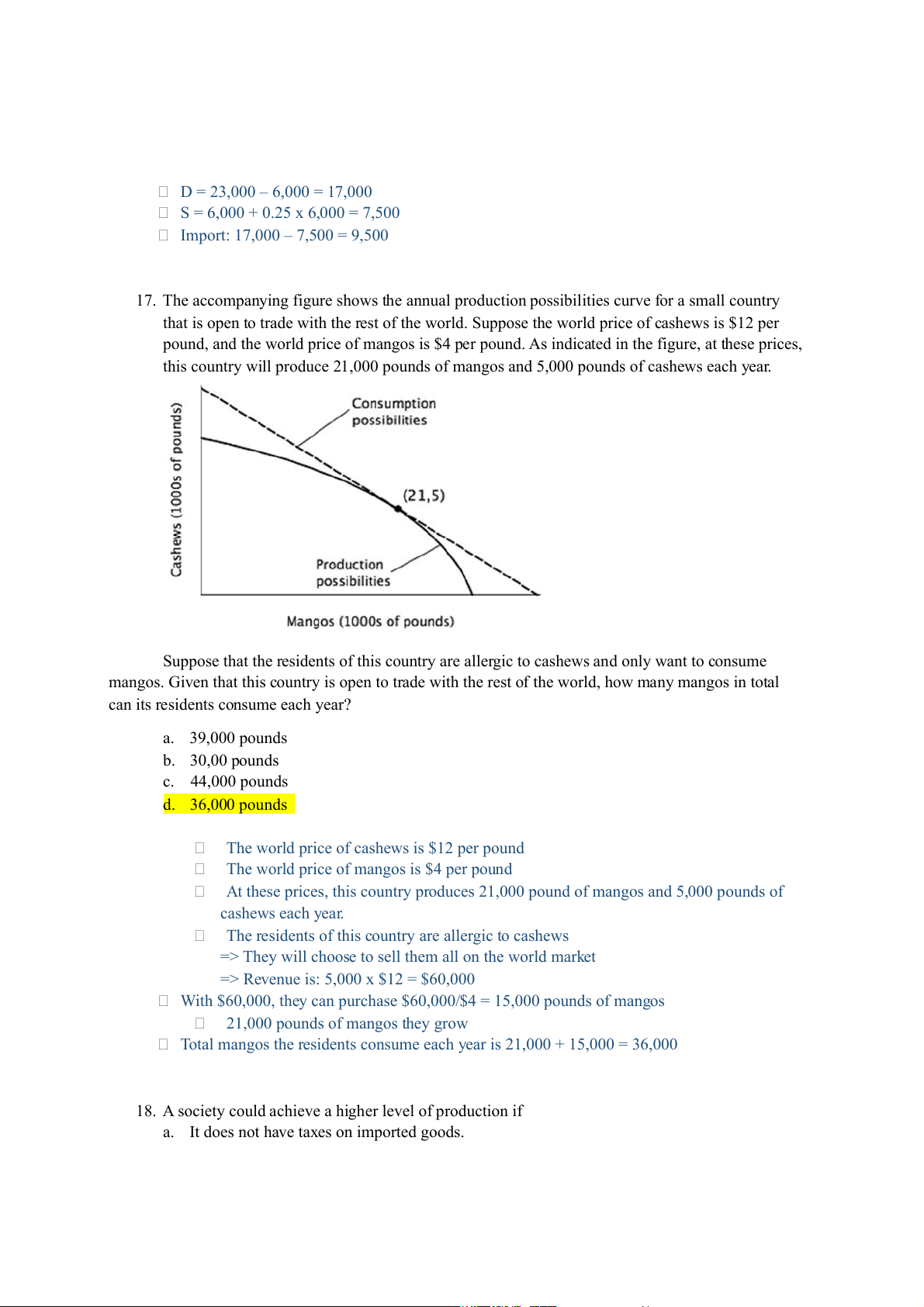
17. The accompanying figure shows the annual production possibilities curve for a small country
that is open to trade with the rest of the world. Suppose the world price of cashews is $12 per
pound, and the world price of mangos is $4 per pound. As indicated in the figure, at these prices,
this country will produce 21,000 pounds of mangos and 5,000 pounds of cashews each year.
Suppose that the residents of this country are allergic to cashews and only want to consume
mangos. Given that this country is open to trade with the rest of the world, how many mangos in total
can its residents consume each year? a. 39,000 pounds b. 30,00 pounds c. 44,000 pounds d. 36,000 pounds
The world price of cashews is $12 per pound
The world price of mangos is $4 per pound
At these prices, this country produces 21,000 pound of mangos and 5,000 pounds of cashews each year.
The residents of this country are allergic to cashews
=> They will choose to sell them all on the world market
=> Revenue is: 5,000 x $12 = $60,000
With $60,000, they can purchase $60,000/$4 = 15,000 pounds of mangos
21,000 pounds of mangos they grow
Total mangos the residents consume each year is 21,000 + 15,000 = 36,000
18. A society could achieve a higher level of production if
a. It does not have taxes on imported goods.
b. Each person in the society is a jack-of-all trades
c. Each person specializes according to their comparative advantage
d. It does not trade with other nations
Specialization according to one’s comparative advantage, combined with trade between
producers of different goods and services, allows a society to achieve a higher level of
productivity and standard of living.
