












Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Lecture2
Chemical Reaction Engineering ( CRE) is the
field that studies the rates and mechanisms of
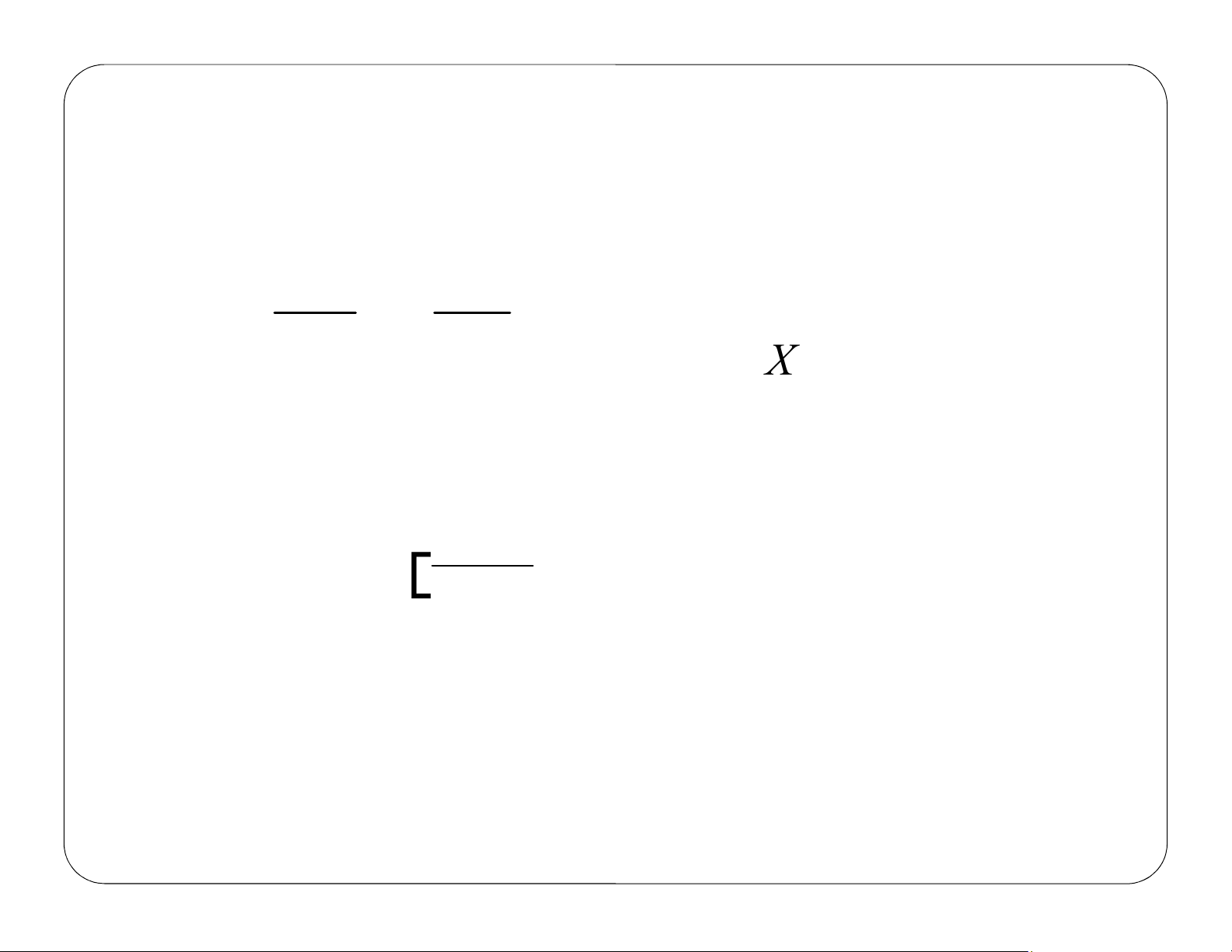
chemical reactions and the design of the reactors in which they take place. lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Lecture 2 Chapter 2 Review of Lecture 1 Definition of Conversion, X Develop the Design Equations in terms of X A Size CSTRs and PFRs given –r = f(X) Conversion for Reactors in Series Review the Fall of the Tower of CRE lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 Differential Reactor Mole Balances Summary
