







Preview text:
MIDTERM EXAM REVISION Chapter 1
1.Enrique can either drive to work, which takes half an hour and uses $1.50 worth of gas,
or take the bus, which takes an hour and costs $1. How should Enrique get to work?
Enrique should drive if saving half an hour is worth $0.50 or more.
Enrique should take the bus if saving half an hour is worth $0.50 or more.
Enrique should take the bus because it costs $0.50 less than driving.
Enrique should drive because it saves half an hour relative to taking the bus.
2.One thing that distinguishes normative economic principles from positive economic principles is that
normative principles tell us how people should behave, and positive principles tell us how people will behave.
normative principles are pessimistic and positive principles are optimistic.
normative principles reflect social norms, and positive principles reflect universal truths.
normative principles tell us how people will behave, and positive principles tell us how people should behave.
3.You are trying to decide whether to purchase a Harry Potter book online or borrow it
from the library. There is no charge for borrowing a book from the library, but going to
the library takes more time than ordering a book online. Regardless of how you get the
book, its benefit to you is the same. If the cost of buying the book online is $13, then you should
borrow the book from the library if the cost of doing so (in terms of the extra time it takes) is less than $13.
borrow the book from the library if the cost of doing so (in terms of the extra time it takes) is greater than $13.
borrow the book from the library because you can get it from the library for free.
buy the book online because it takes less time.
4.You won a free ticket to see the latest superhero movie this Friday night (which you
can costlessly resell for its face value of $15). Your favorite band is also performing on
Friday and is your only alternative activity. Friday is your last chance to see either the
movie or the band. Tickets to see your favorite band cost $30, and on any given day, you
would be willing to pay as much as $50 for a ticket. Based on this information, what is
your opportunity cost of going to see the movie on Friday? $30 $50 $35 $0
5.A study of the impact of various government policies on economic growth would be considered microeconomics. marginal economics. government economics. macroeconomics.
6.The marginal cost of an activity is the
change in the level of the activity divided by the change in the cost of the activity.
total cost of the activity divided by the change in the level of the activity.