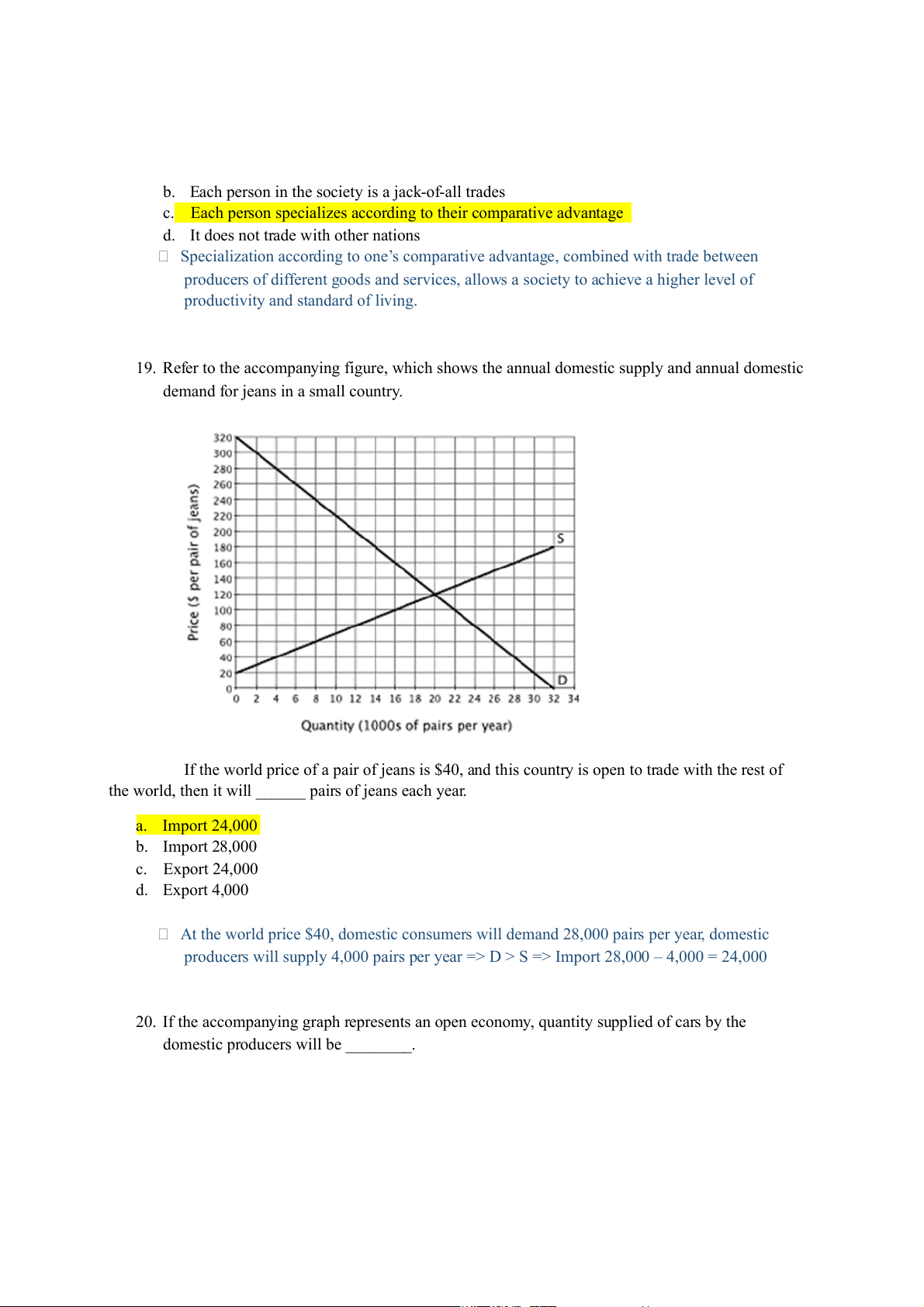
19. Refer to the accompanying figure, which shows the annual domestic supply and annual domestic
demand for jeans in a small country.
If the world price of a pair of jeans is $40, and this country is open to trade with the rest of
the world, then it will ______ pairs of jeans each year. a. Import 24,000 b. Import 28,000 c. Export 24,000 d. Export 4,000
At the world price $40, domestic consumers will demand 28,000 pairs per year, domestic
producers will supply 4,000 pairs per year => D > S => Import 28,000 – 4,000 = 24,000
20. If the accompanying graph represents an open economy, quantity supplied of cars by the
domestic producers will be ________.
If the economy is open, the domestic
price of cars will become the world
price of cars. At a price of $10.000 per
car, the quantity of cars supplied will be 20,000