The GMBE appliedto the fourmajor reactortypes and ( → the general reactionA B) Reactor Algebraic Integral N N A A dNA t = rV N A 0 A t F A − F 0 A −r A F F A A dF V = A dr F A A 0 V F F A A dF W = A ′ lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Batch dNA = r VA dt CSTR V = PFR dFA = rA dV PBR dF A = r A′ dW lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 CSTR – Example Problem
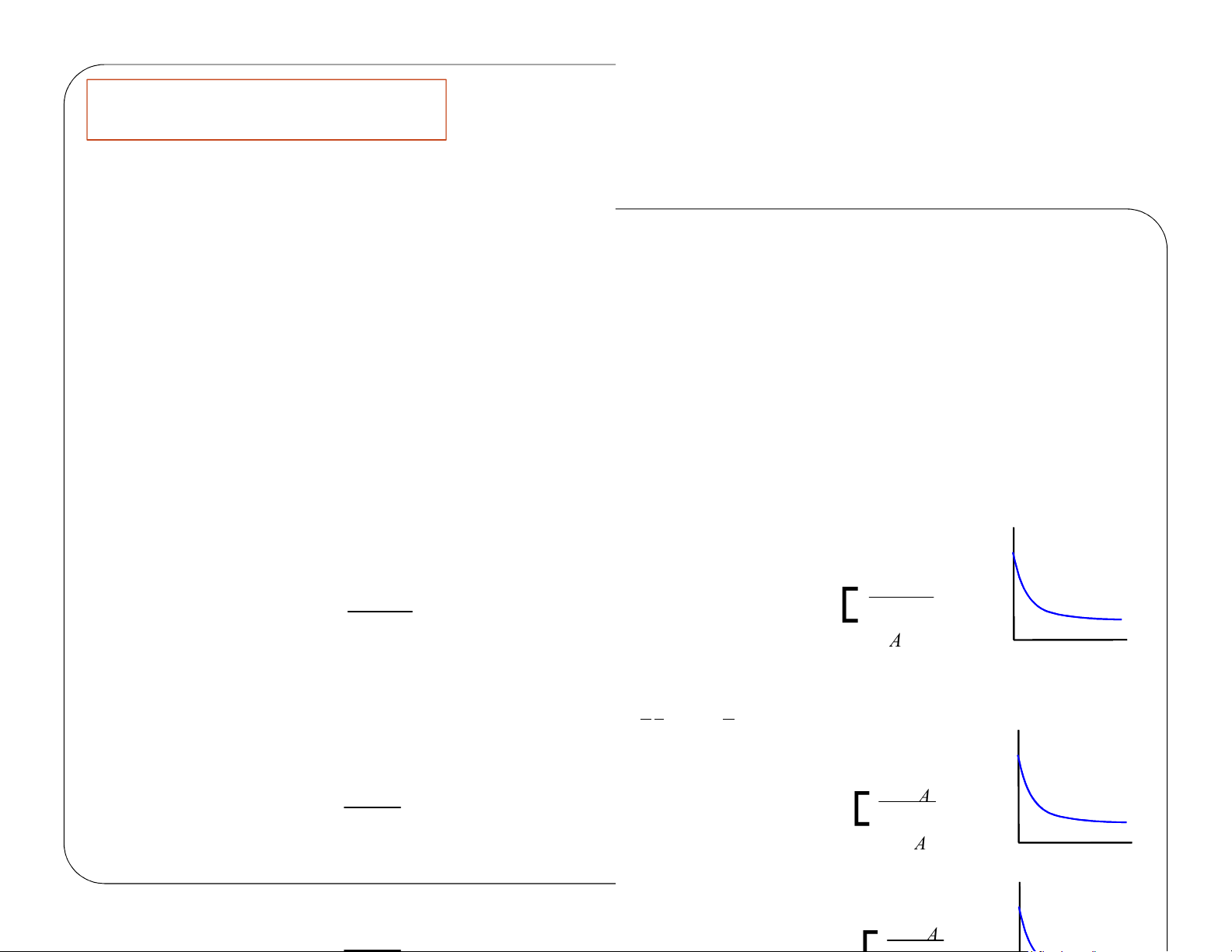
Given the following information, Find V 3 dm υ0 = 3 10 min dm υυ== 10 0 C min A 0 V =? CA =0.1 C A 0 A F υ = C 0 0 A 0 A F υ = C A Liquidphase υ =υ 0 F = C A υ 0 A lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 CSTR – Example Problem 0 A 0 A 0 A = − A r lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 (1) Mole Balance: υ F [