change in the total cost of the activity that results from carrying out an additional unit of the activity.
total cost of the activity divided by the level of the activity.
7.If one fails to account for implicit costs in decision making, then applying the cost-
benefit rule will be flawed because the costs will be understated.
the benefits will be overstated. the costs will be overstated.
the benefits will be understated.
8.An implication of scarcity is that people will never be happy.
some people will always be poor. people must make trade-offs.
making trade-offs becomes unnecessary as wealth increases.
9.Suppose that the extra cost to Ava of a third glass of soda is zero because she's at a
restaurant that gives free refills. According to the Cost-Benefit Principle Ava should
not drink a third glass of soda.
drink a third glass of soda if the extra benefit of doing so is positive. drink a third glass of soda.
drink a third glass of soda if her total benefit from drinking soda is positive.
10.Every time you go to the grocery store, you try to wait in the shortest line. But the
lines always seem to be roughly the same length. Why?
Other people are trying to choose the shortest line too.
Random chance equalizes the length of the lines.
The cashiers do not have an incentive to work faster.
The cashiers work at the same speed. Chapter 2
In general, individuals and nations should specialize in producing those goods for which they have a(n) absolute advantage.
absolute advantage and a comparative advantage.
absolutely comparative advantage. comparative advantage.2
Working efficiently and splitting her time equally between the two tasks, Jordan can
write 3 essays and outline 4 chapters each week. If Jordan's production possibilities curve
is a straight line, it must be true that
3 essays and 5 chapter outlines would be attainable but inefficient.
2 essays and 3 chapter outlines would be both attainable and efficient.
2 essays and 3 chapter outlines would be unattainable but efficient.
3 essays and 5 chapter outlines would be unattainable.3
Economic growth can result from a(n)
decrease in the number of workers available.
increase in the amount of consumer goods produced.
increase in the amount of productive resources.
increase in number of the minimum wage jobs.4
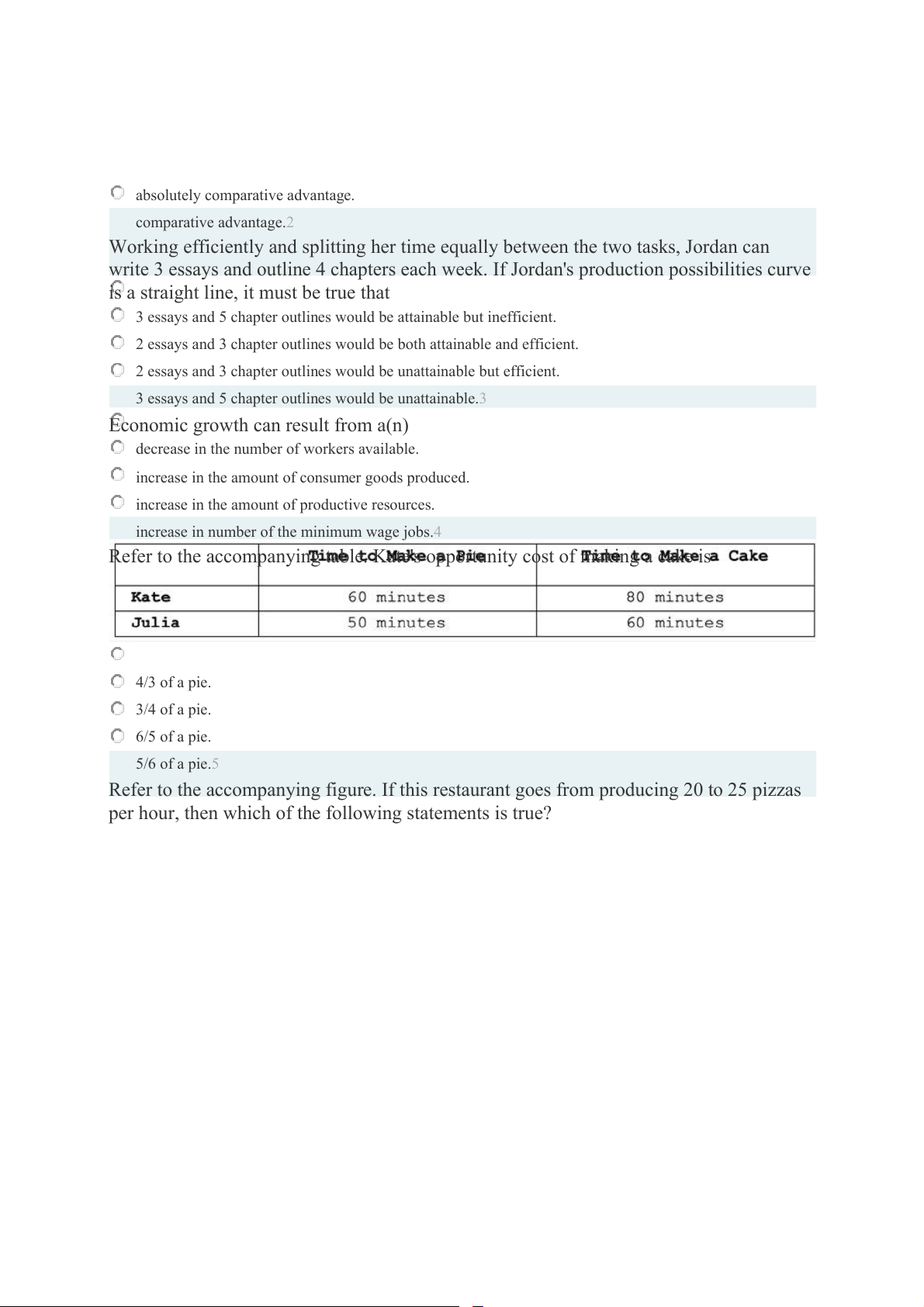
Refer to the accompanying table. Kate's opportunity cost of making a cake is 4/3 of a pie. 3/4 of a pie. 6/5 of a pie. 5/6 of a pie.5
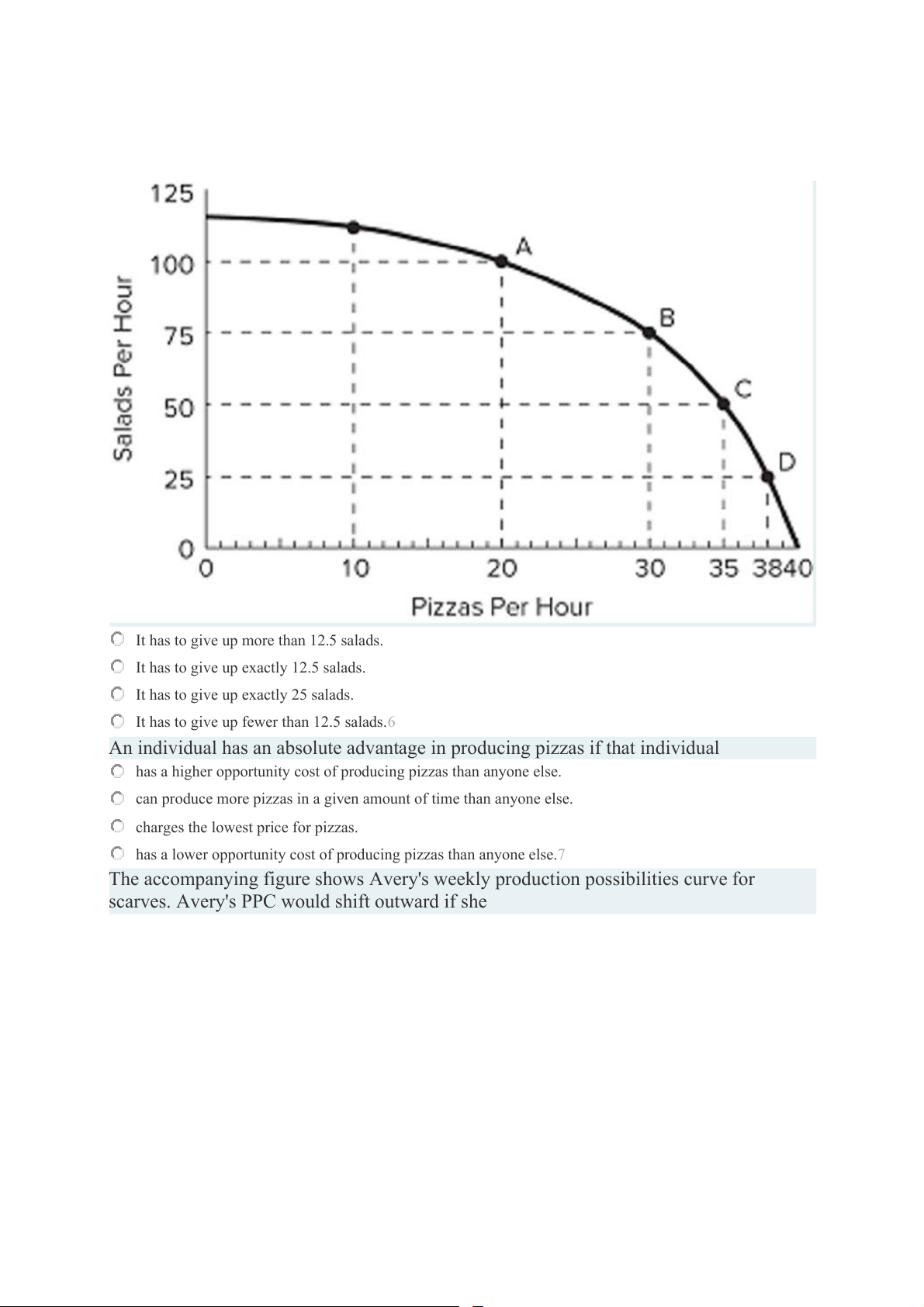
Refer to the accompanying figure. If this restaurant goes from producing 20 to 25 pizzas
per hour, then which of the following statements is true?
