

Preview text:
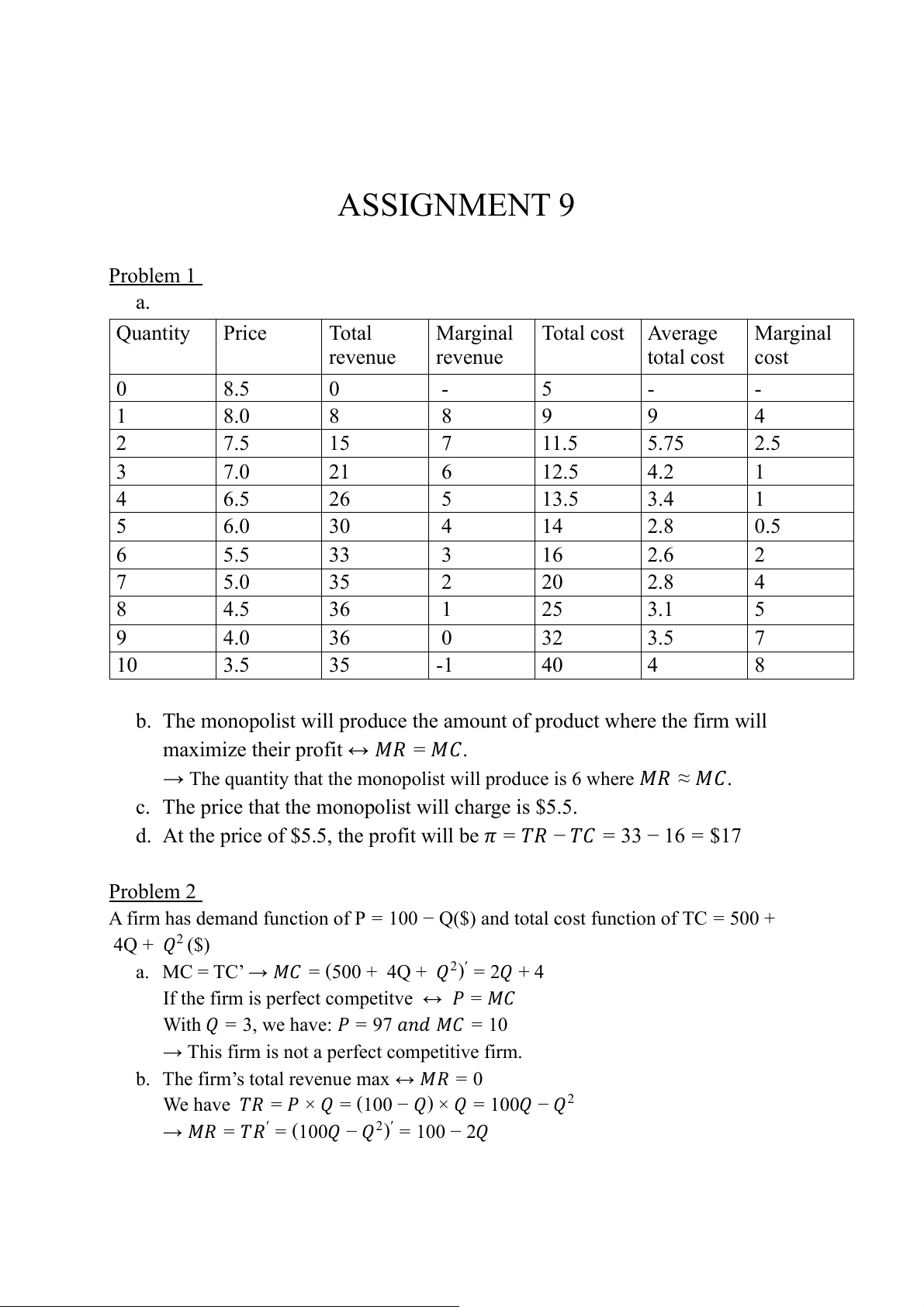
ASSIGNMENT 9 Problem 1 a. Quantity Price Total Marginal Total cost Average Marginal revenue revenue total cost cost 0 8.5 0 - 5 - - 1 8.0 8 8 9 9 4 2 7.5 15 7 11.5 5.75 2.5 3 7.0 21 6 12.5 4.2 1 4 6.5 26 5 13.5 3.4 1 5 6.0 30 4 14 2.8 0.5 6 5.5 33 3 16 2.6 2 7 5.0 35 2 20 2.8 4 8 4.5 36 1 25 3.1 5 9 4.0 36 0 32 3.5 7 10 3.5 35 -1 40 4 8
b. The monopolist will produce the amount of product where the firm will
maximize their profit ↔ 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶.