A0 − FA υ0CA0 −υC C −C ] V = = −r A −rA (2) Rate Law: −rA =kCA (3) Stoichiometry: F FA lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 CA = = A υ υ0 lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 V = CSTR – Example Problem (4) Combine: υ C [ −C ] 0 A 0 A kC A (5) Evaluate: C = C 0.1 A0 3 10dm [CA − C 0.1 0 A0 ] min − [ 101 ] 0.1 3 ( − = dm 1 0.23min 0.1C ( A0 0.230.1 ( ) ) ) ) 900 3 ( V = =391 dm lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Review Lecture 1 A V = lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 a Chapter 2 Define conversion, X
Consider the generic reaction: → + c C d D
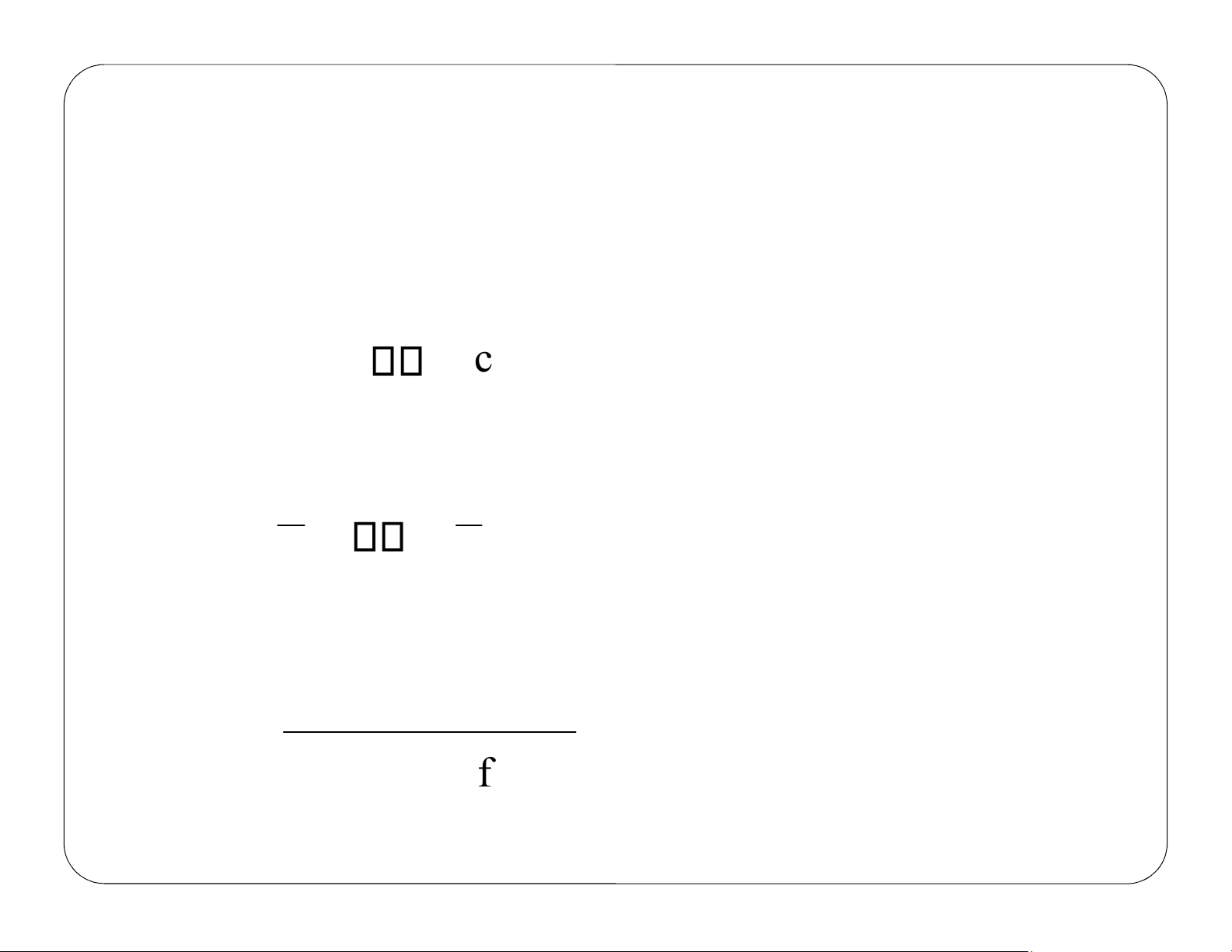