It has to give up more than 12.5 salads.
It has to give up exactly 12.5 salads.
It has to give up exactly 25 salads.
It has to give up fewer than 12.5 salads.6
An individual has an absolute advantage in producing pizzas if that individual
has a higher opportunity cost of producing pizzas than anyone else.
can produce more pizzas in a given amount of time than anyone else.
charges the lowest price for pizzas.
has a lower opportunity cost of producing pizzas than anyone else.7
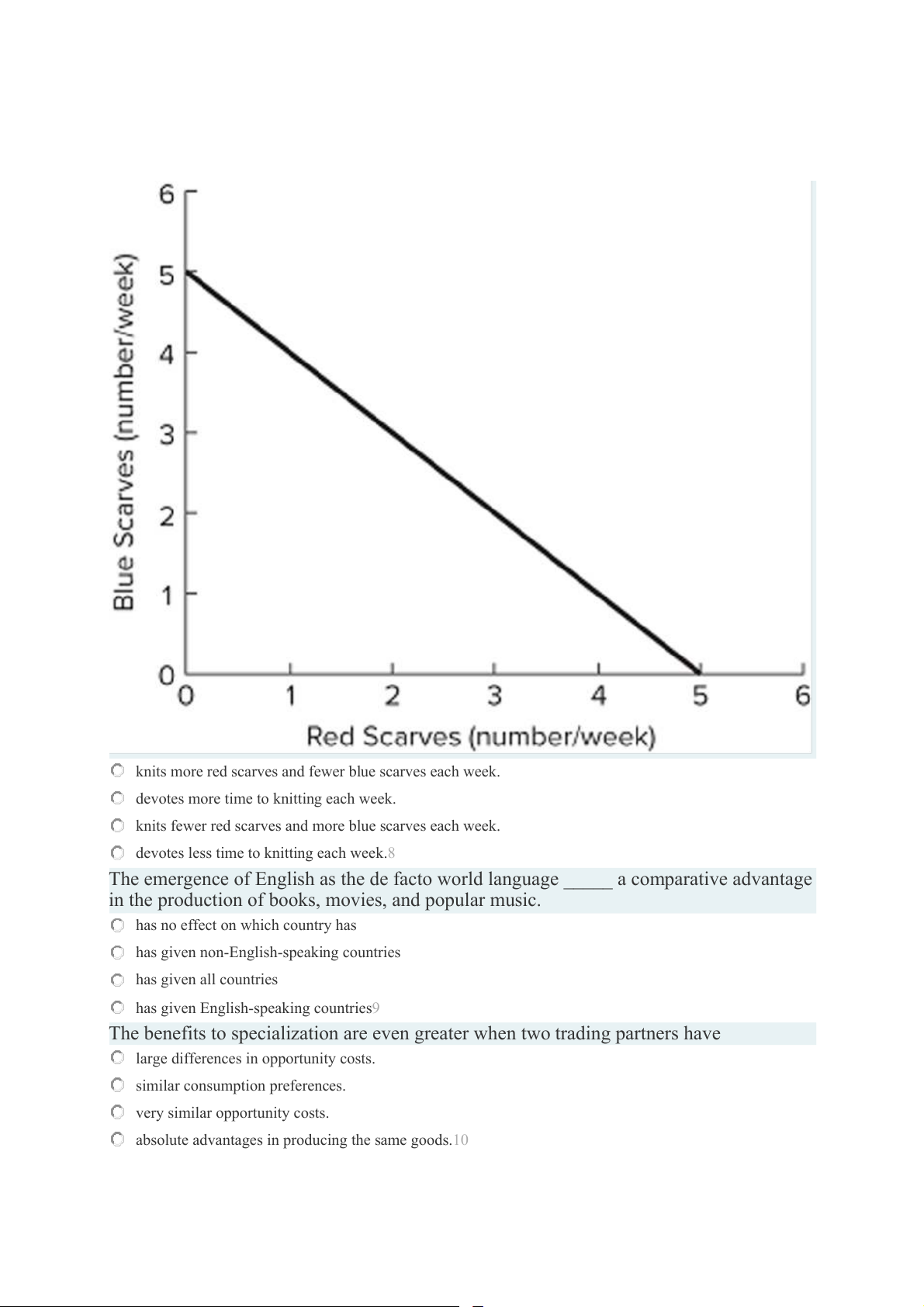
The accompanying figure shows Avery's weekly production possibilities curve for
scarves. Avery's PPC would shift outward if she
knits more red scarves and fewer blue scarves each week.
devotes more time to knitting each week.
knits fewer red scarves and more blue scarves each week.
devotes less time to knitting each week.8
The emergence of English as the de facto world language _____ a comparative advantage
in the production of books, movies, and popular music.
has no effect on which country has
has given non-English-speaking countries has given all countries
has given English-speaking countries9
The benefits to specialization are even greater when two trading partners have
large differences in opportunity costs.
similar consumption preferences.
very similar opportunity costs.
absolute advantages in producing the same goods.10
If country A can produce more of practically everything than can country B, then which
of the following statements is true?
