









Preview text:
Seminar 3 By Le Thanh Ha
Type I: True/False question (give a brief explanation)
1. Necessities tend to have inelastic demands, whereas luxuries have elastic demands. T
Xa xỉ phẩm được định nghĩa là có cầu rất co giãn theo thu nhập
Giải thích: Đây là đặc điểm kinh tế quan trọng nhất để phân biệt xa xỉ phẩm với hàng
hóa thông thường và nhu yếu phẩm:
Khi thu nhập tăng 1%, lượng cầu đối với xa xỉ phẩm sẽ tăng hơn 1% (tăng nhanh hơn mức tăng thu nhập).
Ngược lại, khi thu nhập giảm, nhu cầu đối với xa xỉ phẩm cũng giảm rất mạnh, thường là
thứ đầu tiên bị cắt khỏi ngân sách.
2. Goods with close substitutes tend to have more elastic demands than do goods without close substitutes. T
Sản phẩm có nhiều hàng hoá thay thế hơn thì có độ co giãn hơn
3. The demand for gasoline will respond more to a change in price over a period of
five weeks than over a period of five years. F
GAS là mặt hàng thiết yếu, trong ngắn hạn khi thay đổi về giá, người dung vẫn
phải mua để sử dụng, ít có sự co giãn, trong dài hạn thì ngta sẽ nghĩ được biện
pháp thay thế nên dài hạn co giãn hơn
4. Price elasticity of demand along a linear, downward-sloping demand curve increases as price falls. F
Độ co giãn của cầu theo giá dọc theo một đường cầu dốc xuống (linear, downward-
sloping demand curve) giảm khi giá giảm.
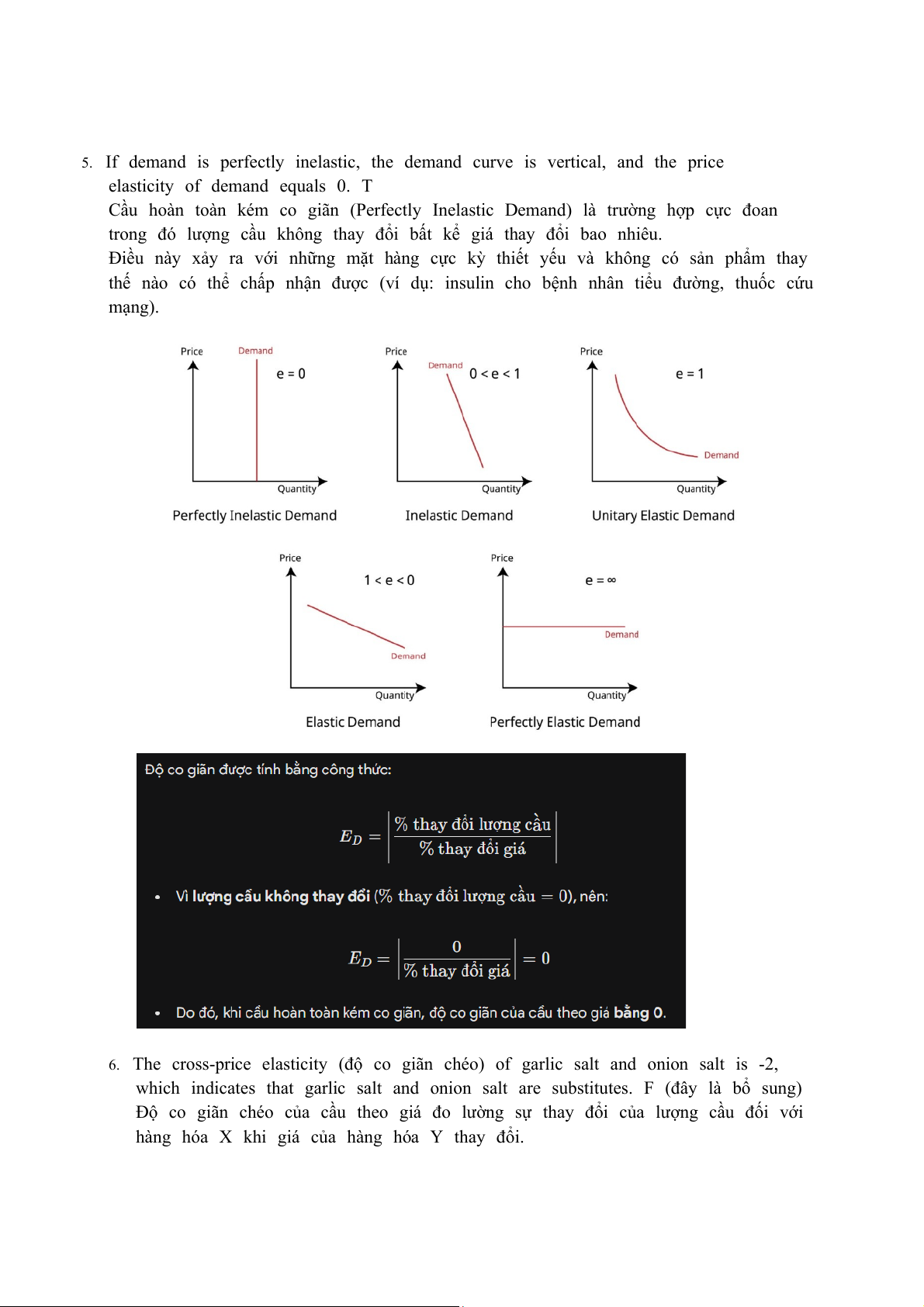
5. If demand is perfectly inelastic, the demand curve is vertical, and the price
elasticity of demand equals 0. T
Cầu hoàn toàn kém co giãn (Perfectly Inelastic Demand) là trường hợp cực đoan
trong đó lượng cầu không thay đổi bất kể giá thay đổi bao nhiêu.
Điều này xảy ra với những mặt hàng cực kỳ thiết yếu và không có sản phẩm thay
thế nào có thể chấp nhận được (ví dụ: insulin cho bệnh nhân tiểu đường, thuốc cứu mạng).
6. The cross-price elasticity (độ co giãn chéo) of garlic salt and onion salt is -2,