→ The quantity that the monopolist will produce is 6 where 𝑀𝑅 ≈ 𝑀𝐶.
c. The price that the monopolist will charge is $5.5.
d. At the price of $5.5, the profit will be 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 33 − 16 = $17 Problem 2
A firm has demand function of P = 100 − Q($) and total cost function of TC = 500 + 4Q + 𝑄2 ($)
a. MC = TC’ → 𝑀𝐶 = (500 + 4Q + 𝑄2)′ = 2𝑄 + 4
If the firm is perfect competitve ↔ 𝑃 = 𝑀𝐶
With 𝑄 = 3, we have: 𝑃 = 97 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑀𝐶 = 10
→ This firm is not a perfect competitive firm.
b. The firm’s total revenue max ↔ 𝑀𝑅 = 0
We have 𝑇𝑅 = 𝑃 × 𝑄 = (100 − 𝑄) × 𝑄 = 100𝑄 − 𝑄2
→ 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑇𝑅′ = (100𝑄 − 𝑄2)′ = 100 − 2𝑄
→ 𝑀𝑅 = 0 ↔ 100 − 2𝑄 = 0 → 𝑄 = 50
The price to maximize total revenue is: 𝑃 = 100 − 50 = $50
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 50 × 50 = $250
c. The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity
where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, that is: MR = MC.
The quantity produced to maximize profit is: 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶 → 100 − 2𝑄 = 2𝑄 + 4 → 𝑄 = 24
The price to maximize profit is: 𝑃 = 100 − 24 = $76
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 76 × 24 = $1824.
The maximum total cost is: TC = 500 + 4 × 24 + 242 = $1172
The maximum profit is: 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 1824 − 1172 = $652
d. Asume government imposes a tax of 8 $ per unit of good sold → 𝑇𝐶 2
1 = 𝑇𝐶 + 8 × 𝑄 = 500 + 4Q + 𝑄 + 8𝑄 = 𝑄2 + 12𝑄 + 500
→ 𝑀𝐶1 = (𝑇𝐶1)′ = (𝑄2 + 12𝑄 + 500)′ = 2𝑄 + 12
The optimal quantity produced to maximize profit is: 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶1
→ 100 − 2𝑄 = 2𝑄 + 12 𝑄 = 22
The price to maximize profit is: 𝑃 = 100 − 22 = $78
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 78 × 22 = $1716
The maximum total cost is: TC = 500 + 4 × 22 + 222 = $1072
The maximum profit is: 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 1716 − 1072 = $644
e. Asume government imposes a fixed tax of $100
→ 𝑇𝐶2 = 𝑇𝐶 + 100 = 500 + 4Q + 𝑄2 + 100 = 𝑄2 + 4𝑄 + 600
→ 𝑀𝐶2 = (𝑇𝐶2)′ = (𝑄2 + 4𝑄 + 600)′ = 2𝑄 + 4
The optimal quantity produced to maximize profit is: 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶2 → 100 − 2𝑄 = 2𝑄 + 4 𝑄 = 24
The price to maximize profit is: 𝑃 = 100 − 24 = $76
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 76 × 24 = $1824
The maximum total cost is: TC = 500 + 4 × 24 + 242 = $1172
The maximum profit is: 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 1716 − 1072 = $652 Problem 3
A monopoly has a demand function of P = 15 − Q ($) and total cost function of TC = 7Q.
