





Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434
Assoc. Prof. PhD. Nguyễn Văn Nhận
ENGLISH FOR SPECIFIC PURPOSES
FOR AUTOMOTIVE STUDENTS
Lesson ESP- 11 ELECTRIC VEHICLES Đà Nẵng – 2022 lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 2
1. OVERVIEW OF ELECTRIC VEHICLES
An Electric Vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric
motors for propulsion. EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail
vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft.
EVs first came into existence in the mid-19th century, when electricity
was among the preferred methods for motor vehicle propulsion, providing a
level of comfort and ease of operation that could not be achieved by the
gasoline cars of the time. Internal combustion engines were the dominant
propulsion method for cars and trucks for about 100 years, but electric power
remained commonplace in other vehicle types, such as trains and smaller vehicles of all types.
In the 21st century, EVs have seen a resurgence due to technological
developments, and an increased focus on renewable energy and the potential
reduction of transportation's impact on climate change and other environmental issues. Electric Tricycle
The first electric vehicle in history to be
displayed to the public in 1881 (Ne = 0.1 HP)
The operational and functional principles in Electric-motor-powered
Vehicle (EV) and Internal-Combustion-Engine-powered Vehicle (ICEV) are
similar, regardless of the type of the engine. The automobile will still have a
frame, a suspension system, a steering system, a brake system, wheels and tires,
and a body. The automobile must be start-able, movable, steerable, and
stoppable, and must enclose and protect the driver and passengers in comfort
and safety. There are, however, some differences between ICEV and EV, such
as the use of a gasoline tank versus batteries, IC engine versus electric motor,
and different transmission requirements. lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 3