Country B cannot have a comparative advantage in the production of any good that country A wants to buy.
Trade can benefit both countries.
Country A has no incentive to trade with country B.
Country B has no incentive to trade with country A. Chapter3
Refer to the accompanying figure. Suppose the solid line shows the current demand curve
for coffee. In response to an announcement that much of next year’s coffee crop has been
destroyed by a storm in Brazil, you should expect
an increase in the quantity of coffee demanded, but no shift in the demand curve.
neither a change in quantity demanded nor a shift in demand because next year’s coffee crop
will not affect the current demand for coffee.
the demand curve to shift to D(A) in anticipation of higher future prices.
the demand curve to shift to D(B) in anticipation of higher future prices.2
The Equilibrium Principle asserts that in a market equilibrium
no unexploited opportunities exist for society.
no unexploited opportunities exist for individuals.
unexploited opportunities exist for both individuals and society.
unexploited opportunities exist for individuals but not for society.3 Two goods are complements if
there are no substitutes for either of them.
people tend to consume either one or the other.
an increase in the price of one good leads to an increase in demand for the other.
an increase in the price of one good leads to a decrease in demand for the other.4
Suppose that when the price of oranges is $3 per pound, the quantity demanded is 4.7
tons per day and the quantity supplied is 3.9 tons. In this case
excess demand will lead the price of oranges to fall.
excess supply will lead the price of oranges to rise.
excess demand will lead the price of oranges to rise.
excess supply will lead the price of oranges to fall.5
A seller's reservation price is generally equal to the market price.
the seller's opportunity cost of producing an additional unit. the buyer's reservation price.
the seller's marginal benefit from producing an additional unit.6
The demand curve illustrates the fact that consumers tend to purchase
name-brand products more frequently than generic products.
more of a good as it becomes more popular.
more of a good as its price falls.
more of a good as their incomes rise.7
You have noticed that there is a persistent shortage of teachers in an urban school district
in your state. Based on this observation, you suspect that
the wage for teachers in that district is lower than the equilibrium wage.
there is an excess supply of teachers in suburban districts.
the demand for teachers in the urban school district is too low.
the wage for teachers in that district is higher than the wage in suburban districts.8
A price ceiling that is set above the equilibrium price
will lead to excess demand in the market. will lead to a black market.
will lead to excess supply in the market.
will have no effect on the market.9
One reason the demand curve slopes ______ is that as prices fall ______.
downward; more people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
upward; fewer people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
downward; fewer people find that the price is now less than their reservation price.
upward; more people find that the price is now less than their reservation price10
The entire group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service makes up the supply curve.
the equilibrium price and quantity. the demand curve. a market. Chapter 4
1.The price elasticity of demand is a measure of the demand for a good.
the change in price of a good that results from a change in its quantity demanded.
how consumers respond to excess demand.
the change in quantity demanded of a good that results from a change in its price.
2.If your income elasticity of demand for hot dogs is negative, then
hot dogs are an inferior good for you.
you must not enjoy eating hot dogs.
hot dogs have no close substitutes for you.
your demand curve for hot dogs is not downward sloping.
3.Suppose a 10% increase in the price of aspirin leads to a 5% decrease in the quantity
demanded of aspirin. The demand for aspirin, therefore, is elastic. perfectly inelastic. unit elastic. inelastic.
4.A firm that produces a good with many substitutes will most likely find that
lowering its price will not affect total revenue.
raising its price will increase total revenue.
lowering its price will decrease total revenue.
lowering its price will increase total revenue.
5.If the demand for electricity is inelastic, and the local utility wants to increase its total
revenue, it should _______ its price. raise not change frequently change reduce
6.A perfectly elastic demand curve has a slope of ______ while a perfectly inelastic
demand curve has a slope of ______. infinity; 0 0; infinity 1; 0 0; 1
7.On a given linear demand curve, as price increases demand becomes more variable. more negative. more elastic. less elastic.
8.If a 1 percent increase in the price of oranges leads to a five percent increase in the
quantity supplied, the price elasticity of supply for oranges is ______. 1/2 2 5 1/5
9.The cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods that are substitutes can never be negative. positive. greater than one. less than one.
10.The inputs used to produce cupcakes (e.g., flour, sugar, butter, and labor) are also used
to produce cookies, cakes, muffins, pies, and many other goods. This suggests that
the elasticity of supply of cupcakes is relatively low.
the elasticity of supply of cupcakes is relatively high.
the supply curve for cupcakes is downward sloping. cupcakes are a normal good. Chapter 5
According to economists, the satisfaction people get from their consumption activities is called a want. demand. a need. utility.2
Suppose the price of an apple is $0.75, and the price of a banana is $0.50. If Hugh is
maximizing his utility, and his marginal utility from consuming an apple is 24 utils, then
his marginal utility from consuming a banana must be 12 utils. 32 utils. 16 utils. 36 utils.3
As the price of computers falls, the quantity of computers demanded increases. This is an application of the law of demand.
the production possibilities curve. the law of supply. needs versus wants.4
Sejal's reservation price for her economics textbook is $100. The week before the
semester begins, Sejal finds a copy of her textbook online for $75. Sejal's consumer
surplus from buying the textbook online is $100. $25. $75. $125.5
It is impossible for total utility to be ______ when marginal utility is ______. decreasing; positive increasing; increasing positive; negative increasing; decreasing6
Suppose a cup of tea costs $0.60 and a scone costs $1.20. If Amelia spends all of her
income on these two goods, and at her current level of consumption, she receives a
marginal utility of 6 utils from the last cup of tea she buys and a marginal utility of 24
utils from the last scone she buys, then Amelia should buy less tea and more scones.