which indicates that garlic salt and onion salt are substitutes. F (đây là bổ sung)
Độ co giãn chéo của cầu theo giá đo lường sự thay đổi của lượng cầu đối với
hàng hóa X khi giá của hàng hóa Y thay đổi.
Mối Quan Hệ Giữa X và Dấu của EXY Ý Nghĩa Y Giá Y tăng Dương
Thay thế (Substitutes)
Lượng cầu X tăng (vì người tiêu dùng chuyển sang mua X). Giá Y tăng Âm
Bổ sung (Complements)
Lượng cầu X giảm (vì X và Y được tiêu thụ cùng nhau). Bằng 0 Độc lập
Type II: Discussion questions
1. Consider the following pairs of goods. For which of the two goods would you expect
the demand to be more price elastic? Why?
a. water or diamonds (xa xỉ phẩm)
b. insulin or nasal decongestant spray (nhiều hàng hoá thay thế, isulin là necessity)
c. food in general or breakfast cereal (hẹp hơn)
d. gasoline over the course of a week or gasoline over the course of a
year(thời gian dài nên đã thích ứng được)
e. personal computers or IBM personal computers(hẹp hơn)
2. Let consider an example: two people go to the gas station they say:
I want to buy two liters of gasoline
I want to buy 50k VND of gasoline
What are their demand function? (elastic, inelastic, unit)
3. The demand function is: Q= 6000-30P. Assume that the current price is 75$. What is
the price elasticity of demand?
4. When the price of orange is 16k/kg and the price of tangerine is 14k/kg, the quantity
demanded of tangerine is 30 kg. When the price of orange decreases to 12k/kg, then the
quantity demanded of tangerine is 22 kg. What is the cross-price elasticity of demand for tangerine?
5. A and B have the following demand for a good Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Demanded (A) (B) 150 2100 1000 200 2000 800 250 1900 600
As the price of tickets rises from $200 to $250, what is the price elasticity of demand
for (i) A and (ii) B? (Use the midpoint method in your calculations.)