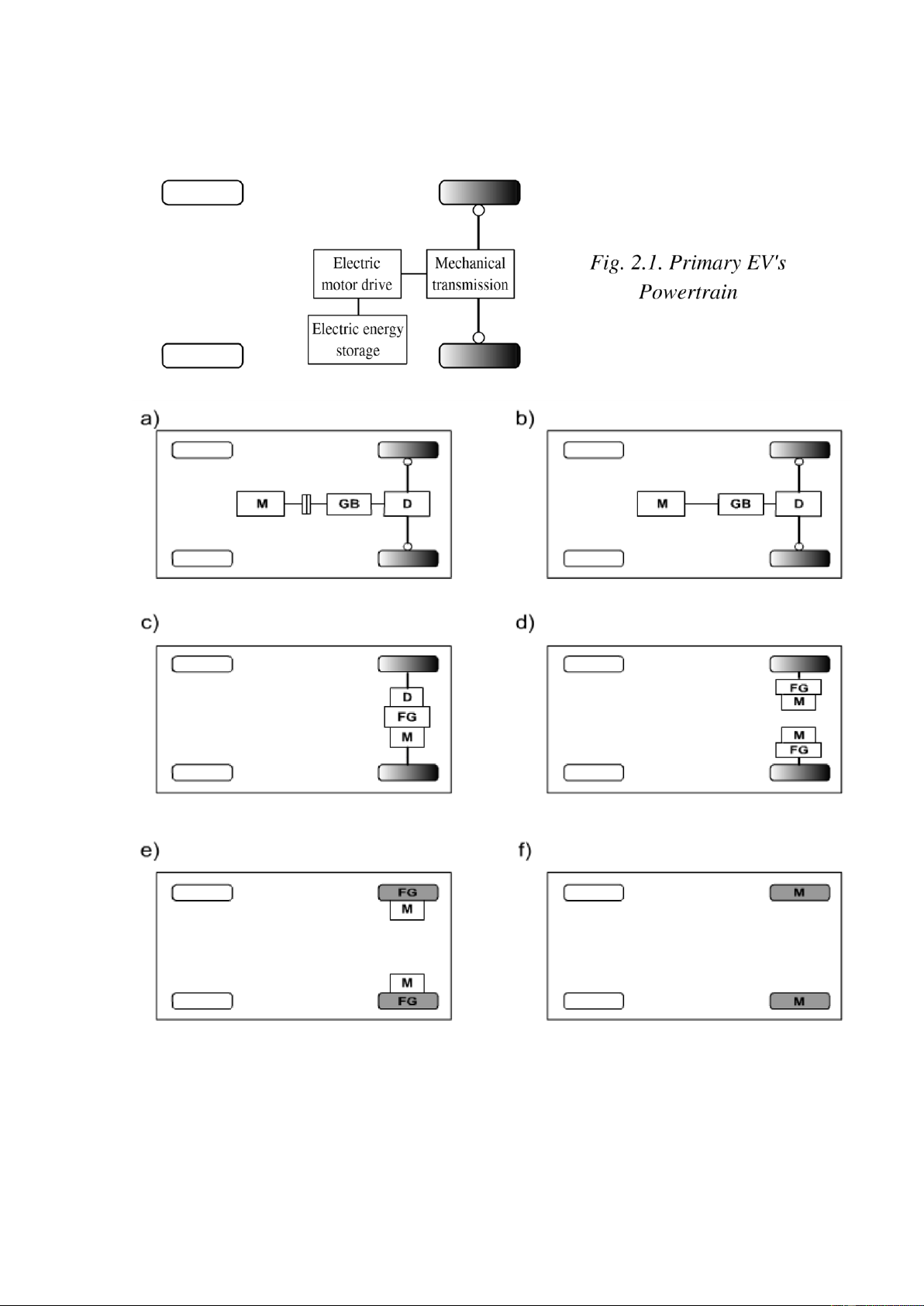
2. POWETRAINS OF ELECTRIC AUTOMOBILES
Fig. 2.2. Modern EV's Powertrains
C- Clutch, D- Differential, FG- Fixed Gearing, GB-
Gearbox, M- Electric motor lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 4
Previously, the EV was mainly converted from the existing ICEV by replacing
the IC engine and fuel tank with an electric motor and battery pack while
retaining all the other components (Fig. 2.1). Drawbacks such as its heavy
weight, lower flexibility, and performance degradation have caused the use of this type of EV to fade out.
The modern EV is purposely built, based on original body and frame designs.
This satisfies the structure requirements unique to EVs and make use of the
greater flexibility of electric propulsion. 3. FUEL CELL
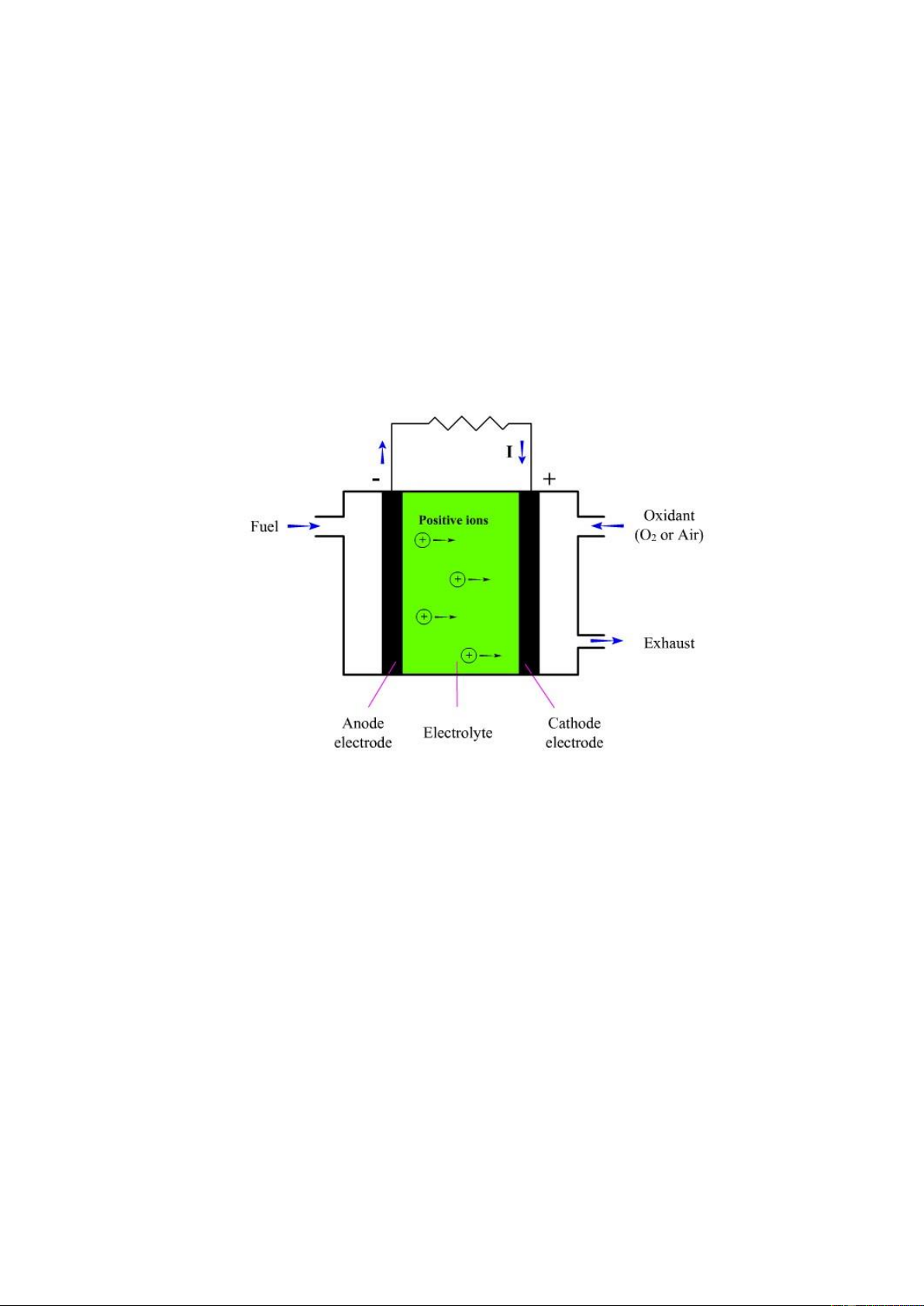
In contrast to a electric battery, the fuel cell generates electric energy
rather than storing it and contributes to do so as long as a fuel supply is
maintained. A fuel cell is a galvanic cell in which the chemical energy of a fuel
is converted directly into electrical energy by means of electrochemical processes.
The fuel and oxidizing agent are continuously and separately supplied to the
two electrodes of the cell, where they undergo a reaction. Electrolyte is
necessary to conduct the ions from one electrode to the other. Fuel is supplied
to the anode, where electrons are released from the fuel under catalyst. The
electrons, under the potential difference between these two electrodes, flow
through the external circuit to the cathode, where combining positive ions and
oxygen, reaction products, or exhaust are produced. lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 5
4. EV's ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
The EV has many advantages over the conventional ICEV, such as
absence of emissions, high efficiency, independence from petroleum, and quiet and smooth operation.
The weakest point blocking the way of EVs to the market is the battery