Chose limiting reactant A as basis of calculation: b c d B → + C D a a a Define conversion, X moles A reacted A moles fed lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 A b B+ A + X = lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Batch Chapter 2 Moles A Moles A = MolesA − remaining r eacted initially A 0 X NA = NA0 − N
dNA = −0 N dXA0 dNA dX lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 =−N A0 = r VA dt dt lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 d Chapter 2 Batch t =0 0 X = t = = tX X t N = A 0
The necessary t to achieve conversion X. lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 NA =− r VA dt NA0 Integrating, X dX −r V 0 A lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 a Chapter 2 CSTR
Consider the generic reaction: → + c C d D
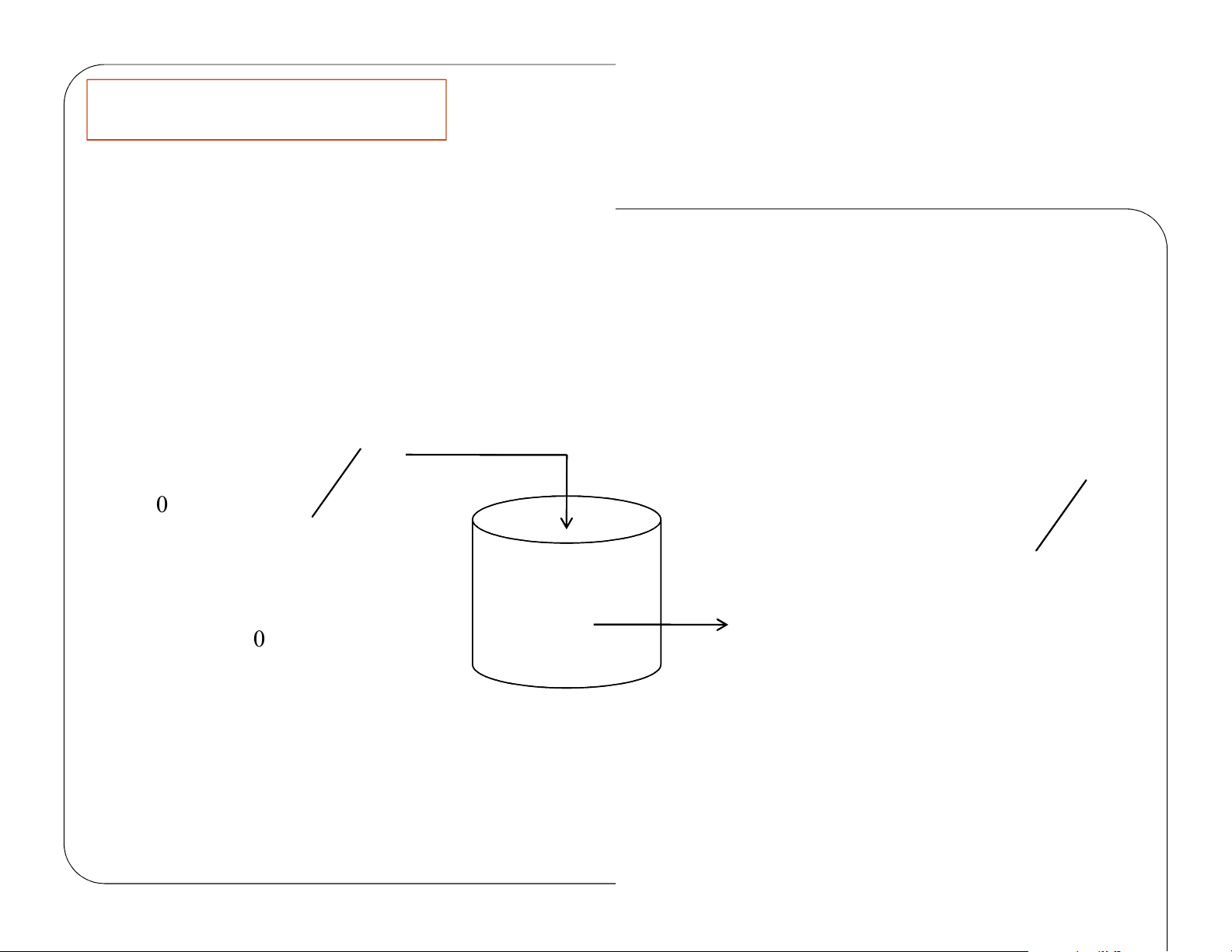
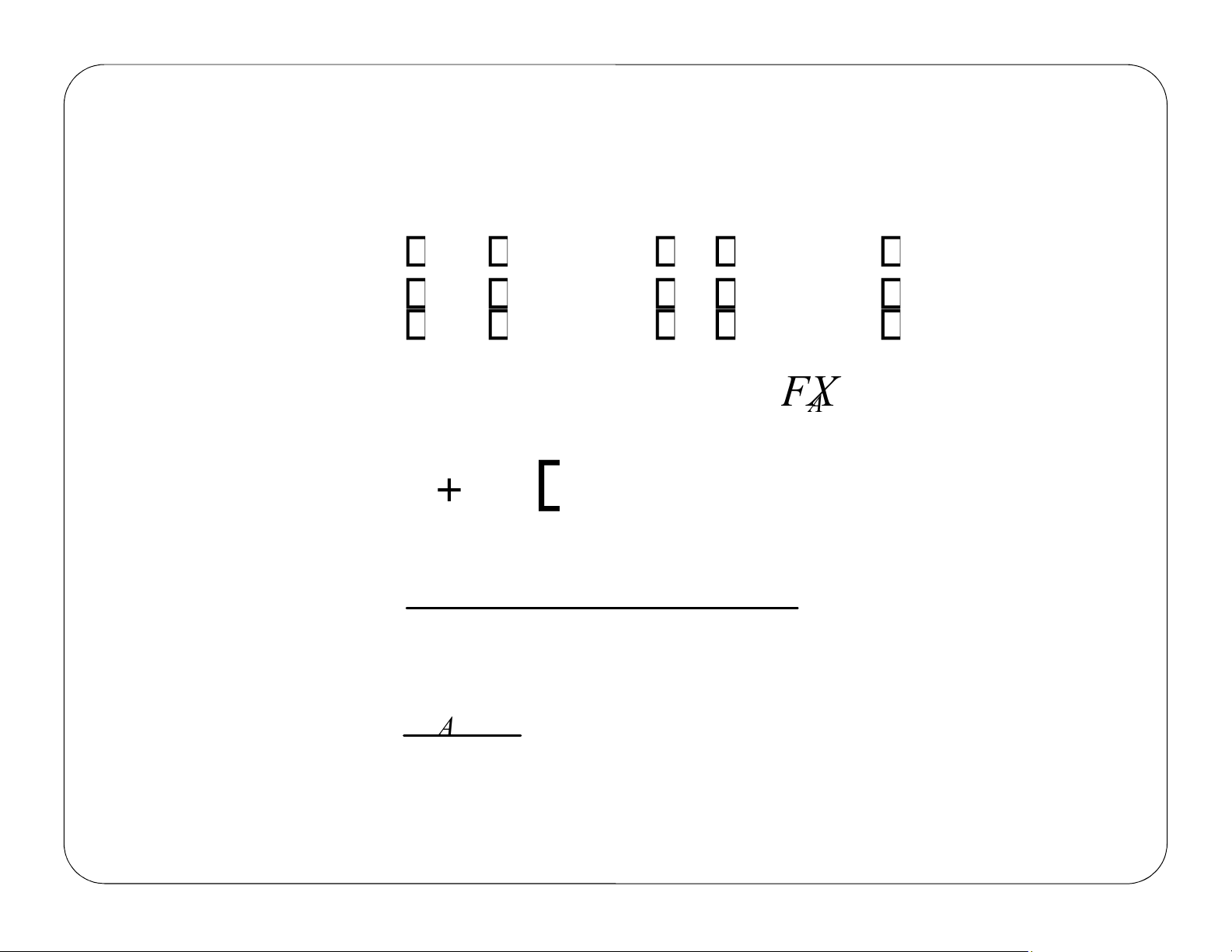
Chose limiting reactant A as basis of calculation: b c d B → + C D a a a Define conversion, X moles A reacted A moles fed lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 A b B+ A + X = CSTR Steady State lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 Well Mixed V = Chapter 2 dN A =0 dt F − F A 0 A −r A rdVrV= A A lOMoAR cPSD| 59078336 C Chapter 2 MolesA MolesA = − entering r eacted F − A 0 FX A 0 F F rdV −+ A A =0 F − F ( −F X) A 0 A 0 A 0 −r A A FX 0 − A r
CSTR volumenecessaryto achieveconversionX.