Type III: Multiple Choices
Ảnh hưởng đến Hình Dạng Loại Co Khoản
Ý Nghĩa (Phản ứng Tổng Doanh thu Đường Giãn g ED
của Lượng cầu) (P×Q) khi P Cầu tăng Hoàn Lượng cầu hoàn toàn toàn Thẳng Tăng (vì P tăng và E = 0 không thay đổi khi giá Kém Co D Đứng Q không đổi) thay đổi. Giãn Lượng cầu thay đổi ít Tăng (vì P tăng Kém Co 0 < ED Rất Dốc
hơn so với mức thay đổi nhanh hơn Q Giãn < 1 của giá. giảm) Không đổi (vì P Co Giãn Hypebol
Lượng cầu thay đổi bằng tăng và Q giảm E = 1 Đơn Vị D (Cong)
với mức thay đổi của giá. cùng tỷ lệ phần trăm) Lượng cầu thay đổi Thoai Giảm (vì Q giảm Co Giãn E D > 1 nhiều hơn so với mức Thoải nhanh hơn P tăng) thay đổi của giá. Ở mức giá này, lượng Hoàn Nằm
cầu là vô hạn. Chỉ cần toàn Co E D = ∞ Giảm về 0 Ngang
giá tăng một chút, lượng Giãn cầu bằng 0.
1. When studying how some event or policy affects a market, elasticity provides information on the
a. equity effects on the market by identifying the winners and losers.
b. Magnitude (mức độ ảnh hưởng) of the effect on the market.
c. speed of adjustment of the market in response to the event or policy.
d. number of market participants who are directly affected by the event or policy.
2. When consumers face rising gasoline prices, they typically
a. reduce their quantity demanded more in the long run than in the
short run. (gthich ở câu T/F)
b. reduce their quantity demanded more in the short run than in the long run.
c. do not reduce their quantity demanded in the short run or the long run.
d. increase their quantity demanded in the short run but reduce
their quantity demanded in the long run.
3. Which of the following statements about the consumers’ responses to rising gasoline prices is correct?
a. About 10 percent of the long-run reduction in quantity demanded
arises because people drive less and about 90 percent arises
because they switch to more fuel-efÏcient cars.
b. About 90 percent of the long-run reduction in quantity demanded
arises because people drive less and about 10 percent arises
because they switch to more fuel-efÏcient cars.
c. About half of the long-run reduction in quantity demanded arises
because people drive less and about half arises because they
switch to more fuel-efÏcient cars.
d. Because gasoline is a necessity, consumers do not decrease their
quantity demanded in either the short run or the long run.
Vì sao KHÔNG chọn câu b? Câu b nói rằng:
90% do người ta lái xe ít hơn và chỉ 10% do đổi sang xe tiết
kiệm nhiên liệu.
Điều này không hợp lý vì:
1. Hành vi lái xe là thứ khó giảm mạnh đến 90% Hầu hết mọi người
cần đi làm, đưa con đi học, đi sinh hoạt hằng ngày. Việc giảm tới
90% lượng xăng chỉ bằng cách “lái ít hơn” là không thực tế.
Trong ngắn hạn, mọi người giảm lái chút ít được, nhưng không
thể giảm quá nhiều, vì đó là nhu cầu thiết yếu.
2. Mua xe tiết kiệm nhiên liệu là yếu tố dài hạn rất quan trọng
Trong dài hạn, người tiêu dùng: đổi sang xe nhỏ hơn chuyển sang hybrid
mua xe tiêu thụ ít xăng khi thay xe cũ
→ Đây là nguồn giảm xăng lớn, không thể chỉ chiếm 10% như phương án (b) nói.
3. Nghiên cứu kinh tế học về demand elasticity cho thấy:
Ngắn hạn → giảm lái xe là chính
Dài hạn → cải thiện hiệu suất xe chiếm tỉ trọng đáng kể
Không nghiên cứu nào cho thấy
90% là do giảm lái xe. Con số đó
quá cực đoan và không phù hợp thực tế hành vi tiêu dùng.