not change her consumption of tea and scones. buy more tea and more scones.
buy more tea and fewer scones.7
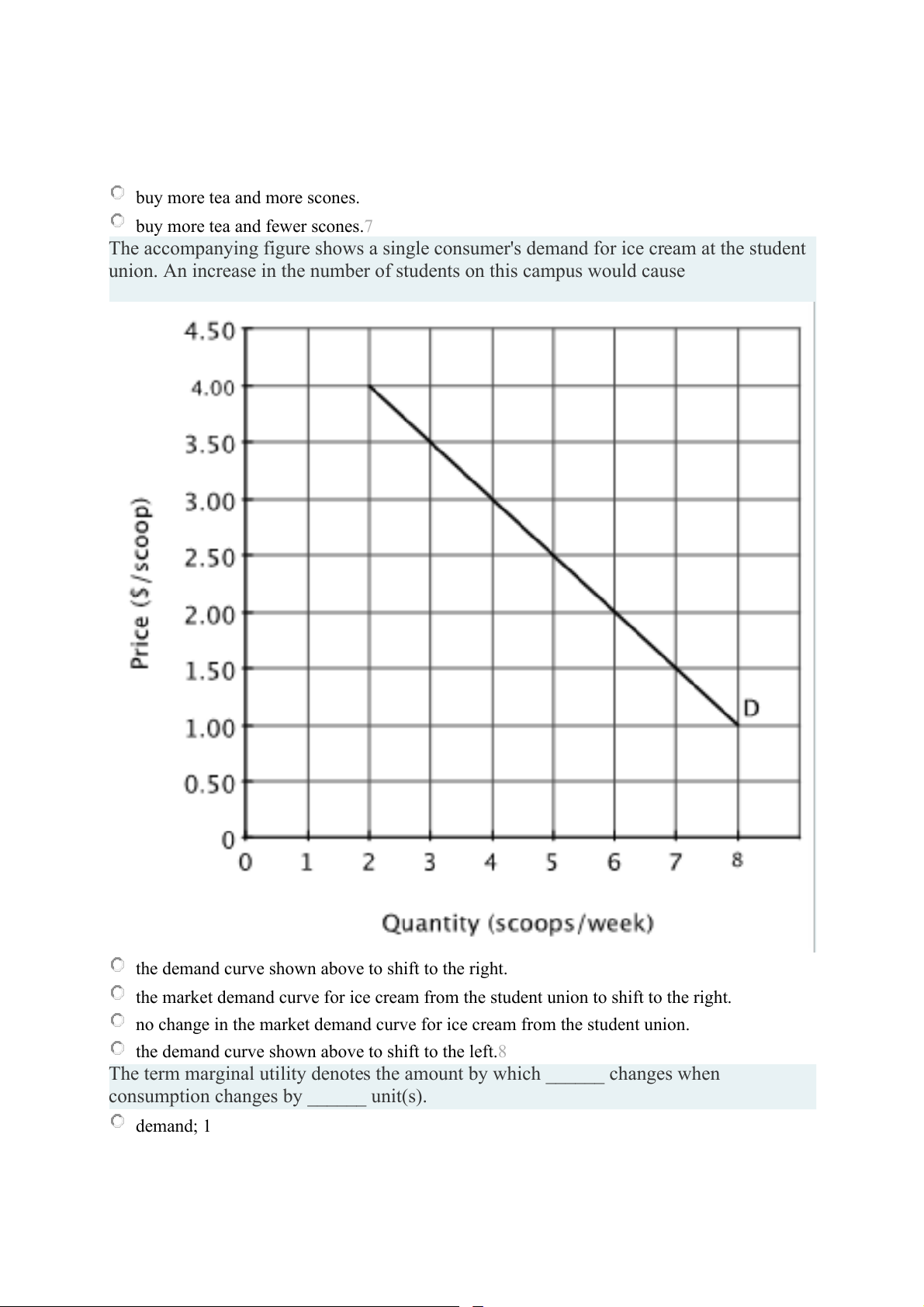
The accompanying figure shows a single consumer's demand for ice cream at the student
union. An increase in the number of students on this campus would cause
the demand curve shown above to shift to the right.
the market demand curve for ice cream from the student union to shift to the right.
no change in the market demand curve for ice cream from the student union.