We have MC = TC’ → 𝑀𝐶 = (7Q)′ = 7
TR = 𝑃 × 𝑄 = (15 − 𝑄)𝑄 = 15𝑄 − 𝑄2
→ 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑇𝑅′ = (15𝑄 − 𝑄2)′ = 15 − 2𝑄
a. The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity
where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost, that is: MR = MC.
The quantity produced to maximize profit is: 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶 → 15 − 2𝑄 = 7 𝑄 = 4
The price to maximize profit is: 𝑃 = 15 − 4 = $11
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 11 × 4 = $44.
The maximum total cost is: TC = 7 × 4 = $28
The maximum profit is: 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 44 − 28 = $16.
Market power of this firm is: 𝐿 = 𝑃−𝑀𝐶 = 11−7 = 4 (0 ≤ 4 ≤ 1: 𝑡ℎỏ𝑎 𝑚ã𝑛) 𝑃 11 11 11
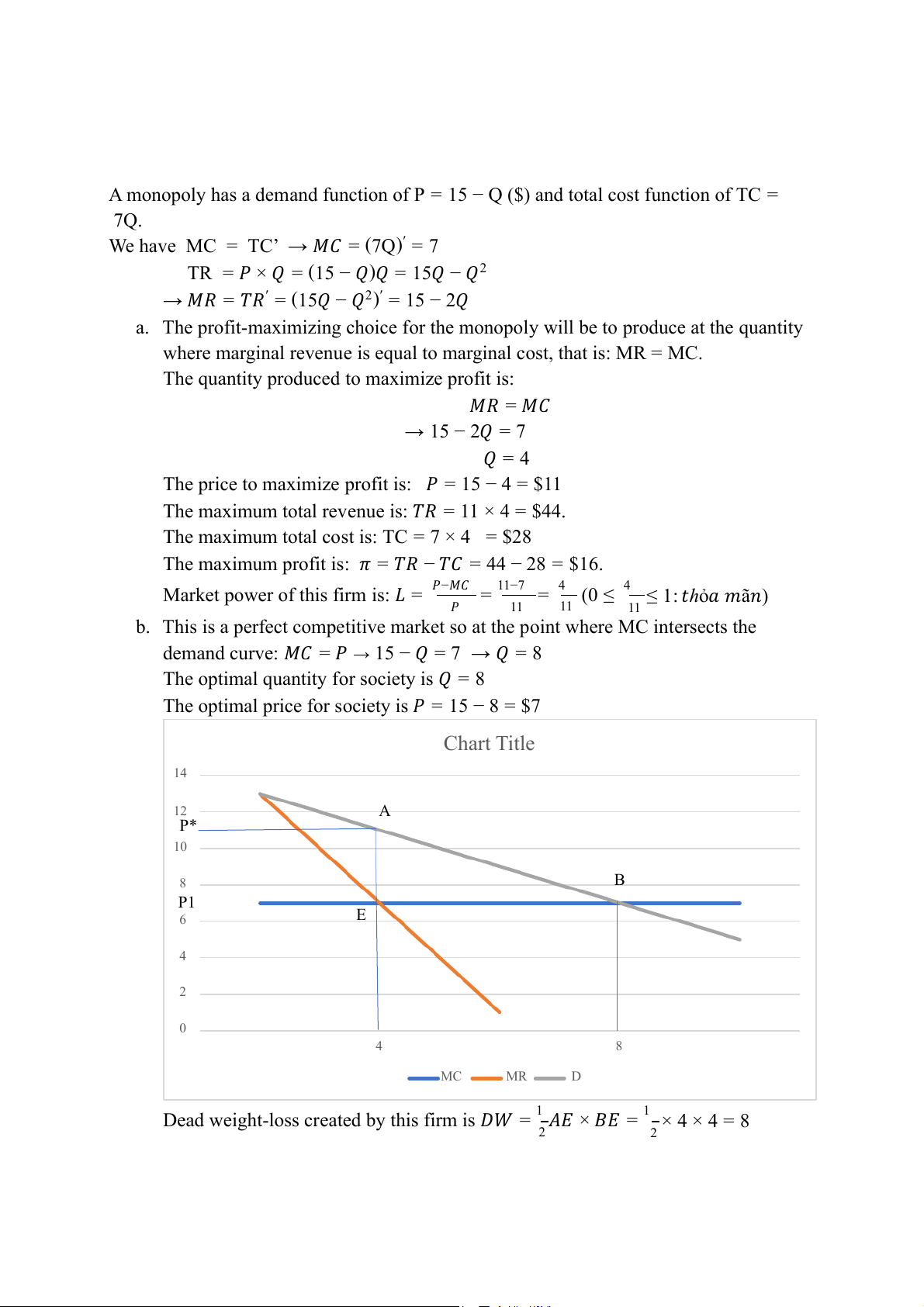
b. This is a perfect competitive market so at the point where MC intersects the
demand curve: 𝑀𝐶 = 𝑃 → 15 − 𝑄 = 7 → 𝑄 = 8