✅ Vì sao chọn câu c? Câu c nói rằng:
Khoảng một nửa do giảm lái xe và một nửa do đổi sang xe
tiết kiệm nhiên liệu. Điều này hợp lý vì:
✔ Trong dài hạn, hai cơ chế đều quan trọng
Người tiêu dùng vẫn giảm bớt việc lái xe (carpool, đi ít hơn,
chuyển phương tiện khác)
Nhưng cũng đầu tư vào xe tiết kiệm xăng hơn (đây là tác động dài hạn mạnh)
✔ Hai yếu tố này thực sự đóng góp gần như ngang nhau
→ Đây là mô tả đúng với elasticity of gasoline demand trong
dài hạn mà nhiều textbook đưa ra. ✨ Kết luận
Không chọn b vì nó phóng đại bất hợp lý mức giảm lái xe đến 90%.
Chọn c vì phản ánh đúng hành vi dài hạn: giảm
lái xe +
đổi xe → tương đương nhau về mức độ đóng góp.
4. For which of the following goods would demand be most elastic? a. clothing b. blue jeans
c. Tommy Hilfiger jeans (nhiều hãng quần, nhiều sự lựa chọn thay thế)
d. All three would have the same elasticity of demand since they are all related.
5. For a particular good, a 2 percent increase in price causes a 12 percent
decrease in quantity demanded. Which of the following statements is most likely applicable to this good?
a. There are no close substitutes for this good. b. The good is a luxury.
c. The market for the good is broadly defined.