the demand curve shown above to shift to the left.8
The term marginal utility denotes the amount by which ______ changes when
consumption changes by ______ unit(s). demand; 1 total utility; 1 demand; 10 total utility; 109
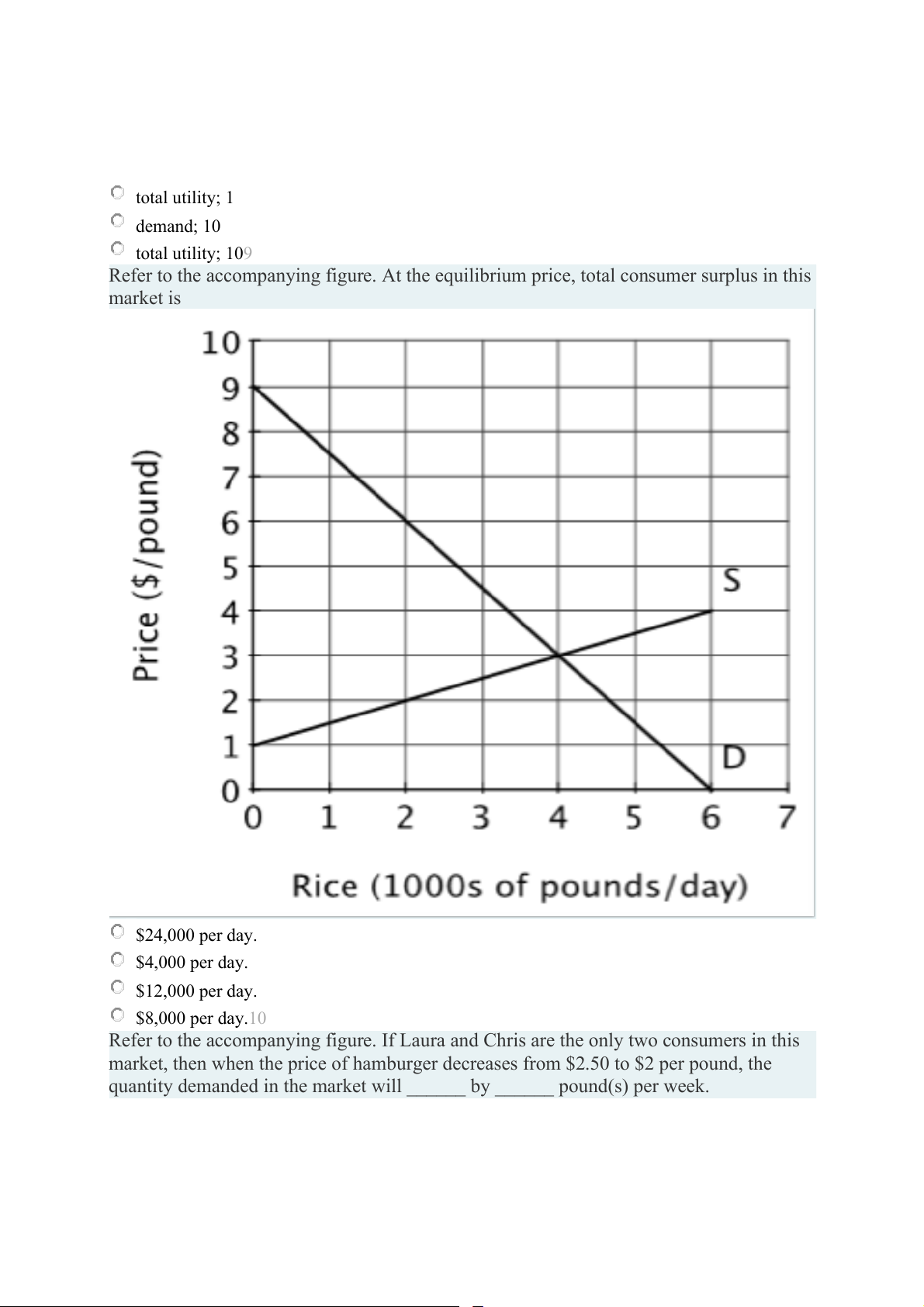
Refer to the accompanying figure. At the equilibrium price, total consumer surplus in this market is $24,000 per day. $4,000 per day. $12,000 per day. $8,000 per day.10
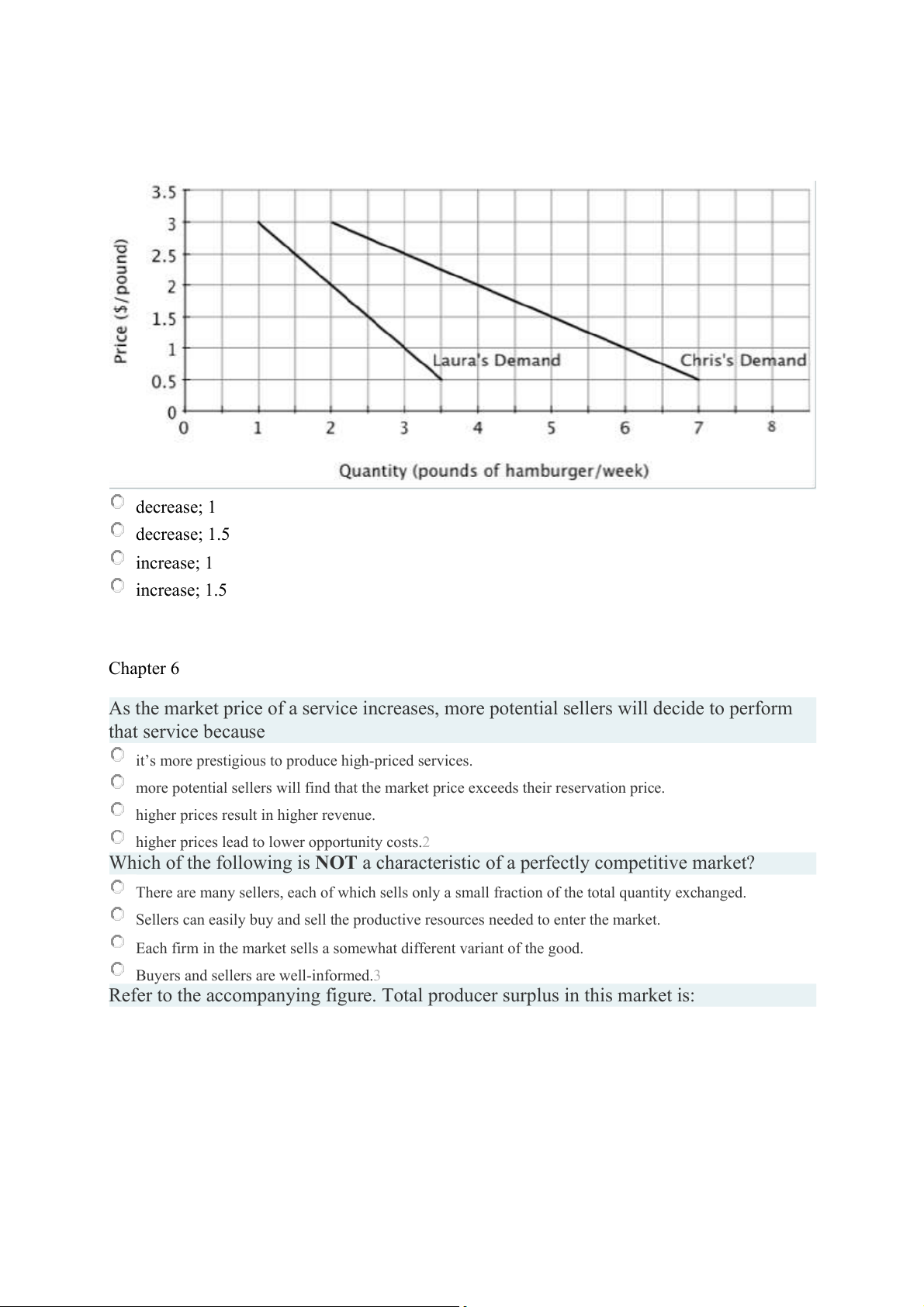
Refer to the accompanying figure. If Laura and Chris are the only two consumers in this
market, then when the price of hamburger decreases from $2.50 to $2 per pound, the
quantity demanded in the market will ______ by ______ pound(s) per week. decrease; 1 decrease; 1.5 increase; 1 increase; 1.5 Chapter 6
As the market price of a service increases, more potential sellers will decide to perform that service because
it’s more prestigious to produce high-priced services.
