

Preview text:
REVIEW QUESTION ABOUT POPULATION Name: Lâm Thành Phát
Class: L10(LT), L19 (BT) Group: 16
1) One of the factors responsible for environment degradation is population growth or population density.
2) There are 10 effects of population growth on the environment:
- Generation of Waste: Waste leads to air and water pollution
- Threat to Biodiversity: Animals have been hunted and plants have disappeared.
- Strain on Forests: Man has established new housing colonies. National highways and
hydropower projects have been built and forests have been wiped out.
- Urbanization: Due to population pressure, natural resources in the cities are depleted at
a fast rate (space, water, food …)
- Industrialisation: The establishment of such industries as fertilizers, iron and steel,
chemicals and refineries have led to land, air and water pollution
- Land Degradation: Intensive farming and excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides
have led to over-exploitation of land and water resources.
- Transport Development: The automobiles release huge quantities of poisonous gases
such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons.
- Climatic Change: Greenhouse gases continue to accumulate in the atmosphere. The
thin skin of air that surrounds the planet is being affected by human activities as never before.
- Productivity: Water pollution has led to declining fisheries in rivers, ponds and canals
in both urban and rural areas. Water shortages have reduced economic activity in towns,
and cities and villages; soil and hazardous wastes have polluted ground water resources
which cannot be used for agricultural and industrial production.
- Technology: Environmental pollution is caused by old technology which releases gases
and pollutants causing chemical and industrial pressure on environment.
3) Soil degradation leading to soil erosion, drought, siltation of reservoirs and blocking of
river and canal transport channels.
4) Deforestation has led to soil erosion and consequent loss of sustainable logging potential.
5) Loss of bio-diversity has resulted in the loss of genetic resources.
6) Atmospheric changes have given rise to disruption of marine food chain, damages to
coastal infrastructure due to sea-rise and regional changes in agriculture productivity due to hurricanes in seas.
7) Environmental degradation not only harms health but also reduces economic productivity.
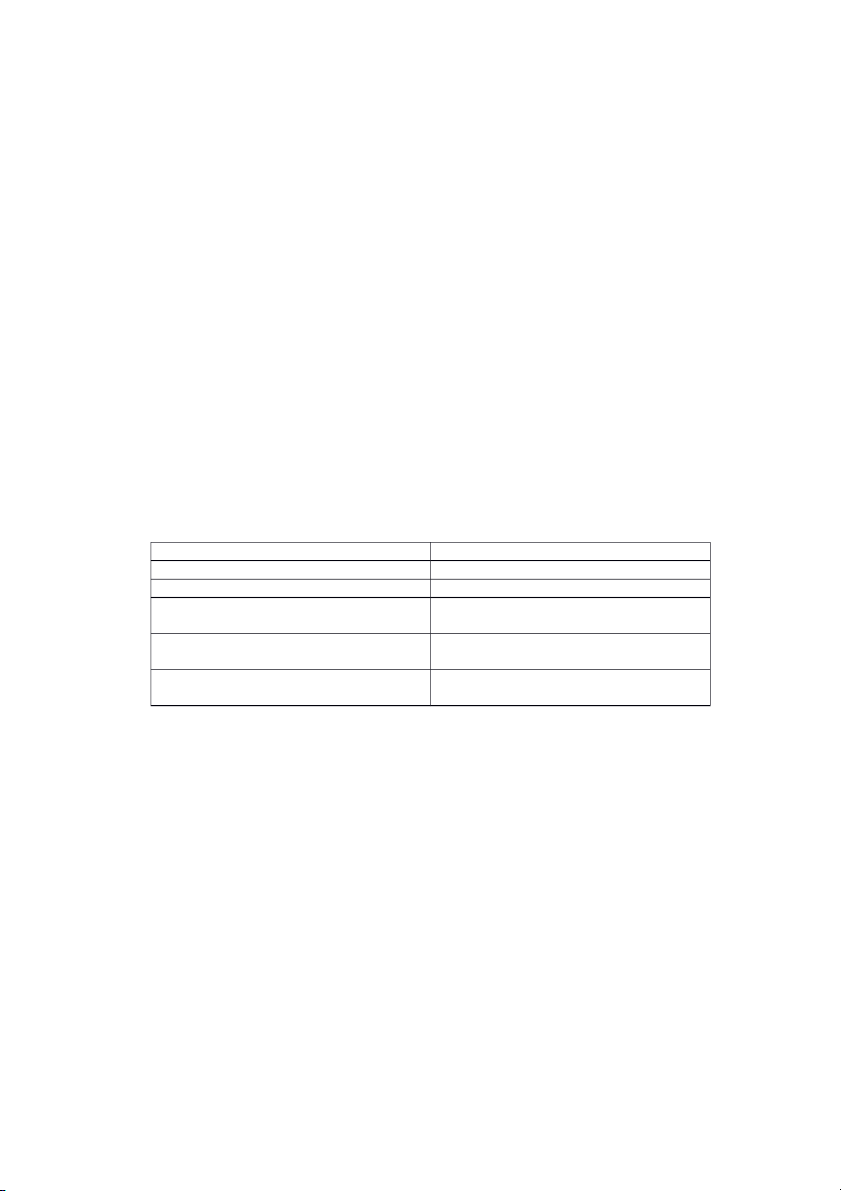
8) In the table 36.1, there are 5 types of polution: Type of polution Effect on health Water polution Disease related to intestines Air polution Chronic cough, lung cancer Soil polution
Enter boby through food cycle and affects adversely Noise polution
Hearing power and fatigue lead to deafness, headache Radioactive polution
Leukaemia, cancer, foetal effects,
chromosomes and genetic damages
9) Public participation is an integral part of environmental protection. Public awareness
and participation are highly effective to improve environmental conditions. Increased
public participation builds a more engaged citizenry, increases the legitimacy of decisions,
and helps ensure that policy-makers have valuable local knowledge. For instance, the use
of indigenous institutions, local voluntary organisations and NGOs can render much help
in educating the masses about the harmful effects of environmental degradation and the
benefits of keeping the environment clean. In addition, cSonducting of formal and
informal education programmes relating to environment management and environmental
awareness programmes can go a long way in controlling environmental degradation and keeping the environment clean. 10)
Definition: An eco-label is a type of label that is granted to products that meet certain
criterias as a government agency or an organization covered by mandated agencies. This
is a relatively comprehensive standard aimed at assessing the impact on the environment
in different stages of the product life cycle: from primary processing, packaging,
distribution, using until being discarded. Effects:
- Effect consumer behavior towards Eco-friendly consumption.
- Assist as a marketing tool for businesses to differentiate their products and attract green consumers.
- Persuade businesses to improve the ecological standard of their products.