d. The relevant time horizon is short.
Nếu thị trường được định nghĩa rộng, thì:
Hàng hóa sẽ ít có sản phẩm thay thế (substitutes).
Khi giá tăng, người tiêu dùng khó chuyển sang hàng khác.
→ Nhu cầu sẽ kém co giãn (inelastic). Ví dụ:
“Đồ uống” (market broadly defined) → khó thay thế, ít co giãn.
“Coca” hay “Pepsi” (market narrowly defined) → nhiều substitute, rất co giãn.
6. The smaller the price elasticity of demand, the
a. steeper the demand curve will be through a given point.
b. flatter the demand curve will be through a given point.
c. more strongly buyers respond to a change in price between any two prices P 1 and P2.
d. smaller the decrease in equilibrium price when the supply curve shifts rightward from S
1 to S2. (Khi đường cung dịch chuyển sang
phải (cung tăng), điều này gây ra sự giảm giá và tăng số lượng cân bằng.)
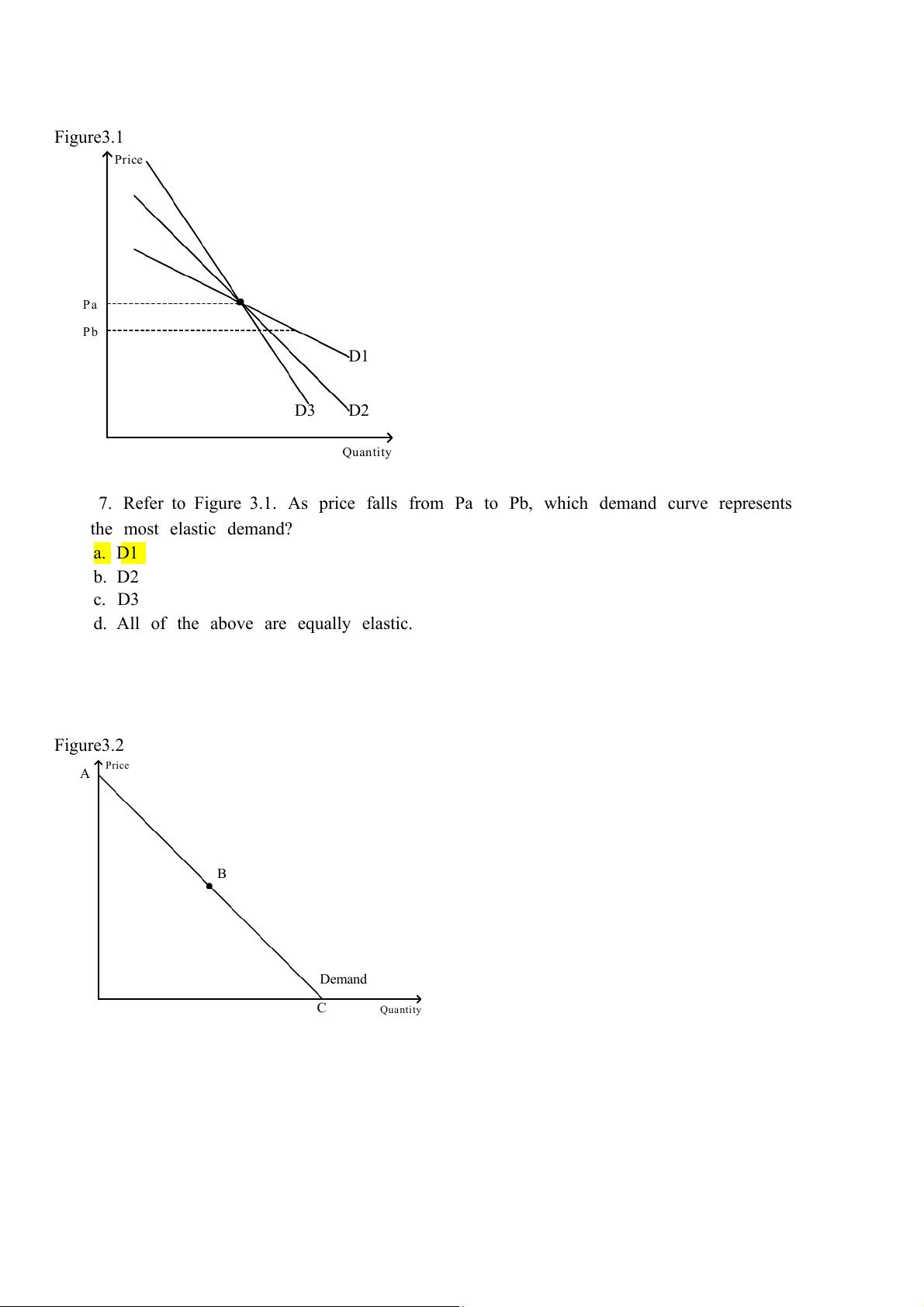
Figure 3.1 Price Pa Pb D1 D3 D2 Quantity
7. Refer to Figure .
3.1 As price falls from Pa to Pb, which demand curve represents the most elastic demand? a. D1 b. D2 c. D3
d. All of the above are equally elastic. Figure 3.2 Price A B Demand C Quantity
8. Refer to Figure .