technology. Great effort and investment have been put into battery research,
with the intention of improving performance to meet the EV requirement. ____________________ ASSIGNMENTS
A. ESSAY TYPE ASSIGNMENTS lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 6
A11.1. What is the primary difference between EVs and ICEVs as regards their construction ?
A11.2. What are the main advantages and disadvantages of an EV over an ICEV ?
A11.3. What is the primary difference between fuel cells and ordinary batteries ?
A11.4. List at least three reasons why EVs would not replace ICEVs in the near future.
A11.5. Select the Vietnamese equivalents of the following English terms. No. English Vietnamese 1) Catalyst 2) Electric Motor 3) Electric Vehicle
4) Electric-Motor-powered Vehicle 5) Electrode 6) Electrolyte 7) Emissions 8) Fuel Cell 9) Internal-Combustion- Enginepowered Vehicle 10) Oxidizing Agent lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 7
B. OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
Choose the single most correct answer.
B11.1. Which of the following are advantages of EVs over ICEVs ?
A. No gasoline required B. Lower amount of pollution
C. Low maintenance D. All of the mentioned advantages
B11.2. All of the following are disadvantages of EVs in comparison with ICEVs, EXCEPT :
A. Shorter driving range B. Easy driving
C. Battery replacement D. Longer recharge time
B11.3. Which is the chief reason why EVs would not replace ICEVs in
Vietnam in the near future ?
A. Global warming B. Battery recharge points
C. Climate change D. Convenience to drive
B11.4. What are the reasons that would make ICEVs being still in use in
Vietnam in incoming years ?
A. The initial investment B. Long driving range
C. Shortage of electricity D. All of the mentioned reasons
B11.5. Which is the main difference between EVs and ICEVs as far as the
construction is concerned ? A. Brakes B. Suspensions
C. Powertrain D. All of the mentioned
------- The End ------- lOMoAR cPSD| 58490434 8