more potential sellers will find that the market price exceeds their reservation price.
higher prices result in higher revenue.
higher prices lead to lower opportunity costs.2
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
There are many sellers, each of which sells only a small fraction of the total quantity exchanged.
Sellers can easily buy and sell the productive resources needed to enter the market.
Each firm in the market sells a somewhat different variant of the good.
Buyers and sellers are well-informed.3
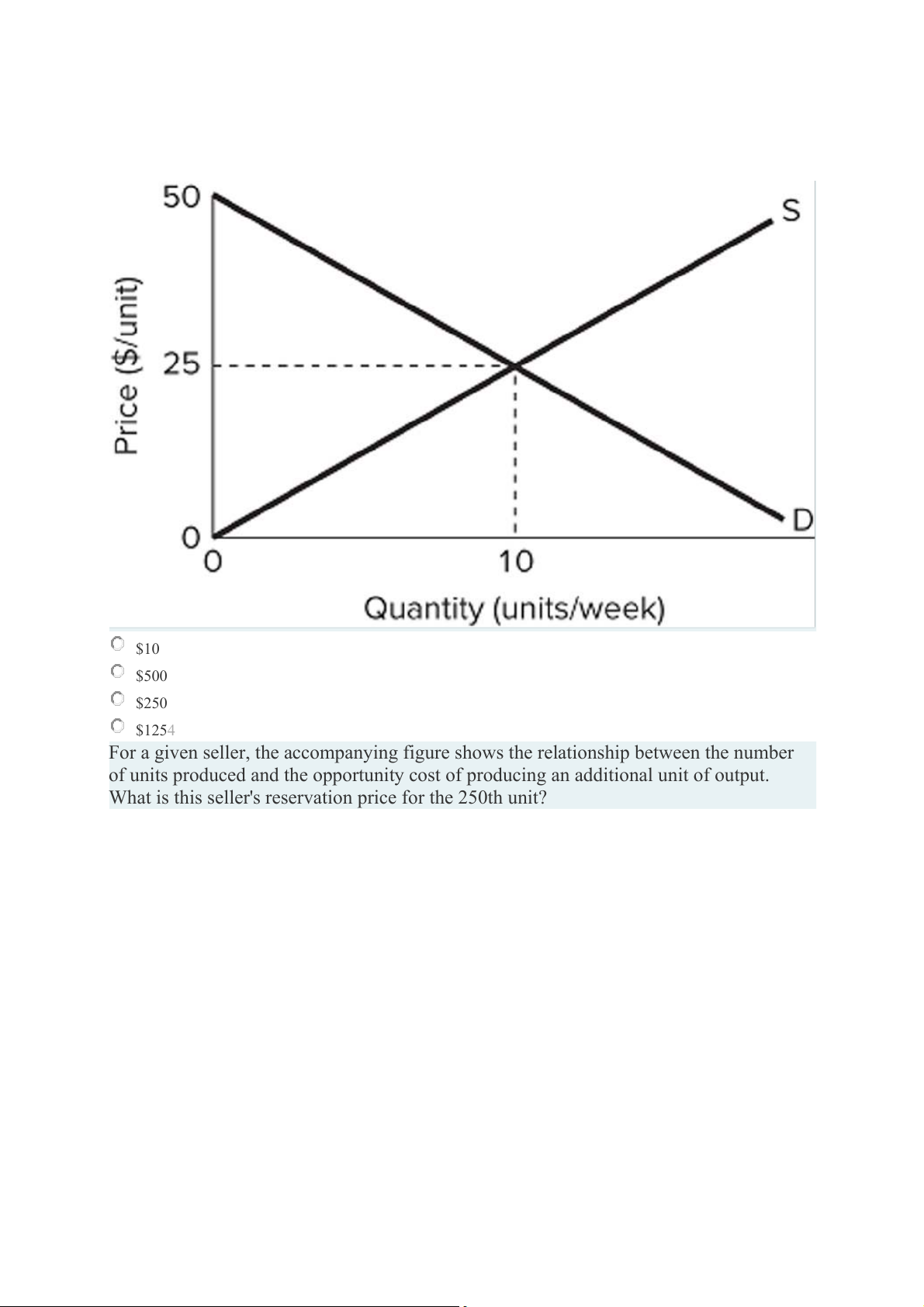
Refer to the accompanying figure. Total producer surplus in this market is: $10 $500 $250 $1254
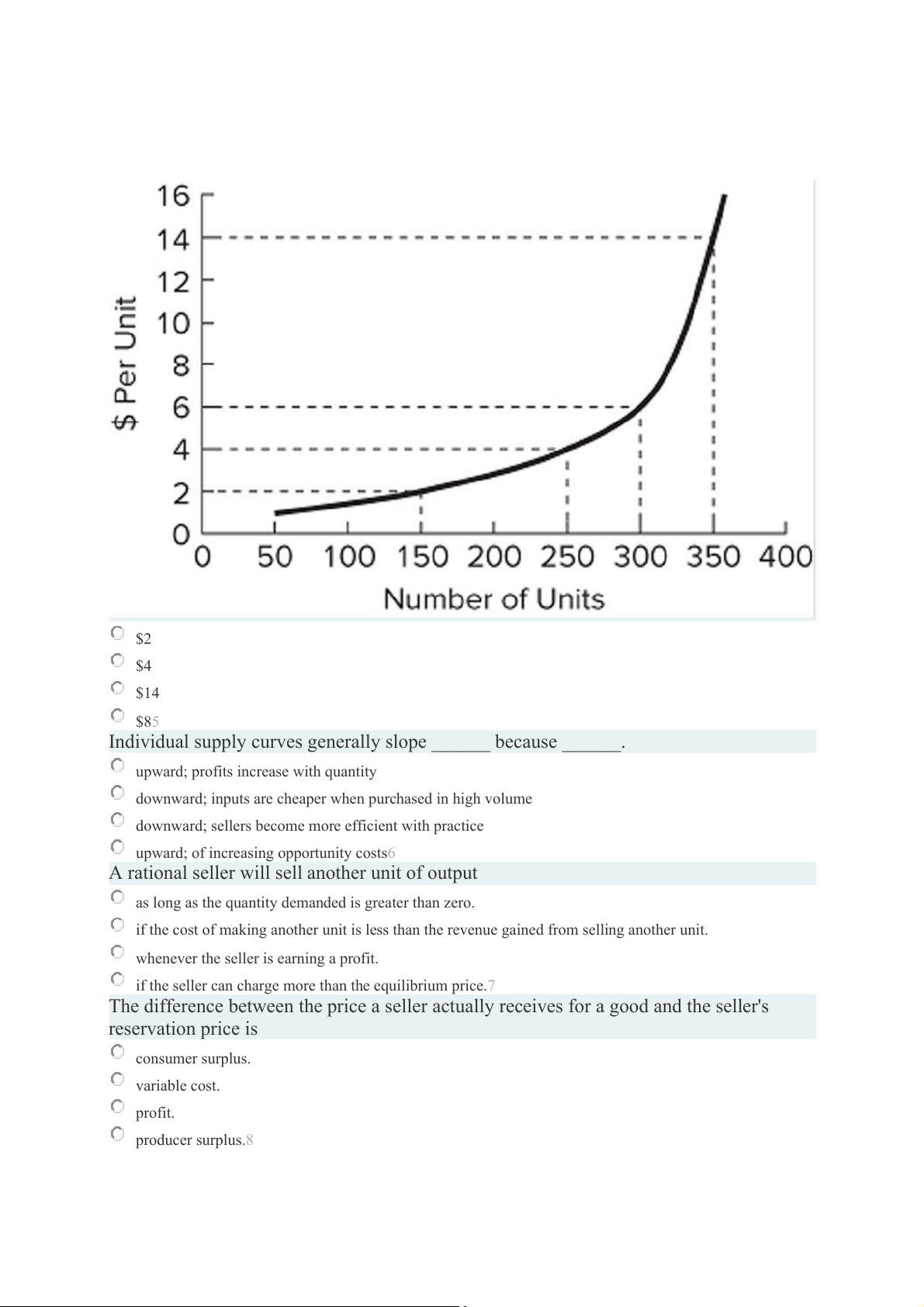
For a given seller, the accompanying figure shows the relationship between the number
of units produced and the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of output.
What is this seller's reservation price for the 250th unit? $2 $4 $14 $85
Individual supply curves generally slope ______ because ______.
upward; profits increase with quantity
downward; inputs are cheaper when purchased in high volume
downward; sellers become more efficient with practice
upward; of increasing opportunity costs6
A rational seller will sell another unit of output
as long as the quantity demanded is greater than zero.
if the cost of making another unit is less than the revenue gained from selling another unit.
whenever the seller is earning a profit.
if the seller can charge more than the equilibrium price.7
The difference between the price a seller actually receives for a good and the seller's reservation price is consumer surplus. variable cost. profit. producer surplus.8
Which of the following is the most likely to be a fixed factor of production at a farm?
The number of workers hired to harvest the crops
The land on which the farm is located
The amount of water used each day
The amount of fertilizer used each week9
Which of the following will cause an increase in market supply?
A decrease in the number of firms in the market.
A technological innovation that lowers the marginal cost of producing the good.
An increase in demand for the good.
An increase in the price of the good.10
If crude oil is a variable factor of production for a firm, then an increase in the price of crude oil will lead to
an increase in the quantity supplied by the firm, but no change in the firm's supply.
a decrease in the firm's supply.
an increase in the firm's supply.
a decrease in the quantity supplied by the firm, but no change in the firm's supply.