3.2 The section of the demand curve from A to B represents the
a. elastic section of the demand curve.
b. inelastic section of the demand curve.
c. unit elastic section of the demand curve.
d. perfectly elastic section of the demand curve.
9. Refer to Figure .
3.2 If the price increases in the region of the demand curve
between points B and C, we can expect total revenue to a. increase. b. stay the same. c. decrease.
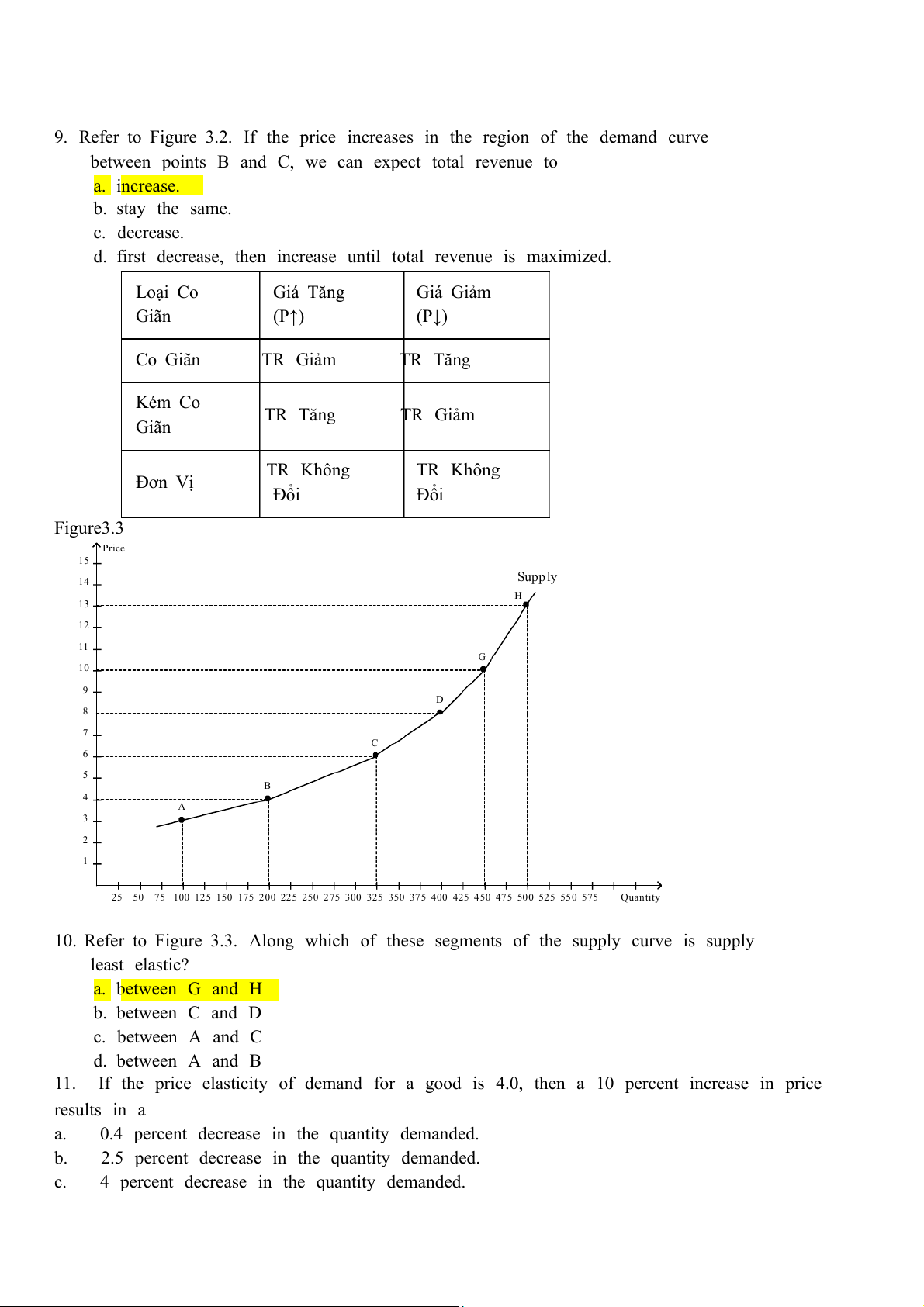
d. first decrease, then increase until total revenue is maximized. Loại Co Giá Tăng Giá Giảm Giãn (P↑) (P↓) Co Giãn TR Giảm TR Tăng Kém Co Giãn TR Tăng TR Giảm TR Không Đơn Vị TR Không Đổi Đổi Figure 3.3 Price 15 Supply 14 H 13 12 11 G 10 9 D 8 7 C 6 5 B 4 A 3 2 1
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500 525 550 575 Quantity
10. Refer to Figure 3.3. Along which of these segments of the supply curve is supply least elastic? a. between G and H b. between C and D c. between A and C d. between A and B
11. If the price elasticity of demand for a good is 4.0, then a 10 percent increase in price results in a
a. 0.4 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
b. 2.5 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