The optimal quantity for society is 𝑄 = 8
The optimal price for society is 𝑃 = 15 − 8 = $7 Chart Title 14 12 A P* 10 8 B P1 6 E 4 2 0 4 8 MC MR D
Dead weight-loss created by this firm is 𝐷𝑊 = 1 𝐴𝐸 × 𝐵𝐸 = 1 × 4 × 4 = 8 2 2 Problem 4
A monopolist has demand function of 𝑃 = 100 − 𝑄 and cost functions of 𝐴𝑉𝐶 = 𝑄 + 4; 𝐹𝐶 = 200.
𝐴𝑉𝐶 = 𝑄 + 4 → 𝑉𝐶 = 𝐴𝑉𝐶 × 𝑄 = (𝑄 + 4)𝑄 = 𝑄2 + 4𝑄
→ 𝑇𝐶 = 𝑉𝐶 + 𝐹𝐶 = 𝑄2 + 4𝑄 + 200
→ 𝑀𝐶 = 𝑇𝐶′ = (𝑄2 + 4𝑄 + 200)′ = 2𝑄 + 4
𝑇𝑅 = 𝑃 × 𝑄 = (100 − 𝑄) × 𝑄 = 100𝑄 − 𝑄2
→ 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑇𝑅′ = (100𝑄 − 𝑄2)′ = −2𝑄 + 100
a. Optimal output level that maximizes profit is : 𝑀𝑅 = 𝑀𝐶
→ −2𝑄 + 100 = 2𝑄 + 4 → 𝑄 = 24
The price to maximize profit is: 𝑃 = 100 − 24 = $76
The maximum total revenue is: 𝑇𝑅 = 76 × 24 = $1824.
The maximum total cost is: TC = 242 + 4 × 24 + 200 = $872
The maximum profit is: 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 = 1824 − 872 = $952.