c. 4 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
d. 40 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
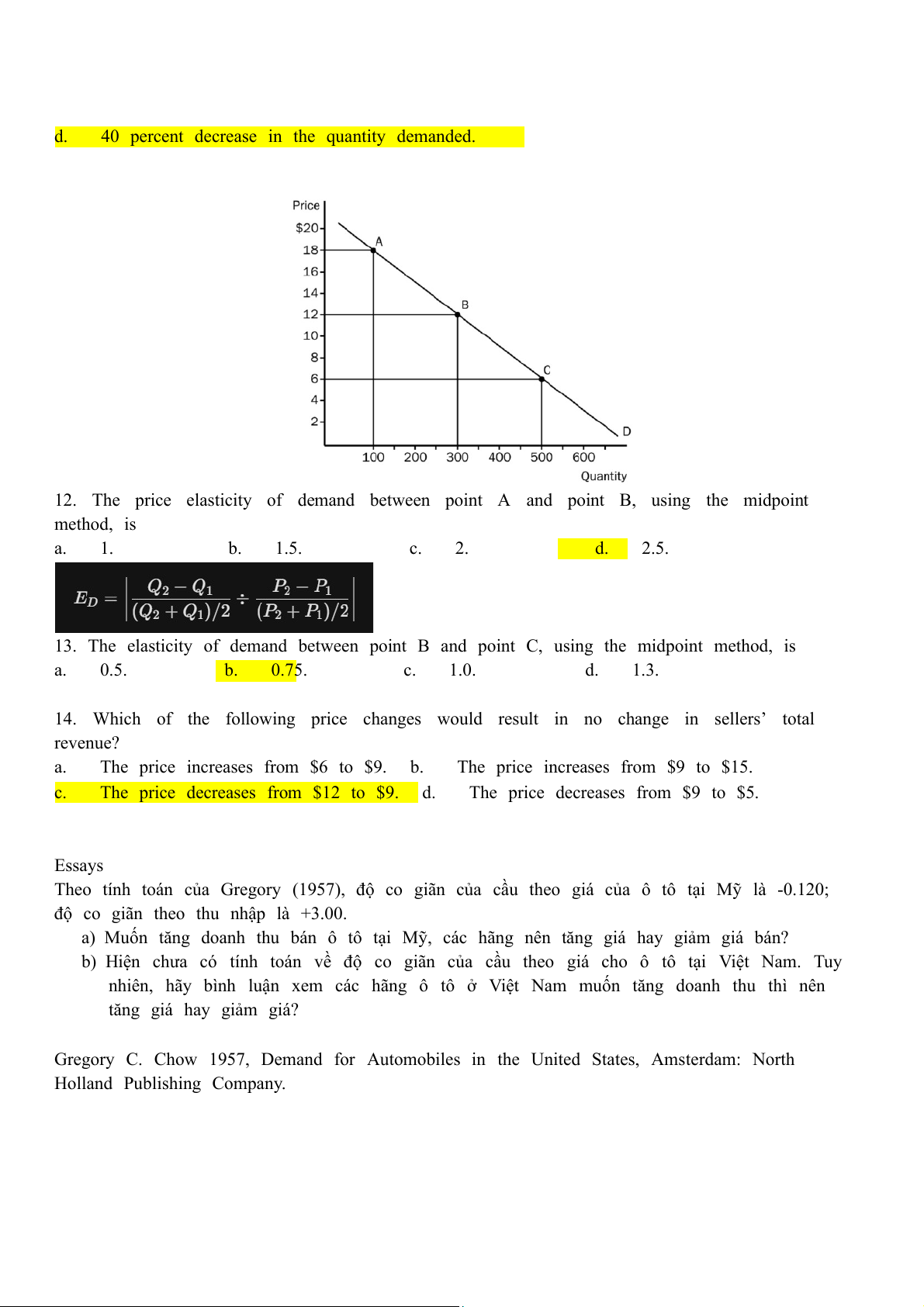
12. The price elasticity of demand between point A and point B, using the midpoint method, is a. 1. b. 1.5. c. 2. d. 2.5.
13. The elasticity of demand between point B and point C, using the midpoint method, is a. 0.5. b. 0.75. c. 1.0. d. 1.3.
14. Which of the following price changes would result in no change in sellers’ total revenue?
a. The price increases from $6 to $9. b. The price increases from $9 to $15.
c. The price decreases from $12 to $9. d. The price decreases from $9 to $5. Essays
Theo tính toán của Gregory (1957), độ co giãn của cầu theo giá của ô tô tại Mỹ là -0.120;
độ co giãn theo thu nhập là +3.00.
a) Muốn tăng doanh thu bán ô tô tại Mỹ, các hãng nên tăng giá hay giảm giá bán?
b) Hiện chưa có tính toán về độ co giãn của cầu theo giá cho ô tô tại Việt Nam. Tuy
nhiên, hãy bình luận xem các hãng ô tô ở Việt Nam muốn tăng doanh thu thì nên tăng giá hay giảm giá?
Gregory C. Chow 1957, Demand for Automobiles in the United States, Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company.