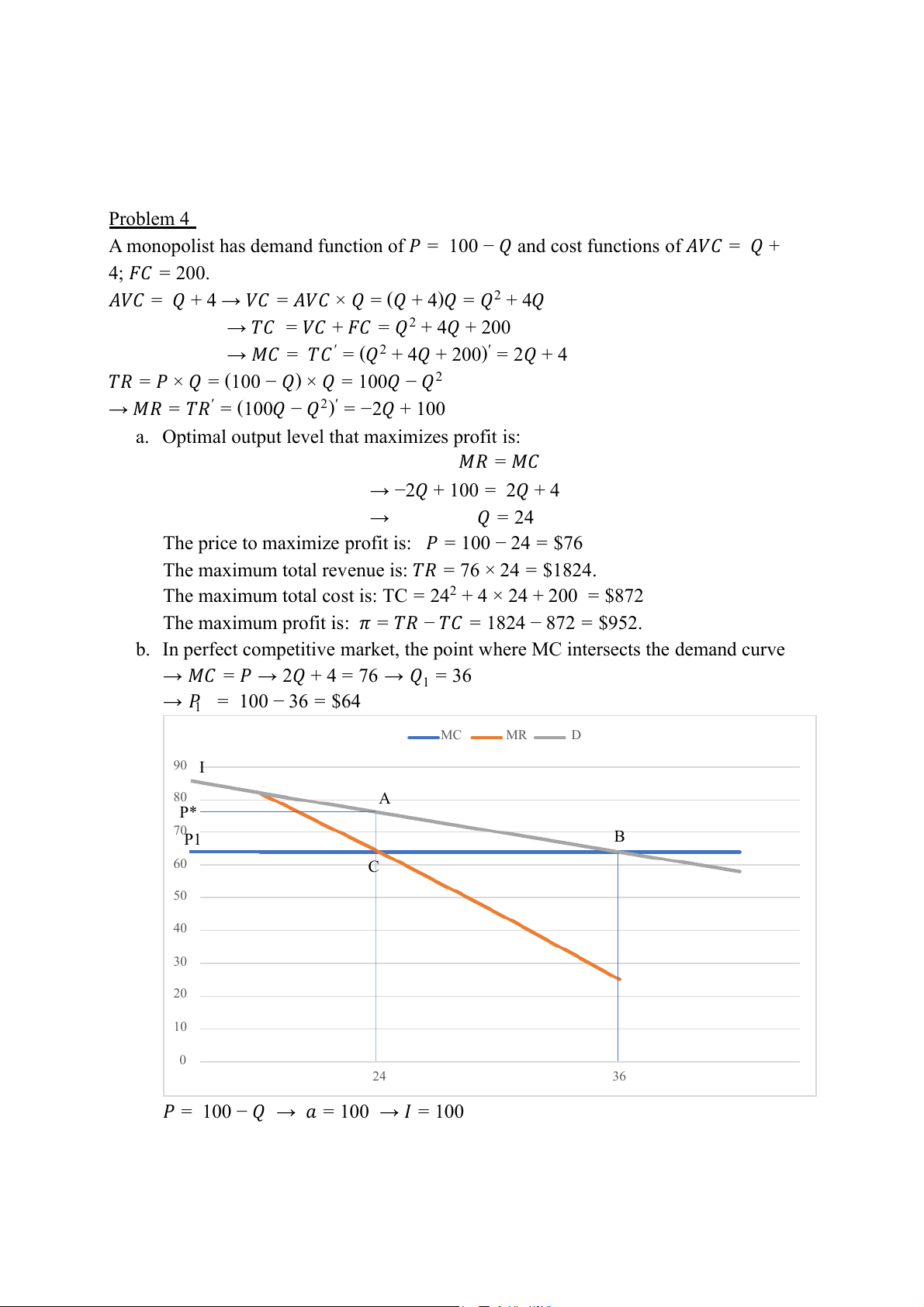
b. In perfect competitive market, the point where MC intersects the demand curve
→ 𝑀𝐶 = 𝑃 → 2𝑄 + 4 = 76 → 𝑄1 = 36 → 𝑃1 = 100 − 36 = $64 MC MR D 90 I 80 A P* 70P1 B 60 C 50 40 30 20 10 0 24 36
𝑃 = 100 − 𝑄 → 𝑎 = 100 → 𝐼 = 100 1 1 𝐶𝑆 = 𝑆 = 𝐼𝑃∗ × 𝐴𝑃∗ = × 24 × 24 = 288 𝐼𝐴𝑃∗ 2 2 1 1 𝐷𝑊 = 𝑆 = × 12 × 12 = 72 𝐴𝐵𝐶 𝐴𝐶 × 𝐵𝐶 = 2 2
c. Assume this firm applies perfect price discrimination.
The quantity of the firm will be 36.
The variable profit of the firm will be:
𝑃𝑆 = 𝐶𝑆 + 𝐷𝑊 + 𝜋 = 288 + 72 + 952 = $1312.
d. By applying perfect price discrimination, consumer surplus and deadweight loss the firm increased profit.




